 Focusing Light on the Retina How is light focused on the retina? Cornea (spherical; curvature) Refraction (air-fluid) Lens (accommodation) Length of eye ball (axial) Focusing problems: Astigmatism; Presbyopia; Myopia; Hyperopia
Focusing Light on the Retina How is light focused on the retina? Cornea (spherical; curvature) Refraction (air-fluid) Lens (accommodation) Length of eye ball (axial) Focusing problems: Astigmatism; Presbyopia; Myopia; Hyperopia
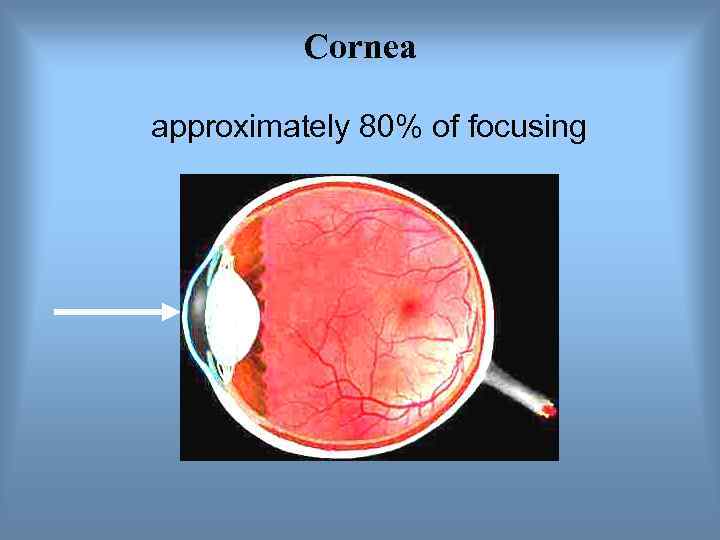 Cornea approximately 80% of focusing
Cornea approximately 80% of focusing
 Astigmatism Aspherical cornea: light at some orientations is focused, while light at others is not
Astigmatism Aspherical cornea: light at some orientations is focused, while light at others is not
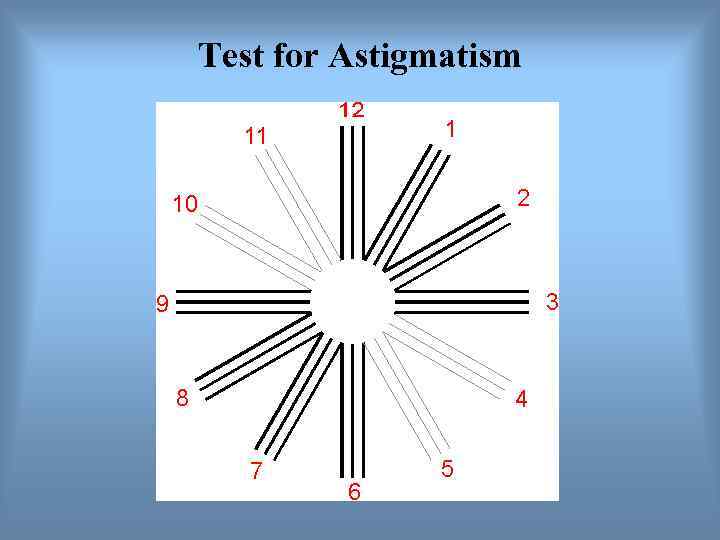 Test for Astigmatism
Test for Astigmatism
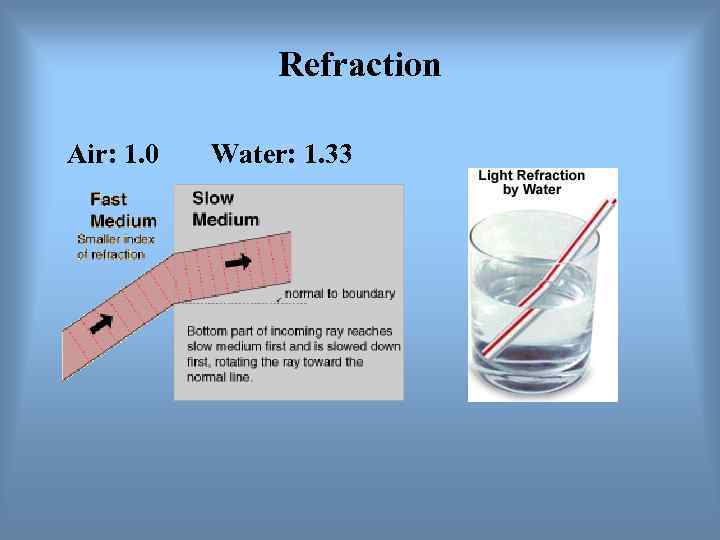 Refraction Air: 1. 0 Water: 1. 33
Refraction Air: 1. 0 Water: 1. 33
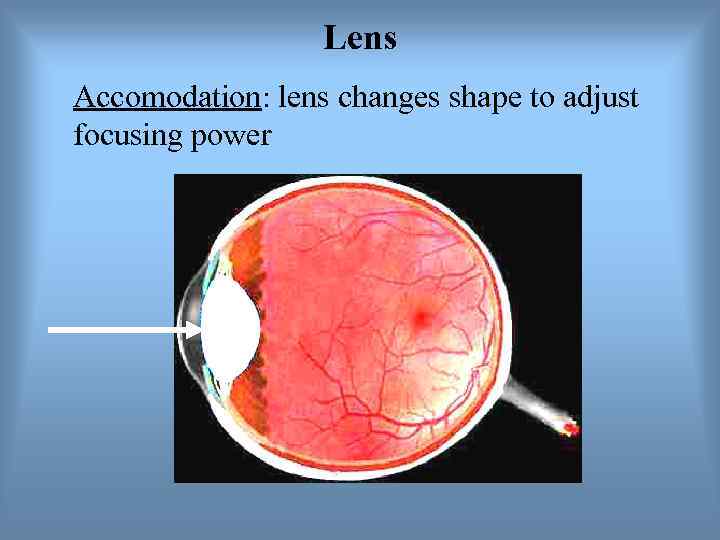 Lens Accomodation: lens changes shape to adjust focusing power
Lens Accomodation: lens changes shape to adjust focusing power
