aad590e957a35fb3eef7c5dcb403de09.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 134
 Foot. Print Caching Chuck Tipton Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Foot. Print Caching Chuck Tipton Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Topics Covered What is Foot. Print caching? – Foot. Print is……. . – Feature Rich CDN Background and Foundation – – – DNS 101 Foot. Print Caching Components of a URL Footprint Supernames URL Modifications DNS Rendezvous • DNS Solution challenges – Best Distributor Selection Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Topics Covered What is Foot. Print caching? – Foot. Print is……. . – Feature Rich CDN Background and Foundation – – – DNS 101 Foot. Print Caching Components of a URL Footprint Supernames URL Modifications DNS Rendezvous • DNS Solution challenges – Best Distributor Selection Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Topics Covered Features and Functionality – – – – Authentication Cookie Support Query. String Handling Footprint Secure FTP Proxy Support SSI and DSI Cache Coupling Cache Peering Content Management and Freshness Control – What happens when content changes – Cache Control Policies • Expires Header • Cache control Header Override Mode – Resource Versioning – On Demand Invalidation Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Topics Covered Features and Functionality – – – – Authentication Cookie Support Query. String Handling Footprint Secure FTP Proxy Support SSI and DSI Cache Coupling Cache Peering Content Management and Freshness Control – What happens when content changes – Cache Control Policies • Expires Header • Cache control Header Override Mode – Resource Versioning – On Demand Invalidation Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Topics Continued Implementation Styles – DNS Delegation • Customers Domain – Examples • DI Domain – Examples – Footprint At the Door (FATD) – Content Rewriter • Content Manager Reports and Statistics – Footprint Manager – Log Files – Footprint Dashboard Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Topics Continued Implementation Styles – DNS Delegation • Customers Domain – Examples • DI Domain – Examples – Footprint At the Door (FATD) – Content Rewriter • Content Manager Reports and Statistics – Footprint Manager – Log Files – Footprint Dashboard Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 More Topics Implementation Tips and Tricks Case Studies Roadmap Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
More Topics Implementation Tips and Tricks Case Studies Roadmap Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
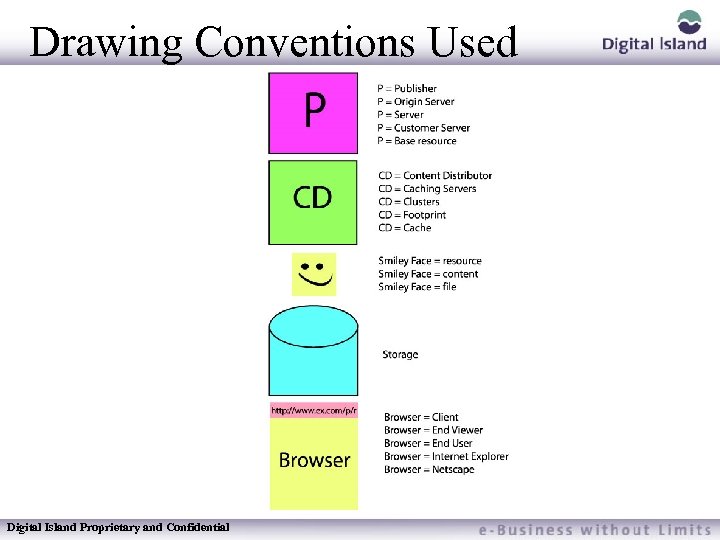 Drawing Conventions Used Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Drawing Conventions Used Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 What is Footprint Caching? Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
What is Footprint Caching? Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Definition of Footprint Caching Footprint caching serves HTTP resources as a cache. Foot. Print takes content from the publisher’s Origin Server based on end viewer demand how those end viewers are being directed to points on Digital Island’s network. That content is replicated on various content distributors (DI’s edge caching servers) as it’s being requested. Once the data is cached the first time, any subsequent requests from other end viewers are served immediately out of the cache. Each server in a server “cluster” is independent and will cache the same files in multiple places in the same rack. Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Definition of Footprint Caching Footprint caching serves HTTP resources as a cache. Foot. Print takes content from the publisher’s Origin Server based on end viewer demand how those end viewers are being directed to points on Digital Island’s network. That content is replicated on various content distributors (DI’s edge caching servers) as it’s being requested. Once the data is cached the first time, any subsequent requests from other end viewers are served immediately out of the cache. Each server in a server “cluster” is independent and will cache the same files in multiple places in the same rack. Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Footprint is……. A globally distributed network of caches – Also known as “Edge Servers” or “Edge Caches” Presented as a single multi-homed host via DNS – Multi-homed host is a computer that is connected to more than one physical data link; these data links may or may not be attached to the same network Provides an intelligent traffic management layer to rendezvous clients with the optimal caching location Serves HTTP based content in response to end viewer browser requests Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Footprint is……. A globally distributed network of caches – Also known as “Edge Servers” or “Edge Caches” Presented as a single multi-homed host via DNS – Multi-homed host is a computer that is connected to more than one physical data link; these data links may or may not be attached to the same network Provides an intelligent traffic management layer to rendezvous clients with the optimal caching location Serves HTTP based content in response to end viewer browser requests Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
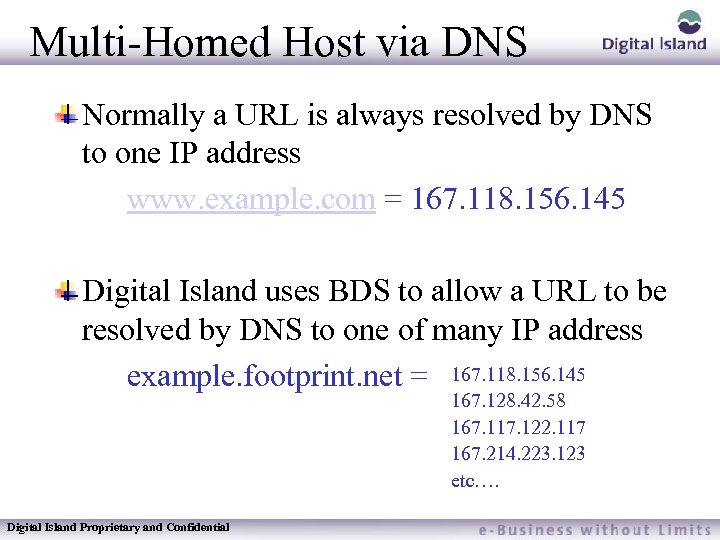 Multi-Homed Host via DNS Normally a URL is always resolved by DNS to one IP address www. example. com = 167. 118. 156. 145 Digital Island uses BDS to allow a URL to be resolved by DNS to one of many IP address example. footprint. net = 167. 118. 156. 145 167. 128. 42. 58 167. 117. 122. 117 167. 214. 223. 123 etc…. Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Multi-Homed Host via DNS Normally a URL is always resolved by DNS to one IP address www. example. com = 167. 118. 156. 145 Digital Island uses BDS to allow a URL to be resolved by DNS to one of many IP address example. footprint. net = 167. 118. 156. 145 167. 128. 42. 58 167. 117. 122. 117 167. 214. 223. 123 etc…. Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
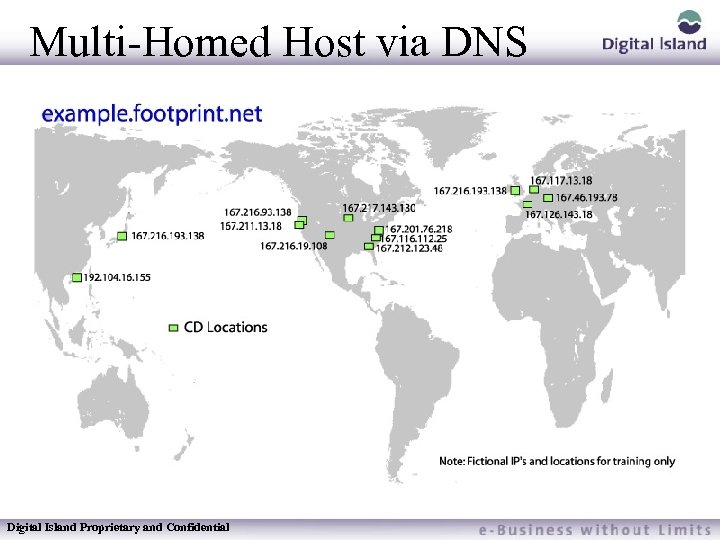 Multi-Homed Host via DNS Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Multi-Homed Host via DNS Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Feature Rich CDN Support Wide Varity of content types – Cookies, Active X, Java and Flash Customers Use FP to Deliver Value Rich Content – Web Sites that generate revenue for our customers Seamless Integration – Simple URL modifications – No huge URL strings to integrate or explain No Network Branding in URL’s – FP stays in the background, maintaining a pure branding experience for our customers – We are In the customers domain name space Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Feature Rich CDN Support Wide Varity of content types – Cookies, Active X, Java and Flash Customers Use FP to Deliver Value Rich Content – Web Sites that generate revenue for our customers Seamless Integration – Simple URL modifications – No huge URL strings to integrate or explain No Network Branding in URL’s – FP stays in the background, maintaining a pure branding experience for our customers – We are In the customers domain name space Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Background and Foundation Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Background and Foundation Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
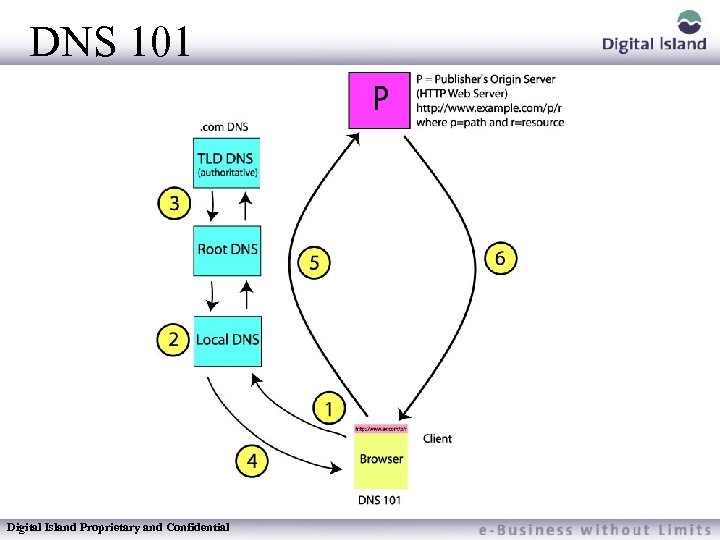 DNS 101 Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
DNS 101 Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 How DNS Works DNS: “The addressing system of the Internet” DNS is the basis for CDN solutions Browser asks for target IP from local nameserver – If local nameserver has IP address stored (cached) will return the target’s IP address – If local nameserver does NOT have the IP, it will ask a remote nameserver for the target (who do I need to talk to? ), and retrieve it from there Local nameserver asks root nameservers – One of 13 that are the center of the DNS system. – Every nameserver on the internet has the root nameservers IP permanently stored Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
How DNS Works DNS: “The addressing system of the Internet” DNS is the basis for CDN solutions Browser asks for target IP from local nameserver – If local nameserver has IP address stored (cached) will return the target’s IP address – If local nameserver does NOT have the IP, it will ask a remote nameserver for the target (who do I need to talk to? ), and retrieve it from there Local nameserver asks root nameservers – One of 13 that are the center of the DNS system. – Every nameserver on the internet has the root nameservers IP permanently stored Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 How DNS Works Root nameservers contain information on which nameservers are responsible for which top level domains (TLD’s) like. com. , . org et cetera – So, if the target is a. com address, the root nameservers will point you to several nameservers that contain AUTHORITATIVE information for the. com TLD . com authoritative nameserver will return IP which domain owner entered when registering the domain Local nameserver now asks that nameserver for the IP address of the target – Target’s nameserver returns that information, plus TTL (Time to Live) – the amount of time the local nameserver should store the IP address it has received Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
