АГЫЛШЫН СЛАЙД, ИНФЕКЦИЙ.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 FOOD INFECTION
FOOD INFECTION
 Infectious process - a set of biological processes occurring in the body during the introduction of pathogenic microorganisms. The incubation period - the time interval from the moment of introduction of pathogenic microbe until the first signs of the disease
Infectious process - a set of biological processes occurring in the body during the introduction of pathogenic microorganisms. The incubation period - the time interval from the moment of introduction of pathogenic microbe until the first signs of the disease
 Pathogenicity is the potential for a certain kind of germs take root in the body, multiply and cause a disease. Virulence - the degree of pathogenic action of microbes. The specificity. - Every kind of germs can cause one specific disease with characteristic symptoms. Toxicopathy. - the ability of pathogenic microorganisms to produce toxic substances - toxins. They can be of two types: the Exo - and endotoxins. Toxins are striking the internal organs and cause poisoning of the body of varying severity.
Pathogenicity is the potential for a certain kind of germs take root in the body, multiply and cause a disease. Virulence - the degree of pathogenic action of microbes. The specificity. - Every kind of germs can cause one specific disease with characteristic symptoms. Toxicopathy. - the ability of pathogenic microorganisms to produce toxic substances - toxins. They can be of two types: the Exo - and endotoxins. Toxins are striking the internal organs and cause poisoning of the body of varying severity.
 THE WAY OF TRANSMISSION Fecal-oral pathogenic microorganisms are transmitted through the air, water, soil, food, contaminated hands, objects, etc. (typhoid, cholera, dysentery, etc. ) Airborne - microorganisms are transmitted through the air by sneezing, coughing (pertussis, influenza, tuberculosis, sore throat) Transmission vectors are insects (ticks, fleas, lice, mosquitoes, flies and rodents.
THE WAY OF TRANSMISSION Fecal-oral pathogenic microorganisms are transmitted through the air, water, soil, food, contaminated hands, objects, etc. (typhoid, cholera, dysentery, etc. ) Airborne - microorganisms are transmitted through the air by sneezing, coughing (pertussis, influenza, tuberculosis, sore throat) Transmission vectors are insects (ticks, fleas, lice, mosquitoes, flies and rodents.
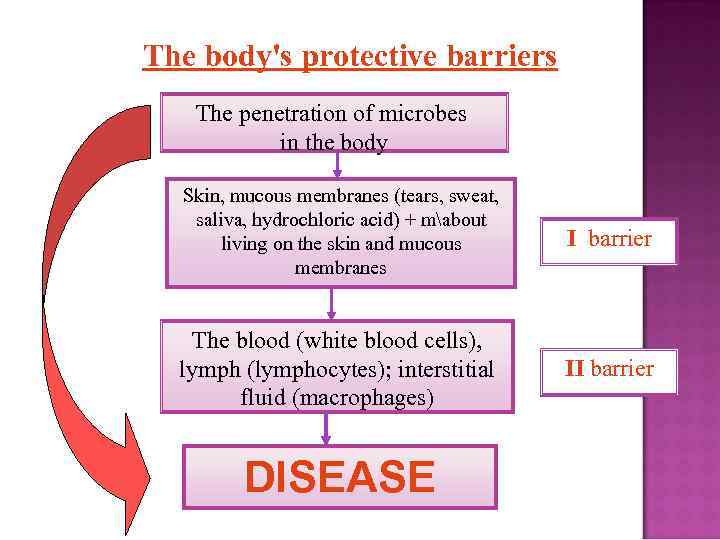 The body's protective barriers The penetration of microbes in the body Skin, mucous membranes (tears, sweat, saliva, hydrochloric acid) + mabout living on the skin and mucous membranes I barrier The blood (white blood cells), lymph (lymphocytes); interstitial fluid (macrophages) II barrier DISEASE
The body's protective barriers The penetration of microbes in the body Skin, mucous membranes (tears, sweat, saliva, hydrochloric acid) + mabout living on the skin and mucous membranes I barrier The blood (white blood cells), lymph (lymphocytes); interstitial fluid (macrophages) II barrier DISEASE
 FOOD INFECTION - infectious diseases in which food products are the transmitters toxicogenic germs, they do not reproduce, but can a long time to maintain the viability and virulence.