 Presbyopia: ciliary muscles can no longer contract as well; lens cannot be made round enough for close vision
Presbyopia: ciliary muscles can no longer contract as well; lens cannot be made round enough for close vision
 Test for Presbyopia Measurement of ‘near point’: -measure with ruler and pin -near point increases with age -average near points: -10 yr. old: 7 cm -40 yr. old: 21 cm -60 yr. old: 100 cm
Test for Presbyopia Measurement of ‘near point’: -measure with ruler and pin -near point increases with age -average near points: -10 yr. old: 7 cm -40 yr. old: 21 cm -60 yr. old: 100 cm
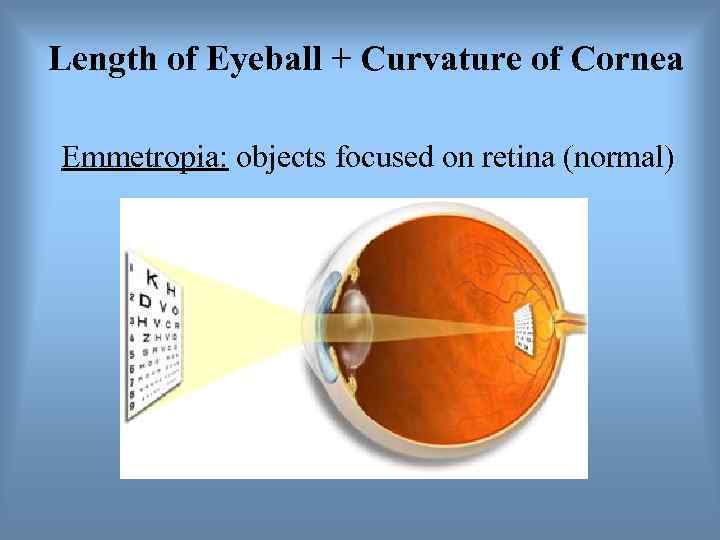 Length of Eyeball + Curvature of Cornea Emmetropia: objects focused on retina (normal)
Length of Eyeball + Curvature of Cornea Emmetropia: objects focused on retina (normal)
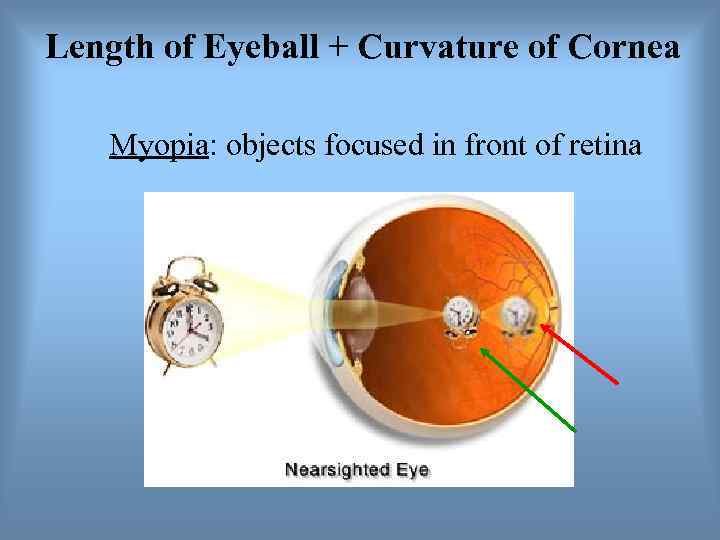 Length of Eyeball + Curvature of Cornea Myopia: objects focused in front of retina
Length of Eyeball + Curvature of Cornea Myopia: objects focused in front of retina
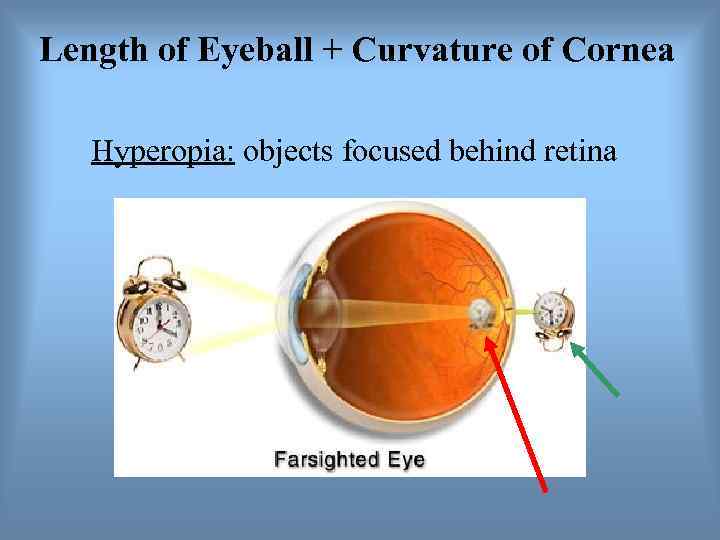 Length of Eyeball + Curvature of Cornea Hyperopia: objects focused behind retina