How DNS Works Root nameservers contain information on which nameservers are responsible for which top level domains (TLD’s) like. com. , . org et cetera – So, if the target is a. com address, the root nameservers will point you to several nameservers that contain AUTHORITATIVE information for the. com TLD . com authoritative nameserver will return IP which domain owner entered when registering the domain Local nameserver now asks that nameserver for the IP address of the target – Target’s nameserver returns that information, plus TTL (Time to Live) – the amount of time the local nameserver should store the IP address it has received Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
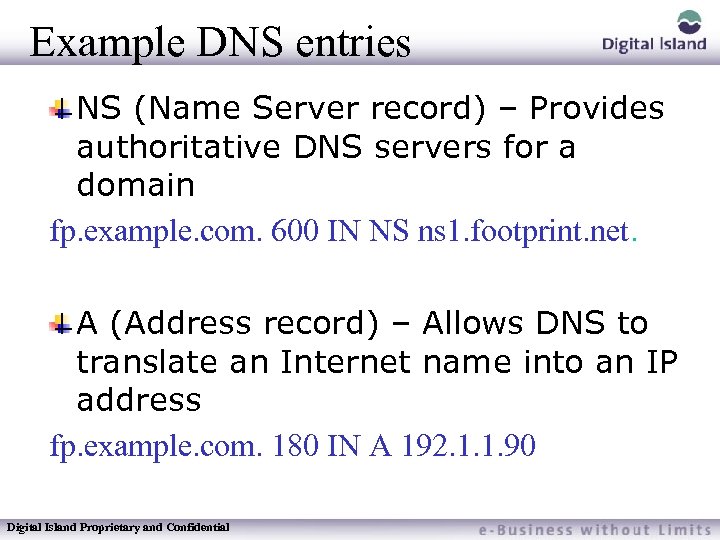 Example DNS entries NS (Name Server record) – Provides authoritative DNS servers for a domain fp. example. com. 600 IN NS ns 1. footprint. net. A (Address record) – Allows DNS to translate an Internet name into an IP address fp. example. com. 180 IN A 192. 1. 1. 90 Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Example DNS entries NS (Name Server record) – Provides authoritative DNS servers for a domain fp. example. com. 600 IN NS ns 1. footprint. net. A (Address record) – Allows DNS to translate an Internet name into an IP address fp. example. com. 180 IN A 192. 1. 1. 90 Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
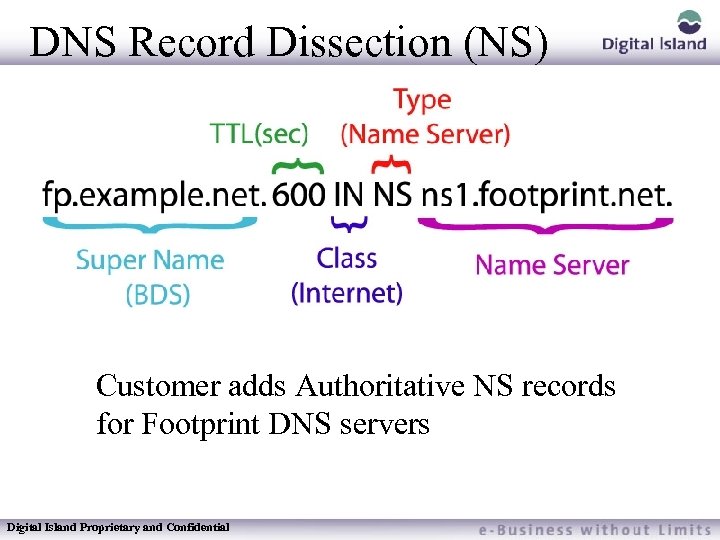 DNS Record Dissection (NS) Customer adds Authoritative NS records for Footprint DNS servers Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
DNS Record Dissection (NS) Customer adds Authoritative NS records for Footprint DNS servers Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
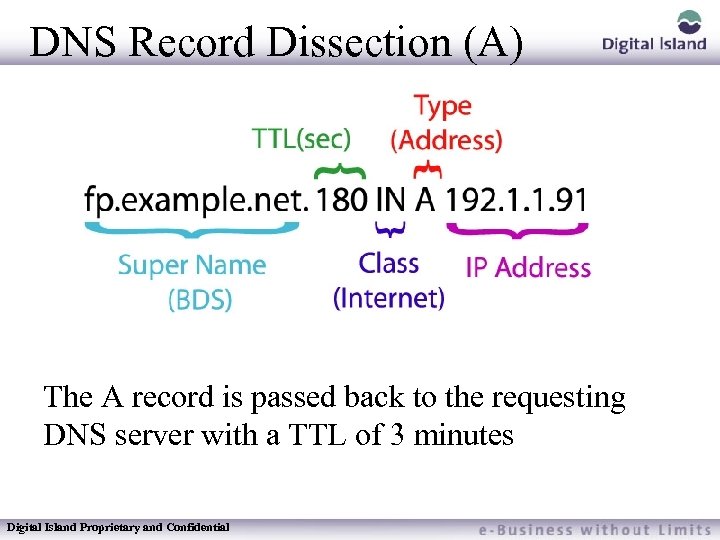 DNS Record Dissection (A) The A record is passed back to the requesting DNS server with a TTL of 3 minutes Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
DNS Record Dissection (A) The A record is passed back to the requesting DNS server with a TTL of 3 minutes Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 DNS Root Servers Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
DNS Root Servers Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
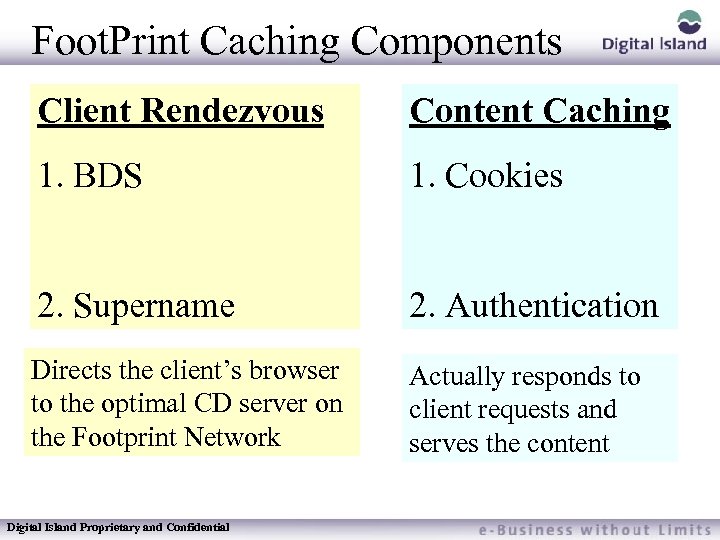 Foot. Print Caching Components Client Rendezvous Content Caching 1. BDS 1. Cookies 2. Supername 2. Authentication Directs the client’s browser to the optimal CD server on the Footprint Network Actually responds to client requests and serves the content Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Foot. Print Caching Components Client Rendezvous Content Caching 1. BDS 1. Cookies 2. Supername 2. Authentication Directs the client’s browser to the optimal CD server on the Footprint Network Actually responds to client requests and serves the content Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
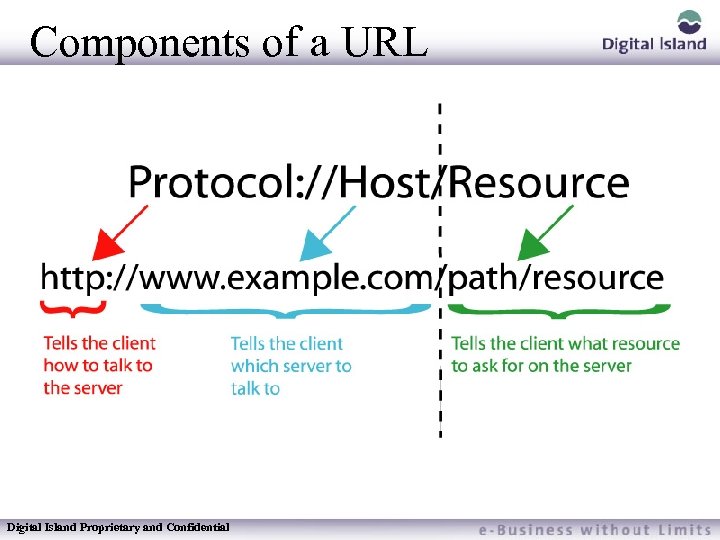 Components of a URL Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Components of a URL Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
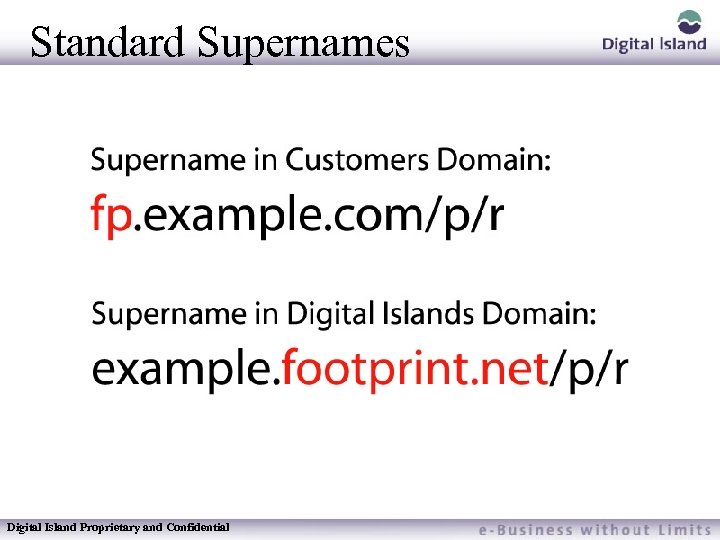
 Footprint Supernames Supername - A domain name that represents all of the CD’s on the Digital Island Network There are three ways a Supername can be implemented – Standard In Customers Domain – Standard In DI’s Domain – Footprint SSL Extended Supernames have been discontinued Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Footprint Supernames Supername - A domain name that represents all of the CD’s on the Digital Island Network There are three ways a Supername can be implemented – Standard In Customers Domain – Standard In DI’s Domain – Footprint SSL Extended Supernames have been discontinued Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
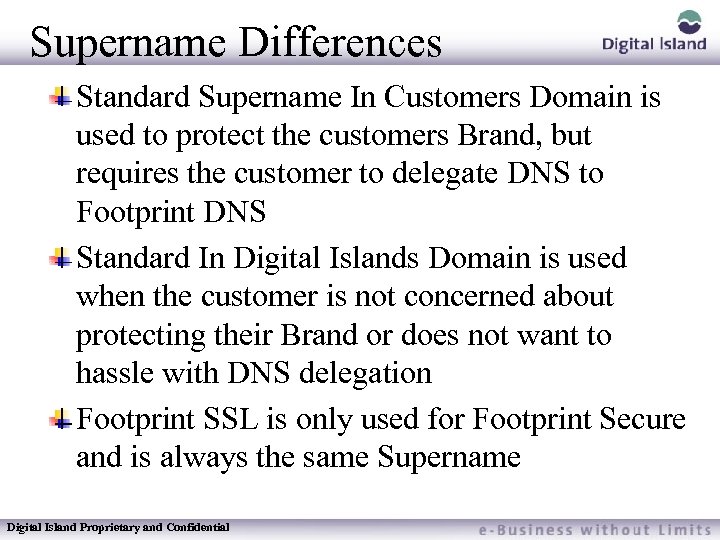 Supername Differences Standard Supername In Customers Domain is used to protect the customers Brand, but requires the customer to delegate DNS to Footprint DNS Standard In Digital Islands Domain is used when the customer is not concerned about protecting their Brand or does not want to hassle with DNS delegation Footprint SSL is only used for Footprint Secure and is always the same Supername Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Supername Differences Standard Supername In Customers Domain is used to protect the customers Brand, but requires the customer to delegate DNS to Footprint DNS Standard In Digital Islands Domain is used when the customer is not concerned about protecting their Brand or does not want to hassle with DNS delegation Footprint SSL is only used for Footprint Secure and is always the same Supername Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Standard Supernames Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Standard Supernames Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Standard Foot. Print URL Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Standard Foot. Print URL Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
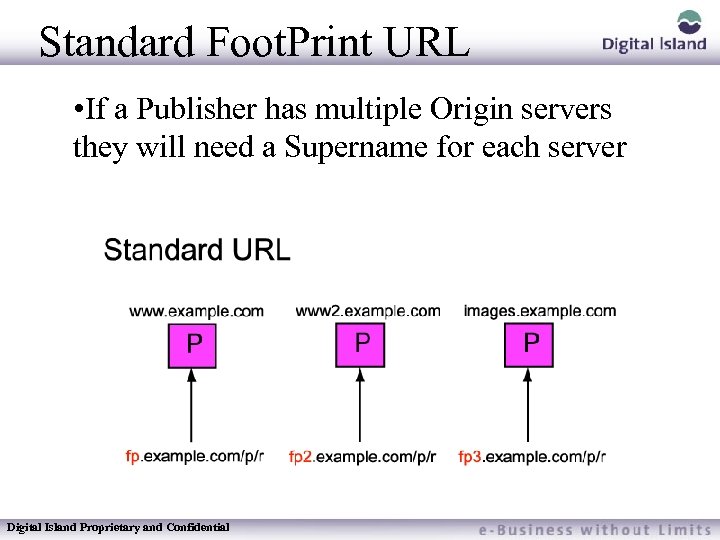 Standard Foot. Print URL • If a Publisher has multiple Origin servers they will need a Supername for each server Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Standard Foot. Print URL • If a Publisher has multiple Origin servers they will need a Supername for each server Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
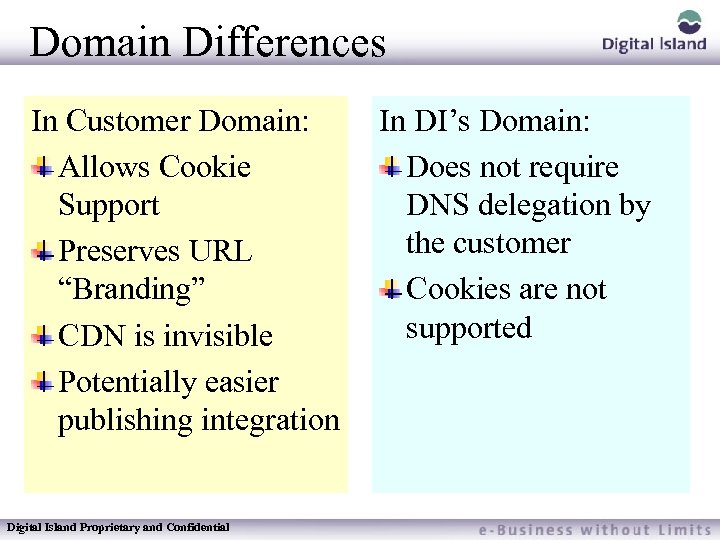 Domain Differences In Customer Domain: Allows Cookie Support Preserves URL “Branding” CDN is invisible Potentially easier publishing integration Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential In DI’s Domain: Does not require DNS delegation by the customer Cookies are not supported
Domain Differences In Customer Domain: Allows Cookie Support Preserves URL “Branding” CDN is invisible Potentially easier publishing integration Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential In DI’s Domain: Does not require DNS delegation by the customer Cookies are not supported
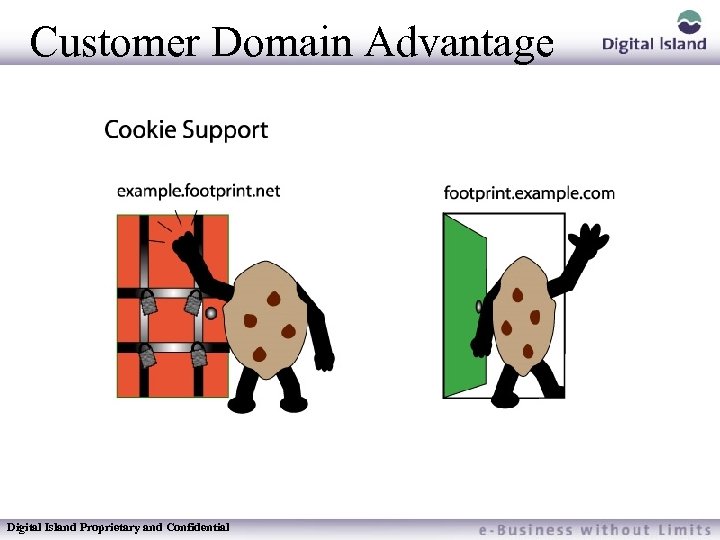 Customer Domain Advantage Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Customer Domain Advantage Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 DNS Delegation Entries In db. userdomain. com file (or equivalent) fp. example. net. 600 IN NS ns 1. footprint. net. fp. example. net. 600 IN NS ns 2. footprint. net. fp. example. net. 600 IN NS ns 3. footprint. net. fp. example. net. 600 IN NS ns 4. footprint. net. fp. example. net. 600 IN NS ns 5. footprint. net. fp. example. net. 600 IN NS ns 6. footprint. net. fp. example. net. 600 IN NS ns 7. footprint. net. fp. example. net. 600 IN NS ns 8. footprint. net. fp. example. net. 600 IN NS ns 9. footprint. net. Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
DNS Delegation Entries In db. userdomain. com file (or equivalent) fp. example. net. 600 IN NS ns 1. footprint. net. fp. example. net. 600 IN NS ns 2. footprint. net. fp. example. net. 600 IN NS ns 3. footprint. net. fp. example. net. 600 IN NS ns 4. footprint. net. fp. example. net. 600 IN NS ns 5. footprint. net. fp. example. net. 600 IN NS ns 6. footprint. net. fp. example. net. 600 IN NS ns 7. footprint. net. fp. example. net. 600 IN NS ns 8. footprint. net. fp. example. net. 600 IN NS ns 9. footprint. net. Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Footprint SSL URL Footprint Secure covered in detail later Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Footprint SSL URL Footprint Secure covered in detail later Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
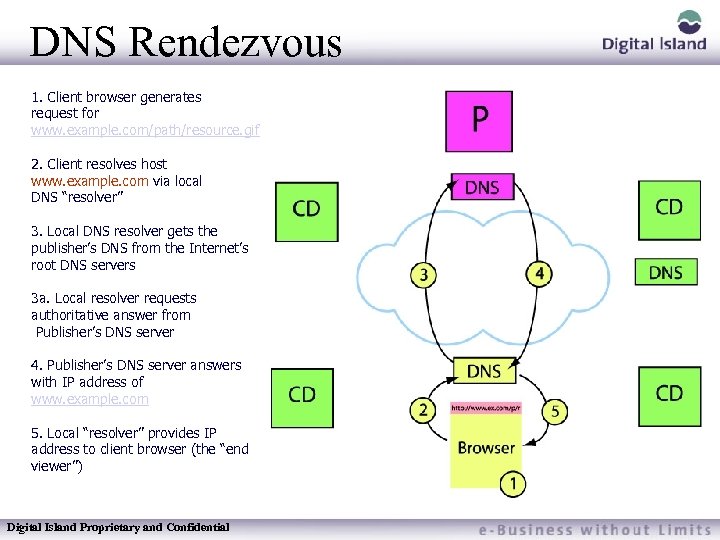 DNS Rendezvous 1. Client browser generates request for www. example. com/path/resource. gif 2. Client resolves host www. example. com via local DNS “resolver” 3. Local DNS resolver gets the publisher’s DNS from the Internet’s root DNS servers 3 a. Local resolver requests authoritative answer from Publisher’s DNS server 4. Publisher’s DNS server answers with IP address of www. example. com 5. Local “resolver” provides IP address to client browser (the “end viewer”) Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
DNS Rendezvous 1. Client browser generates request for www. example. com/path/resource. gif 2. Client resolves host www. example. com via local DNS “resolver” 3. Local DNS resolver gets the publisher’s DNS from the Internet’s root DNS servers 3 a. Local resolver requests authoritative answer from Publisher’s DNS server 4. Publisher’s DNS server answers with IP address of www. example. com 5. Local “resolver” provides IP address to client browser (the “end viewer”) Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
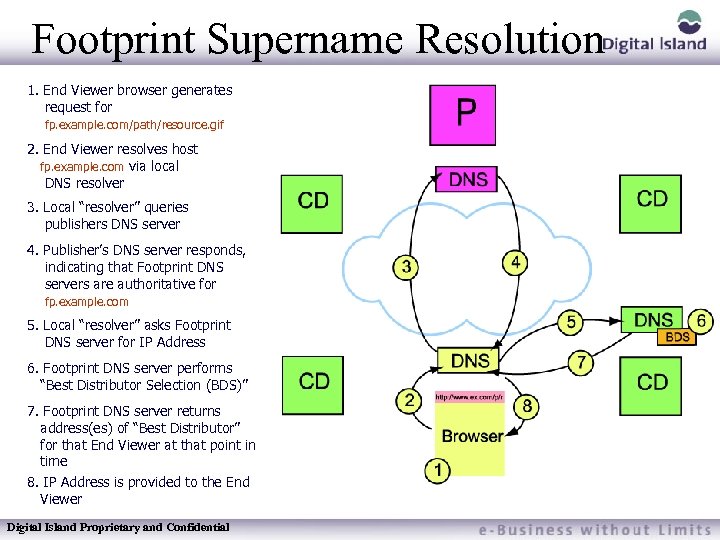 Footprint Supername Resolution 1. End Viewer browser generates request for fp. example. com/path/resource. gif 2. End Viewer resolves host fp. example. com via local DNS resolver 3. Local “resolver” queries publishers DNS server 4. Publisher’s DNS server responds, indicating that Footprint DNS servers are authoritative for fp. example. com 5. Local “resolver” asks Footprint DNS server for IP Address 6. Footprint DNS server performs “Best Distributor Selection (BDS)” 7. Footprint DNS server returns address(es) of “Best Distributor” for that End Viewer at that point in time 8. IP Address is provided to the End Viewer Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Footprint Supername Resolution 1. End Viewer browser generates request for fp. example. com/path/resource. gif 2. End Viewer resolves host fp. example. com via local DNS resolver 3. Local “resolver” queries publishers DNS server 4. Publisher’s DNS server responds, indicating that Footprint DNS servers are authoritative for fp. example. com 5. Local “resolver” asks Footprint DNS server for IP Address 6. Footprint DNS server performs “Best Distributor Selection (BDS)” 7. Footprint DNS server returns address(es) of “Best Distributor” for that End Viewer at that point in time 8. IP Address is provided to the End Viewer Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 DNS Rendezvous: Benefits Standards-based – Uses the standard DNS protocol Extremely Responsive – Short DNS Time to Live (TTL) values on addresses provided by Footprint to ensure responsiveness to changing conditions, keeps data fresh Redundant – Options to provide local fail-over by providing multiple IP addresses – Footprint utilizes redundant, distributed DNS servers to ensure availability and performance Footprint uses standard bind V. 8 with proprietary extensions to incorporate BDS (Best Distributor Selection) Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
