26d4daa77c0f3406486e61b3b099bd08.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 Foreign Exchange Markets (or chapter 6)
Foreign Exchange Markets (or chapter 6)
 Agenda § Description of foreign exchange market • • • Size? Functions? Participants? Transactions? Rates & Quotations? Inter-market Arbitrage?
Agenda § Description of foreign exchange market • • • Size? Functions? Participants? Transactions? Rates & Quotations? Inter-market Arbitrage?
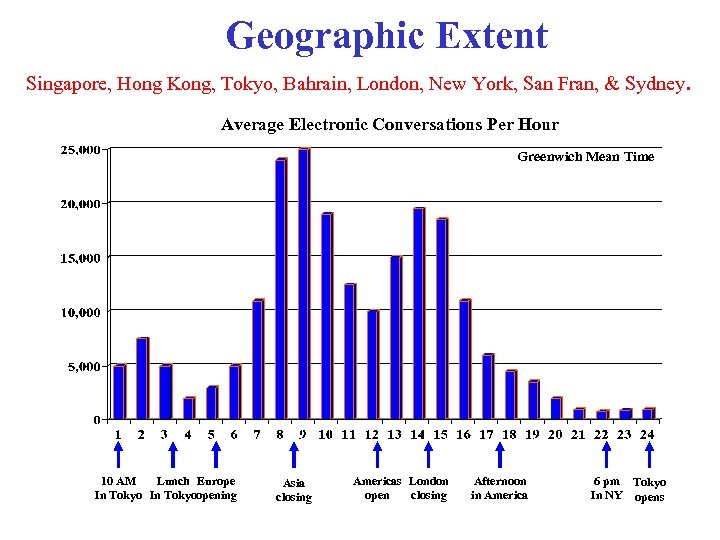 Geographic Extent Singapore, Hong Kong, Tokyo, Bahrain, London, New York, San Fran, & Sydney. Average Electronic Conversations Per Hour Greenwich Mean Time 10 AM Lunch Europe In Tokyoopening Asia closing Americas London open closing Afternoon in America 6 pm Tokyo In NY opens
Geographic Extent Singapore, Hong Kong, Tokyo, Bahrain, London, New York, San Fran, & Sydney. Average Electronic Conversations Per Hour Greenwich Mean Time 10 AM Lunch Europe In Tokyoopening Asia closing Americas London open closing Afternoon in America 6 pm Tokyo In NY opens
 Functions of FOREX Market § Transfer purchasing power between countries. § Obtain/ provide credit for international trade. § Minimize exposure to exchange rate risk.
Functions of FOREX Market § Transfer purchasing power between countries. § Obtain/ provide credit for international trade. § Minimize exposure to exchange rate risk.
 Size, Structure, & Participants § Daily global net turnover in forex US$1. 21 trn (April’ 01), data by Bank for Int’l Settlements - Switzerland § FOREX market has two tiers § Five categories participants: • interbank (wholesale) market. • client (retail) market. • • • Bank & non-bank forex dealers. Individuals & firms. Speculators & arbitragers. Central banks & treasuries. Forex brokers.
Size, Structure, & Participants § Daily global net turnover in forex US$1. 21 trn (April’ 01), data by Bank for Int’l Settlements - Switzerland § FOREX market has two tiers § Five categories participants: • interbank (wholesale) market. • client (retail) market. • • • Bank & non-bank forex dealers. Individuals & firms. Speculators & arbitragers. Central banks & treasuries. Forex brokers.
 Transactions in the Interbank Market § Transactions: spot, forward, or swap basis • Spot transaction requires almost immediate delivery of foreign exchange • Forward transaction requires delivery of foreign exchange at some future date • Swap transaction is the simultaneous exchange of one foreign currency for another
Transactions in the Interbank Market § Transactions: spot, forward, or swap basis • Spot transaction requires almost immediate delivery of foreign exchange • Forward transaction requires delivery of foreign exchange at some future date • Swap transaction is the simultaneous exchange of one foreign currency for another
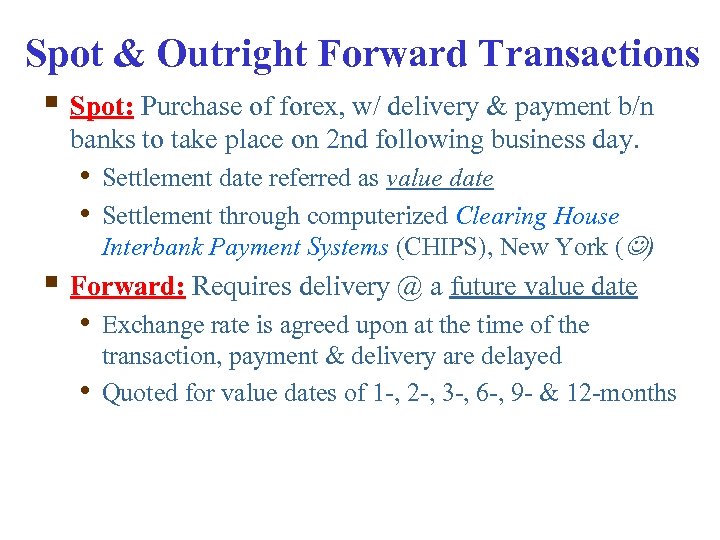 Spot & Outright Forward Transactions § Spot: Purchase of forex, w/ delivery & payment b/n banks to take place on 2 nd following business day. • Settlement date referred as value date • Settlement through computerized Clearing House Interbank Payment Systems (CHIPS), New York ( ) § Forward: Requires delivery @ a future value date • Exchange rate is agreed upon at the time of the • transaction, payment & delivery are delayed Quoted for value dates of 1 -, 2 -, 3 -, 6 -, 9 - & 12 -months
Spot & Outright Forward Transactions § Spot: Purchase of forex, w/ delivery & payment b/n banks to take place on 2 nd following business day. • Settlement date referred as value date • Settlement through computerized Clearing House Interbank Payment Systems (CHIPS), New York ( ) § Forward: Requires delivery @ a future value date • Exchange rate is agreed upon at the time of the • transaction, payment & delivery are delayed Quoted for value dates of 1 -, 2 -, 3 -, 6 -, 9 - & 12 -months
