4a3b59ba51e3a0f6f52ed67d77da7fa4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 66

FMEA Intelligent use of FMEA Presented by Quality Associates International Visit us at: www. quality-one. com This guideline is for training purposes only; Not ISO controlled
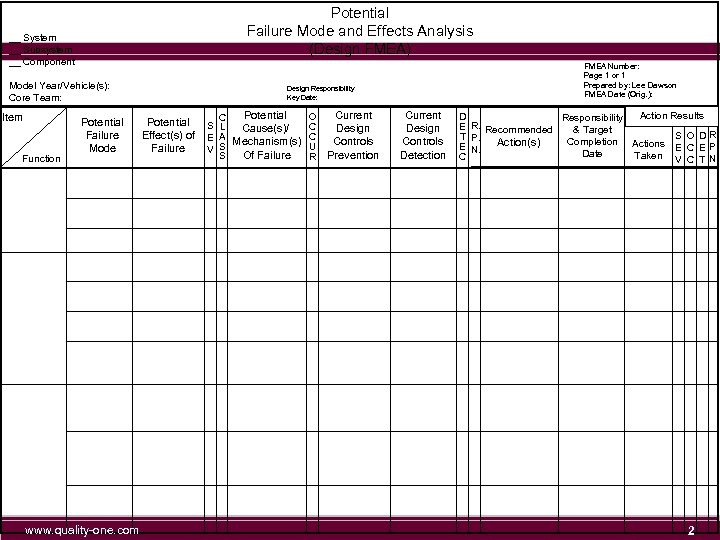
Potential Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (Design FMEA) __ System __ Subsystem __ Component Model Year/Vehicle(s): Core Team: Item Function Potential Failure Mode www. quality-one. com FMEA Number: Page 1 or 1 Prepared by: Lee Dawson FMEA Date (Orig. ): Design Responsibility Key Date: Potential Effect(s) of Failure Potential O C S L C Cause(s)/ E A Mechanism(s) C U V S Of Failure S R Current Design Controls Prevention Current Design Controls Detection Action Results D Responsibility E R. Recommended & Target S O D R. T P. Completion Actions Action(s) E N. E C E P. Date Taken V C T N. C 2

What Is An FMEA? n Opportunity to Defeat Murphy’s Law n Focus on Prevention n Failure Mode And Effects Analysis is An assessment of Risk MURPHY’S LAW Safety Regulatory Customer Satisfaction Program Coordinated/Documented team effort To determine what can go wrong A method to determine the need and priority of actions It is not designed to record previously designed elements www. quality-one. com 3
FMEA Deployment n A layered approach is highly recommended as FMEAs can get complex. n FMEAs are like ONIONS/LAYERS. Each layer is closer to the root cause Each layer is more detailed The closer to core the more detail Core gets to the root cause n. Do too many and you will cry. www. quality-one. com 4

FMEA Strategy Strategic Deployment of FMEA to support DFSS (Design for Six Sigma) The requirements cascade to achieve success www. quality-one. com 5
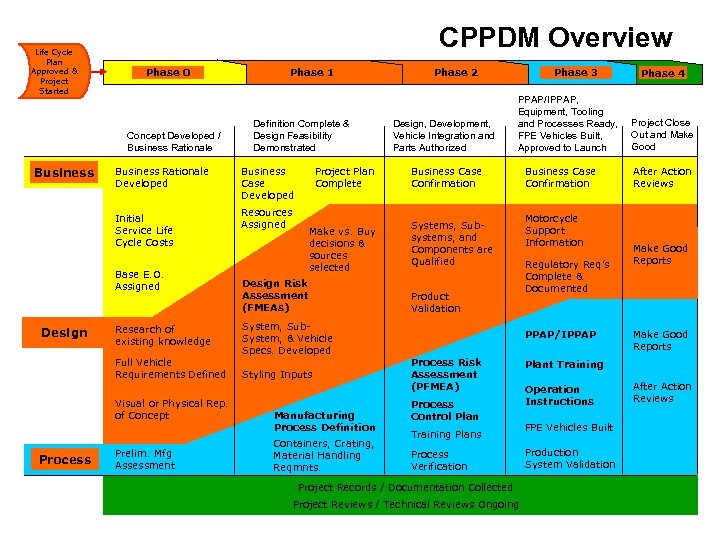
CPPDM Overview Life Cycle Plan Approved & Project Started Phase 0 Concept Developed / Business Rationale Developed Initial Service Life Cycle Costs Base E. O. Assigned Design Research of existing knowledge Full Vehicle Requirements Defined Visual or Physical Rep. of Concept Process Prelim. Mfg Assessment Phase 1 Definition Complete & Design Feasibility Demonstrated Business Case Developed Resources Assigned Project Plan Complete Make vs. Buy decisions & sources selected Design Risk Assessment (FMEAs) System, Sub. System, & Vehicle Specs. Developed Styling Inputs Manufacturing Process Definition Containers, Crating, Material Handling Reqmnts. Phase 2 Design, Development, Vehicle Integration and Parts Authorized Phase 3 PPAP/IPPAP, Equipment, Tooling and Processes Ready, FPE Vehicles Built, Approved to Launch Business Case Confirmation Systems, Subsystems, and Components are Qualified Product Validation Business Case Confirmation Motorcycle Support Information Regulatory Req’s Complete & Documented PPAP/IPPAP Process Risk Assessment (PFMEA) Process Control Plan Training Plans Process Verification Phase 4 Project Close Out and Make Good After Action Reviews Make Good Reports Plant Training Operation Instructions After Action Reviews FPE Vehicles Built Production System Validation Project Records / Documentation Collected Project Reviews / Technical Reviews Ongoing www. quality-one. com 6
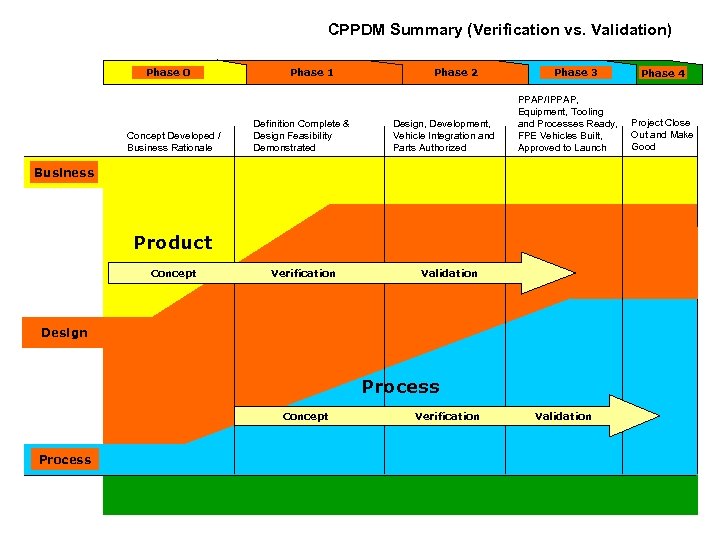