DNS Rendezvous: Benefits Standards-based – Uses the standard DNS protocol Extremely Responsive – Short DNS Time to Live (TTL) values on addresses provided by Footprint to ensure responsiveness to changing conditions, keeps data fresh Redundant – Options to provide local fail-over by providing multiple IP addresses – Footprint utilizes redundant, distributed DNS servers to ensure availability and performance Footprint uses standard bind V. 8 with proprietary extensions to incorporate BDS (Best Distributor Selection) Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Some DNS Challenges DNS Proximity – ISP’s DNS far away from actual end viewer – BDS may return the CD cluster closest to ISP’s DNS, not the CD cluster closest to the End Viewer Recursive DNS Settings – Publishers Servers Set to Recurse • i. e. don’t pass the request on to others, but try to resolve the request themselves – BDS (Best Distributor Selection) will reply with the optimal CD to the publishers DNS server and not the ISP (end viewers) DNS Server Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Some DNS Challenges DNS Proximity – ISP’s DNS far away from actual end viewer – BDS may return the CD cluster closest to ISP’s DNS, not the CD cluster closest to the End Viewer Recursive DNS Settings – Publishers Servers Set to Recurse • i. e. don’t pass the request on to others, but try to resolve the request themselves – BDS (Best Distributor Selection) will reply with the optimal CD to the publishers DNS server and not the ISP (end viewers) DNS Server Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
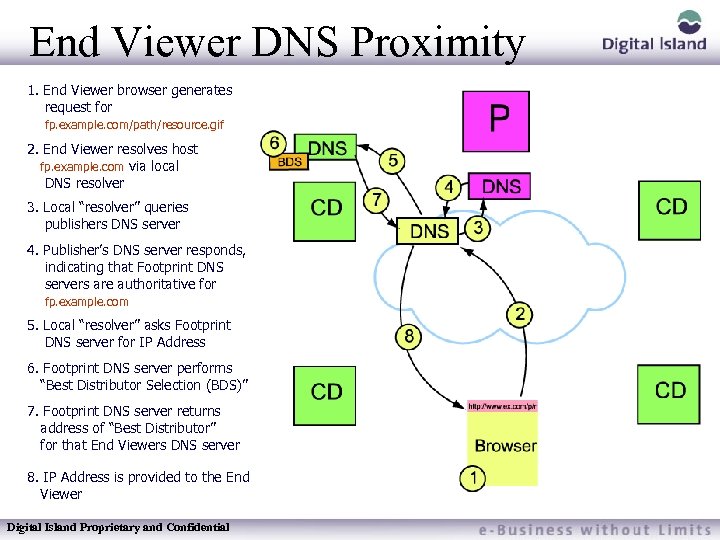 End Viewer DNS Proximity 1. End Viewer browser generates request for fp. example. com/path/resource. gif 2. End Viewer resolves host fp. example. com via local DNS resolver 3. Local “resolver” queries publishers DNS server 4. Publisher’s DNS server responds, indicating that Footprint DNS servers are authoritative for fp. example. com 5. Local “resolver” asks Footprint DNS server for IP Address 6. Footprint DNS server performs “Best Distributor Selection (BDS)” 7. Footprint DNS server returns address of “Best Distributor” for that End Viewers DNS server 8. IP Address is provided to the End Viewer Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
End Viewer DNS Proximity 1. End Viewer browser generates request for fp. example. com/path/resource. gif 2. End Viewer resolves host fp. example. com via local DNS resolver 3. Local “resolver” queries publishers DNS server 4. Publisher’s DNS server responds, indicating that Footprint DNS servers are authoritative for fp. example. com 5. Local “resolver” asks Footprint DNS server for IP Address 6. Footprint DNS server performs “Best Distributor Selection (BDS)” 7. Footprint DNS server returns address of “Best Distributor” for that End Viewers DNS server 8. IP Address is provided to the End Viewer Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
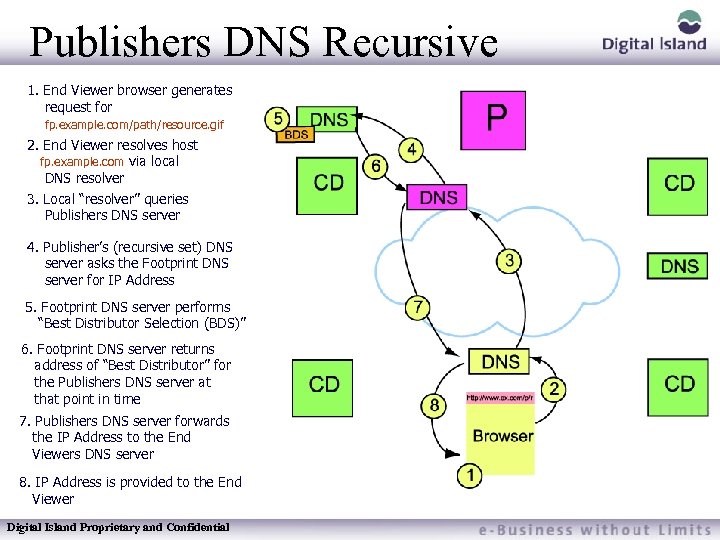 Publishers DNS Recursive 1. End Viewer browser generates request for fp. example. com/path/resource. gif 2. End Viewer resolves host fp. example. com via local DNS resolver 3. Local “resolver” queries Publishers DNS server 4. Publisher’s (recursive set) DNS server asks the Footprint DNS server for IP Address 5. Footprint DNS server performs “Best Distributor Selection (BDS)” 6. Footprint DNS server returns address of “Best Distributor” for the Publishers DNS server at that point in time 7. Publishers DNS server forwards the IP Address to the End Viewers DNS server 8. IP Address is provided to the End Viewer Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Publishers DNS Recursive 1. End Viewer browser generates request for fp. example. com/path/resource. gif 2. End Viewer resolves host fp. example. com via local DNS resolver 3. Local “resolver” queries Publishers DNS server 4. Publisher’s (recursive set) DNS server asks the Footprint DNS server for IP Address 5. Footprint DNS server performs “Best Distributor Selection (BDS)” 6. Footprint DNS server returns address of “Best Distributor” for the Publishers DNS server at that point in time 7. Publishers DNS server forwards the IP Address to the End Viewers DNS server 8. IP Address is provided to the End Viewer Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Best Distributor Selection (BDS) Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Best Distributor Selection (BDS) Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
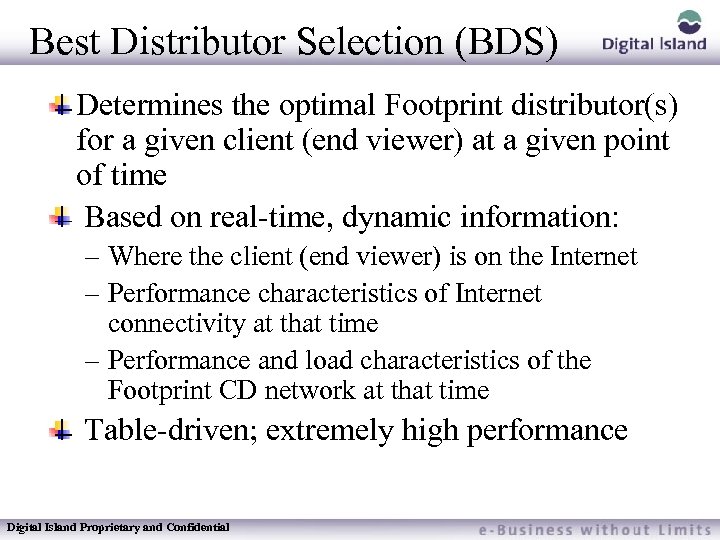 Best Distributor Selection (BDS) Determines the optimal Footprint distributor(s) for a given client (end viewer) at a given point of time Based on real-time, dynamic information: – Where the client (end viewer) is on the Internet – Performance characteristics of Internet connectivity at that time – Performance and load characteristics of the Footprint CD network at that time Table-driven; extremely high performance Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Best Distributor Selection (BDS) Determines the optimal Footprint distributor(s) for a given client (end viewer) at a given point of time Based on real-time, dynamic information: – Where the client (end viewer) is on the Internet – Performance characteristics of Internet connectivity at that time – Performance and load characteristics of the Footprint CD network at that time Table-driven; extremely high performance Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
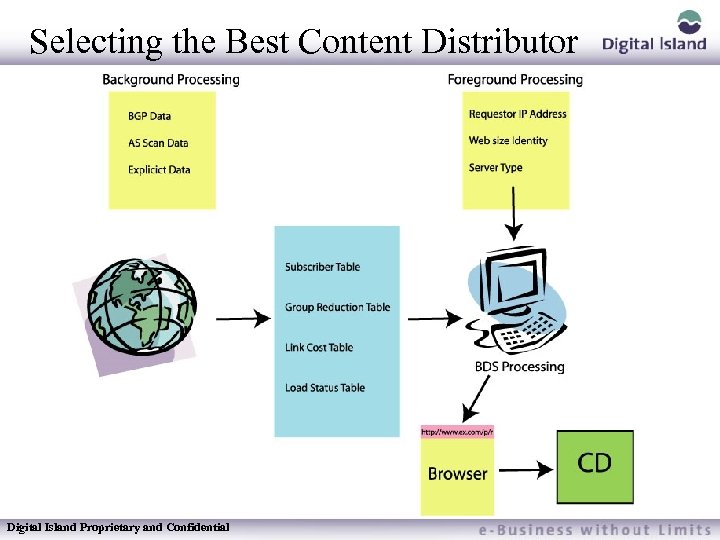
 Selecting the Best Content Distributor Key to Footprint routing is BDS – Process that determines which CD is most appropriate for a particular end viewer Foreground Process – Must make a selection quickly Background Processes – Prepare data to be used by the foreground processes Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Selecting the Best Content Distributor Key to Footprint routing is BDS – Process that determines which CD is most appropriate for a particular end viewer Foreground Process – Must make a selection quickly Background Processes – Prepare data to be used by the foreground processes Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Selecting the Best Content Distributor Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Selecting the Best Content Distributor Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 BDS Details Inputs – Requestor IP address – Web Site Identity – Service Type Table Driven Algorithms – Routing Process must be fast – Publishers put special emphasis on index page being loaded quickly Four Tables – – Subscriber Table Group Reduction Table Link Cost Table Load Status Table Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
BDS Details Inputs – Requestor IP address – Web Site Identity – Service Type Table Driven Algorithms – Routing Process must be fast – Publishers put special emphasis on index page being loaded quickly Four Tables – – Subscriber Table Group Reduction Table Link Cost Table Load Status Table Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
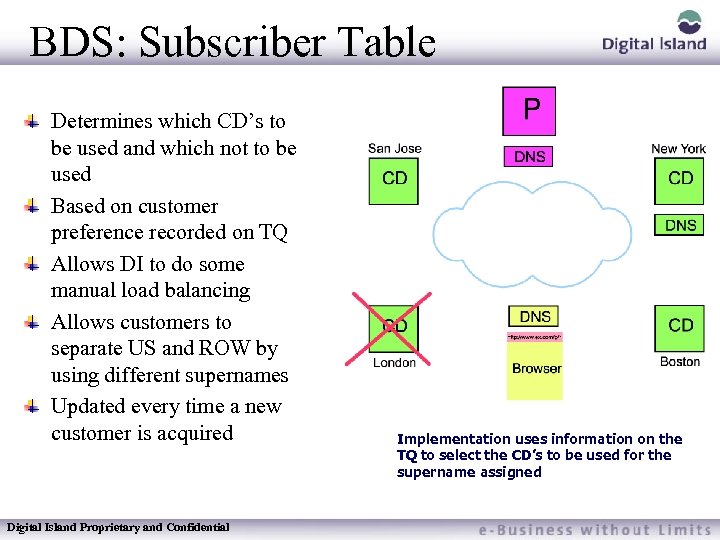 BDS: Subscriber Table Determines which CD’s to be used and which not to be used Based on customer preference recorded on TQ Allows DI to do some manual load balancing Allows customers to separate US and ROW by using different supernames Updated every time a new customer is acquired Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential Implementation uses information on the TQ to select the CD’s to be used for the supername assigned
BDS: Subscriber Table Determines which CD’s to be used and which not to be used Based on customer preference recorded on TQ Allows DI to do some manual load balancing Allows customers to separate US and ROW by using different supernames Updated every time a new customer is acquired Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential Implementation uses information on the TQ to select the CD’s to be used for the supername assigned
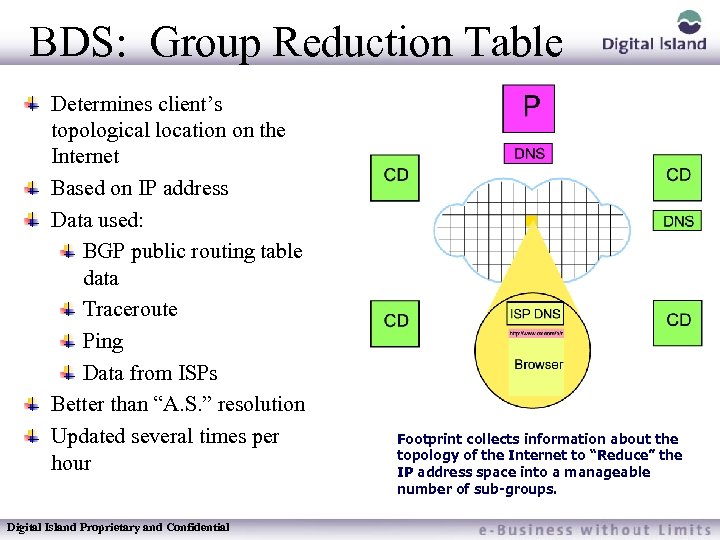 BDS: Group Reduction Table Determines client’s topological location on the Internet Based on IP address Data used: BGP public routing table data Traceroute Ping Data from ISPs Better than “A. S. ” resolution Updated several times per hour Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential Footprint collects information about the topology of the Internet to “Reduce” the IP address space into a manageable number of sub-groups.
BDS: Group Reduction Table Determines client’s topological location on the Internet Based on IP address Data used: BGP public routing table data Traceroute Ping Data from ISPs Better than “A. S. ” resolution Updated several times per hour Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential Footprint collects information about the topology of the Internet to “Reduce” the IP address space into a manageable number of sub-groups.