FOOD INFECTION - infectious diseases in which food products are the transmitters toxicogenic germs, they do not reproduce, but can a long time to maintain the viability and virulence.
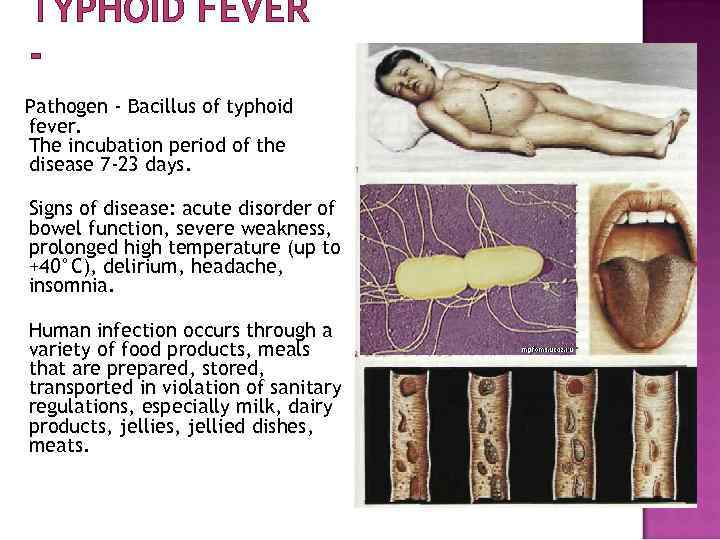 TYPHOID FEVER Pathogen - Bacillus of typhoid fever. The incubation period of the disease 7 -23 days. Signs of disease: acute disorder of bowel function, severe weakness, prolonged high temperature (up to +40°C), delirium, headache, insomnia. Human infection occurs through a variety of food products, meals that are prepared, stored, transported in violation of sanitary regulations, especially milk, dairy products, jellied dishes, meats.
TYPHOID FEVER Pathogen - Bacillus of typhoid fever. The incubation period of the disease 7 -23 days. Signs of disease: acute disorder of bowel function, severe weakness, prolonged high temperature (up to +40°C), delirium, headache, insomnia. Human infection occurs through a variety of food products, meals that are prepared, stored, transported in violation of sanitary regulations, especially milk, dairy products, jellied dishes, meats.
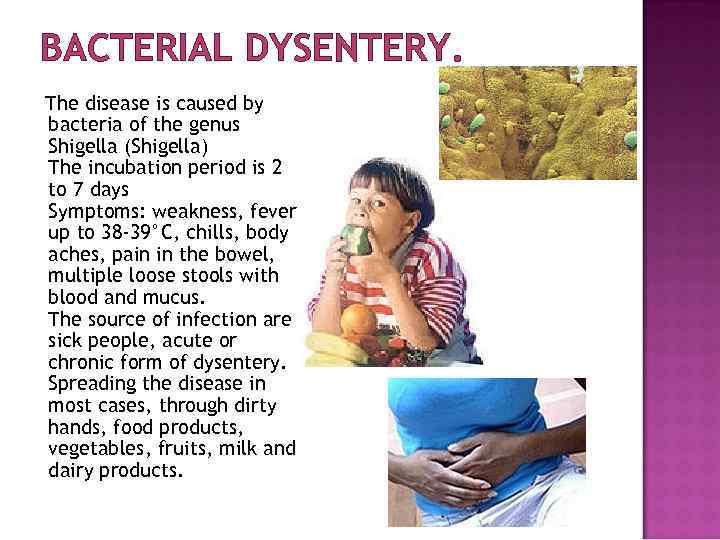 BACTERIAL DYSENTERY. The disease is caused by bacteria of the genus Shigella (Shigella) The incubation period is 2 to 7 days Symptoms: weakness, fever up to 38 -39°C, chills, body aches, pain in the bowel, multiple loose stools with blood and mucus. The source of infection are sick people, acute or chronic form of dysentery. Spreading the disease in most cases, through dirty hands, food products, vegetables, fruits, milk and dairy products.
