DIGESTIVE SYSTEM.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 79


FOOD • A nutrient is a substance required by the body for energy, growth, repair, and maintenance. Nutrients in food and beverages include carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, vitamins, and minerals.


Energy and Building Materials • Each nutrient plays a different role in maintaining a healthy body. • Carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids are involved in providing both energy and building materials to the cells.


Carbohydrates that exist as single sugar molecules are called monosaccharides or simple carbohydrates. Carbohydrates made of two or many sugar molecules linked together by chemical bonds are called complex carbohydrates. Complex carbohydrates must be broken down into simple sugars before cells can use their energy.

Proteins Amino acids from proteins are used by the body for making additional proteins. Extra amino acids in the diet are used for energy or converted to fat. The body needs 20 different amino acids to function. Ten amino acids (called essential amino acids) must be obtained directly from food.

Lipids The body uses lipids to make steroid hormones and cell membranes and to store energy. Fats are lipids that store energy in plants and animals. Fats are also stored around organs and act as padding and insulation.


• Vitamins are organic substances that occur in foods in small Vitamins, Minerals, and Water amounts. They are necessary in trace amounts for the normal metabolic functioning of the body. • Minerals are naturally occurring inorganic substances that re used to make certain body structures and substances. They are also needed for normal nerve and muscle function.




DIGESTION Organisms must break down their foodstuffs into their components for passing through the cell membrane. This process is called digestion.

TYPES OF DIGESTION There are two types of digestion. These are; • Mechanical digestion • Chemical digestion

MECHANICAL DIGESTION Pieces of food are firstly cut, crushed, or broken into smaller particles without being changed chemically. This process is called mechanical digestion. Mechanical breakdown increases the surface area of the food particles. . Protein


CHEMICAL DIGESTION • Chemical digestion is series of reactions in which foods are hydrolyzed, aided by water and enzymes. Food split into its monomers by means of chemical digestion. STARCH + WATER n GLUCOSE


TYPES OF DIGESTION ACCORDING TO THEIR MEDIUM • There are two types digestion according to their medium. These are • EXTRACELLULAR DIGESTION • INTRACELLULAR DIGESTION

INTRACELLULAR DIGESTION • In unicellular organisms foodstuffs are digested within food vacuoles in the cytoplasm. They are taken into cell by pinocytosis or phagositosis.

EXTRACELLULAR DIGESTION In this process, digestion of food takes place within an area external to the organism by the secretion of digestive enzymes. Extracellular digestion is seen in protista, invertebrates and all vertebrates.


HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system is made up of highly specialized digestive tube and several organs. Human Digestive System includes; • Mouth • Eusophagus • Stomach • Small Intestine • Large Intestine





MOUTH • Food enters the body through the mouth. • Mechanical and chemical digestion occur in mouth. Teeth help in mechanical digestion. • There are three pairs of salivary glands in the lining of the mouth. Salivary glands secrete saliva into the mouth. They help in chemical digestion


TEETH • Teeth are adapted for mechanical digestion of food. • Each tooth is composed of crown and root • The crown is covered with enamel. It is hardest material of our body.





TYPES OF TEETH • There are 4 types of teeth. These are 1 - Molars 12 2 - Pre molars 8 3 - Canines 4 4 - Incisors 8 TOTAL 32





ESOPHAGUS • After chewing of food, it is pushed by the tongue to the esophagus. The esophagus connects mouth with the stomach. • Peristalsis begins in the esophagus. Peristalsis is the series rhythmic muscles contraction and relaxations. Food moves through the digestion system by peristalsis.




STOMACH • Food is stored temporarily in the stomach. Mechanical and chemical digestion occur in mouth. Food is broken down mechanically into smaller particles by the contractions of the muscles. • Stomach secretes enzymes for chemical digestion





SMALL INTESTINE • Most digestion and absorption occur in small intestine. Most chemical digestion and all absorption occur in ileum. All digestion is completed in the small intestine. • The small intestine has three parts. They are duodenum jejunum and ileum.






LARGE INTESTINE • Undigested materials pass from the small intestine into the large intestine. There is no digestion in this part. • The large intestine contains many bacteria. They produce vitamins such as vitamin K. • Large intestine opens to the outside of the body through the anus.