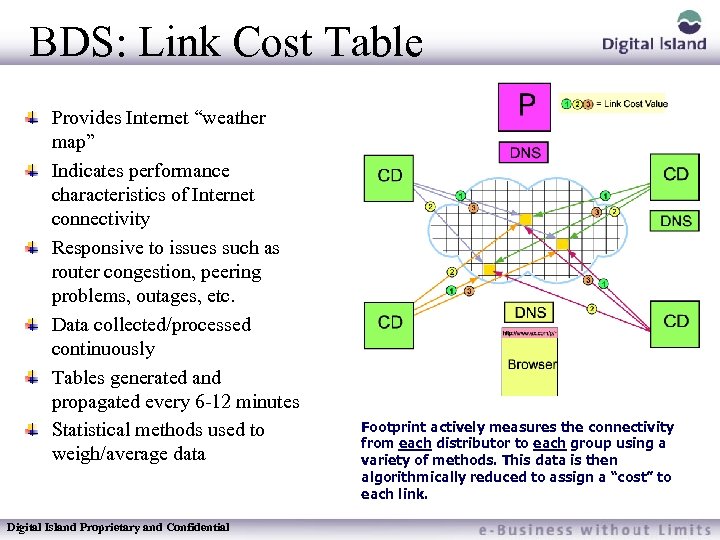 BDS: Link Cost Table Provides Internet “weather map” Indicates performance characteristics of Internet connectivity Responsive to issues such as router congestion, peering problems, outages, etc. Data collected/processed continuously Tables generated and propagated every 6 -12 minutes Statistical methods used to weigh/average data Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential Footprint actively measures the connectivity from each distributor to each group using a variety of methods. This data is then algorithmically reduced to assign a “cost” to each link.
BDS: Link Cost Table Provides Internet “weather map” Indicates performance characteristics of Internet connectivity Responsive to issues such as router congestion, peering problems, outages, etc. Data collected/processed continuously Tables generated and propagated every 6 -12 minutes Statistical methods used to weigh/average data Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential Footprint actively measures the connectivity from each distributor to each group using a variety of methods. This data is then algorithmically reduced to assign a “cost” to each link.
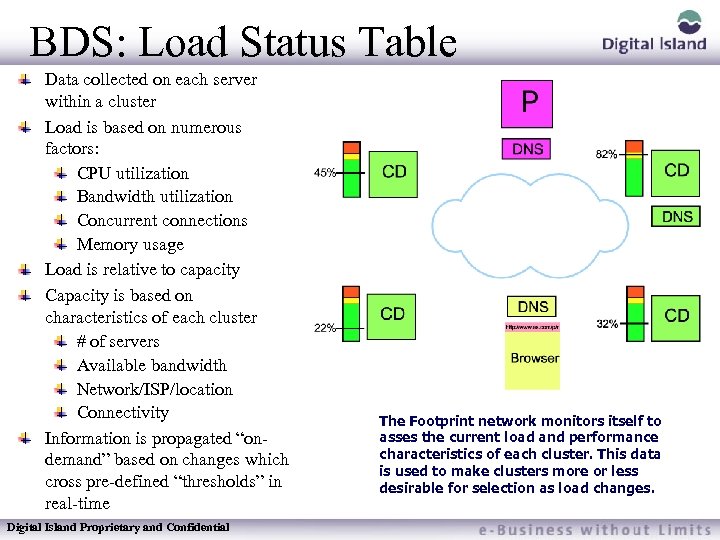 BDS: Load Status Table Data collected on each server within a cluster Load is based on numerous factors: CPU utilization Bandwidth utilization Concurrent connections Memory usage Load is relative to capacity Capacity is based on characteristics of each cluster # of servers Available bandwidth Network/ISP/location Connectivity Information is propagated “ondemand” based on changes which cross pre-defined “thresholds” in real-time Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential The Footprint network monitors itself to asses the current load and performance characteristics of each cluster. This data is used to make clusters more or less desirable for selection as load changes.
BDS: Load Status Table Data collected on each server within a cluster Load is based on numerous factors: CPU utilization Bandwidth utilization Concurrent connections Memory usage Load is relative to capacity Capacity is based on characteristics of each cluster # of servers Available bandwidth Network/ISP/location Connectivity Information is propagated “ondemand” based on changes which cross pre-defined “thresholds” in real-time Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential The Footprint network monitors itself to asses the current load and performance characteristics of each cluster. This data is used to make clusters more or less desirable for selection as load changes.
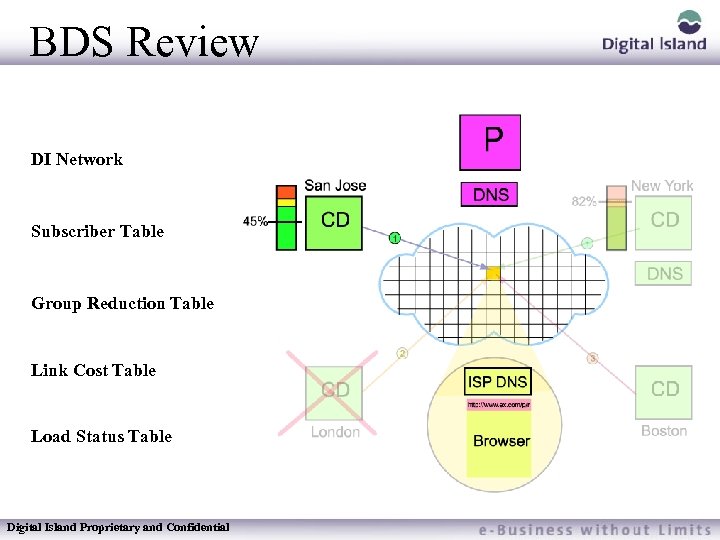 BDS Review DI Network Subscriber Table Group Reduction Table Link Cost Table Load Status Table Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
BDS Review DI Network Subscriber Table Group Reduction Table Link Cost Table Load Status Table Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 BDS Updates Table Updates are performed by broadcasting incremental changes throughout the CDN – Subscriber Tables are updated as necessary when new customers are added or their status changes – Group Reduction Tables are updated several times per hour – Link Cost Tables are updated every 6 -12 minutes – Load Status Tables are updated on-demand based on changes which cross pre-defined “thresholds” set on the CD’s in real-time Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
BDS Updates Table Updates are performed by broadcasting incremental changes throughout the CDN – Subscriber Tables are updated as necessary when new customers are added or their status changes – Group Reduction Tables are updated several times per hour – Link Cost Tables are updated every 6 -12 minutes – Load Status Tables are updated on-demand based on changes which cross pre-defined “thresholds” set on the CD’s in real-time Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Validation of the BDS process BDS is continually monitored to verify that the routing process is working effectively The Footprint CDN regularly performs the following kinds of measurements and metrics to ensure optimal routing: – Continuous real-time monitoring of network performance through special instrumentation installed in every content distributor, as well as standard SNMP based information – Regular analysis of logs to learn how clients are distributed within the Footprint network – Use of third-party metrics from Internet measurement companies such as Keynote. This service provides charts comparing the performance of customer Web sites with and without Footprint. This service also provides valuable “early warning” data about network congestion and outages. Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Validation of the BDS process BDS is continually monitored to verify that the routing process is working effectively The Footprint CDN regularly performs the following kinds of measurements and metrics to ensure optimal routing: – Continuous real-time monitoring of network performance through special instrumentation installed in every content distributor, as well as standard SNMP based information – Regular analysis of logs to learn how clients are distributed within the Footprint network – Use of third-party metrics from Internet measurement companies such as Keynote. This service provides charts comparing the performance of customer Web sites with and without Footprint. This service also provides valuable “early warning” data about network congestion and outages. Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Caching Rack Contents Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Caching Rack Contents Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Rack Process Flow Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Rack Process Flow Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Features and Functionality Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Features and Functionality Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Request and Response Headers are imbedded in HTML pages to produce a desired result Headers are used to enable certain functionality within the Footprint network Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Request and Response Headers are imbedded in HTML pages to produce a desired result Headers are used to enable certain functionality within the Footprint network Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Request and Response Headers Request Headers: – Host (multiple virtual servers (domains) on one physical server) – Browser type (IE v 5. 5 w/128 bit encryption) – Cookies, which are presented as a header Response Headers (those that are sent from the publishers server): – – Expires Set a cookie (create a cookie on the client browser) I am server type IIS v. 5 A Footprint custom header Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Request and Response Headers Request Headers: – Host (multiple virtual servers (domains) on one physical server) – Browser type (IE v 5. 5 w/128 bit encryption) – Cookies, which are presented as a header Response Headers (those that are sent from the publishers server): – – Expires Set a cookie (create a cookie on the client browser) I am server type IIS v. 5 A Footprint custom header Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
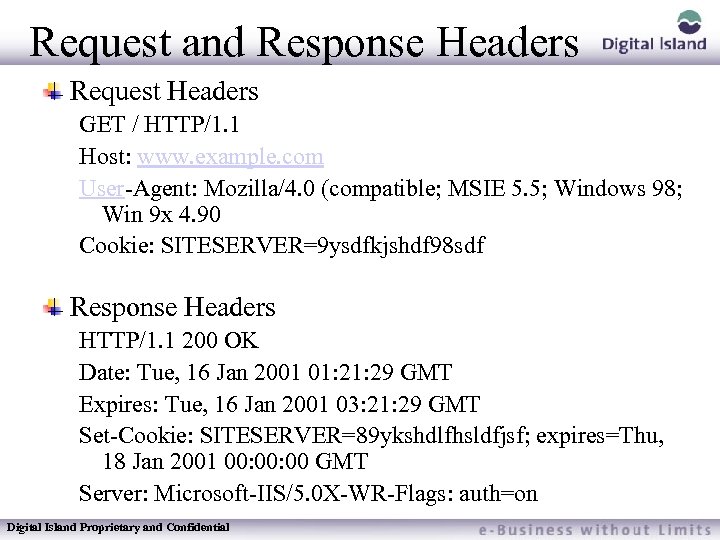 Request and Response Headers Request Headers GET / HTTP/1. 1 Host: www. example. com User-Agent: Mozilla/4. 0 (compatible; MSIE 5. 5; Windows 98; Win 9 x 4. 90 Cookie: SITESERVER=9 ysdfkjshdf 98 sdf Response Headers HTTP/1. 1 200 OK Date: Tue, 16 Jan 2001 01: 29 GMT Expires: Tue, 16 Jan 2001 03: 21: 29 GMT Set-Cookie: SITESERVER=89 ykshdlfhsldfjsf; expires=Thu, 18 Jan 2001 00: 00 GMT Server: Microsoft-IIS/5. 0 X-WR-Flags: auth=on Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Request and Response Headers Request Headers GET / HTTP/1. 1 Host: www. example. com User-Agent: Mozilla/4. 0 (compatible; MSIE 5. 5; Windows 98; Win 9 x 4. 90 Cookie: SITESERVER=9 ysdfkjshdf 98 sdf Response Headers HTTP/1. 1 200 OK Date: Tue, 16 Jan 2001 01: 29 GMT Expires: Tue, 16 Jan 2001 03: 21: 29 GMT Set-Cookie: SITESERVER=89 ykshdlfhsldfjsf; expires=Thu, 18 Jan 2001 00: 00 GMT Server: Microsoft-IIS/5. 0 X-WR-Flags: auth=on Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
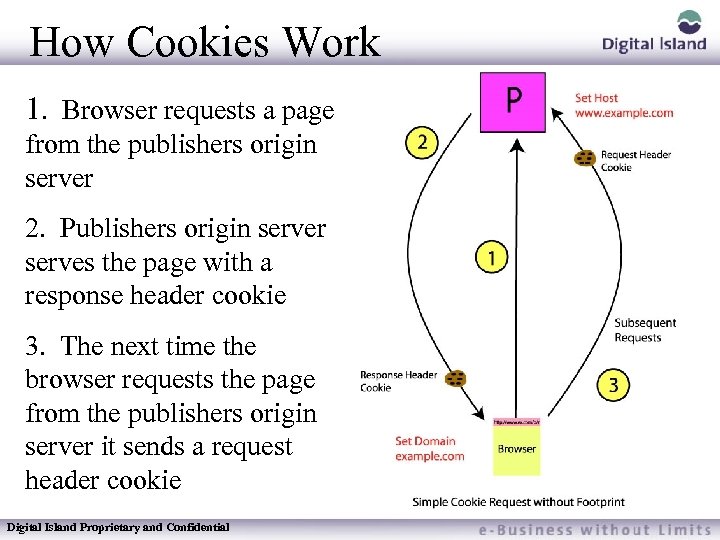 How Cookies Work 1. Browser requests a page from the publishers origin server 2. Publishers origin server serves the page with a response header cookie 3. The next time the browser requests the page from the publishers origin server it sends a request header cookie Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
How Cookies Work 1. Browser requests a page from the publishers origin server 2. Publishers origin server serves the page with a response header cookie 3. The next time the browser requests the page from the publishers origin server it sends a request header cookie Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Definition of Cookies A cookie is a piece of text that a web server (publisher) can store on an end viewers hard disk. Cookies allow a web site to store information on an end viewers machine and later retrieve it. The pieces of information are stored as name-value pairs. For example, a web site might generate a unique ID number for each end viewer and store the ID number on each end viewers machine using a cookie file. Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Definition of Cookies A cookie is a piece of text that a web server (publisher) can store on an end viewers hard disk. Cookies allow a web site to store information on an end viewers machine and later retrieve it. The pieces of information are stored as name-value pairs. For example, a web site might generate a unique ID number for each end viewer and store the ID number on each end viewers machine using a cookie file. Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
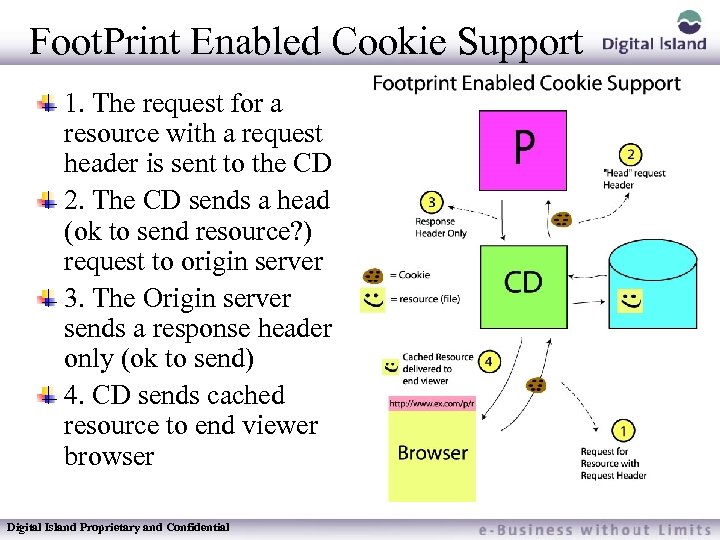 Foot. Print Enabled Cookie Support 1. The request for a resource with a request header is sent to the CD 2. The CD sends a head (ok to send resource? ) request to origin server 3. The Origin server sends a response header only (ok to send) 4. CD sends cached resource to end viewer browser Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Foot. Print Enabled Cookie Support 1. The request for a resource with a request header is sent to the CD 2. The CD sends a head (ok to send resource? ) request to origin server 3. The Origin server sends a response header only (ok to send) 4. CD sends cached resource to end viewer browser Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
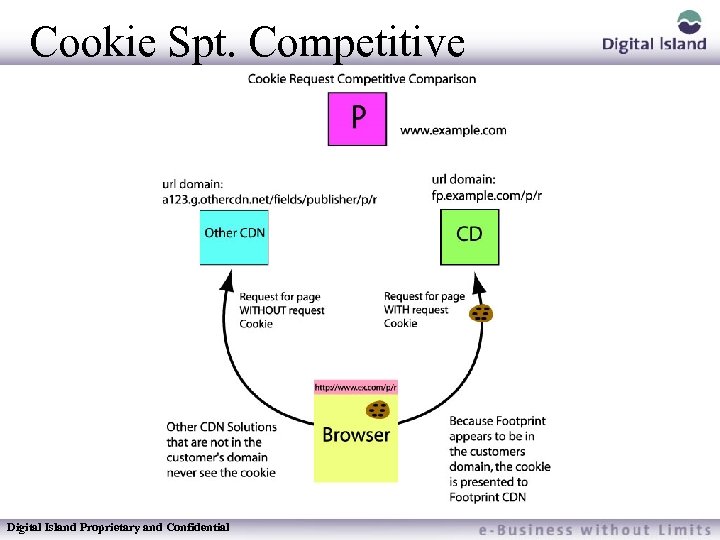 Cookie Spt. Competitive Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Cookie Spt. Competitive Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Cookie Support for Content There are 3 modes of Cookie support – Cookie Mode: Assign – Cookie Mode: Check – Cookie Mode: Fresh Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Cookie Support for Content There are 3 modes of Cookie support – Cookie Mode: Assign – Cookie Mode: Check – Cookie Mode: Fresh Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
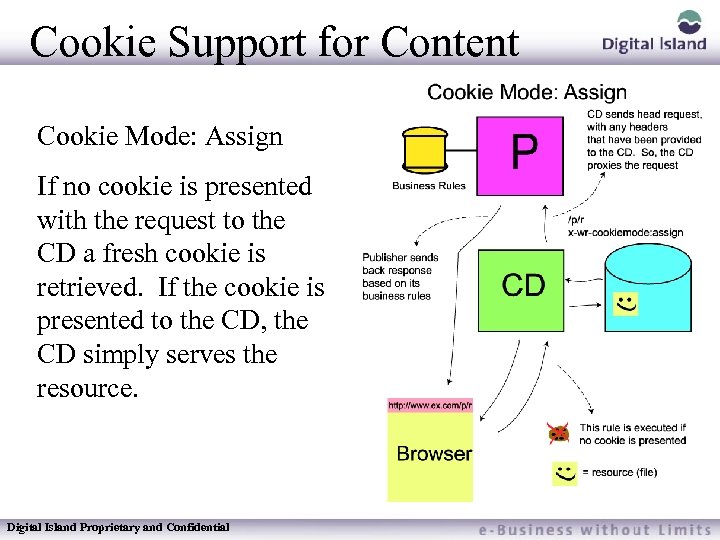 Cookie Support for Content Cookie Mode: Assign If no cookie is presented with the request to the CD a fresh cookie is retrieved. If the cookie is presented to the CD, the CD simply serves the resource. Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Cookie Support for Content Cookie Mode: Assign If no cookie is presented with the request to the CD a fresh cookie is retrieved. If the cookie is presented to the CD, the CD simply serves the resource. Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