CPPDM Summary (Verification vs. Validation) Phase 0 Concept Developed / Business Rationale Phase 1 Definition Complete & Design Feasibility Demonstrated Phase 2 Design, Development, Vehicle Integration and Parts Authorized Phase 3 PPAP/IPPAP, Equipment, Tooling and Processes Ready, FPE Vehicles Built, Approved to Launch Phase 4 Project Close Out and Make Good Business Product Concept Verification Validation Design Process Concept Verification Validation Process www. quality-one. com 7
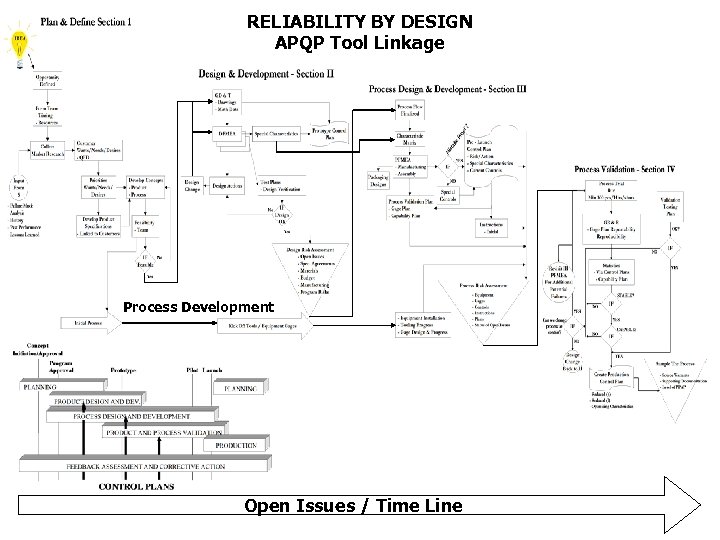
RELIABILITY BY DESIGN APQP Tool Linkage Process Development Open Issues / Time Line www. quality-one. com 8

Requirements Cascade How Fmea fits into Product and Process Development This guideline is for training purposes only; Not ISO controlled
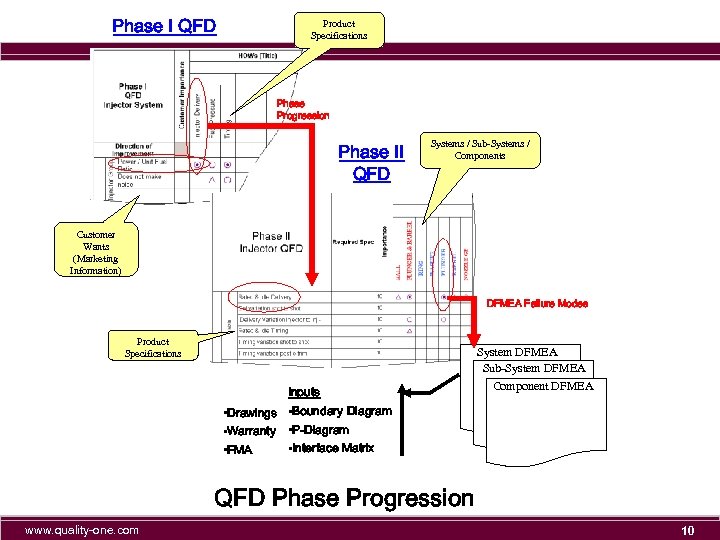
Phase I QFD Product Specifications Phase Progression Phase II QFD Systems / Sub-Systems / Components Customer Wants (Marketing Information) DFMEA Failure Modes Product Specifications System DFMEA Sub-System DFMEA Inputs Component DFMEA • Drawings • Boundary Diagram • Warranty • P-Diagram • Interface Matrix • FMA QFD Phase Progression www. quality-one. com 10
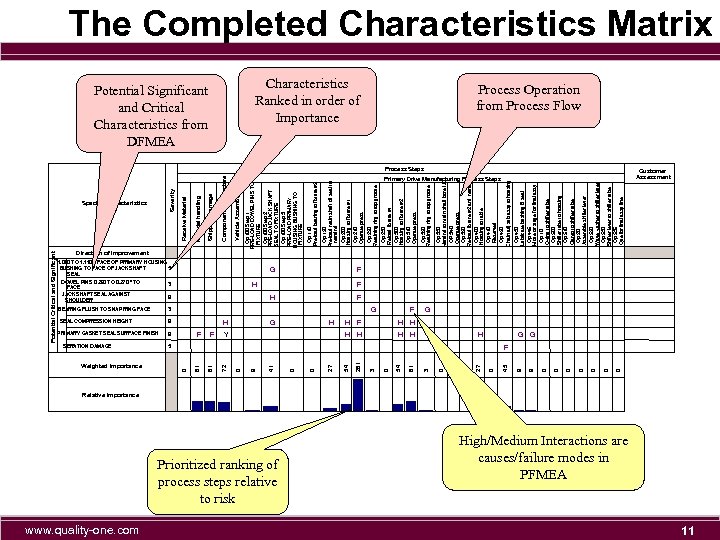
Weighted Importance www. quality-one. com Prioritized ranking of process steps relative to risk H H 27 5 H F G 9 0 0 0 0 G 9 45 Shipping Damage Primary Drive Manufacturing Process Steps Op 430 Lubricate bushing & seal Op 445 Move or stage for final assy Op 10 O-ring to shifter tube Op 500 Shifter tube to housing Op 510 Clamp to shifter tube Op 20 Assemble shifter lever Op 520 Wave washer to shifter lever Op 530 Shifter lever to shifter tube Op 535 Que for final assy line Op 420 Chain adj sub assy to housing Op 330 Mandrel to main shaft bore I. D. OP 340 Operate press Op 350 Re-load fixture #2 and mandrel Op 400 Housing to table Op 410 Reserved Op 320 Retaining ring to top groove Op 230 Reload fixture #1 Op 300 Housing to fixture #2 Op 310 Operate press Op 220 Retaining ring to top groove Op 120 Pre-load main shaft oil seal to mandrel Op 200 Housing to fixture #1 Op 210 Operate press Op 110 Pre-load bearing to fixture #2 Op 100 Step 1 PRE-LOAD DOWEL PINS TO FIXTURE Op 100 Step 2 PRE-LOAD JACK SHAFT SEAL TO FIXTURE Op 100 Step 3 PRE-LOAD PRIMARY HOUSING BUSHING TO FIXTURE Vehicle Assembly Component Manufacture Characteristics Ranked in order of Importance 0 H H 0 F 0 H 0 G 81 F 3 3 54 H 0 H 261 G 3 Y H H H 54 F G 27 F 0 H 0 1. 090 TO 1. 110 " FACE OF PRIMARY HOUSING 5 BUSHING TO FACE OF JACK SHAFT SEAL DOWEL PINS 0. 260 TO 0. 270 " TO 3 FACE JACK SHAFT SEAL AGAINST 9 SHOULDER 41 9 Material handling Potential Significant and Critical Characteristics from DFMEA 9 9 0 PRIMARY GASKET SEAL SURFACE FINISH 81 SEAL COMPRESSION HEIGHT 72 BEARING FLUSH TO SNAP RING FACE Receive Material Severity Special Characteristics Matrix 81 SERATION DAMAGE 0 Potential Critical and Significant The Completed Characteristics Matrix Process Operation from Process Flow Process Steps Customer Assessment Direction of Improvement F F F G Relative Importance High/Medium Interactions are causes/failure modes in PFMEA 11
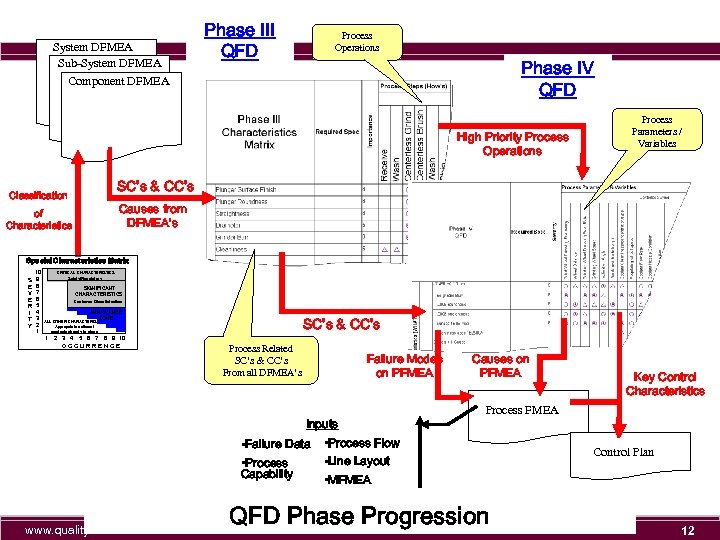
System DFMEA Sub-System DFMEA Phase III QFD Process Operations Phase IV QFD Component DFMEA High Priority Process Operations Process Parameters / Variables SC’s & CC’s Classification Causes from DFMEA’s of Characteristics Special Characteristics Matrix S E V E R I T Y 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 CRITICAL CHARACTERISTICS Safety/Regulatory SIGNIFICANT CHARACTERISTICS Customer Dissatisfaction ANNOYANCE ZONE SC’s & CC’s ALL OTHER CHARACTERISTICS Appropriate actions / controls already in place 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 OCCURRENCE Process Related SC’s & CC’s From all DFMEA’s Failure Modes on PFMEA Inputs • Failure Data • Process Capability www. quality-one. com Causes on PFMEA Key Control Characteristics Process FMEA • Process Flow • Line Layout • MFMEA QFD Phase Progression Control Plan 12
