fbe4c5cd5b50ddcf4afc0b548d3d8fb8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 61

Food and Drink read the information about the family

Read the cartoon.


Read the Gibson’s thoughts. Look at the words in bold.

What type of words are they?

modal auxiliary verbs So, can’t, may, mustn’t, needn’t, have to and don’t have to are extra words that go before verbs. They change the meaning of the verb – they modify it. So we call them modal auxiliaries or modals.
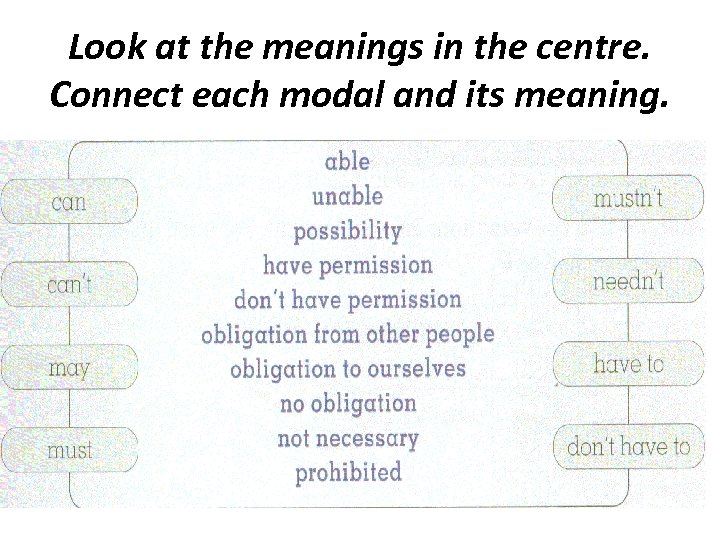
Look at the meanings in the centre. Connect each modal and its meaning.
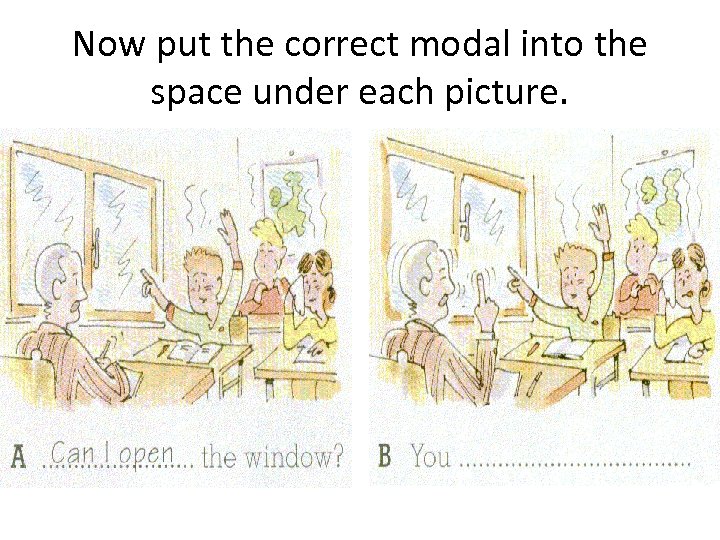
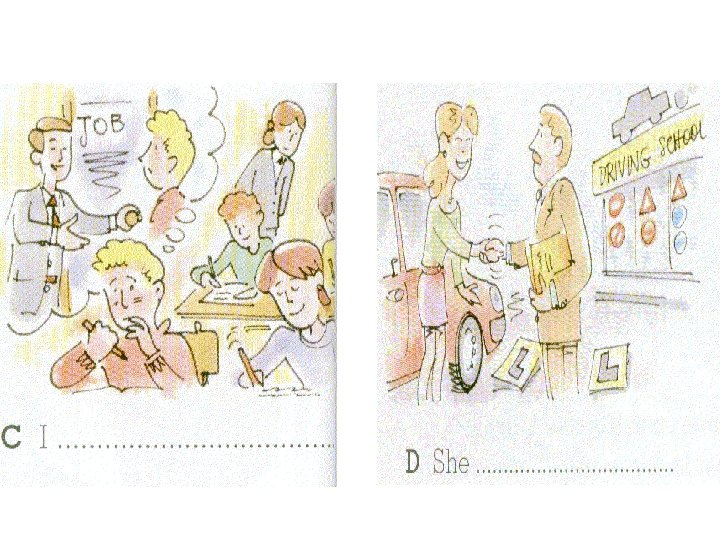
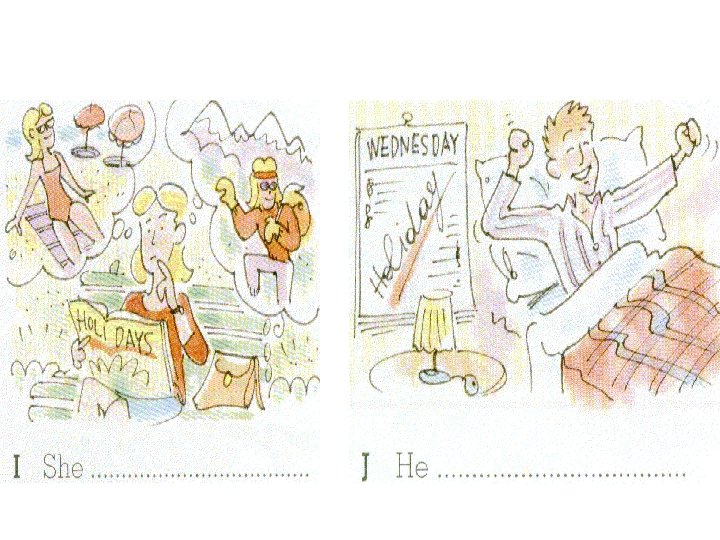
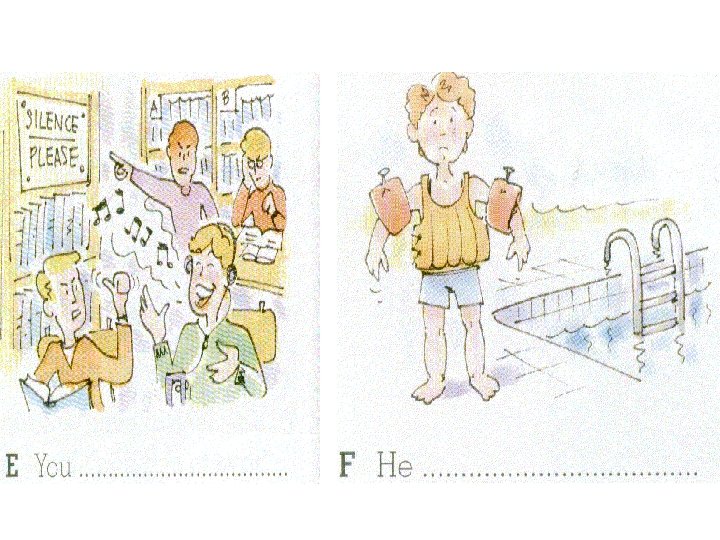
Now put the correct modal into the space under each picture.

