fe12a67d6db5af0d5c7ce3f313698863.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 Foreign Policy
Foreign Policy
 Learning Outcomes LO 1 Define foreign policy, and discuss moral idealism versus political realism in foreign policy. LO 2 Describe recent foreign policy challenges that involve the use of force, including terrorism and the wars in Afghanistan and Iraq. LO 3 Discuss the use of diplomacy in addressing such issues as nuclear proliferation, the rise of China, the confrontation between Israel and the Palestinians, and the economic crisis in Europe. LO 4 Explain the roles of the president, executive agencies, and Congress in making U. S. foreign policy. LO 5 Cite the main themes in the history of U. S. foreign policy. Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 2
Learning Outcomes LO 1 Define foreign policy, and discuss moral idealism versus political realism in foreign policy. LO 2 Describe recent foreign policy challenges that involve the use of force, including terrorism and the wars in Afghanistan and Iraq. LO 3 Discuss the use of diplomacy in addressing such issues as nuclear proliferation, the rise of China, the confrontation between Israel and the Palestinians, and the economic crisis in Europe. LO 4 Explain the roles of the president, executive agencies, and Congress in making U. S. foreign policy. LO 5 Cite the main themes in the history of U. S. foreign policy. Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 2
 Facing the World: Foreign and Defense Policy National Security and Defense Policies Diplomacy Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 3
Facing the World: Foreign and Defense Policy National Security and Defense Policies Diplomacy Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 3
 Facing the World: Foreign and Defense Policy Idealism versus Realism in Foreign Policy Moral idealism Political realism American foreign policy—A mixture of both Problems with intervention Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 4
Facing the World: Foreign and Defense Policy Idealism versus Realism in Foreign Policy Moral idealism Political realism American foreign policy—A mixture of both Problems with intervention Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 4
 Terrorism and Warfare The Emergence of Terrorism September 11 Al Qaeda’s aims Domestic terrorism in U. S. Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 5
Terrorism and Warfare The Emergence of Terrorism September 11 Al Qaeda’s aims Domestic terrorism in U. S. Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 5
 A Syrian rebel loads his machine gun in 2013 during a battle with regime forces in the city of Aleppo. Why should the United States be concerned about the fighting in Syria? Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 6
A Syrian rebel loads his machine gun in 2013 during a battle with regime forces in the city of Aleppo. Why should the United States be concerned about the fighting in Syria? Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 6
 Terrorism and Warfare The War on Terrorism A new kind of war Opposition to the Bush Doctrine Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 7
Terrorism and Warfare The War on Terrorism A new kind of war Opposition to the Bush Doctrine Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 7
 Terrorism and Warfare Wars in Iraq Second Gulf War—The Iraq War Occupied Iraq The insurgency Iraqi endgame Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 8
Terrorism and Warfare Wars in Iraq Second Gulf War—The Iraq War Occupied Iraq The insurgency Iraqi endgame Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 8
 Terrorism and Warfare Afghanistan The return of Taliban Obama and Afghanistan The death of bin Laden May 1, 2011 Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 9
Terrorism and Warfare Afghanistan The return of Taliban Obama and Afghanistan The death of bin Laden May 1, 2011 Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 9
 The late Osama bin Laden, leader of al Qaeda. On May 1, 2011, U. S. Navy SEALs raided bin Laden’s hiding place in Abbottabad, Pakistan, and killed him. Why had it been so hard for the United States to track bin Laden down? Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 10
The late Osama bin Laden, leader of al Qaeda. On May 1, 2011, U. S. Navy SEALs raided bin Laden’s hiding place in Abbottabad, Pakistan, and killed him. Why had it been so hard for the United States to track bin Laden down? Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 10