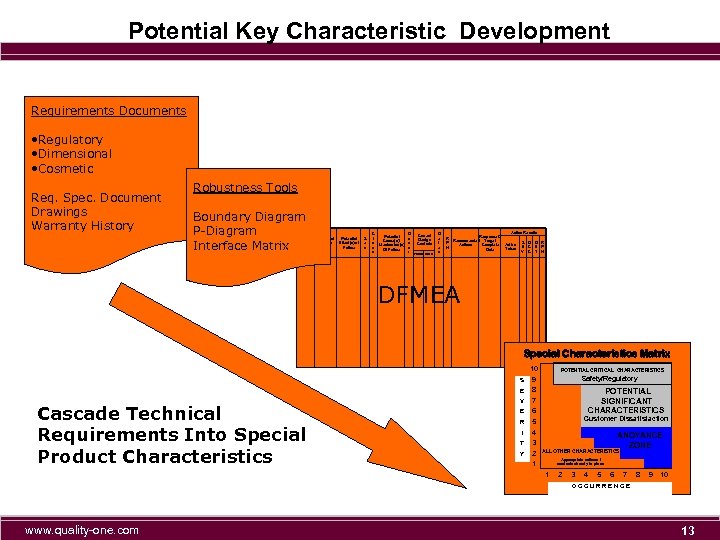
Potential Key Characteristic Development Requirements Documents • Regulatory • Dimensional • Cosmetic Req. Spec. Document Drawings Warranty History Robustness Tools Boundary Diagram P-Diagram Interface Matrix Item / Process Step Function Potential Failure Mode Potential Effect(s) of Failure S e v C l a s s O Potential c Cause(s)/ c Mechanism(s) u Of Failure r Current Design Controls Prevent Detect D e t e c Action Results Response & R Recommended Target S O D R P Actions Complete Action E C E P N Taken Date V C T N DFMEA Special Characteristics Matrix S E Cascade Technical Requirements Into Special Product Characteristics 10 9 8 V 7 6 5 E R I T Y POTENTIAL CRITICAL CHARACTERISTICS Safety/Regulatory POTENTIAL SIGNIFICANT CHARACTERISTICS Customer Dissatisfaction 4 3 2 1 ANOYANCE ZONE ALL OTHER CHARACTERISTICS Appropriate actions / controls already in place 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 OCCURRENCE www. quality-one. com 13
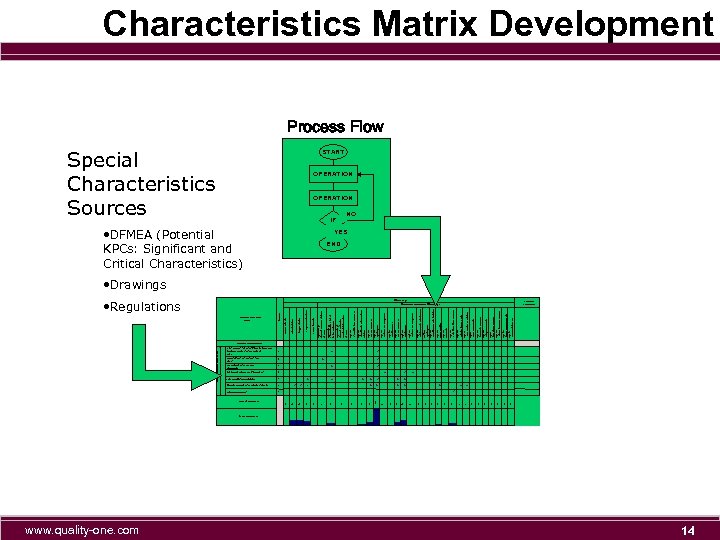
www. quality-one. com Weighted Importance 81 45 0 0 0 G 0 H 9 F 9 H 0 H H 27 G 0 H H 0 F H 0 Y H 3 H 54 G 0 F H 261 5 F G 54 SERATION DAMAGE H 3 9 H 27 9 PRIMARY GASKET SEAL SURFACE FINISH Que for final assy line Op 535 Shifter lever to shifter tube Op 530 Op 520 Wave washer to shifter lever Assemble shifter lever Op 20 Clamp to shifter tube Op 510 Op 500 Shifter tube to housing O-ring to shifter tube Op 10 Move or stage for final assy Op 445 Lubricate bushing & seal Op 430 Chain adj sub assy to housing Op 420 Op 410 Reserved Housing to table Op 400 Re-load fixture #2 and mandrel Op 350 Operate press OP 340 Op 330 Mandrel to main shaft bore I. D. Op 320 Retaining ring to top groove Op 310 Operate press Op 300 Housing to fixture #2 Reload fixture #1 Op 230 Retaining ring to top groove Op 220 Op 210 Operate press Op 200 Housing to fixture #1 Pre-load main shaft oil seal to mandrel Op 120 Pre-load bearing to fixture #2 Op 110 HOUSING BUSHING TO FIXTURE PRE-LOAD PRIMARY Op 100 Step 3 SEAL TO FIXTURE Op 100 Step 2 PRE-LOAD JACK SHAFT FIXTURE Op 100 Step 1 PRE-LOAD DOWEL PINS TO Vehicle Assembly Component Manufacture Shipping Damage IF 0 3 SEAL COMPRESSION HEIGHT 0 9 BEARING FLUSH TO SNAP RING FACE Material handling • DFMEA (Potential KPCs: Significant and Critical Characteristics) 41 3 JACK SHAFT SEAL AGAINST SHOULDER 9 5 DOWEL PINS 0. 260 TO 0. 270 " TO FACE Receive Material Special Characteristics Sources 0 BUSHING TO FACE OF JACK SHAFT SEAL 72 Matrix 81 Special Characteristics Severity • Regulations 81 0 Potential Critical and Significant Characteristics Matrix Development Process Flow START OPERATION NO END YES • Drawings Process Steps Primary Drive Manufacturing Process Steps Assessment Customer 1. 090 TO 1. 110 " FACE OF PRIMARY HOUSING Direction of Improvement F F F G Relative Importance 14
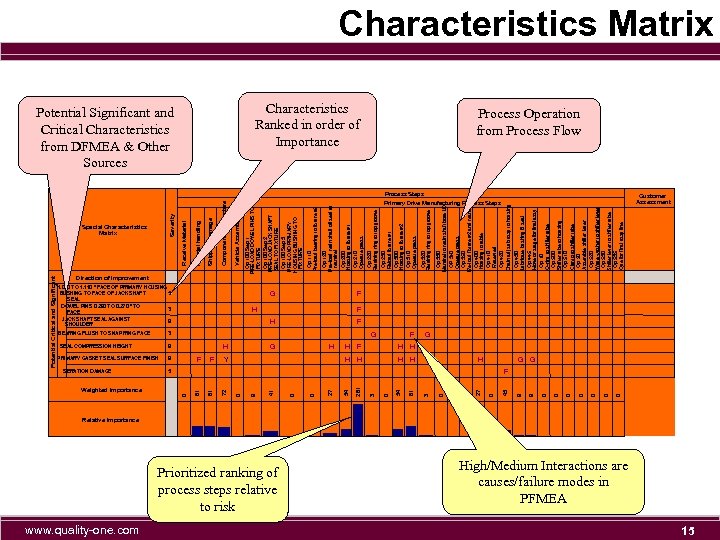