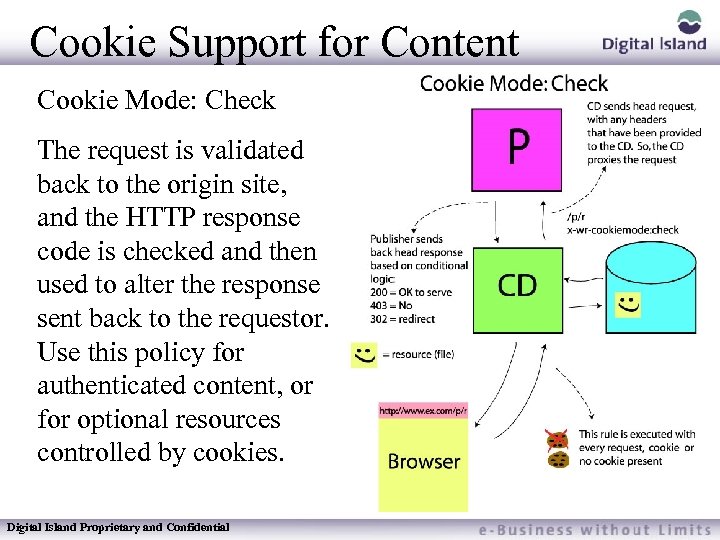 Cookie Support for Content Cookie Mode: Check The request is validated back to the origin site, and the HTTP response code is checked and then used to alter the response sent back to the requestor. Use this policy for authenticated content, or for optional resources controlled by cookies. Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Cookie Support for Content Cookie Mode: Check The request is validated back to the origin site, and the HTTP response code is checked and then used to alter the response sent back to the requestor. Use this policy for authenticated content, or for optional resources controlled by cookies. Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
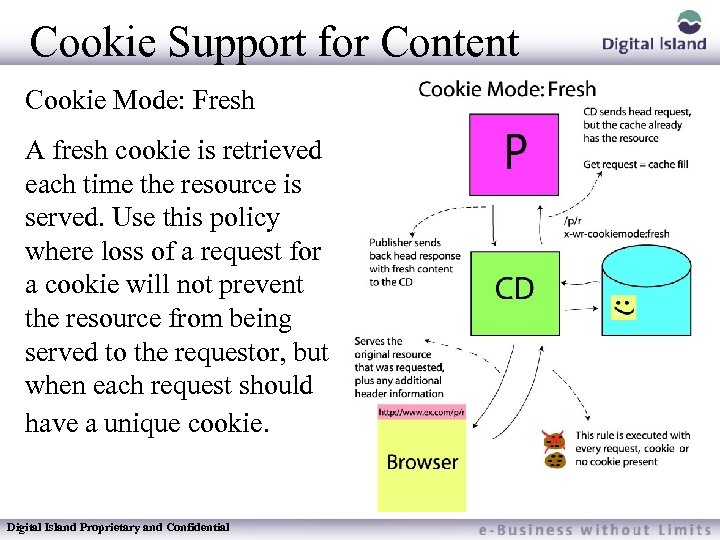 Cookie Support for Content Cookie Mode: Fresh A fresh cookie is retrieved each time the resource is served. Use this policy where loss of a request for a cookie will not prevent the resource from being served to the requestor, but when each request should have a unique cookie. Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Cookie Support for Content Cookie Mode: Fresh A fresh cookie is retrieved each time the resource is served. Use this policy where loss of a request for a cookie will not prevent the resource from being served to the requestor, but when each request should have a unique cookie. Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Query String Handling A Query String is used to store information – Shopping Cart Items – Location (country specific) – User Name Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Query String Handling A Query String is used to store information – Shopping Cart Items – Location (country specific) – User Name Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
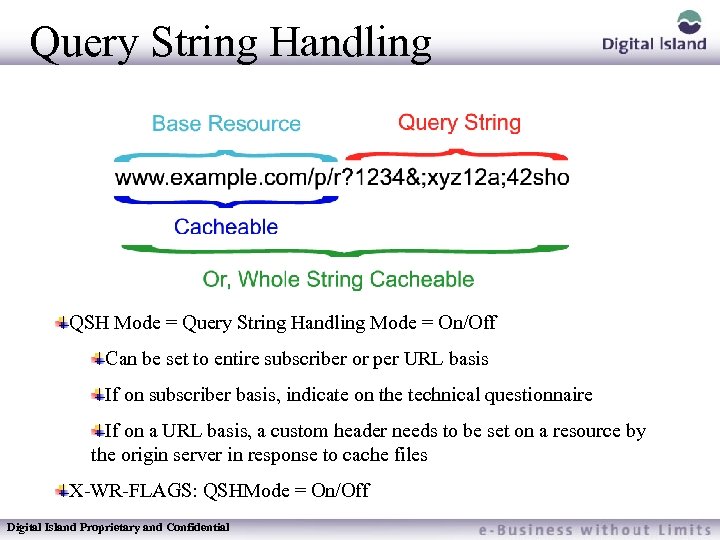 Query String Handling QSH Mode = Query String Handling Mode = On/Off Can be set to entire subscriber or per URL basis If on subscriber basis, indicate on the technical questionnaire If on a URL basis, a custom header needs to be set on a resource by the origin server in response to cache files X-WR-FLAGS: QSHMode = On/Off Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Query String Handling QSH Mode = Query String Handling Mode = On/Off Can be set to entire subscriber or per URL basis If on subscriber basis, indicate on the technical questionnaire If on a URL basis, a custom header needs to be set on a resource by the origin server in response to cache files X-WR-FLAGS: QSHMode = On/Off Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Query String Usage Examples Base Resource Only – If the Query information contains USER name information, Footprint would only cache one instance of the resource, not an instance of it for every unique USER Entire Query String – If the Query information contains a Country Code, this may determine the attributes of the resource, such as an English version or French version. Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Query String Usage Examples Base Resource Only – If the Query information contains USER name information, Footprint would only cache one instance of the resource, not an instance of it for every unique USER Entire Query String – If the Query information contains a Country Code, this may determine the attributes of the resource, such as an English version or French version. Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
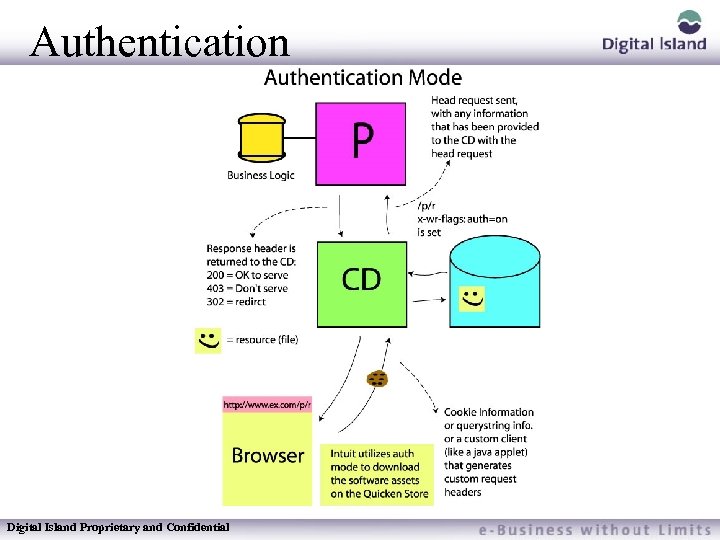
 Authentication Used to protect cacheable resources from being downloaded without a password or filing out information first Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Authentication Used to protect cacheable resources from being downloaded without a password or filing out information first Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Authentication Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Authentication Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Authentication Set with header information – “XW-R-Flags” header set to “auth=on” Cookie based authentication is supported – Supername must be in Customers Domain HTTP authentication would still require customers input each time a resource was requested Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Authentication Set with header information – “XW-R-Flags” header set to “auth=on” Cookie based authentication is supported – Supername must be in Customers Domain HTTP authentication would still require customers input each time a resource was requested Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Footprint Secure serves ‘shared content’ on a secured page from standard HTTP caches. We are not caching the SSL content! Shared Content is non secure content that has no need to be served from an HTTPS server – Lowers Overhead on Secure Server Shared content is served as HTTPS content from specific Footprint Secure enabled CD’s No Warning of Non-Secure content being served Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Footprint Secure serves ‘shared content’ on a secured page from standard HTTP caches. We are not caching the SSL content! Shared Content is non secure content that has no need to be served from an HTTPS server – Lowers Overhead on Secure Server Shared content is served as HTTPS content from specific Footprint Secure enabled CD’s No Warning of Non-Secure content being served Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
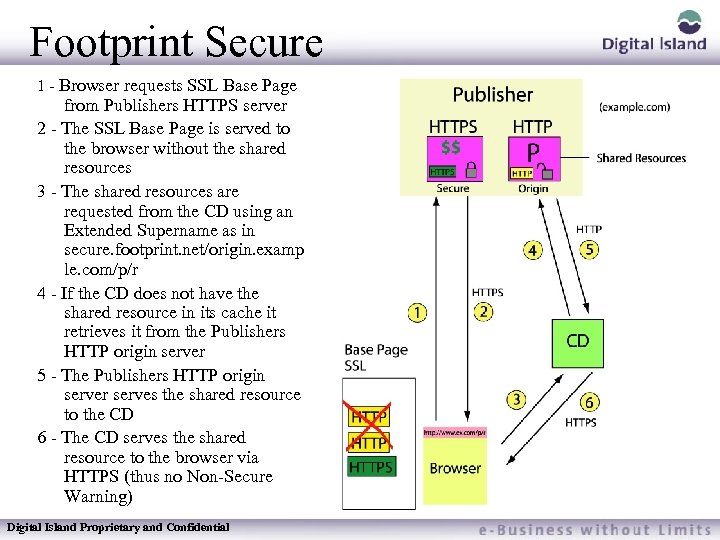 Footprint Secure 1 - Browser requests SSL Base Page from Publishers HTTPS server 2 - The SSL Base Page is served to the browser without the shared resources 3 - The shared resources are requested from the CD using an Extended Supername as in secure. footprint. net/origin. examp le. com/p/r 4 - If the CD does not have the shared resource in its cache it retrieves it from the Publishers HTTP origin server 5 - The Publishers HTTP origin server serves the shared resource to the CD 6 - The CD serves the shared resource to the browser via HTTPS (thus no Non-Secure Warning) Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Footprint Secure 1 - Browser requests SSL Base Page from Publishers HTTPS server 2 - The SSL Base Page is served to the browser without the shared resources 3 - The shared resources are requested from the CD using an Extended Supername as in secure. footprint. net/origin. examp le. com/p/r 4 - If the CD does not have the shared resource in its cache it retrieves it from the Publishers HTTP origin server 5 - The Publishers HTTP origin server serves the shared resource to the CD 6 - The CD serves the shared resource to the browser via HTTPS (thus no Non-Secure Warning) Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
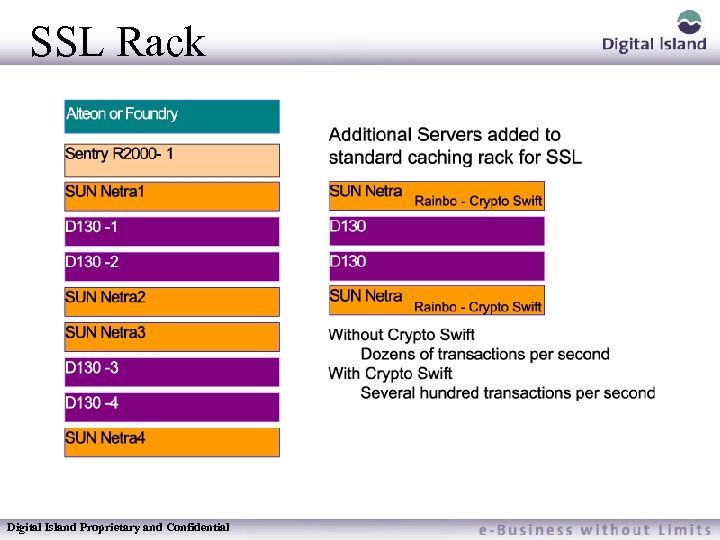 SSL Rack Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
SSL Rack Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 SSL Customer Requirements Customer must move shared content (non-secure) from HTTPS server to HTTP server Must use Footprint SSL URL secure. footprint. net – Needed to prevent the Non-Secure Warning – SSL servers have certificates for secure. footprint. net Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
SSL Customer Requirements Customer must move shared content (non-secure) from HTTPS server to HTTP server Must use Footprint SSL URL secure. footprint. net – Needed to prevent the Non-Secure Warning – SSL servers have certificates for secure. footprint. net Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
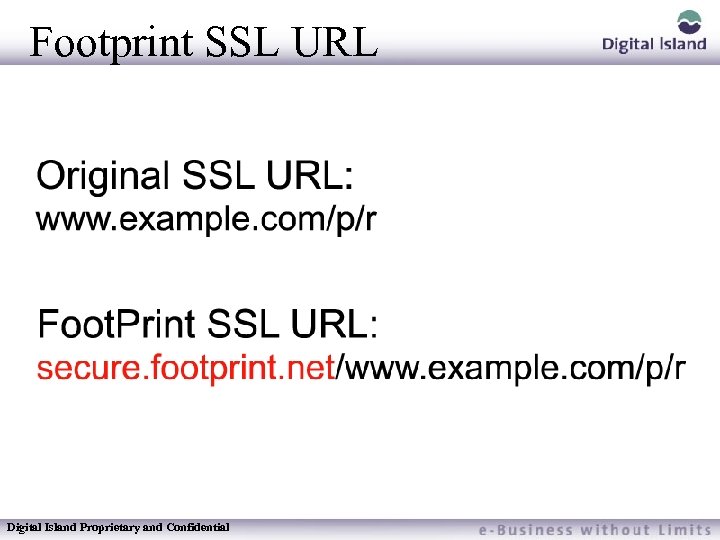 Footprint SSL URL Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Footprint SSL URL Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 FTP Proxy Support Footprint Caching only serves HTTP content so one is led to believe that FTP resources cannot be cached – Not so Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
FTP Proxy Support Footprint Caching only serves HTTP content so one is led to believe that FTP resources cannot be cached – Not so Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
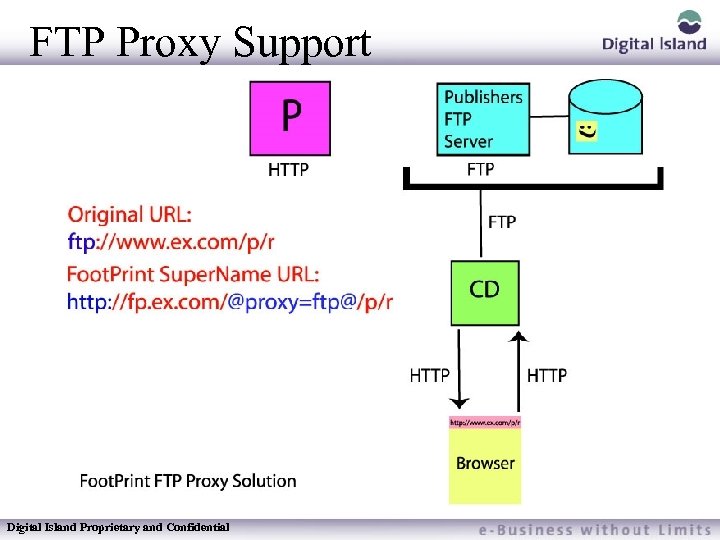 FTP Proxy Support Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
FTP Proxy Support Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Server Side Includes (SSI) Server – This refers to the publishers server (origin server where the original content is stored) Side – This means all actions occur on the server’s side of the fence. Java Scripts are client side commands that make the end viewer’s browser do something. Server Side commands, on the other hand, occur within a program on the publishers server, not the end viewer’s browser Includes – Means that whatever action is taken by the server, it's output is included (inserted) in the html document at whatever location the command is placed Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Server Side Includes (SSI) Server – This refers to the publishers server (origin server where the original content is stored) Side – This means all actions occur on the server’s side of the fence. Java Scripts are client side commands that make the end viewer’s browser do something. Server Side commands, on the other hand, occur within a program on the publishers server, not the end viewer’s browser Includes – Means that whatever action is taken by the server, it's output is included (inserted) in the html document at whatever location the command is placed Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
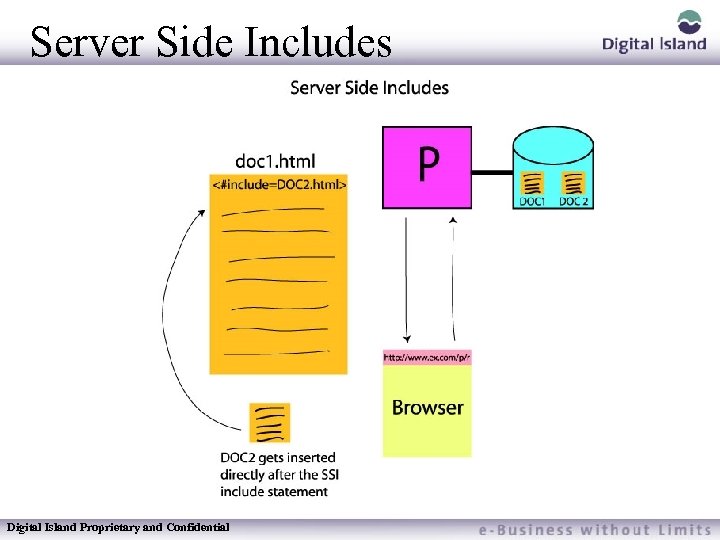 Server Side Includes Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Server Side Includes Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Common SSI Uses Catalog Sites – Individual items being changed and updated from time to time so sections of the entire site can be modifies with SSI capabilities Shopping Carts – Shopping Carts are built as an End Viewer add items to the “carts”. When viewing the contents of the shopping cart SSI is being used to build the page from Individual items Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Common SSI Uses Catalog Sites – Individual items being changed and updated from time to time so sections of the entire site can be modifies with SSI capabilities Shopping Carts – Shopping Carts are built as an End Viewer add items to the “carts”. When viewing the contents of the shopping cart SSI is being used to build the page from Individual items Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Distributor Side Includes Distributor – This refers to the Content Distributor (CD) where the cached resource is stored Side – This means all actions occur on the CD’s side of the fence. Java Scripts are client side commands that make the end viewer’s browser do something. Distributor Side commands, on the other hand, occur within a program on the CDN’s server, not the end viewer’s browser or the publishers server Includes – Means that whatever action is taken by the CD, it's output is included (inserted) in the html document at whatever location fp. DSI command is placed Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Distributor Side Includes Distributor – This refers to the Content Distributor (CD) where the cached resource is stored Side – This means all actions occur on the CD’s side of the fence. Java Scripts are client side commands that make the end viewer’s browser do something. Distributor Side commands, on the other hand, occur within a program on the CDN’s server, not the end viewer’s browser or the publishers server Includes – Means that whatever action is taken by the CD, it's output is included (inserted) in the html document at whatever location fp. DSI command is placed Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