BACTERIAL DYSENTERY. The disease is caused by bacteria of the genus Shigella (Shigella) The incubation period is 2 to 7 days Symptoms: weakness, fever up to 38 -39°C, chills, body aches, pain in the bowel, multiple loose stools with blood and mucus. The source of infection are sick people, acute or chronic form of dysentery. Spreading the disease in most cases, through dirty hands, food products, vegetables, fruits, milk and dairy products.
 cholera The causative agent is Vibrio cholerae having the shape of a comma. The infection is transmitted through water and food prepared and stored in hygienic conditions. The incubation period of this disease is 2 -6 days. Symptoms: sudden, uncontrollable diarrhea and vomiting, severely dehydrating the body, weakness, headache, dizziness, temperature +35°C, convulsions, and sometimes death.
cholera The causative agent is Vibrio cholerae having the shape of a comma. The infection is transmitted through water and food prepared and stored in hygienic conditions. The incubation period of this disease is 2 -6 days. Symptoms: sudden, uncontrollable diarrhea and vomiting, severely dehydrating the body, weakness, headache, dizziness, temperature +35°C, convulsions, and sometimes death.
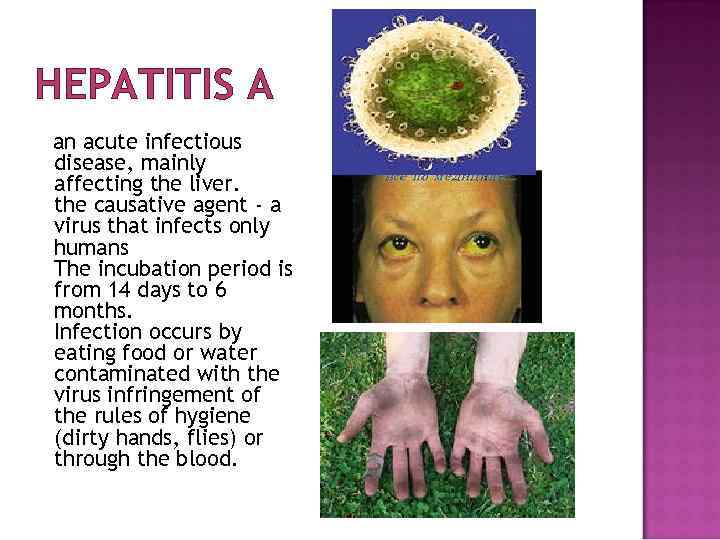 HEPATITIS A an acute infectious disease, mainly affecting the liver. the causative agent - a virus that infects only humans The incubation period is from 14 days to 6 months. Infection occurs by eating food or water contaminated with the virus infringement of the rules of hygiene (dirty hands, flies) or through the blood.
HEPATITIS A an acute infectious disease, mainly affecting the liver. the causative agent - a virus that infects only humans The incubation period is from 14 days to 6 months. Infection occurs by eating food or water contaminated with the virus infringement of the rules of hygiene (dirty hands, flies) or through the blood.
 Prevention of acute intestinal infections in enterprises of public catering Observance of rules of personal hygiene cook, clean hands and the workplace; The destruction of flies, cockroaches and rodents as carriers of infection. Thorough washing and disinfection of tableware, kitchen equipment, compliance with marking cutting boards; Thorough washing of vegetables, berries, especially going into the food; Boiling of milk, heat treatment of meals from unpasteurized cheese; Conducting secondary heat treatment of perishable foods: jelly, water, pates, boiled meat in the cooking process. Fast cooking chopped semi-finished products. including from kotlety mass thereby not allowing the reproduction of Salmonella. Thorough boiling and frying meat and fish dishes, especially products from kotlety mass. Compliance operations primary processing of fresh fish that do not allow contamination of its intestinal contents. The use of eggs of waterfowl only in the baking industry, chicken eggs before use, should be washed.