Weighted Importance www. quality-one. com Prioritized ranking of process steps relative to risk 0 0 0 0 H 9 5 45 H 27 Shipping Damage Primary Drive Manufacturing Process Steps Op 430 Lubricate bushing & seal Op 445 Move or stage for final assy Op 10 O-ring to shifter tube Op 500 Shifter tube to housing Op 510 Clamp to shifter tube Op 20 Assemble shifter lever Op 520 Wave washer to shifter lever Op 530 Shifter lever to shifter tube Op 535 Que for final assy line Op 420 Chain adj sub assy to housing Op 330 Mandrel to main shaft bore I. D. OP 340 Operate press Op 350 Re-load fixture #2 and mandrel Op 400 Housing to table Op 410 Reserved Op 320 Retaining ring to top groove Op 230 Reload fixture #1 Op 300 Housing to fixture #2 Op 310 Operate press Op 220 Retaining ring to top groove Op 120 Pre-load main shaft oil seal to mandrel Op 200 Housing to fixture #1 Op 210 Operate press Op 110 Pre-load bearing to fixture #2 Op 100 Step 1 PRE-LOAD DOWEL PINS TO FIXTURE Op 100 Step 2 PRE-LOAD JACK SHAFT SEAL TO FIXTURE Op 100 Step 3 PRE-LOAD PRIMARY HOUSING BUSHING TO FIXTURE Vehicle Assembly Component Manufacture Characteristics Ranked in order of Importance 0 H H 0 F 0 H 0 G 81 F 3 3 54 H 0 H 261 G 3 Y H H H 54 F G 27 F 0 H 0 1. 090 TO 1. 110 " FACE OF PRIMARY HOUSING 5 BUSHING TO FACE OF JACK SHAFT SEAL DOWEL PINS 0. 260 TO 0. 270 " TO 3 FACE JACK SHAFT SEAL AGAINST 9 SHOULDER 41 9 Material handling Potential Significant and Critical Characteristics from DFMEA & Other Sources 9 9 0 PRIMARY GASKET SEAL SURFACE FINISH 81 SEAL COMPRESSION HEIGHT 72 BEARING FLUSH TO SNAP RING FACE Receive Material Severity Special Characteristics Matrix 81 SERATION DAMAGE 0 Potential Critical and Significant Characteristics Matrix Process Operation from Process Flow Process Steps Customer Assessment Direction of Improvement F F F G G Relative Importance High/Medium Interactions are causes/failure modes in PFMEA 15
FMEA Preparation Vertical Approach n Key Elements of Efficient Development n Identify all functions/process steps Boundary Diagram P Diagram n Identify all failure modes via brainstorming/data/warranty/COQ n Identify all effects via brainstorming/data Customer focus n Develop data pools for Failure Modes, Effects and Causes for future/ faster FMEA development www. quality-one. com 16
System/Subsystem/ Design FMEA n Failure Mode: Pure anti-function FUNCTION (ANTI) www. quality-one. com 17
System/Subsystem/ Design FMEA n Effect Customer view/customers words Regulation violation Level of dissatisfaction n Consider All Customers End User Engineering Community Manufacturing Community (Operators/Employees) Regulatory Body www. quality-one. com 18
Severity Column www. quality-one. com 19
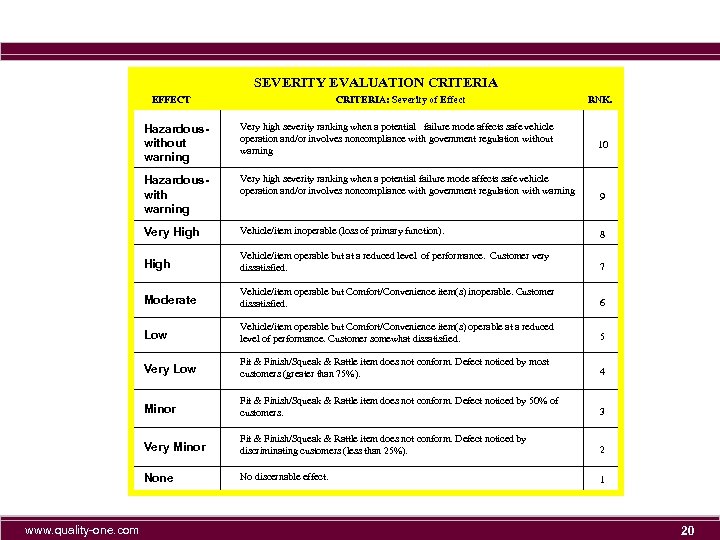
SEVERITY EVALUATION CRITERIA EFFECT CRITERIA: Severity of Effect RNK. Hazardouswithout warning Hazardouswith warning Very high severity ranking when a potential failure mode affects safe vehicle operation and/or involves noncompliance with government regulation with warning Very High Vehicle/item inoperable (loss of primary function). 8 High Vehicle/item operable but at a reduced level of performance. Customer very dissatisfied. 7 Moderate Vehicle/item operable but Comfort/Convenience item(s) inoperable. Customer dissatisfied. 6 Low Vehicle/item operable but Comfort/Convenience item(s) operable at a reduced level of performance. Customer somewhat dissatisfied. 5 Very Low Fit & Finish/Squeak & Rattle item does not conform. Defect noticed by most customers (greater than 75%). 4 Minor Fit & Finish/Squeak & Rattle item does not conform. Defect noticed by 50% of customers. 3 Very Minor Fit & Finish/Squeak & Rattle item does not conform. Defect noticed by discriminating customers (less than 25%). 2 None www. quality-one. com Very high severity ranking when a potential failure mode affects safe vehicle operation and/or involves noncompliance with government regulation without warning No discernable effect. 1 10 9 20