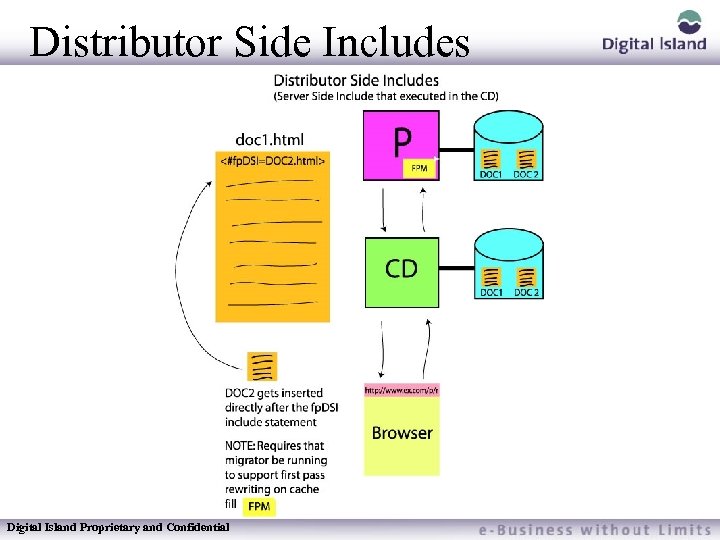 Distributor Side Includes Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Distributor Side Includes Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Distributor Side Include Footprint Manager must be used for DSI to work Not widely used – because Footprint Manager is not very popular Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Distributor Side Include Footprint Manager must be used for DSI to work Not widely used – because Footprint Manager is not very popular Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Cache Coupling The ability of our CD’s to be configured to talk to other caches over what we call the FP Managed cache protocol aka Cache Coupling Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Cache Coupling The ability of our CD’s to be configured to talk to other caches over what we call the FP Managed cache protocol aka Cache Coupling Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
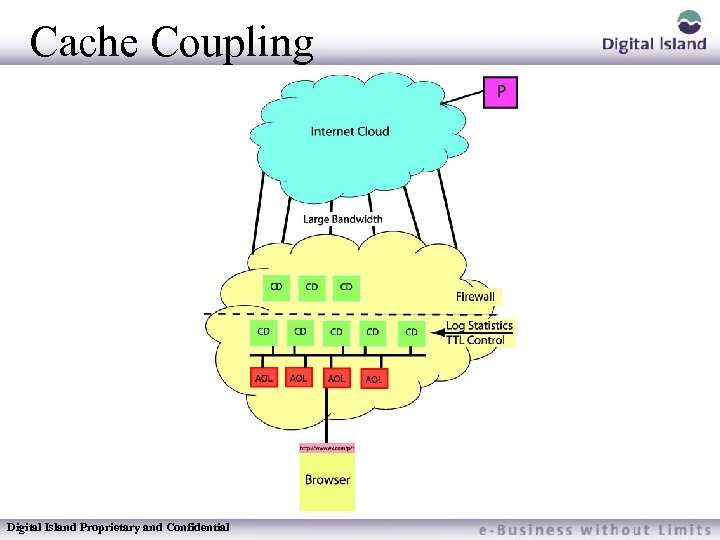 Cache Coupling Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Cache Coupling Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 AOL & Cache Coupling AOL is Investor with Digital Island – CC adds value to their users AOL Cache and DI CD’s Talk to each other – DI’s TTL takes precedence – Able to provide our customers log statistics and TTL control of cached resources Cache Coupling can be utilized at any ISP Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
AOL & Cache Coupling AOL is Investor with Digital Island – CC adds value to their users AOL Cache and DI CD’s Talk to each other – DI’s TTL takes precedence – Able to provide our customers log statistics and TTL control of cached resources Cache Coupling can be utilized at any ISP Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
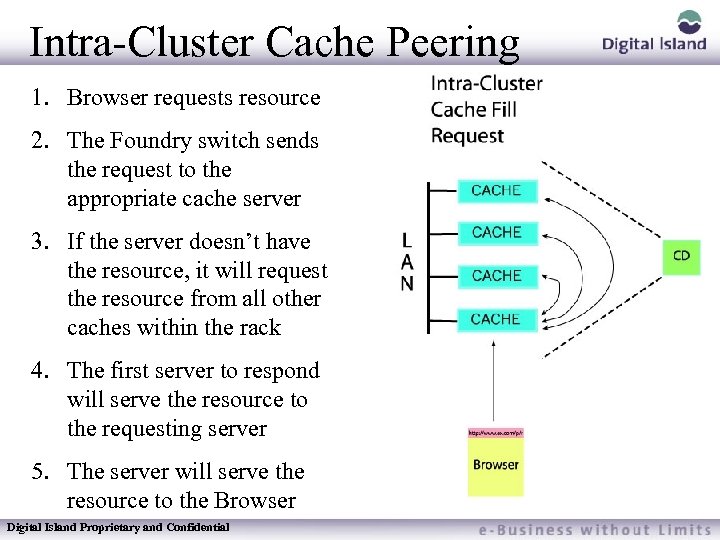 Intra-Cluster Cache Peering 1. Browser requests resource 2. The Foundry switch sends the request to the appropriate cache server 3. If the server doesn’t have the resource, it will request the resource from all other caches within the rack 4. The first server to respond will serve the resource to the requesting server 5. The server will serve the resource to the Browser Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Intra-Cluster Cache Peering 1. Browser requests resource 2. The Foundry switch sends the request to the appropriate cache server 3. If the server doesn’t have the resource, it will request the resource from all other caches within the rack 4. The first server to respond will serve the resource to the requesting server 5. The server will serve the resource to the Browser Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
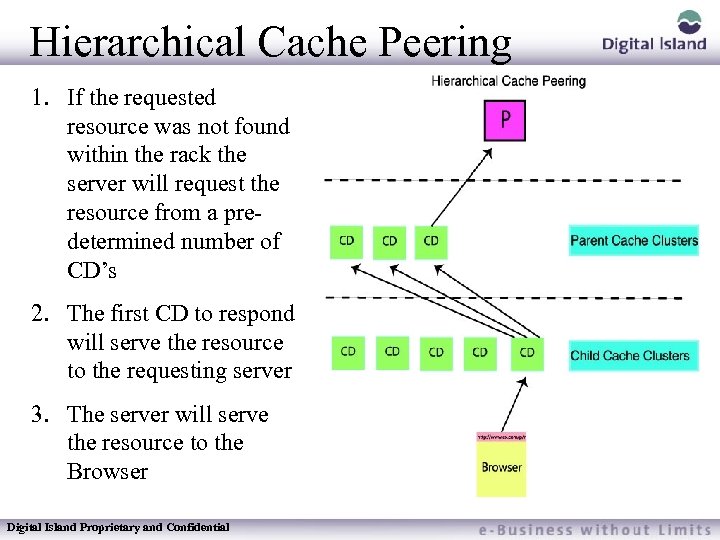 Hierarchical Cache Peering 1. If the requested resource was not found within the rack the server will request the resource from a predetermined number of CD’s 2. The first CD to respond will serve the resource to the requesting server 3. The server will serve the resource to the Browser Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Hierarchical Cache Peering 1. If the requested resource was not found within the rack the server will request the resource from a predetermined number of CD’s 2. The first CD to respond will serve the resource to the requesting server 3. The server will serve the resource to the Browser Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Deployment of Cache Peering Intra-Cluster Cache Peering – completed as of mid Feb Hierarchical Cache Peering – will be started after Intra-Cluster Cache Peering is fully tested (no time frame as of yet) Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Deployment of Cache Peering Intra-Cluster Cache Peering – completed as of mid Feb Hierarchical Cache Peering – will be started after Intra-Cluster Cache Peering is fully tested (no time frame as of yet) Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Content Management and Freshness Control Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Content Management and Freshness Control Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
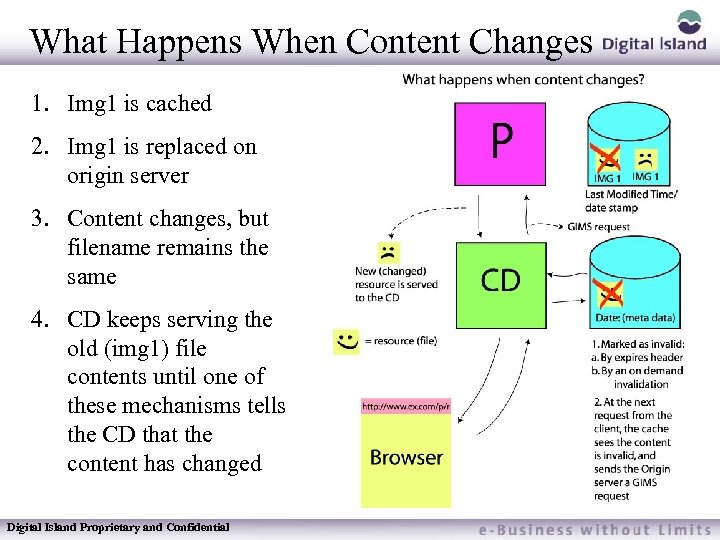 What Happens When Content Changes 1. Img 1 is cached 2. Img 1 is replaced on origin server 3. Content changes, but filename remains the same 4. CD keeps serving the old (img 1) file contents until one of these mechanisms tells the CD that the content has changed Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
What Happens When Content Changes 1. Img 1 is cached 2. Img 1 is replaced on origin server 3. Content changes, but filename remains the same 4. CD keeps serving the old (img 1) file contents until one of these mechanisms tells the CD that the content has changed Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 When Content Changes GIMS = Get If modified since – One parameter of a GIMS request is a request header [get the date] – Standard HTTP functionality If the file system on the publisher reports a newer resource, it sends that resource to the CD If the resource has NOT changed, the publisher sends a response code stating no change Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
When Content Changes GIMS = Get If modified since – One parameter of a GIMS request is a request header [get the date] – Standard HTTP functionality If the file system on the publisher reports a newer resource, it sends that resource to the CD If the resource has NOT changed, the publisher sends a response code stating no change Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 More on GIMS Up until the expire date/time of a resource the CD will serve the resource from the CD When does a GIMS occur? – After the resources expiration date/time (that the publisher has set) has lapsed Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
More on GIMS Up until the expire date/time of a resource the CD will serve the resource from the CD When does a GIMS occur? – After the resources expiration date/time (that the publisher has set) has lapsed Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
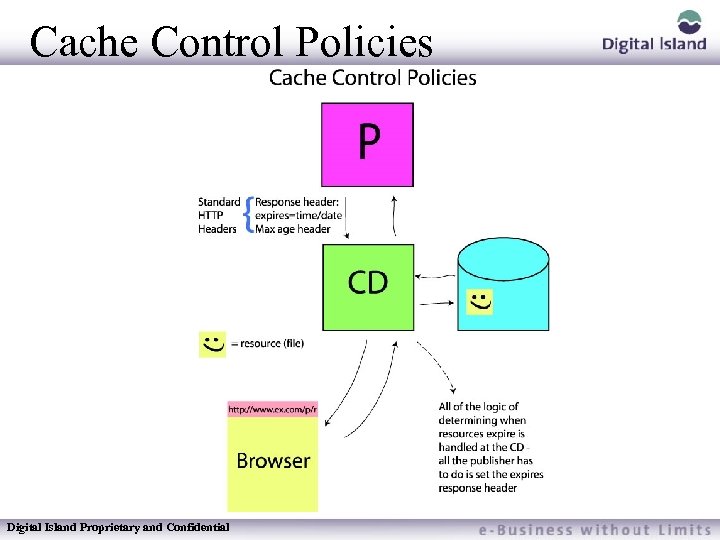 Cache Control Policies Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Cache Control Policies Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Expires header Specifies the expiration date of a document or file Expires=Mon, 01 Sep 2000 14: 11: 01 GMT – specifies date and time which a document expires. GMT should be used. This requires a line in the head of the HTML document like: If the Expires directive is also supplied in the index. htm file it will override the expiration date in the document. Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Expires header Specifies the expiration date of a document or file Expires=Mon, 01 Sep 2000 14: 11: 01 GMT – specifies date and time which a document expires. GMT should be used. This requires a line in the head of the HTML document like: If the Expires directive is also supplied in the index. htm file it will override the expiration date in the document. Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Max-Age response Header Specifies the Cache-Control and Expires headers – The line Max-Age= 10 days specifies that a Cache-Control header should be sent to expire the document in the specified time. If no Expires Header has been set elsewhere in the index. htm file or in the file itself, if it is an HTML file, then the Expires header will also be sent with a value equal to the current time plus the time period of the Max-Age header. The time period in the Max-Age header can be specified in units of seconds, minutes, hours, days or weeks, but more than one unit (as in 2 weeks and 3 days) is not allowed. Max-Age= 10 days after last-mod specifies that a Cache-Control header and the Expires header (if none is set elsewhere) should be set to expire the document in the specified amount of time after the last-modified date of the document. Negative time values for the Cache-Control header will be ignored, but Expires headers with dates in the past will be used. Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Max-Age response Header Specifies the Cache-Control and Expires headers – The line Max-Age= 10 days specifies that a Cache-Control header should be sent to expire the document in the specified time. If no Expires Header has been set elsewhere in the index. htm file or in the file itself, if it is an HTML file, then the Expires header will also be sent with a value equal to the current time plus the time period of the Max-Age header. The time period in the Max-Age header can be specified in units of seconds, minutes, hours, days or weeks, but more than one unit (as in 2 weeks and 3 days) is not allowed. Max-Age= 10 days after last-mod specifies that a Cache-Control header and the Expires header (if none is set elsewhere) should be set to expire the document in the specified amount of time after the last-modified date of the document. Negative time values for the Cache-Control header will be ignored, but Expires headers with dates in the past will be used. Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Resource Versioning Allows customers to update contents of Footprint caches without changing the path or the filename of the resource at the origin server – Uses version string embedded in the URL – Sequence numbers, timestamps, other unique identifiers can be used Standard FP rewriting tools can be used Ensures that the CDN is serving fresh content Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Resource Versioning Allows customers to update contents of Footprint caches without changing the path or the filename of the resource at the origin server – Uses version string embedded in the URL – Sequence numbers, timestamps, other unique identifiers can be used Standard FP rewriting tools can be used Ensures that the CDN is serving fresh content Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Resource Versioning • Allows for a more immediate form of invalidation • Customer can control freshness in an automated and controlled way Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Resource Versioning • Allows for a more immediate form of invalidation • Customer can control freshness in an automated and controlled way Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Header Override Mode Over Rides the information in the Headers that may adversely effect the cacheability of a resource Usually used during testing periods because customers may not want to change Headers until they know for sure they will use Typical information in Headers are: – Expires – Progma-no cache – Set cookie Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Header Override Mode Over Rides the information in the Headers that may adversely effect the cacheability of a resource Usually used during testing periods because customers may not want to change Headers until they know for sure they will use Typical information in Headers are: – Expires – Progma-no cache – Set cookie Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