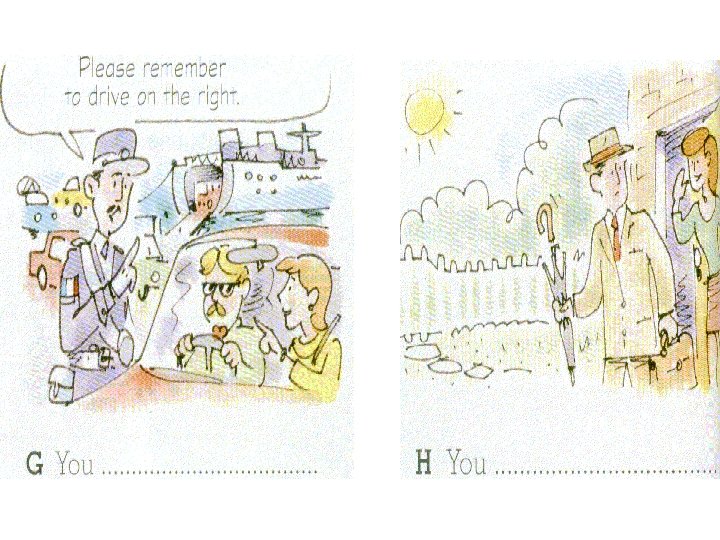


Think about the meaning of can and may. can (ability) can’t (lack of ability) can (permission) can’t (no permission) may/may not (possibility) In the following slide choose either can, can’t, may or may not for each space. If more than one is possible, choose the most likely.