 U. S. Diplomatic Efforts Nuclear Weapons Nuclear stockpiles Nuclear proliferation: Iran Nuclear proliferation: North Korea Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 11
U. S. Diplomatic Efforts Nuclear Weapons Nuclear stockpiles Nuclear proliferation: Iran Nuclear proliferation: North Korea Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 11
 North Korean leader Kim Jong Un and former NBA star Dennis Rodman watch North Korean and U. S. players in an exhibition basketball game in North Korea. Rodman was heavily criticized in the United States for this appearance. Why might he have drawn such a reaction? Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 12
North Korean leader Kim Jong Un and former NBA star Dennis Rodman watch North Korean and U. S. players in an exhibition basketball game in North Korea. Rodman was heavily criticized in the United States for this appearance. Why might he have drawn such a reaction? Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 12
 U. S. Diplomatic Efforts The New Power: China’s explosive economic growth The issue of Taiwan Chinese nationalism Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 13
U. S. Diplomatic Efforts The New Power: China’s explosive economic growth The issue of Taiwan Chinese nationalism Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 13
 U. S. Diplomatic Efforts Israel and the Palestinians Talks with the PLO The collapse of Israeli-Palestinian peace process The rise of Hamas The blockade of Gaza UN Recognition Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 14
U. S. Diplomatic Efforts Israel and the Palestinians Talks with the PLO The collapse of Israeli-Palestinian peace process The rise of Hamas The blockade of Gaza UN Recognition Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 14
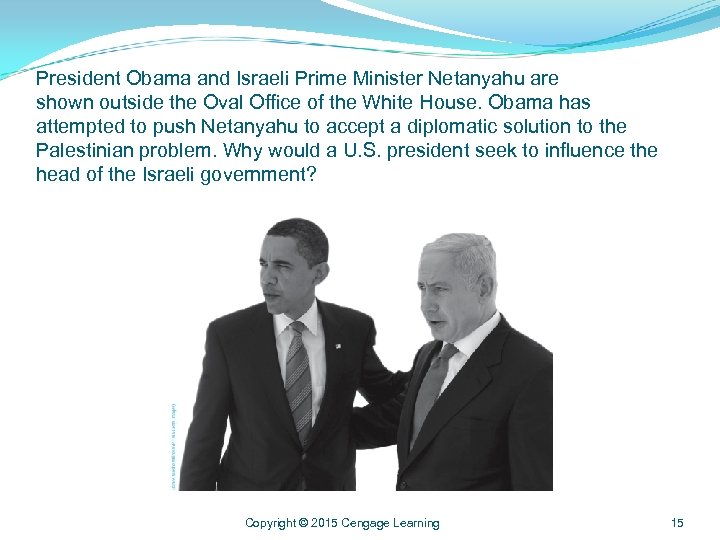 President Obama and Israeli Prime Minister Netanyahu are shown outside the Oval Office of the White House. Obama has attempted to push Netanyahu to accept a diplomatic solution to the Palestinian problem. Why would a U. S. president seek to influence the head of the Israeli government? Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 15
President Obama and Israeli Prime Minister Netanyahu are shown outside the Oval Office of the White House. Obama has attempted to push Netanyahu to accept a diplomatic solution to the Palestinian problem. Why would a U. S. president seek to influence the head of the Israeli government? Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 15
 U. S. Diplomatic Efforts The Economic Crisis in Europe The debt crisis The German question Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 16
U. S. Diplomatic Efforts The Economic Crisis in Europe The debt crisis The German question Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 16
 Who Makes Foreign Policy? Constitutional Powers of the President War powers Treaties and executive agreements Other constitutional powers Appoint ambassadors, other public ministers, and consuls; recognize foreign governments Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 17
Who Makes Foreign Policy? Constitutional Powers of the President War powers Treaties and executive agreements Other constitutional powers Appoint ambassadors, other public ministers, and consuls; recognize foreign governments Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 17
 Who Makes Foreign Policy? The Executive Branch and Foreign Policymaking The Department of State The National Security Council The intelligence community Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 18
Who Makes Foreign Policy? The Executive Branch and Foreign Policymaking The Department of State The National Security Council The intelligence community Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 18
 President Bush is shown with his National Security Council (NSC) the day after the terrorist attacks on September 11, 2001. At that time, the NSC consisted of the director of the Central Intelligence Agency, the secretary of Defense, the secretary of State, the vice president, the chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, and, of course, the national security adviser. How important is the NSC’s role in determining U. S. foreign policy? Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 19