FMEA General For High Severity 9/10 www. quality-one. com 21
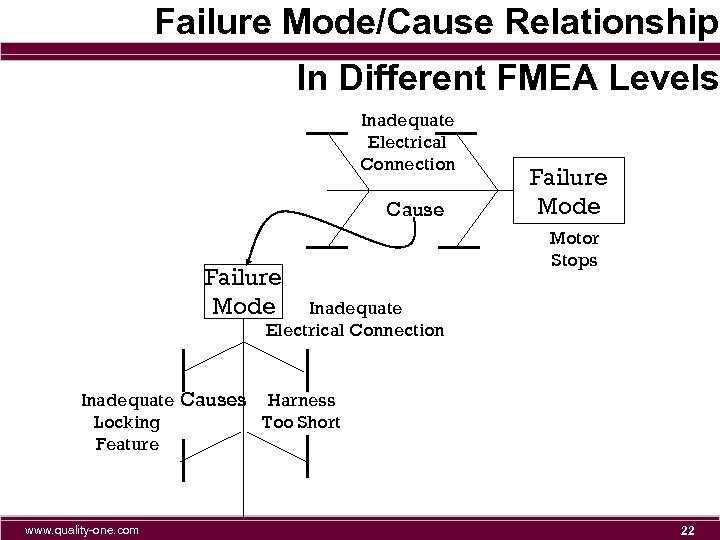
Failure Mode/Cause Relationship In Different FMEA Levels Inadequate Electrical Connection Cause Failure Mode Motor Stops Inadequate Electrical Connection Inadequate Causes Harness Locking Too Short Feature www. quality-one. com 22

Causes n Causes from P-Diagram Noise factors n. Continue through all failure modes. n Note that many causes are recurring. www. quality-one. com 23
Occurrence Column www. quality-one. com 24
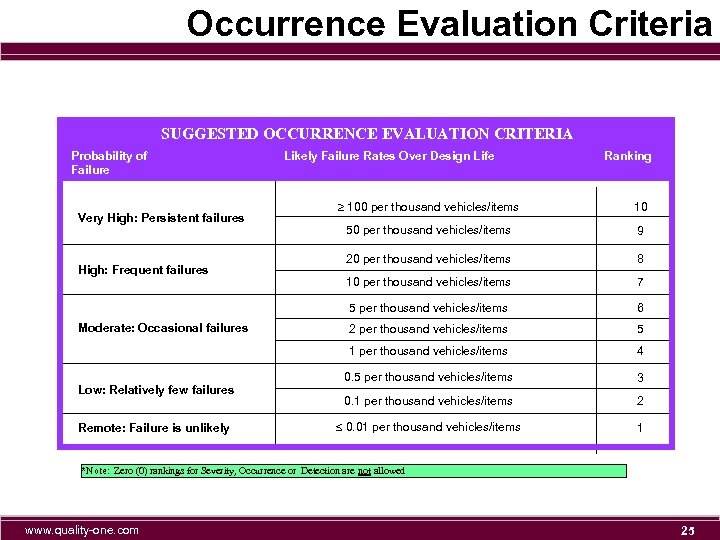
Occurrence Evaluation Criteria SUGGESTED OCCURRENCE EVALUATION CRITERIA Probability of Failure Likely Failure Rates Over Design Life Ranking Moderate: Occasional failures Low: Relatively few failures Remote: Failure is unlikely 10 50 per thousand vehicles/items 9 20 per thousand vehicles/items 8 10 per thousand vehicles/items 7 6 2 per thousand vehicles/items 5 1 per thousand vehicles/items High: Frequent failures 100 per thousand vehicles/items 5 per thousand vehicles/items Very High: Persistent failures 4 0. 5 per thousand vehicles/items 3 0. 1 per thousand vehicles/items 2 0. 01 per thousand vehicles/items 1 *Note: Zero (0) rankings for Severity, Occurrence or Detection are not allowed www. quality-one. com 25

Occurrence Rating n If an action would effectively eliminate the possibility of the cause occurring, the action is listed as described earlier. Occurrence of 1 or 2 require proof using a surrogate product or mistake proofing. DATA www. quality-one. com HARD FACTS 26
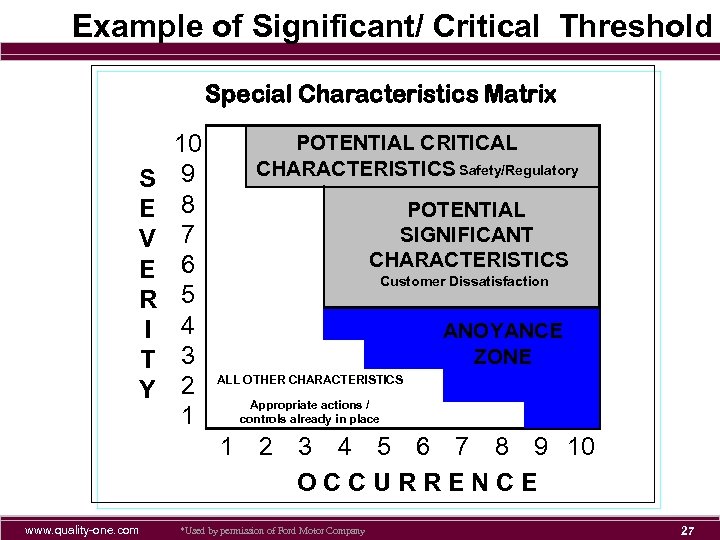
Example of Significant/ Critical Threshold Special Characteristics Matrix S E V E R I T Y 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 POTENTIAL CRITICAL CHARACTERISTICS Safety/Regulatory POTENTIAL SIGNIFICANT CHARACTERISTICS Customer Dissatisfaction ANOYANCE ZONE ALL OTHER CHARACTERISTICS Appropriate actions / controls already in place 1 www. quality-one. com 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 OCCURRENCE *Used by permission of Ford Motor Company 27
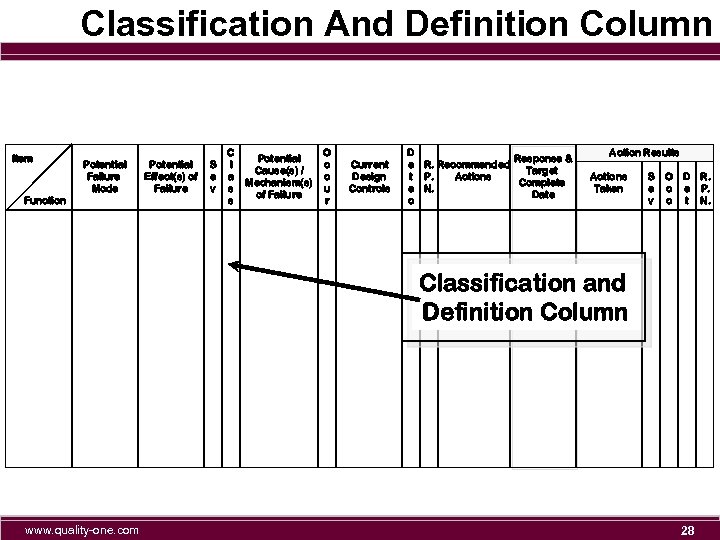
Classification And Definition Column Item Potential Failure Mode Function Potential Effect(s) of Failure S e v C l a s s Potential Cause(s) / Mechanism(s) of Failure O c c u r Current Design Controls D Response & e R. Recommended Target Actions t P. Complete e N. Date c Action Results Actions Taken S e v O c c D R. e P. t N. Classification and Definition Column www. quality-one. com 28

Design Verification (Current Design Controls) n Think of Design Control in two ways; Prevention and Detection. List them separately. n To save time, add any new (untried) prevention/detection ideas to the document under Recommended Actions column. Prevention is specifically related to reduction or elimination of a cause. Detection is how well the test or series of tests may find the design flaw Causes Failure Mode www. quality-one. com 29
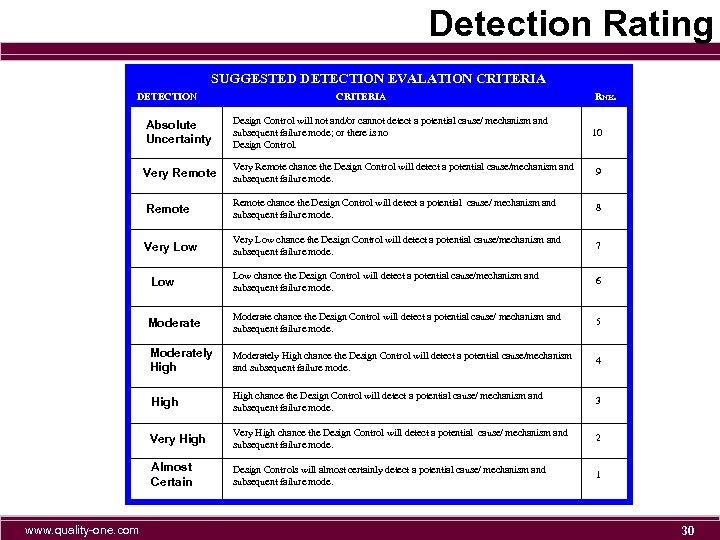