1. I’m not sure about my hair. I ___ get it cut really short. 2. You ___ drive on the right in Britain. 3. You’re free tomorrow? OK, ___ I meet you for lunch? 4. Ask him to speak slower. I ___ understand what he’s saying. 5. You ___ like what he says but listen to him anyway. 6. What a great voice! Mary ___ really sing! 7. Yes Ok, you ___ park your car round the back.

9. Billy ___ swim like a fish but he just plays on the beach. 10. Mum – Dad says I ___ stay up and watch the film. Is that OK? 11. It’s an interesting theory but it ___ be wrong.

must or have to • must (internal obligation) Something you think you have to do or someone else has to do. • have to (external obligation) Something another person has told you or someone else to do.

Write either must or have to in each space. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. I’m sorry – I ___ go. I’ve got a meeting. You ___ remember to phone your brother. I really ___ tidy up the garden sometime. The doctor says I ___ take more exercise. If you ___ smoke, please do it outside. The teacher says we ___ do the homework for tomorrow. 7. He ___ see a dentist. He’s got terrible toothache.

Uefa president Michel Platini say he 1. __________ not support his Fifa counterpart Sepp Blatter at next year's election. Blatter, 78, who has 2. __________ under pressure over 3. __________ 2022 Qatar World Cup, recently indicated he was to seek re-election 4. __________ a fifth term. "I do not support him, I am not in favour of 5. __________ having a new term, " said Platini, 58. "I 6. __________ him. I think Fifa needs a new breath of fresh air. " Platini is yet to decide whether to contest the Fifa presidency 7. __________. The Frenchman said he agreed with his fellow Uefa members that it 8. __________ time for Blatter, who has been in power since 1998, to call it a day when his mandate ends next year. "I 9. __________ known him for a long time and I like him but I am not in favour of him having a new term, " added Platini. "I supported him in 1998 but I do not support him 10. __________ BENJAMIN C. PIM 2014.

Uefa president Michel Platini say he 1. will not support his Fifa counterpart Sepp Blatter at next year's election. Blatter, 78, who has been 2. under pressure over 3. the 2022 Qatar World Cup, recently indicated he was to seek re-election 4. for a fifth term. "I do not support him, I am not in favour of 5. him having a new term, " said Platini, 58. "I 6. told him. I think Fifa needs a new breath of fresh air. " Platini is yet to decide whether to contest the Fifa presidency 7. himself. The Frenchman said he agreed with his fellow Uefa members that it 8. was time for Blatter, who has been in power since 1998, to call it a day when his mandate ends next year. "I 9. have known him for a long time and I like him but I am not in favour of him having a new term, " added Platini. "I supported him in 1998 but I do not support him 10. in 2014. BENJAMIN C. PIM

And in the future I will not support Mr Blatter. " Platini, who won great praise in 1998 for his organisation of the World Cup hosted by France, indicated that he and his members 11. __________ not been happy with the Fifa Congress in Sao Paulo 12. __________ Wednesday. Several of Platini's colleagues confronted Blatter following his claims the British media's motivation 13. __________ investigating the Qatar bid were "racist". Uefa members 14. __________ the claims were without foundation. Football Association chairman Greg Dyke called those 15. __________ "totally unacceptable" and has 16. __________ urged the Swiss to step 17. __________ next year. The Fifa leader was helped in his bid for re-election by a congress vote not to consider age and termlimits for officials. Platini still 18. __________ not commit himself to a run for the Fifa presidency and at present there is just one candidate - former Fifa deputy secretary-general Jerome Champagne. "It is an option to run, " said Platini. "But it is not 19. __________ Sepp Blatter is running that Michel Platini will not 20. __________ and it is not because Blatter is not running that Platini will run. "My only concern is knowing what I want to 21. __________. I am 60 soon and I need to know what I want. I will take my time. ” BENJAMIN C. PIM