President Bush is shown with his National Security Council (NSC) the day after the terrorist attacks on September 11, 2001. At that time, the NSC consisted of the director of the Central Intelligence Agency, the secretary of Defense, the secretary of State, the vice president, the chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, and, of course, the national security adviser. How important is the NSC’s role in determining U. S. foreign policy? Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 19
 Who Makes Foreign Policy? The Executive Branch and Foreign Policymaking The intelligence community and war on terrorism Department of Defense Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 20
Who Makes Foreign Policy? The Executive Branch and Foreign Policymaking The intelligence community and war on terrorism Department of Defense Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 20
 Who Makes Foreign Policy? Congress Balances the Presidency The War Powers Resolution (1973) The power of the purse Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 21
Who Makes Foreign Policy? Congress Balances the Presidency The War Powers Resolution (1973) The power of the purse Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 21
 The Major Foreign Policy Themes The Formative Years: Avoiding Entanglements The Monroe Doctrine The Spanish-American War and World War I Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 22
The Major Foreign Policy Themes The Formative Years: Avoiding Entanglements The Monroe Doctrine The Spanish-American War and World War I Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 22
 The Major Foreign Policy Themes The Era of Internationalism The Cold War Containment Policy Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 23
The Major Foreign Policy Themes The Era of Internationalism The Cold War Containment Policy Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 23
 The Major Foreign Policy Themes Superpower Relations The Cuban missile crisis Period of détente Nuclear arms agreements with the Soviet Union Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 24
The Major Foreign Policy Themes Superpower Relations The Cuban missile crisis Period of détente Nuclear arms agreements with the Soviet Union Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 24
 President Truman ordered two atomic bomb attacks in Japan in 1945. Was his decision justified? Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 25
President Truman ordered two atomic bomb attacks in Japan in 1945. Was his decision justified? Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 25
 In a famous meeting in Yalta in February 1945, British prime minister Winston Churchill (left), U. S. president Franklin Roosevelt (center), and Soviet leader Joseph Stalin (right) decided the fate of several nations in Europe, including Germany. What happened to Germany immediately after World War II? Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 26
In a famous meeting in Yalta in February 1945, British prime minister Winston Churchill (left), U. S. president Franklin Roosevelt (center), and Soviet leader Joseph Stalin (right) decided the fate of several nations in Europe, including Germany. What happened to Germany immediately after World War II? Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 26
 The Major Foreign Policy Themes Superpower Relations The dissolution of Soviet Union Russia after the Soviet Union Russia’s future Vladimir Putin Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 27
The Major Foreign Policy Themes Superpower Relations The dissolution of Soviet Union Russia after the Soviet Union Russia’s future Vladimir Putin Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 27
 Foreign Policy and the U. S. Constitution Click picture to play video Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 28
Foreign Policy and the U. S. Constitution Click picture to play video Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 28
 Foreign Policy and the U. S. Constitution Taking a closer look: 1. What role does the president play in developing foreign policy? Should Congress play a larger role? 2. Is this treaty representative of an idealistic or realistic viewpoint? 3. Which nations are now considered superpowers? Which nations are declining in power? Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 29
Foreign Policy and the U. S. Constitution Taking a closer look: 1. What role does the president play in developing foreign policy? Should Congress play a larger role? 2. Is this treaty representative of an idealistic or realistic viewpoint? 3. Which nations are now considered superpowers? Which nations are declining in power? Copyright © 2015 Cengage Learning 29