 Swap Transactions § § § Simultaneous purchase & sale of of foreign exchange for two different value dates Both purchase & sale w/ same counterparty Common types of swaps • Spot against forward: buy currency in spot market & simultaneously • sells same amount back to same bank in forward market Forward-forward swaps: Dealer sells £ 20, 000 forward for $, delivery in 2 months @ $1. 687/£ & simultaneously buys £ 20, 000 forward for delivery in 3 months @ $1. 682/£ – Difference b/n buying and selling price is interest rate differential. – Can be viewed as way for collateralized borrowing another currency. • Non-deliverable forwards (NDF): same as traditional forward contracts except they are settled only in US$. Foreign currency sold/ bought forward not delivered. – NDF contracted offshore & are beyond reach & regulation of home governments – Pricing NDF reflects basic interest rate differentials.
Swap Transactions § § § Simultaneous purchase & sale of of foreign exchange for two different value dates Both purchase & sale w/ same counterparty Common types of swaps • Spot against forward: buy currency in spot market & simultaneously • sells same amount back to same bank in forward market Forward-forward swaps: Dealer sells £ 20, 000 forward for $, delivery in 2 months @ $1. 687/£ & simultaneously buys £ 20, 000 forward for delivery in 3 months @ $1. 682/£ – Difference b/n buying and selling price is interest rate differential. – Can be viewed as way for collateralized borrowing another currency. • Non-deliverable forwards (NDF): same as traditional forward contracts except they are settled only in US$. Foreign currency sold/ bought forward not delivered. – NDF contracted offshore & are beyond reach & regulation of home governments – Pricing NDF reflects basic interest rate differentials.
 § Rates & Quotes What is a quote? • Inter-bank Quotes – Foreign currency for a dollar (SF 1. 60/$). European quote – Dollar for unit foreign currency ($0. 625/SF). American quote – All European currencies quoted in European way, except: – Pound Sterling, Euro, Australian, & New Zealand $. • Direct & Indirect Quotes – Direct: home currency per unit of foreign – Indirect: foreign currency per unit home currency – SF 1. 60/$ indirect quote in US, $0. 625/SF is direct quote in US • Bid & Ask Quotes – Interbank quotes given as bid & ask (offer) – Bid is the price at which a dealer will buy another currency – Ask or offer is the price at which a dealer will sell another currency – E. g. : ¥ 118. 27 - ¥ 118. 37/$ is the bid/ask for Japanese yen – Bank will buy yen @ ¥ 118. 27 per US$ & sell yen @ ¥ 118. 37 per US$ making profit on spread.
§ Rates & Quotes What is a quote? • Inter-bank Quotes – Foreign currency for a dollar (SF 1. 60/$). European quote – Dollar for unit foreign currency ($0. 625/SF). American quote – All European currencies quoted in European way, except: – Pound Sterling, Euro, Australian, & New Zealand $. • Direct & Indirect Quotes – Direct: home currency per unit of foreign – Indirect: foreign currency per unit home currency – SF 1. 60/$ indirect quote in US, $0. 625/SF is direct quote in US • Bid & Ask Quotes – Interbank quotes given as bid & ask (offer) – Bid is the price at which a dealer will buy another currency – Ask or offer is the price at which a dealer will sell another currency – E. g. : ¥ 118. 27 - ¥ 118. 37/$ is the bid/ask for Japanese yen – Bank will buy yen @ ¥ 118. 27 per US$ & sell yen @ ¥ 118. 37 per US$ making profit on spread.