Prevention of acute intestinal infections in enterprises of public catering Observance of rules of personal hygiene cook, clean hands and the workplace; The destruction of flies, cockroaches and rodents as carriers of infection. Thorough washing and disinfection of tableware, kitchen equipment, compliance with marking cutting boards; Thorough washing of vegetables, berries, especially going into the food; Boiling of milk, heat treatment of meals from unpasteurized cheese; Conducting secondary heat treatment of perishable foods: jelly, water, pates, boiled meat in the cooking process. Fast cooking chopped semi-finished products. including from kotlety mass thereby not allowing the reproduction of Salmonella. Thorough boiling and frying meat and fish dishes, especially products from kotlety mass. Compliance operations primary processing of fresh fish that do not allow contamination of its intestinal contents. The use of eggs of waterfowl only in the baking industry, chicken eggs before use, should be washed.
 ZOONOTIC INFECTIONS Infectious diseases transmitted to humans from animals. These include anthrax, brucellosis, foot and mouth disease, tuberculosis, tularemia, and many others. The cause of the human disease can be consumption of meat and milk from sick animals, eggs sick birds
ZOONOTIC INFECTIONS Infectious diseases transmitted to humans from animals. These include anthrax, brucellosis, foot and mouth disease, tuberculosis, tularemia, and many others. The cause of the human disease can be consumption of meat and milk from sick animals, eggs sick birds
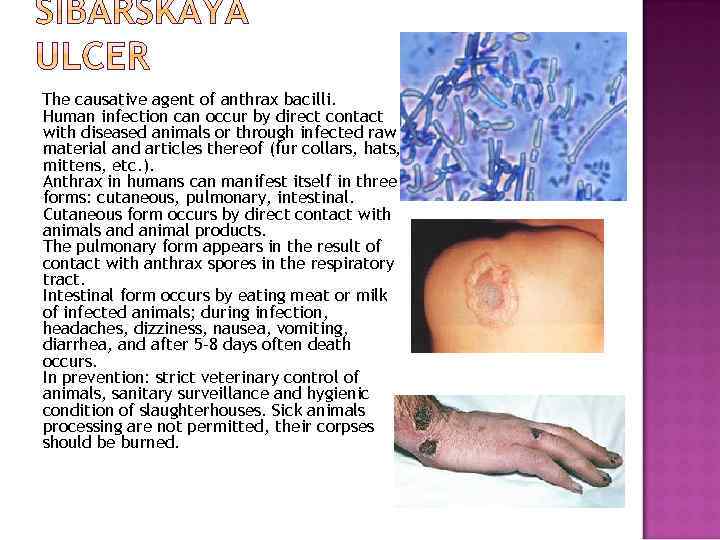 The causative agent of anthrax bacilli. Human infection can occur by direct contact with diseased animals or through infected raw material and articles thereof (fur collars, hats, mittens, etc. ). Anthrax in humans can manifest itself in three forms: cutaneous, pulmonary, intestinal. Cutaneous form occurs by direct contact with animals and animal products. The pulmonary form appears in the result of contact with anthrax spores in the respiratory tract. Intestinal form occurs by eating meat or milk of infected animals; during infection, headaches, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and after 5 -8 days often death occurs. In prevention: strict veterinary control of animals, sanitary surveillance and hygienic condition of slaughterhouses. Sick animals processing are not permitted, their corpses should be burned.