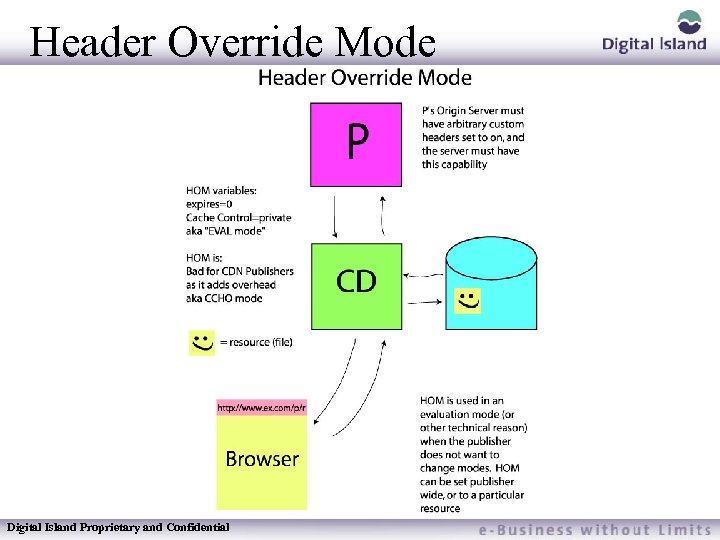 Header Override Mode Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Header Override Mode Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Header Override Mostly used in evaluations Set to On or Off based on the TQ If set to On for testing purposes, remember to notify Footprint Operations after the test period is over to turn it off if desired Set on a subscriber level (not individual server or supername) Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Header Override Mostly used in evaluations Set to On or Off based on the TQ If set to On for testing purposes, remember to notify Footprint Operations after the test period is over to turn it off if desired Set on a subscriber level (not individual server or supername) Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Invalidation On Demand Used when a customer wants to expire a resource on the CD’s before is expires from another Invalidation method. Causes resource to become stale so that subsequent requests for it will go to the Origin server for an updated copy. Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Invalidation On Demand Used when a customer wants to expire a resource on the CD’s before is expires from another Invalidation method. Causes resource to become stale so that subsequent requests for it will go to the Origin server for an updated copy. Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
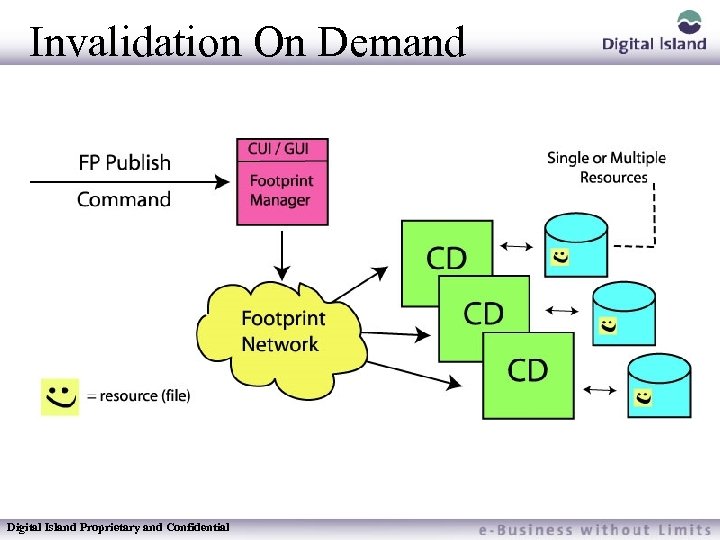 Invalidation On Demand Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Invalidation On Demand Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Invalidation On Demand Executed by Footprint Manager thru the GUI Interface, or by integrating the Fppublish command script FPM communicates with FP Network to indicate that a resource has been changed Effect of marking all resources stale that match the pattern provided Can be used to invalidate a single or multiple resources Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Invalidation On Demand Executed by Footprint Manager thru the GUI Interface, or by integrating the Fppublish command script FPM communicates with FP Network to indicate that a resource has been changed Effect of marking all resources stale that match the pattern provided Can be used to invalidate a single or multiple resources Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Implementation Styles Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Implementation Styles Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
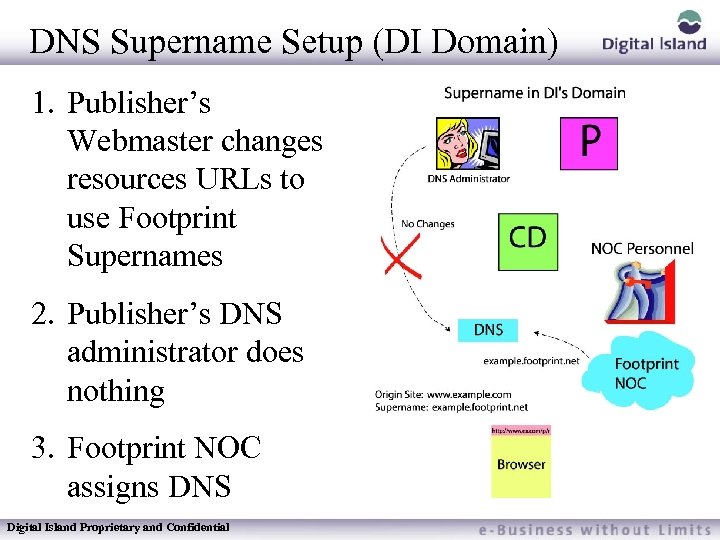 DNS Supername Setup (DI Domain) 1. Publisher’s Webmaster changes resources URLs to use Footprint Supernames 2. Publisher’s DNS administrator does nothing 3. Footprint NOC assigns DNS Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
DNS Supername Setup (DI Domain) 1. Publisher’s Webmaster changes resources URLs to use Footprint Supernames 2. Publisher’s DNS administrator does nothing 3. Footprint NOC assigns DNS Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
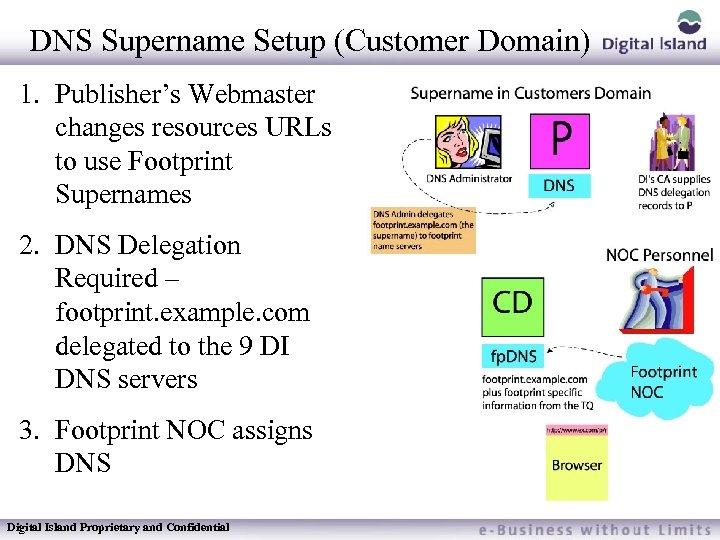 DNS Supername Setup (Customer Domain) 1. Publisher’s Webmaster changes resources URLs to use Footprint Supernames 2. DNS Delegation Required – footprint. example. com delegated to the 9 DI DNS servers 3. Footprint NOC assigns DNS Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
DNS Supername Setup (Customer Domain) 1. Publisher’s Webmaster changes resources URLs to use Footprint Supernames 2. DNS Delegation Required – footprint. example. com delegated to the 9 DI DNS servers 3. Footprint NOC assigns DNS Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Footprint at the door (FATD) A way of configuring Footprint by delegating the original website name to the Footprint CDN – Serves all resources for the website (that is, those served from a particular domain name) from Footprint servers, whether static or dynamic. Requires no modification to web server -- can often be done with no rewriting of HTML – Great benefit and ease of use to publishers Gets much better performance overall than just serving images, if the HTML is mostly cacheable DI’s Website measured a six-fold performance increase by enabling FATD alone Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Footprint at the door (FATD) A way of configuring Footprint by delegating the original website name to the Footprint CDN – Serves all resources for the website (that is, those served from a particular domain name) from Footprint servers, whether static or dynamic. Requires no modification to web server -- can often be done with no rewriting of HTML – Great benefit and ease of use to publishers Gets much better performance overall than just serving images, if the HTML is mostly cacheable DI’s Website measured a six-fold performance increase by enabling FATD alone Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 FATD continued DNS Delegation Based – Delegate original origin server – Create alias for New origin server www 1 or origin (real origin server) Just modify the content or resources that the publisher does NOT want to cache Maximum Flash Crowd Protection Cache most of the site – Example: E-commerce page or SSI still goes to origin server – No content rewriting, supports relative links too!! Easy for customer to implement Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
FATD continued DNS Delegation Based – Delegate original origin server – Create alias for New origin server www 1 or origin (real origin server) Just modify the content or resources that the publisher does NOT want to cache Maximum Flash Crowd Protection Cache most of the site – Example: E-commerce page or SSI still goes to origin server – No content rewriting, supports relative links too!! Easy for customer to implement Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 FATD and types of content Java Scripts are tricky – Java Sandbox Specification • Part of Java Security Model • Java Back door Most All Content types available for FATD – HTML – Images – Active X Components – Flash content Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
FATD and types of content Java Scripts are tricky – Java Sandbox Specification • Part of Java Security Model • Java Back door Most All Content types available for FATD – HTML – Images – Active X Components – Flash content Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
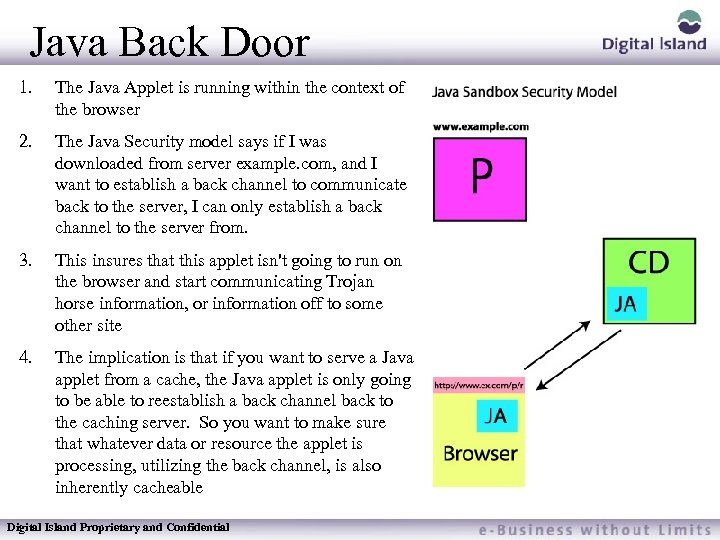 Java Back Door 1. The Java Applet is running within the context of the browser 2. The Java Security model says if I was downloaded from server example. com, and I want to establish a back channel to communicate back to the server, I can only establish a back channel to the server from. 3. This insures that this applet isn't going to run on the browser and start communicating Trojan horse information, or information off to some other site 4. The implication is that if you want to serve a Java applet from a cache, the Java applet is only going to be able to reestablish a back channel back to the caching server. So you want to make sure that whatever data or resource the applet is processing, utilizing the back channel, is also inherently cacheable Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Java Back Door 1. The Java Applet is running within the context of the browser 2. The Java Security model says if I was downloaded from server example. com, and I want to establish a back channel to communicate back to the server, I can only establish a back channel to the server from. 3. This insures that this applet isn't going to run on the browser and start communicating Trojan horse information, or information off to some other site 4. The implication is that if you want to serve a Java applet from a cache, the Java applet is only going to be able to reestablish a back channel back to the caching server. So you want to make sure that whatever data or resource the applet is processing, utilizing the back channel, is also inherently cacheable Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Java Back Door A good example of this is a stock ticker, that every 30 seconds it's going to request the update of the data that's coming down. This is still an appropriate example for caching. Many applets are entirely self contained. Those are the ones that we can cache. Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Java Back Door A good example of this is a stock ticker, that every 30 seconds it's going to request the update of the data that's coming down. This is still an appropriate example for caching. Many applets are entirely self contained. Those are the ones that we can cache. Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Reports and Statistics Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Reports and Statistics Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Reports and Statistics Footprint Manager – Being phased out for Footprint Dashboard (old name FATM) – For real time statistics and monitoring of Footprint traffic and utilization Footprint Log Files – Raw log files are available every 24 hours – Coalesced from all distribution points on the network – FM is tool to retrieve Log Files from the Footprint Caching Network – Available in several different formats (IIS, NCSA, W 3 C extended) Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Reports and Statistics Footprint Manager – Being phased out for Footprint Dashboard (old name FATM) – For real time statistics and monitoring of Footprint traffic and utilization Footprint Log Files – Raw log files are available every 24 hours – Coalesced from all distribution points on the network – FM is tool to retrieve Log Files from the Footprint Caching Network – Available in several different formats (IIS, NCSA, W 3 C extended) Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Reports and Statistics Footprint Manager is still needed for – Statistics – Log Access – On-Demand Invalidation As soon as these functions are replaced through Footprint Dashboard, FP Manager will no longer be offered Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Reports and Statistics Footprint Manager is still needed for – Statistics – Log Access – On-Demand Invalidation As soon as these functions are replaced through Footprint Dashboard, FP Manager will no longer be offered Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Vista. Ware ACCESS Web-Based Interface Access through www. digitalisland. net Secure Login Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Vista. Ware ACCESS Web-Based Interface Access through www. digitalisland. net Secure Login Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Vista. Ware ONLINE VISTAWARE DEMO vistaware. digitialisland. net/acme username = acme 2 password = roadrunner 2 Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Vista. Ware ONLINE VISTAWARE DEMO vistaware. digitialisland. net/acme username = acme 2 password = roadrunner 2 Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
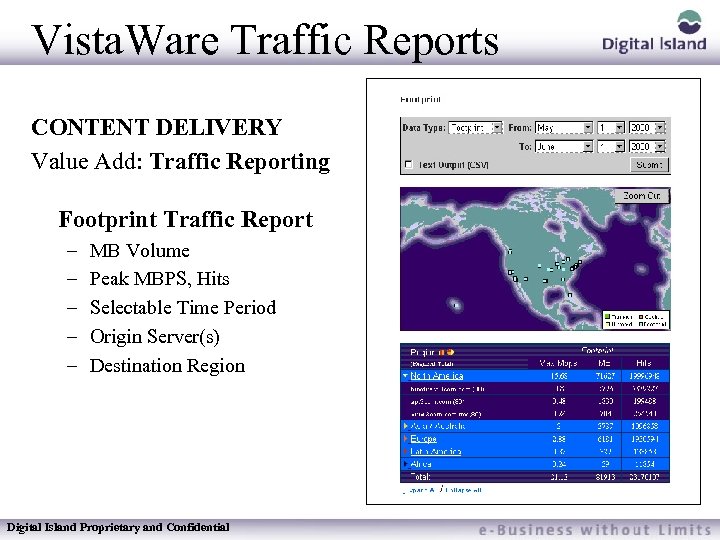 Vista. Ware Traffic Reports CONTENT DELIVERY Value Add: Traffic Reporting Footprint Traffic Report – – – MB Volume Peak MBPS, Hits Selectable Time Period Origin Server(s) Destination Region Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Vista. Ware Traffic Reports CONTENT DELIVERY Value Add: Traffic Reporting Footprint Traffic Report – – – MB Volume Peak MBPS, Hits Selectable Time Period Origin Server(s) Destination Region Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