FUNCTIONS OF LARGE INTESTINE • Reabsorption of water • Absoption of vitamins • Eliminations of undigested materials


DIGESTION OF CARBOHYDRATES IN THE MOUTH • Chemical digestion of carbohydrate starts in mouth. Salivary glands secrete saliva into the mouth. Saliva is juice which contain digestive enzyme is called ptyalin or amylase. • Amylase breaks down starch into dextrin and maltose. Starch + Water Amylase Dextrin + Maltose

DIGESTION OF CARBOHYDRATES IN THE STOMACH • Stomach is an acidic area. Amylase can not work in acidic region. • Therefore chemical digestion of carbohydrates stop in stomach.

DIGESTION OF CARBOHYDRATES IN THE SMALL INTESTINE When food passes into the small intestine from stomach, it stimulates cells of small intestine. Than small intestine secretes two hormones into the blood. These hormones are secretin and cholecystokinin.

They stimulate pancreas and it secretes pancreatic enzymes to small intestine. Enzymes act on every types of carbohydrates. Pancreatic juice includes amylase, maltase, lactase and sucrase.


Dextrin + H 2 O Maltose + H 2 O Sucrose + H 2 O Lactose + H 2 O Amylase Maltase Sucrase Lactase Glucose +…… Glucose + Fructose Glucose + Galactose Digestion of carbohydrates is completed in small intestine.


DIGESTION OF PROTEINS • Digestion of protein starts in stomach and complete in small intestine. • When food enter the stomach, it stimulates some stomach cells. These cells secretes GASTRINE hormone. This hormone stimulates gastric gland it produces gastric juice. • Gastric Juice is composed of; Mucus, HCl and Pepsinogen

REACTIONS IN THE STOMACH Pepsinogen + HCl Protein + H 2 O Milk + H 2 O Casein+ H 2 O Pepsin Rennin Pepsin Peptones Casein Peptones + a. a….

DIGESTION OF PROTEINS IN THE INTESTINE • Tripsinogen and Chymotripsinogen take role in the digestion of proteins that are secreted by pancreas. • Enterocinase and Erepsin are secreted by intestinal glands to digest proteins.
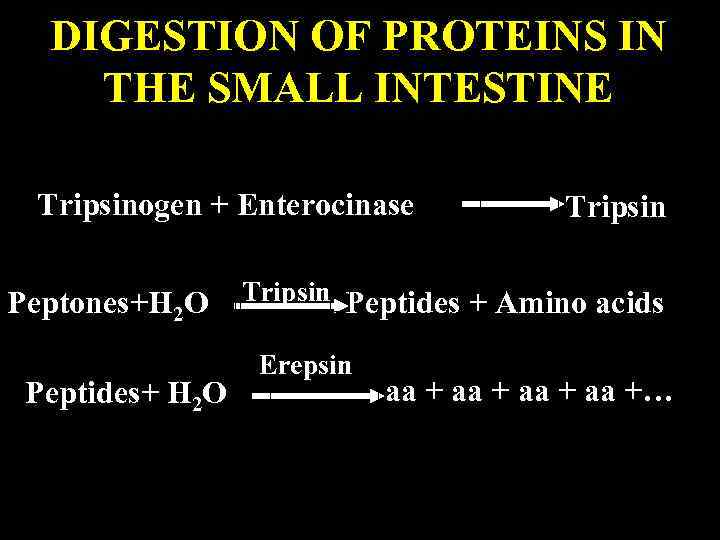
DIGESTION OF PROTEINS IN THE SMALL INTESTINE Tripsinogen + Enterocinase Tripsin Peptones+H 2 O Tripsin Peptides + Amino acids Peptides+ H 2 O Erepsin aa +…


DIGESTION OF LIPIDS • Digestion of lipid occurs only in small intestine. The cells of the liver produce bile. Than it is stored in gall bladder. When food enters to small intestine it secretes cholecystokinin hormone. This hormone causes removing of bile from gall bladder to small intestine.

• Bile does not contain enzyme but it aids mechanical digestion of lipid. This process is called emulsification.



Lipid Bile Small lipid particles Lipase is secreted from pancreas. Lipase breaks down lipid molecules into fatty acids and glycerol. Lipid + H 2 O Lipase 3 Fatty acid + Glycerol


ABSORBTION • There are many finger like projections in lining of small intestine. They are called VILLI. • Villi increas the absorption surface of small intestine. • Passing of digested materials from small intestine to blood is called absorption. • Vitamins and inorganic materials pass into the blood without digestion.


• The digestive products of carbohydrates, aminoacids and vitamins pass from the microvilli to the venules (the small branches of the veins). • Fatty acids and glycerol pass from the microvilli to the lymph circulation.
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM.ppt