 Rates & Quotes § Forward Quotations on a Points Basis • Outright quotes. • Forward quotes different & usually quoted in points • A point: last digit of quote, w/ convention dictating number of digits to the right of decimal. => a point = 0. 0001 most currencies
Rates & Quotes § Forward Quotations on a Points Basis • Outright quotes. • Forward quotes different & usually quoted in points • A point: last digit of quote, w/ convention dictating number of digits to the right of decimal. => a point = 0. 0001 most currencies
 Rates & Quotes § Expressing Forward Quotations on Points Basis • Yen quoted only to 2 decimal points • Forward quote is not forex rate, but difference b/n spot • & forward. Example: Bid Outright spot: Plus points (3 months) Outright forward: Ask ¥ 118. 27 ¥ 118. 37 -1. 43 -1. 40 ¥ 116. 84 ¥ 116. 97
Rates & Quotes § Expressing Forward Quotations on Points Basis • Yen quoted only to 2 decimal points • Forward quote is not forex rate, but difference b/n spot • & forward. Example: Bid Outright spot: Plus points (3 months) Outright forward: Ask ¥ 118. 27 ¥ 118. 37 -1. 43 -1. 40 ¥ 116. 84 ¥ 116. 97
 Rates & Quotes • Can have forward quotes as % p. a. deviation from spot. • Important: which currency is home currency? – Indirect quotes (i. e. foreign per domestic) – Direct quotes (i. e. domestic per foreign currency) – For example: S = Yen 105. 65/$, F 30 = Yen 105. 04/$ ¥
Rates & Quotes • Can have forward quotes as % p. a. deviation from spot. • Important: which currency is home currency? – Indirect quotes (i. e. foreign per domestic) – Direct quotes (i. e. domestic per foreign currency) – For example: S = Yen 105. 65/$, F 30 = Yen 105. 04/$ ¥
 Cross Rates & Intermarket Arbitrage Japanese yen § Suppose Mexican peso § Cross rate is: ¥ 121. 13/$. Ps 9. 190/$. ¥ ¥ $0. 9045/€. Barclays Bank $1. 4443/£. Dresdner Bank • Assume Citibank € 1. 6200/£. • Cross rate Citibank & Barclays: • Cross rate =/= Dresdner rate € 1. 62/£. £ € € £
Cross Rates & Intermarket Arbitrage Japanese yen § Suppose Mexican peso § Cross rate is: ¥ 121. 13/$. Ps 9. 190/$. ¥ ¥ $0. 9045/€. Barclays Bank $1. 4443/£. Dresdner Bank • Assume Citibank € 1. 6200/£. • Cross rate Citibank & Barclays: • Cross rate =/= Dresdner rate € 1. 62/£. £ € € £
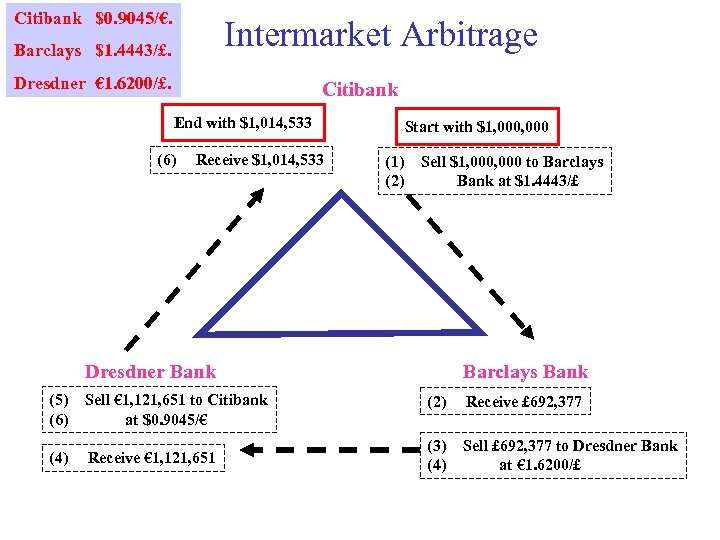 Citibank $0. 9045/€. Intermarket Arbitrage Barclays $1. 4443/£. Dresdner € 1. 6200/£. Citibank End with $1, 014, 533 (6) Receive $1, 014, 533 Start with $1, 000 (1) (2) Sell $1, 000 to Barclays Bank at $1. 4443/£ Dresdner Bank (5) (6) Sell € 1, 121, 651 to Citibank at $0. 9045/€ (4) Receive € 1, 121, 651 Barclays Bank (2) Receive £ 692, 377 (3) (4) Sell £ 692, 377 to Dresdner Bank at € 1. 6200/£
Citibank $0. 9045/€. Intermarket Arbitrage Barclays $1. 4443/£. Dresdner € 1. 6200/£. Citibank End with $1, 014, 533 (6) Receive $1, 014, 533 Start with $1, 000 (1) (2) Sell $1, 000 to Barclays Bank at $1. 4443/£ Dresdner Bank (5) (6) Sell € 1, 121, 651 to Citibank at $0. 9045/€ (4) Receive € 1, 121, 651 Barclays Bank (2) Receive £ 692, 377 (3) (4) Sell £ 692, 377 to Dresdner Bank at € 1. 6200/£
 Things to remember • Market Participants • Transaction types • Quotations • Inter-market arbitrage
Things to remember • Market Participants • Transaction types • Quotations • Inter-market arbitrage