Detection Rating SUGGESTED DETECTION EVALATION CRITERIA DETECTION CRITERIA RNK. Absolute Uncertainty Design Control will not and/or cannot detect a potential cause/ mechanism and subsequent failure mode; or there is no Design Control. Very Remote chance the Design Control will detect a potential cause/mechanism and subsequent failure mode. 9 Remote chance the Design Control will detect a potential cause/ mechanism and subsequent failure mode. 8 Very Low chance the Design Control will detect a potential cause/mechanism and subsequent failure mode. 7 Low chance the Design Control will detect a potential cause/mechanism and subsequent failure mode. 6 Moderate chance the Design Control will detect a potential cause/ mechanism and subsequent failure mode. 5 Moderately High chance the Design Control will detect a potential cause/mechanism and subsequent failure mode. 4 High chance the Design Control will detect a potential cause/ mechanism and subsequent failure mode. 3 Very High chance the Design Control will detect a potential cause/ mechanism and subsequent failure mode. 2 Almost Certain Design Controls will almost certainly detect a potential cause/ mechanism and subsequent failure mode. 1 Low www. quality-one. com 10 30

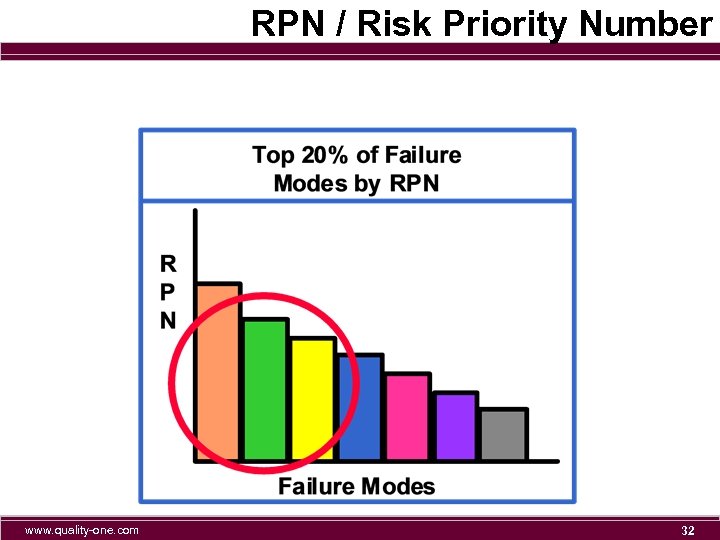
Analysis Of Risk n RPN / RISK PRIORITY NUMBER n What Is Risk? n Probability of danger n Severity/Occurrence/Cause www. quality-one. com 31
RPN / Risk Priority Number www. quality-one. com 32

Evaluation by RPN Only n Case 1 S=5 O=5 D=2 RPN = 50 n Case 2 S=3 O=3 D=6 RPN = 54 n Case 3 S=2 O=10, D=10 = 200 WHICH ONE IS WORSE? n Case 4 S=9 O=2 D=3 = 54 www. quality-one. com 33

Example n Extreme Safety/Regulatory Risk =9 & 10 Severity n High Risk to Customer Satisfaction Sev. > or = to 5 and Occ > or = 4 n Consider Detection only as a measure of Test Capability. www. quality-one. com 34
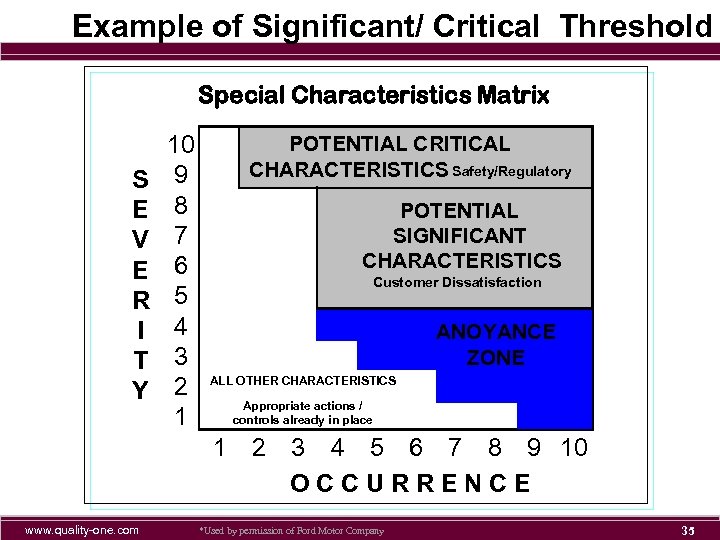
Example of Significant/ Critical Threshold Special Characteristics Matrix S E V E R I T Y 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 POTENTIAL CRITICAL CHARACTERISTICS Safety/Regulatory POTENTIAL SIGNIFICANT CHARACTERISTICS Customer Dissatisfaction ANOYANCE ZONE ALL OTHER CHARACTERISTICS Appropriate actions / controls already in place 1 www. quality-one. com 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 OCCURRENCE *Used by permission of Ford Motor Company 35
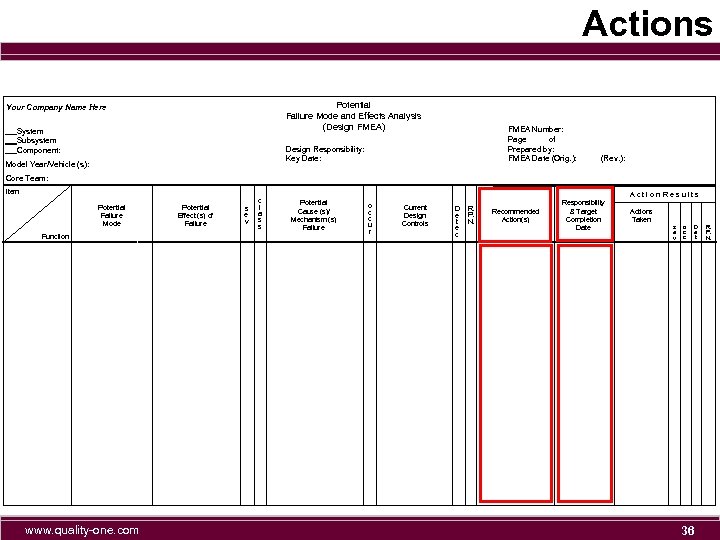
Actions Potential Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (Design FMEA) Your Company Name Here System Subsystem Component: FMEA Number: Page of Prepared by: FMEA Date (Orig. ): Design Responsibility: Key Date: Model Year/Vehicle (s): (Rev. ): Core Team: Item Potential Failure Mode Function www. quality-one. com Potential Effect (s) of Failure s e v c l a s s Action Results Potential Cause (s)/ Mechanism (s) Failure o c c u r Current Design Controls D e t e c R. P. N. Recommended Action(s) Responsibility & Target Completion Date Actions Taken s e v o c c D e t 36 R. P. N.
Actions www. quality-one. com 37
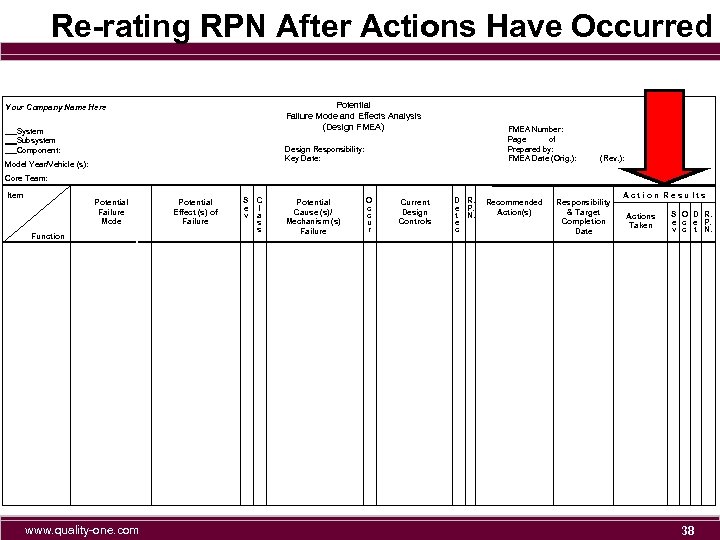
Re-rating RPN After Actions Have Occurred Potential Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (Design FMEA) Your Company Name Here System Subsystem Component: FMEA Number: Page of Prepared by: FMEA Date (Orig. ): Design Responsibility: Key Date: Model Year/Vehicle (s): (Rev. ): Core Team: Item Potential Failure Mode Function www. quality-one. com Potential Effect (s) of Failure S C e l v a s s Potential Cause (s)/ Mechanism (s) Failure O c c u r Current Design Controls D R. e P. t N. e c Recommended Action(s) Responsibility & Target Completion Date Action Results Actions Taken S O D R. e c e P. v c t N. 38