And in the future I will not support Mr Blatter. " Platini, who won great praise in 1998 for his organisation of the World Cup hosted by France, indicated that he and his members 11. had not been happy with the Fifa Congress in Sao Paulo 12. on Wednesday. Several of Platini's colleagues confronted Blatter following his claims the British media's motivation 13. in investigating the Qatar bid were "racist". Uefa members 14. said the claims were without foundation. Football Association chairman Greg Dyke called those 15. claims "totally unacceptable" and has 16. also urged the Swiss to step 17. down next year. The Fifa leader was helped in his bid for reelection by a congress vote not to consider age and term-limits for officials. Platini still 18. would not commit himself to a run for the Fifa presidency and at present there is just one candidate - former Fifa deputy secretary-general Jerome Champagne. "It is an option to run, " said Platini. "But it is not 19. because Sepp Blatter is running that Michel Platini will not 20. run and it is not because Blatter is not running that Platini will run. "My only concern is knowing what I want to 21. do. I am 60 soon and I need to know what I want. I will BENJAMIN C. PIM take my time. ”

8. My mother ___ take pills for her blood pressure. 9. I ___ see the dentist today. She’s given me an appointment at 3 o’clock. 10. You ___ do something about your hair – it’s awful.

mustn’t, needn’t or not have to? • mustn’t • needn’t • don’t have to (prohibition) (no necessity) (no obligation) • Remember that needn’t and don’t have to are very similar in meaning – so you can decide which to use.

Write either mustn’t, needn’t or the correct form of don’t have to in each of the spaces below 1. You ___ be so angry. I didn’t mean to break it. 2. You ___ tell me the details. I know how bad he is. 3. Jimmy – you really ___ speak like that to your mother. 4. Tell them they ___ stand up. The President is very informal. 5. You ___ bring mobile phones into the exam room.

6. He ___ tell Mary – she already knows. 7. Here’s a list of things you ___ bring into the country. 8. You ___ come crying to me. I told you he was no good. 9. You ___ ride a motorcycle without a helmet. 10. Workers ___ leave this office before 4. 45.

Correct questions. • 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Two of these sentences are wrong. Which two and why? Can I come in? Must she pay for this? Do I can borrow your pen? Do we must arrive before 9. 00? Do they have to fill in this form?



Modals: ability, obligation (present I future)

ability: can, can't, cannot • Can't is the negative, with cannot as a formal and written form. • There is no third person -s form. • Question forms are Can I, Can you etc.

Use can / can’t • to describe ability or lack of it. Many animals can see clearly in the dark. Human beings can't do this. • to describe what is allowed or not allowed. You can look at the animals in the zoo but you can't touch them. • with a future meaning. Sorry, but I can't come to the party next week. • with verbs of perception: hear, see, taste, feel, smell. What can you see? I can smell gas!

ability: be able to • This has the same meaning as can. • Use be able to instead of can. Many animals are able to see in the dark.

ability: be able to • When can is unsuitable. Because can has only present and past forms, we use be able to for other tenses, and infinitive form. I haven't been able to finish my project. We hope to be able to visit you next month.

obligation: have to / has to • The forms follow have: I have to, he / she has to etc; do I have to, does she have to; I don't have to etc. Use have to / has to • to describe what is necessary, a rule, or something we do because other people tell us to. Baby birds have to learn how to fly or they won 't survive. Do we have to buy another ticket to see this part of the castle?

• The negative form, don't / doesn't have to, is used to describe something unnecessary. I don 't have to go to work tomorrow. There's a holiday

obligation: must / mustn't • The negative is mustn't, with must not as a formal and written form. There is no third person -s form. • Question form is must I, must you etc. • Use must to describe something we personally think is necessary and important to do.

• There is sometimes little difference between first person I must and I have to. Sorry, I really have to go now. Sorry, I really must go now! • In other contexts, there is a difference. You must be more careful! (= personal opinion of the speaker) We have to wear safety goggles. (= an 'outside' opinion or rule) • We usually use the question form of have to for must. Do I have to sit here? • We use mustn't when we think an action is against the rules. You mustn't throw things in the science lab! It's dangerous!

Compare mustn't and don't have to. • You mustn't use a pencil. (it's not allowed) • You don't have to use a pen. (it's not necessary - use a pen or a pencil)

Use should, ought to • to say what we think is right or correct, or is a good idea in your opinion. This is not as strong as must. You should pay more attention. You shouldn't talk so much. • to give advice. I think you should study biology next year. • in the same way. Ought to / ought not to has the same meaning as should / should not.

