 Food Chains & Energy Flow
Food Chains & Energy Flow
 Food Chains n Food chain: sequence of organisms, showing how energy and nutrients move from one to another
Food Chains n Food chain: sequence of organisms, showing how energy and nutrients move from one to another
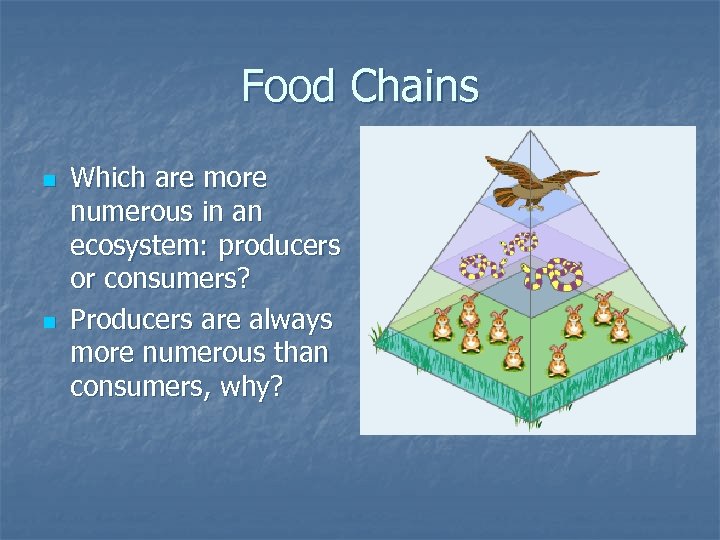 Food Chains n n Which are more numerous in an ecosystem: producers or consumers? Producers are always more numerous than consumers, why?
Food Chains n n Which are more numerous in an ecosystem: producers or consumers? Producers are always more numerous than consumers, why?
 Energy Loss n Of the energy that an organism consumes, only a small fraction (ecological efficiency of about 10%) is transferred to the next trophic level
Energy Loss n Of the energy that an organism consumes, only a small fraction (ecological efficiency of about 10%) is transferred to the next trophic level
 Where does that energy go? n Most of the energy is lost as heat That’s hot.
Where does that energy go? n Most of the energy is lost as heat That’s hot.
 House Analogy n Just like how much of the energy used to heat a house is wasted, much of the energy used by organisms is wasted
House Analogy n Just like how much of the energy used to heat a house is wasted, much of the energy used by organisms is wasted
 Efficiency Example n Cars are only about 25% efficient Only 25% of the total energy in gasoline is used to make cars move n What happens to the other 75%? ? ? n
Efficiency Example n Cars are only about 25% efficient Only 25% of the total energy in gasoline is used to make cars move n What happens to the other 75%? ? ? n
 Energy Efficiency n Why is it more energy efficient to eat grains directly, rather than the meat of grain-eating animals? 15 lbs. of feed 1 lb. of beef
Energy Efficiency n Why is it more energy efficient to eat grains directly, rather than the meat of grain-eating animals? 15 lbs. of feed 1 lb. of beef
 Energy Efficiency n Why is it more energy efficient to eat grains directly, rather than the meat of grain-eating animals? 6 lbs. of feed 1 lb. of pork
Energy Efficiency n Why is it more energy efficient to eat grains directly, rather than the meat of grain-eating animals? 6 lbs. of feed 1 lb. of pork
 Energy Efficiency n Why is it more energy efficient to eat grains directly, rather than the meat of grain-eating animals? 5 lbs. of feed 1 lb. of chicken
Energy Efficiency n Why is it more energy efficient to eat grains directly, rather than the meat of grain-eating animals? 5 lbs. of feed 1 lb. of chicken
 Energy Efficiency n Why is it more energy efficient to eat grains directly, rather than the meat of grain-eating animals? 2 lbs. of feed 1 lb. of fish
Energy Efficiency n Why is it more energy efficient to eat grains directly, rather than the meat of grain-eating animals? 2 lbs. of feed 1 lb. of fish
 Summary Question n Why do food chains rarely have more than 4 or 5 trophic levels?
Summary Question n Why do food chains rarely have more than 4 or 5 trophic levels?