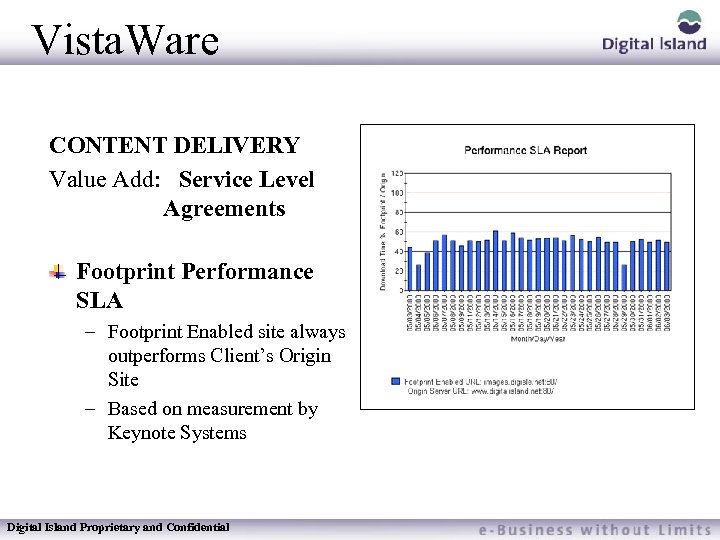 Vista. Ware CONTENT DELIVERY Value Add: Service Level Agreements Footprint Performance SLA – Footprint Enabled site always outperforms Client’s Origin Site – Based on measurement by Keynote Systems Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Vista. Ware CONTENT DELIVERY Value Add: Service Level Agreements Footprint Performance SLA – Footprint Enabled site always outperforms Client’s Origin Site – Based on measurement by Keynote Systems Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Vista. Ware Footprint Performance SLA: Download time of content located on the Footprint Network will always be faster than download time of content located on the Customer’s Origin server based on a daily average measurement from Keynote Systems. Measured using Keynote World 10: New York, San Francisco, Los Angeles, Atlanta, Chicago, Washington DC, London, Tokyo, Hong Kong , Germany 100% Refund of Footprint Traffic Bill for every day SLA is missed up to $5000/month. Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Vista. Ware Footprint Performance SLA: Download time of content located on the Footprint Network will always be faster than download time of content located on the Customer’s Origin server based on a daily average measurement from Keynote Systems. Measured using Keynote World 10: New York, San Francisco, Los Angeles, Atlanta, Chicago, Washington DC, London, Tokyo, Hong Kong , Germany 100% Refund of Footprint Traffic Bill for every day SLA is missed up to $5000/month. Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
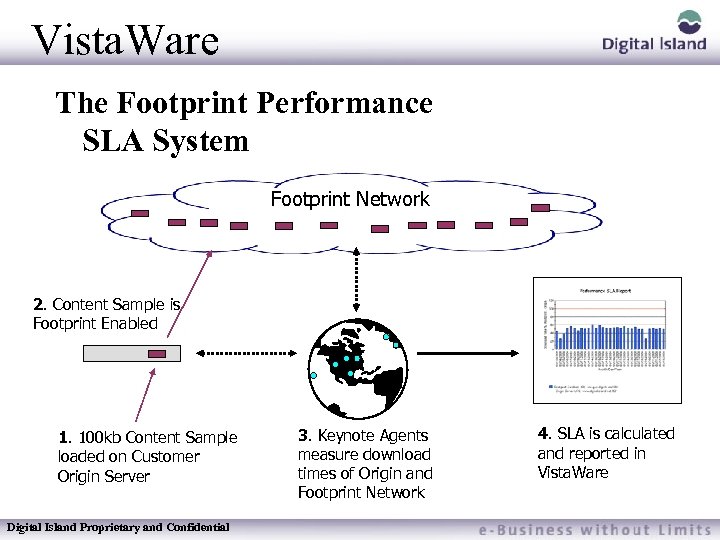 Vista. Ware The Footprint Performance SLA System Footprint Network 2. Content Sample is Footprint Enabled 1. 100 kb Content Sample loaded on Customer Origin Server Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential 3. Keynote Agents measure download times of Origin and Footprint Network 4. SLA is calculated and reported in Vista. Ware
Vista. Ware The Footprint Performance SLA System Footprint Network 2. Content Sample is Footprint Enabled 1. 100 kb Content Sample loaded on Customer Origin Server Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential 3. Keynote Agents measure download times of Origin and Footprint Network 4. SLA is calculated and reported in Vista. Ware
 Implementation Tips and Tricks Ways to go on technical collateral – Why FPU is in business Start with Technical Questionnaire – Marketing/Products/Footprint in hopper – Check Back Often, we send out field alerts when changes are made too Try to fill out as much information as possible – Customers Environment, tools they use, OS IIS has some quirky features Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Implementation Tips and Tricks Ways to go on technical collateral – Why FPU is in business Start with Technical Questionnaire – Marketing/Products/Footprint in hopper – Check Back Often, we send out field alerts when changes are made too Try to fill out as much information as possible – Customers Environment, tools they use, OS IIS has some quirky features Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Implementation Tips and Tricks Watch out for Firewalls • Footprint Manager needs certain ports to be open (8806 and 8807) Load Balancers may send the CD to stale content – Multiple servers behind the load balancer may not be in sync, and serve the CDN stale content TQ then goes to the CA Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Implementation Tips and Tricks Watch out for Firewalls • Footprint Manager needs certain ports to be open (8806 and 8807) Load Balancers may send the CD to stale content – Multiple servers behind the load balancer may not be in sync, and serve the CDN stale content TQ then goes to the CA Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Roadmap Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Roadmap Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Roadmap Footprint v 2. x – Existing Footprint Software Release – Additional Features/Functionality in response to customer requirements/market demands – Elimination of Footprint Manager software (improve ease -of-implementation, decrease time-to-bill) – Version 2. 03 – has been released and is in production as of Jan 15 – Version 2. 1 – projected release date Apr 1, 2001 – this target has slipped 30 days from last update due to some reprioritization of features – Version 3. 0 – will introduce Inktomi Traffic Server into the existing v 2. x network Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Roadmap Footprint v 2. x – Existing Footprint Software Release – Additional Features/Functionality in response to customer requirements/market demands – Elimination of Footprint Manager software (improve ease -of-implementation, decrease time-to-bill) – Version 2. 03 – has been released and is in production as of Jan 15 – Version 2. 1 – projected release date Apr 1, 2001 – this target has slipped 30 days from last update due to some reprioritization of features – Version 3. 0 – will introduce Inktomi Traffic Server into the existing v 2. x network Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Roadmap Footprint Next Generation – Improved scalability, manageability, and performance – Native integration of Inktomi Traffic Server – More robust platform to support Edge Computing and other future services – Projected release date Jun-Jul, 2001 Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Roadmap Footprint Next Generation – Improved scalability, manageability, and performance – Native integration of Inktomi Traffic Server – More robust platform to support Edge Computing and other future services – Projected release date Jun-Jul, 2001 Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Roadmap Adaptive Traffic Control (old name g. BDS) – New service offering to provide intelligent traffic management for any customer application – Leverages and expands intellectual property derived from BDS within Footprint – High level of interest by customers/partners such as Microsoft, AOL, Cisco, F 5 – New revenue creation opportunity – Beta testing has begun with Microsoft in early Feb 2001 – Projected release date Mar-Apr, 2001 Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Roadmap Adaptive Traffic Control (old name g. BDS) – New service offering to provide intelligent traffic management for any customer application – Leverages and expands intellectual property derived from BDS within Footprint – High level of interest by customers/partners such as Microsoft, AOL, Cisco, F 5 – New revenue creation opportunity – Beta testing has begun with Microsoft in early Feb 2001 – Projected release date Mar-Apr, 2001 Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Roadmap Bigfoot (Footprint Broadband) – Footprint caching with large storage to accommodate large libraries of content at the edge – Major development project/partnership with Sony Pictures Digital Entertainment to launch new payper-download movie service – Will provide platform for offering additional capabilities to other Media/Entertainment and Software enterprises – Sony’s anticipated launch date: Apr 1, 2001 Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Roadmap Bigfoot (Footprint Broadband) – Footprint caching with large storage to accommodate large libraries of content at the edge – Major development project/partnership with Sony Pictures Digital Entertainment to launch new payper-download movie service – Will provide platform for offering additional capabilities to other Media/Entertainment and Software enterprises – Sony’s anticipated launch date: Apr 1, 2001 Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
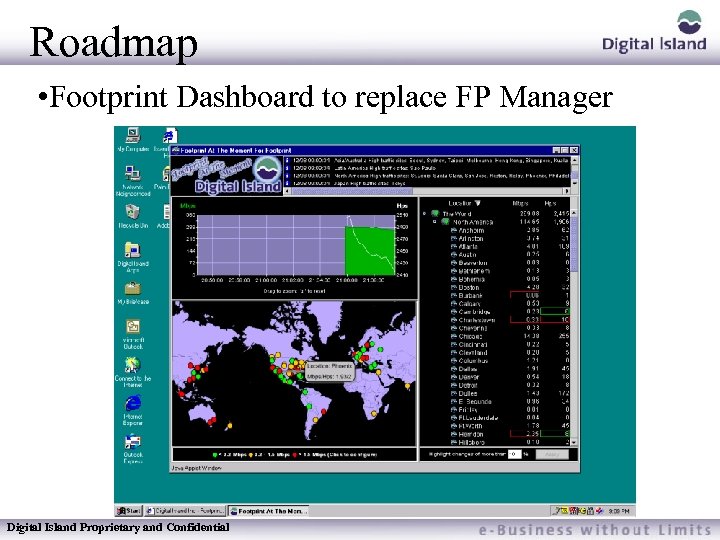 Roadmap • Footprint Dashboard to replace FP Manager Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Roadmap • Footprint Dashboard to replace FP Manager Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Roadmap Content Preparation/Rewriting Tools – Development of improved toolset to ease adoption of Content Delivery service by Content Providers – Stand-alone content preparation tools provided to customer by Digital Island – SDK to facilitate integration with 3 rd party tool vendors (Vignette, Broadvision, ATG, Blue Martini, etc) – Engineering specifications to facilitate development/integration with 3 rd party appliances (Cisco, F 5, Novell, Microsoft, etc) – Outsourced project with Stellcom – Delivery anticipated Mar 1, 2001 Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Roadmap Content Preparation/Rewriting Tools – Development of improved toolset to ease adoption of Content Delivery service by Content Providers – Stand-alone content preparation tools provided to customer by Digital Island – SDK to facilitate integration with 3 rd party tool vendors (Vignette, Broadvision, ATG, Blue Martini, etc) – Engineering specifications to facilitate development/integration with 3 rd party appliances (Cisco, F 5, Novell, Microsoft, etc) – Outsourced project with Stellcom – Delivery anticipated Mar 1, 2001 Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Roadmap Content Alliances – Development of clear strategy for participation in various content alliance programs (Content Bridge, Content Alliance, Content Exchange, etc) – Positioning of Digital Island’s core technologies/intellectual properties as key enabling technologies within these initiatives – Ensuring that developed business models drive profitable traffic to the Digital Island CDN Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Roadmap Content Alliances – Development of clear strategy for participation in various content alliance programs (Content Bridge, Content Alliance, Content Exchange, etc) – Positioning of Digital Island’s core technologies/intellectual properties as key enabling technologies within these initiatives – Ensuring that developed business models drive profitable traffic to the Digital Island CDN Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
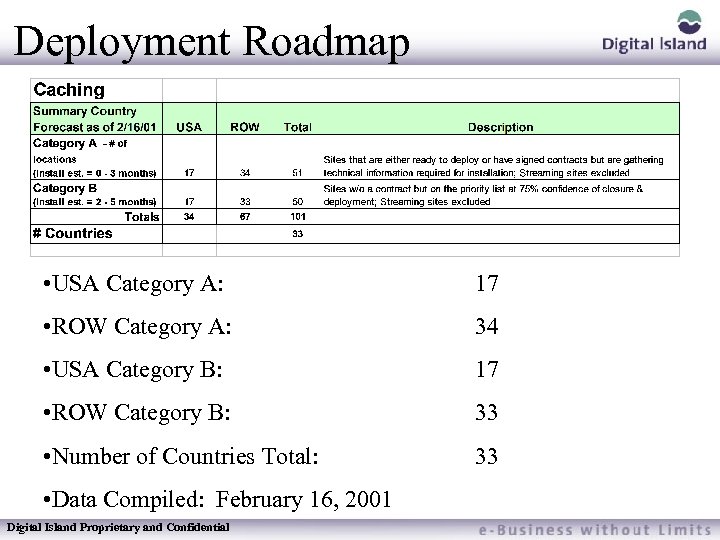 Deployment Roadmap • USA Category A: 17 • ROW Category A: 34 • USA Category B: 17 • ROW Category B: 33 • Number of Countries Total: 33 • Data Compiled: February 16, 2001 Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Deployment Roadmap • USA Category A: 17 • ROW Category A: 34 • USA Category B: 17 • ROW Category B: 33 • Number of Countries Total: 33 • Data Compiled: February 16, 2001 Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
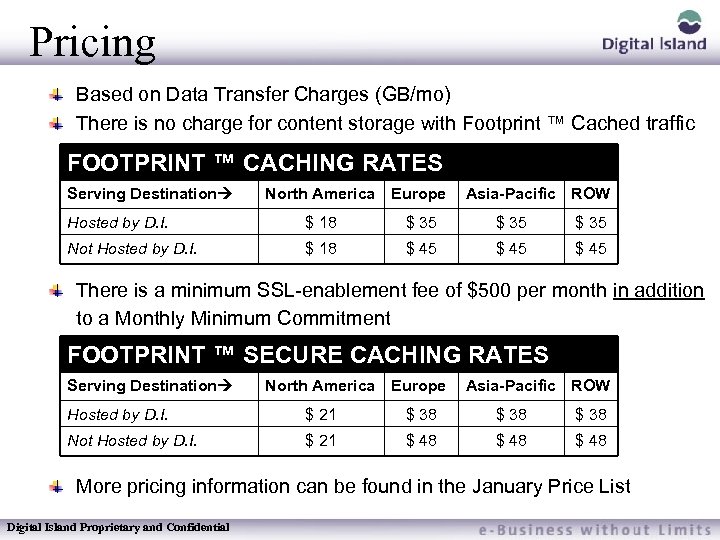 Pricing Based on Data Transfer Charges (GB/mo) There is no charge for content storage with Footprint ™ Cached traffic FOOTPRINT ™ CACHING RATES Serving Destination North America Europe Asia-Pacific ROW Hosted by D. I. $ 18 $ 35 Not Hosted by D. I. $ 18 $ 45 There is a minimum SSL-enablement fee of $500 per month in addition to a Monthly Minimum Commitment FOOTPRINT ™ SECURE CACHING RATES Serving Destination North America Europe Asia-Pacific ROW Hosted by D. I. $ 21 $ 38 Not Hosted by D. I. $ 21 $ 48 More pricing information can be found in the January Price List Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Pricing Based on Data Transfer Charges (GB/mo) There is no charge for content storage with Footprint ™ Cached traffic FOOTPRINT ™ CACHING RATES Serving Destination North America Europe Asia-Pacific ROW Hosted by D. I. $ 18 $ 35 Not Hosted by D. I. $ 18 $ 45 There is a minimum SSL-enablement fee of $500 per month in addition to a Monthly Minimum Commitment FOOTPRINT ™ SECURE CACHING RATES Serving Destination North America Europe Asia-Pacific ROW Hosted by D. I. $ 21 $ 38 Not Hosted by D. I. $ 21 $ 48 More pricing information can be found in the January Price List Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 TQ Overview Footprint Technical Questionnaire Review Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
TQ Overview Footprint Technical Questionnaire Review Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
 Thanks for Learning! Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential
Thanks for Learning! Digital Island Proprietary and Confidential