The causative agent of anthrax bacilli. Human infection can occur by direct contact with diseased animals or through infected raw material and articles thereof (fur collars, hats, mittens, etc. ). Anthrax in humans can manifest itself in three forms: cutaneous, pulmonary, intestinal. Cutaneous form occurs by direct contact with animals and animal products. The pulmonary form appears in the result of contact with anthrax spores in the respiratory tract. Intestinal form occurs by eating meat or milk of infected animals; during infection, headaches, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and after 5 -8 days often death occurs. In prevention: strict veterinary control of animals, sanitary surveillance and hygienic condition of slaughterhouses. Sick animals processing are not permitted, their corpses should be burned.
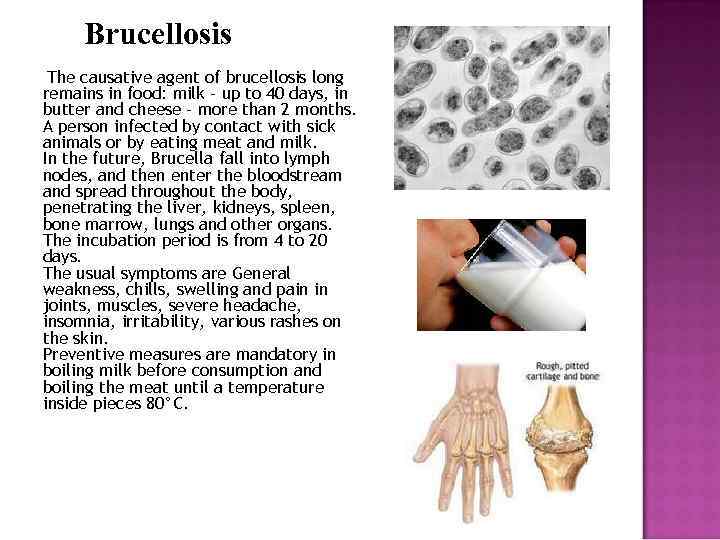 Brucellosis The causative agent of brucellosis long remains in food: milk - up to 40 days, in butter and cheese - more than 2 months. A person infected by contact with sick animals or by eating meat and milk. In the future, Brucella fall into lymph nodes, and then enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body, penetrating the liver, kidneys, spleen, bone marrow, lungs and other organs. The incubation period is from 4 to 20 days. The usual symptoms are General weakness, chills, swelling and pain in joints, muscles, severe headache, insomnia, irritability, various rashes on the skin. Preventive measures are mandatory in boiling milk before consumption and boiling the meat until a temperature inside pieces 80°C.
Brucellosis The causative agent of brucellosis long remains in food: milk - up to 40 days, in butter and cheese - more than 2 months. A person infected by contact with sick animals or by eating meat and milk. In the future, Brucella fall into lymph nodes, and then enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body, penetrating the liver, kidneys, spleen, bone marrow, lungs and other organs. The incubation period is from 4 to 20 days. The usual symptoms are General weakness, chills, swelling and pain in joints, muscles, severe headache, insomnia, irritability, various rashes on the skin. Preventive measures are mandatory in boiling milk before consumption and boiling the meat until a temperature inside pieces 80°C.