Use had better • to say what we think someone should do. There is only one form had better /'d better. • The negative is had better not. You'd better wear your raincoat. It's going to rain. You'd better not wait too long. You’ll be late.

Use need to • with the same meaning as have to. • Need to is not a modal verb. You need to work harder. You don't need to come tomorrow Do I need to bring my dictionary?

Complete the sentence with mustn't, or don't / doesn't have to. a. You__ stand on the desk. You'll break it. b We __ take an umbrella. I'm sure it isn't going to rain. c You __ put a stamp on this letter. It says freepost on it. d We __ forget to take the presents with us when we go. e In our country children __ go to school on Saturday. f You __ touch the ball. It's against the rules.

answers a. b. c. d. e. f. Mustn’t Don’t have to Mustn’t


answers


answers


modals: ability, obligation, criticism (past)

past ability: could, couldn't, was / were able to • Could / couldn't are past forms of can / can't. • Could not is used in formal speech and writing. Use could / couldn't • to describe past ability. We don't know how fast Ancient Greek athletes could run. • to describe what was allowed or not allowed. Women couldn't compete or watch the ancient Olympic Games.

• We can use was / were able to in the place of could / couldn't to describe past ability in general. He tried hard but wasn't able to win the race. • We use was / were able to, not could / couldn't, when we mean that we could do something and we actually did it. One runner fell badly, but fortunately was able to finish the race.

past obligation: had to, didn't have to • Had to / didn't have to / did you have to etc are past forms of have to and must. Use had to • to describe past obligation, for both must and have to. Athletes who cheated in the Olympic Games had to pay for a statue of the god Zeus. • Of course, in ancient times athletes didn't have to take drugs tests.

past necessity: needed to, didn't need to, needn't have • Use needed to (regular verb) to describe what was necessary. He needed to stop for a drink, but he kept running. • Use didn't need to to describe what was not necessary. In ancient Greece, winning athletes didn't need to work again. • The question form is did you need to etc

• Use needn't have + past participle (a form of modal verb need) to explain that someone did something, but what they did was unnecessary. I was worried because I thought that my tickets for the Games wouldn't arrive in time. But I needn't have worried. They arrived this morning!

past criticism: should have / shouldn't have, ought to have, ought not to have • Use should have / shouldn't have + past participle to criticize a past action. ‘You started before the gun! You shouldn't have done that. ’ 'But it was an accident!' 'Well, you should have been more careful" • Use ought to have / ought not to have + past participle in the same way

Complete the text with had to, didn't have to, could or couldn't + the verbs in brackets. Life for children in Victorian Britain was very different from the life children lead today. Firstly, Victorian children a (go)___ to school, and in any case poor families b (pay) ___ for lessons because they didn't have enough money. So children c (find)___ jobs at an early age, starting in the coal mines, for example, at the age of five.

The more fortunate children became apprentices, learning a trade and working at the same time. Such children d (work)__ for fifty or sixty hours a week, usually for very low wages, and e (sign)__an agreement which kept them with the same master for a number of years. The worst jobs were in factories, where many children under the age of nine were employed. Children were also employed to clean chimneys, and known as 'chimney sweeps'.

These children f (climb)__ up chimneys and clean them. They g (be)___small, or else they would get stuck in the chimney. Using children to do this job was banned in 1840, but employers then h (use)__ special brushes, which were expensive, and so they continued to use children. The employers i (pay)__ a small fine if they were caught.

• After the Factory Act of 1833, employers in textile factories j (employ)__children under the age of nine, though children aged nine to 11 k (work) __eight hours a day. However, nothing changed in coal mines and in other factories, where employers I (put)__ children to work in dangerous and dirty conditions. It wasn't until 1847 that employers m (limit)___the working day to ten hours, for both children and adults.

answers a didn't have to go b couldn't pay c had to find d had to work e had to sign f had to climb g had to be h had to use i had to pay j couldn't employ k could work I could put m had to limit
fbe4c5cd5b50ddcf4afc0b548d3d8fb8.ppt