Re-rating RPN After Actions Have Occurred n Severity typically stays the same. n Occurrence is the primary item to reduce / focus on. n Detection is reduced only as a last resort. n Do not plan to REDUCE RPN with detection actions!!! 100% inspection is only 80% effective! Reducing RPN with detection does not eliminate failure mode, or reduce probability of causes Detection of 10 is not bad if occurrence is 1 www. quality-one. com 39

FMEA & Requirement/Specification Cascades for CPPDM This guideline is for training purposes only; Not ISO controlled
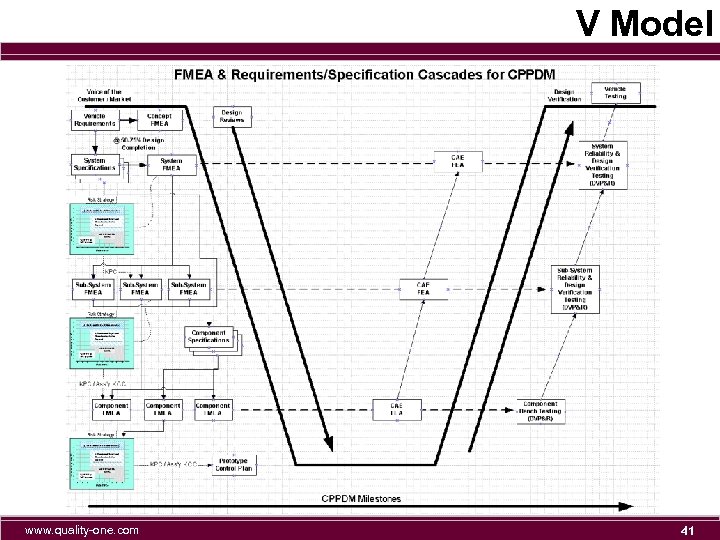
V Model www. quality-one. com 41
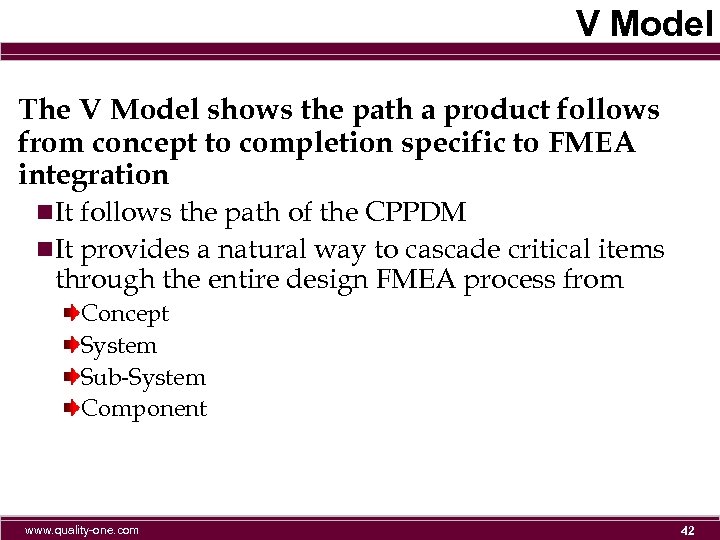
V Model The V Model shows the path a product follows from concept to completion specific to FMEA integration n. It follows the path of the CPPDM n. It provides a natural way to cascade critical items through the entire design FMEA process from Concept System Sub-System Component www. quality-one. com 42
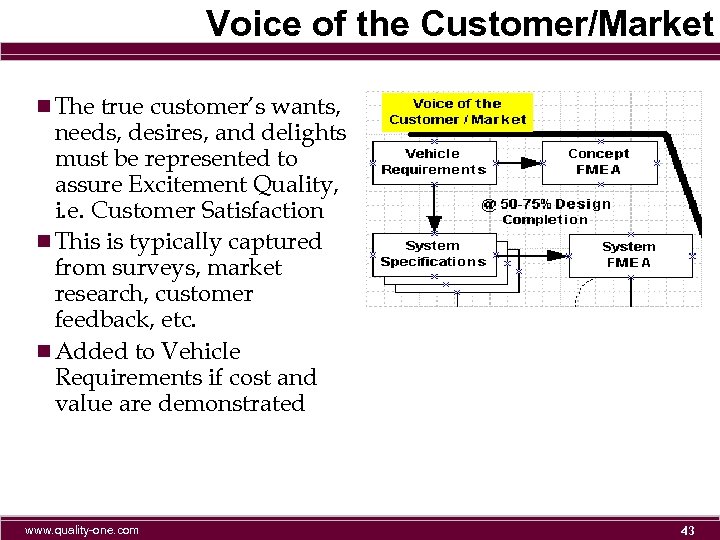
Voice of the Customer/Market n The true customer’s wants, needs, desires, and delights must be represented to assure Excitement Quality, i. e. Customer Satisfaction n This is typically captured from surveys, market research, customer feedback, etc. n Added to Vehicle Requirements if cost and value are demonstrated www. quality-one. com 43
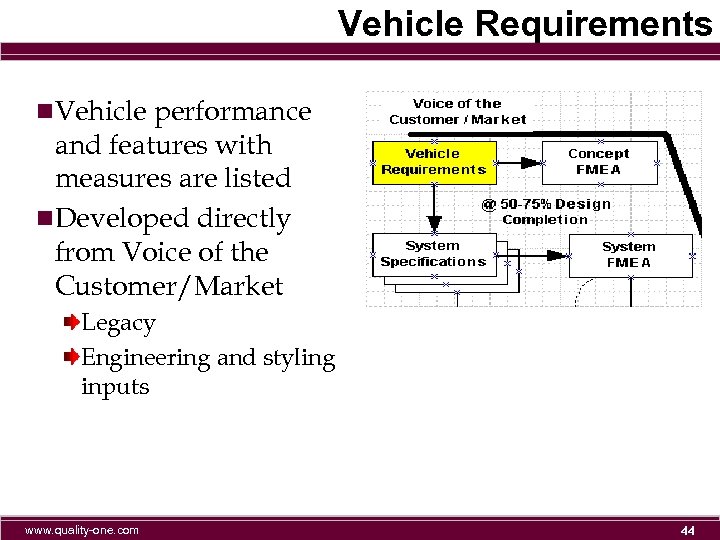
Vehicle Requirements n. Vehicle performance and features with measures are listed n. Developed directly from Voice of the Customer/Market Legacy Engineering and styling inputs www. quality-one. com 44
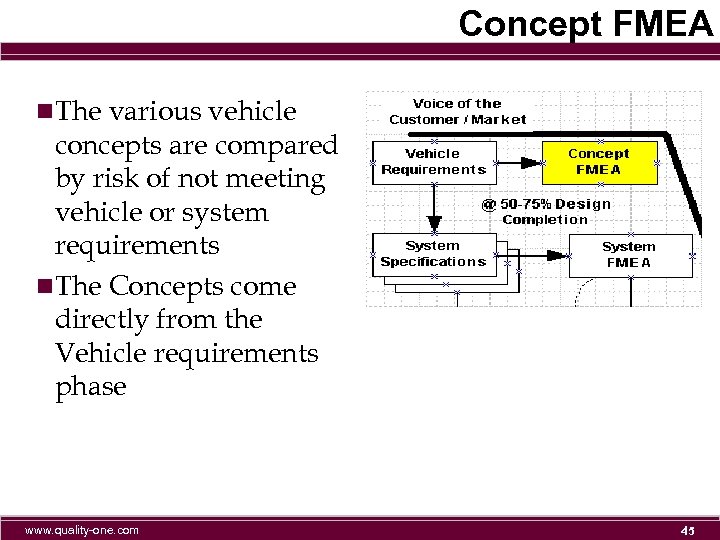
Concept FMEA n. The various vehicle concepts are compared by risk of not meeting vehicle or system requirements n. The Concepts come directly from the Vehicle requirements phase www. quality-one. com 45
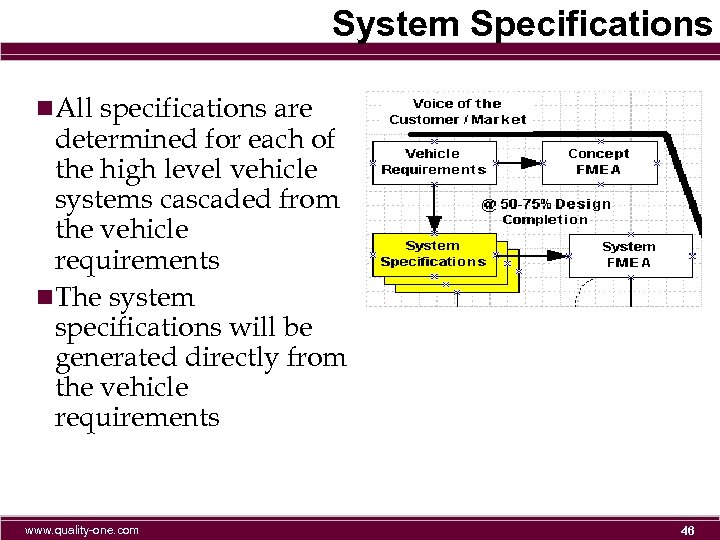
System Specifications n. All specifications are determined for each of the high level vehicle systems cascaded from the vehicle requirements n. The system specifications will be generated directly from the vehicle requirements www. quality-one. com 46
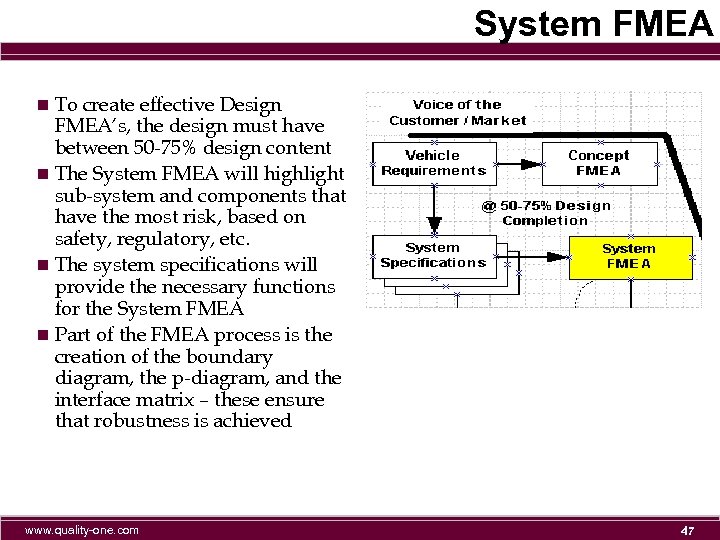
System FMEA n To create effective Design FMEA’s, the design must have between 50 -75% design content n The System FMEA will highlight sub-system and components that have the most risk, based on safety, regulatory, etc. n The system specifications will provide the necessary functions for the System FMEA n Part of the FMEA process is the creation of the boundary diagram, the p-diagram, and the interface matrix – these ensure that robustness is achieved www. quality-one. com 47
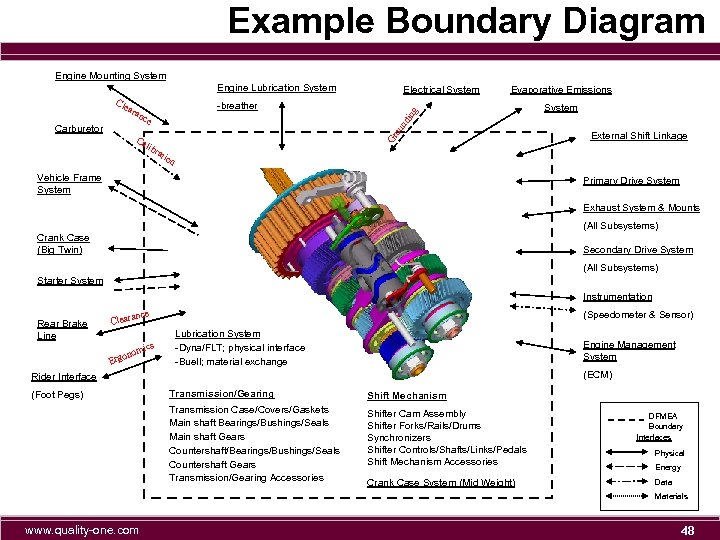
Example Boundary Diagram Engine Mounting System Engine Lubrication System -breather ara Evaporative Emissions ou Gr Ca System nd nce Carburetor Electrical System ing Cle lib External Shift Linkage rat ion Vehicle Frame System Primary Drive System Exhaust System & Mounts (All Subsystems) Crank Case (Big Twin) Secondary Drive System (All Subsystems) Starter System Instrumentation Rear Brake Line nce Cleara cs omi on Erg (Speedometer & Sensor) Lubrication System -Dyna/FLT; physical interface -Buell; material exchange Engine Management System (ECM) Rider Interface Transmission/Gearing Shift Mechanism Transmission Case/Covers/Gaskets Main shaft Bearings/Bushings/Seals Main shaft Gears Countershaft/Bearings/Bushings/Seals Countershaft Gears Transmission/Gearing Accessories (Foot Pegs) Shifter Cam Assembly Shifter Forks/Rails/Drums Synchronizers Shifter Controls/Shafts/Links/Pedals Shift Mechanism Accessories Crank Case System (Mid Weight) DFMEA Boundary Interfaces Physical Energy Data Materials www. quality-one. com 48