Length of Eyeball + Curvature of Cornea Hyperopia: objects focused behind retina
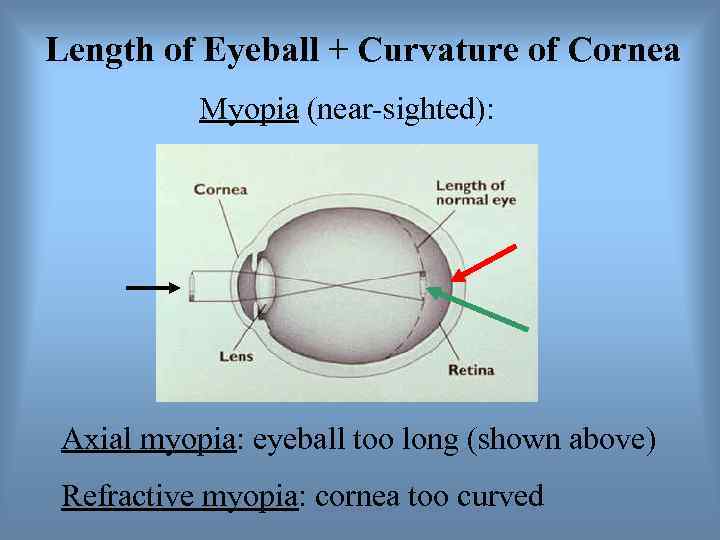 Length of Eyeball + Curvature of Cornea Myopia (near-sighted): Axial myopia: eyeball too long (shown above) Refractive myopia: cornea too curved
Length of Eyeball + Curvature of Cornea Myopia (near-sighted): Axial myopia: eyeball too long (shown above) Refractive myopia: cornea too curved
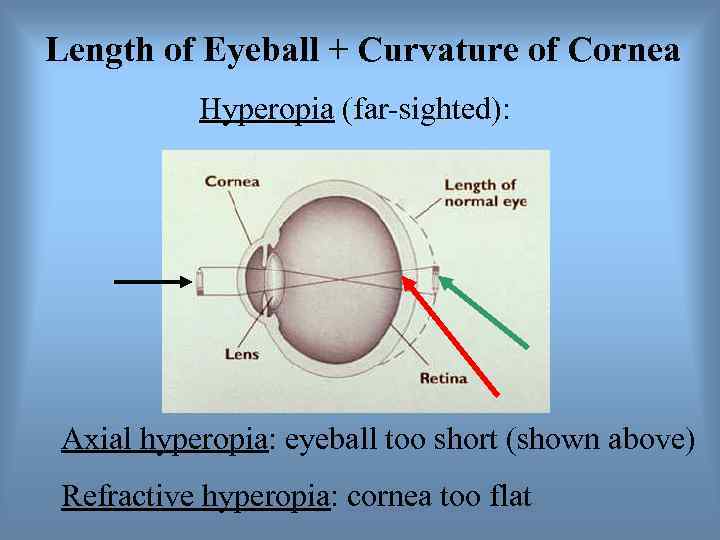 Length of Eyeball + Curvature of Cornea Hyperopia (far-sighted): Axial hyperopia: eyeball too short (shown above) Refractive hyperopia: cornea too flat
Length of Eyeball + Curvature of Cornea Hyperopia (far-sighted): Axial hyperopia: eyeball too short (shown above) Refractive hyperopia: cornea too flat
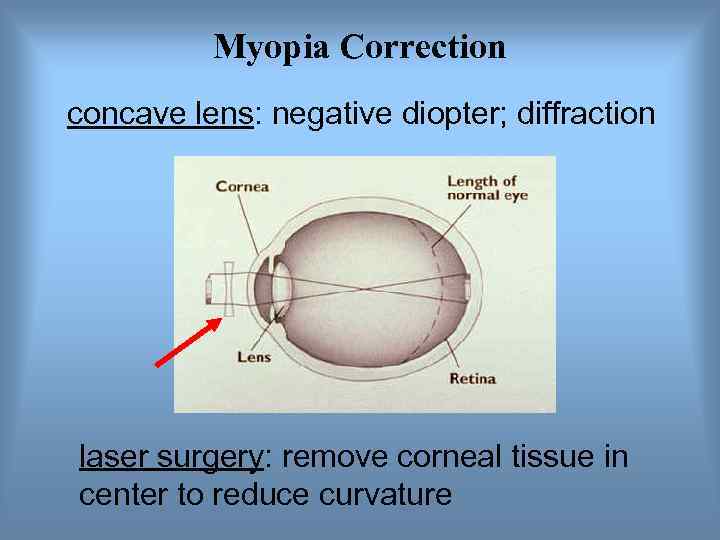 Myopia Correction concave lens: negative diopter; diffraction laser surgery: remove corneal tissue in center to reduce curvature
Myopia Correction concave lens: negative diopter; diffraction laser surgery: remove corneal tissue in center to reduce curvature