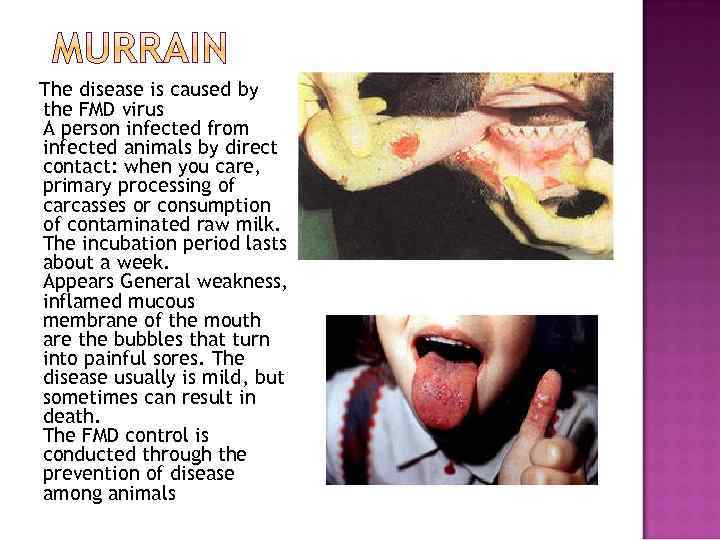 The disease is caused by the FMD virus A person infected from infected animals by direct contact: when you care, primary processing of carcasses or consumption of contaminated raw milk. The incubation period lasts about a week. Appears General weakness, inflamed mucous membrane of the mouth are the bubbles that turn into painful sores. The disease usually is mild, but sometimes can result in death. The FMD control is conducted through the prevention of disease among animals
The disease is caused by the FMD virus A person infected from infected animals by direct contact: when you care, primary processing of carcasses or consumption of contaminated raw milk. The incubation period lasts about a week. Appears General weakness, inflamed mucous membrane of the mouth are the bubbles that turn into painful sores. The disease usually is mild, but sometimes can result in death. The FMD control is conducted through the prevention of disease among animals
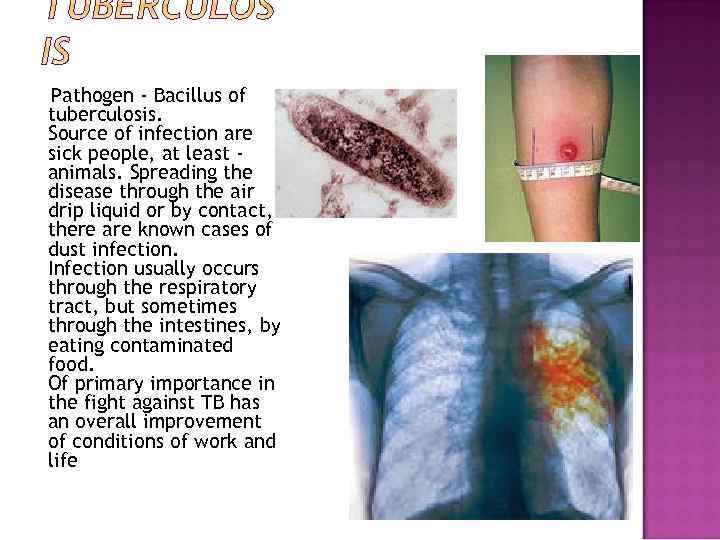 Pathogen - Bacillus of tuberculosis. Source of infection are sick people, at least animals. Spreading the disease through the air drip liquid or by contact, there are known cases of dust infection. Infection usually occurs through the respiratory tract, but sometimes through the intestines, by eating contaminated food. Of primary importance in the fight against TB has an overall improvement of conditions of work and life
Pathogen - Bacillus of tuberculosis. Source of infection are sick people, at least animals. Spreading the disease through the air drip liquid or by contact, there are known cases of dust infection. Infection usually occurs through the respiratory tract, but sometimes through the intestines, by eating contaminated food. Of primary importance in the fight against TB has an overall improvement of conditions of work and life
 PREVENTIVE MEASURES IN ENTERPRISES OF PUBLIC CATERING FOOD INFECTIOUS DISEASES TRANSMISSIBLE FROM INFECTED ANIMALS Checking for stamps on meat carcasses, testifying to veterinary-sanitary inspection of raw materials. Thorough boiling and frying meat dishes. Boiling milk, the use of sour-Smokvica only for making the test, and unpasteurized cheese for cooking, subjected to heat treatment.
PREVENTIVE MEASURES IN ENTERPRISES OF PUBLIC CATERING FOOD INFECTIOUS DISEASES TRANSMISSIBLE FROM INFECTED ANIMALS Checking for stamps on meat carcasses, testifying to veterinary-sanitary inspection of raw materials. Thorough boiling and frying meat dishes. Boiling milk, the use of sour-Smokvica only for making the test, and unpasteurized cheese for cooking, subjected to heat treatment.
 THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION!!!
THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION!!!