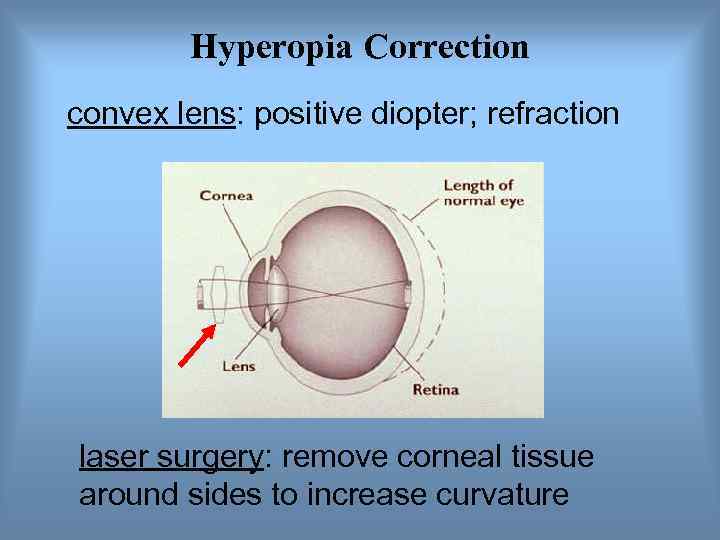 Hyperopia Correction convex lens: positive diopter; refraction laser surgery: remove corneal tissue around sides to increase curvature
Hyperopia Correction convex lens: positive diopter; refraction laser surgery: remove corneal tissue around sides to increase curvature
 Testing Acuity Retinoscope: -streak of light is projected into eye and reflected back to ophthalmologist -retinoscope is moved slowly side-to-side -if streak moves in opposite direction: myopia -if streak moves in same direction: hyperopia -if whole pupil fills with light: emmetropia
Testing Acuity Retinoscope: -streak of light is projected into eye and reflected back to ophthalmologist -retinoscope is moved slowly side-to-side -if streak moves in opposite direction: myopia -if streak moves in same direction: hyperopia -if whole pupil fills with light: emmetropia
 Testing Acuity “E” charts; Bailey-Lovie charts 20/20 you emmetrope “What you can read at 20 feet an emmetrope can read at ___feet”
Testing Acuity “E” charts; Bailey-Lovie charts 20/20 you emmetrope “What you can read at 20 feet an emmetrope can read at ___feet”