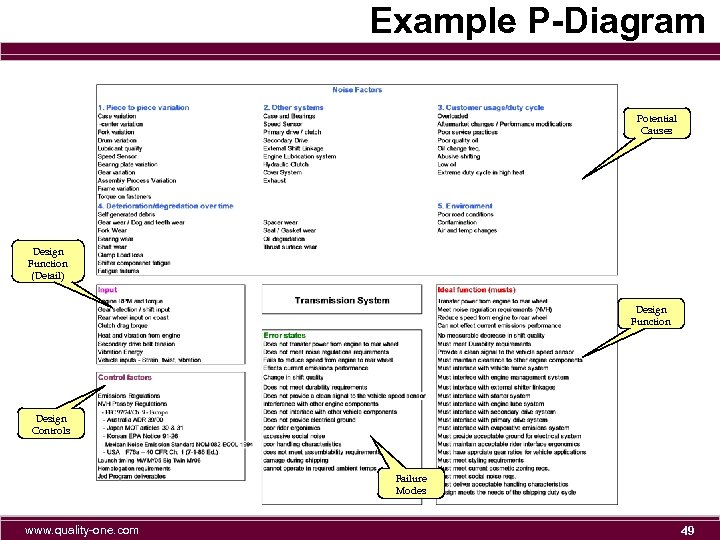
Example P-Diagram Potential Causes Design Function (Detail) Design Function Design Controls Failure Modes www. quality-one. com 49
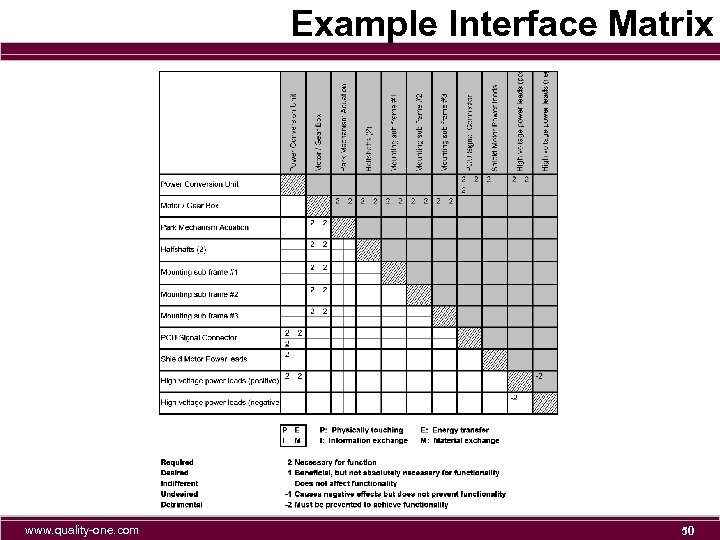
Example Interface Matrix www. quality-one. com 50
System Verification Testing (DVP&R) n. The outputs from the System FMEA will drive the DV www. quality-one. com 51
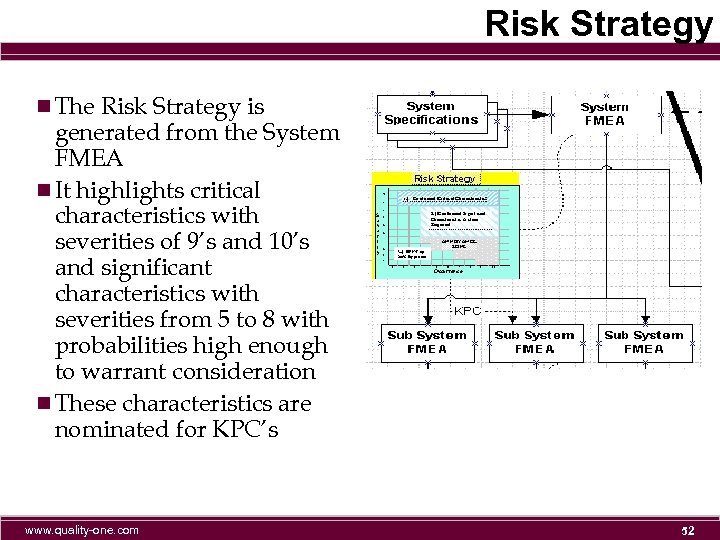
Risk Strategy n The Risk Strategy is generated from the System FMEA n It highlights critical characteristics with severities of 9’s and 10’s and significant characteristics with severities from 5 to 8 with probabilities high enough to warrant consideration n These characteristics are nominated for KPC’s www. quality-one. com 52
Sub-System FMEA n The Sub-System FMEA is similar to the System FMEA n It may not be necessary in all instances, as the System FMEA may be cascaded directly to the Component FMEA n Example System = Styled surfaces Sub-System Fenders Tour Pack www. quality-one. com 53
Sub-System Verification Testing (DVP&R) n. The outputs from the Sub-System FMEA will drive th n. Noise factors which must be considered in the testing www. quality-one. com 54
Component Specifications n All component specifications are cascaded from the System Specifications, the System FMEA, and the Sub-System FMEA n The component specifications will be used to determine, in conjunction with the risk strategy from the Sub-System FMEA, which component FMEA’s need to be completed. www. quality-one. com 55
Risk Strategy n The Risk Strategy is generated from the Sub. System FMEA n It highlights critical characteristics with severities of 9’s and 10’s and significant characteristics with severities from 5 to 8 with probabilities high enough to warrant consideration www. quality-one. com 56
Component FMEA n The Component FMEA will highlight characteristics that have the most risk, based on safety, regulatory, etc. n Component FMEA’s are only necessary for components that contribute to higher level failure system/sub-system New technology Changed product Past failures New environment for use n The boundary diagram, the p- diagram, and the interface matrix are also created for components similar to system/sub-systems n The Risk Strategy, Sub-System FMEA, and Component Specifications dictate which components need to be addressed www. quality-one. com 57
Component Bench Testing (DVP&R) n. The outputs from the Component FMEA will drive th Bench tests www. quality-one. com 58
Risk Strategy n The Risk Strategy used in the Component FMEA determines which characteristics need to be addressed n It highlights critical characteristics with severities of 9’s and 10’s and significant characteristics with severities from 5 to 8 with probabilities high enough to warrant consideration n These become KPC/KCC at manufacturing www. quality-one. com 59
Prototype Control Plan n. The characteristics that are required to be correct for appropriate design verification are listed on the prototype control plan n. The prototype control plans are used by those producing the prototypes www. quality-one. com 60
Design Review n There are vehicle level design reviews which focus on vehicle level indicators, such as cost, timing, weight, etc. n There are system level design reviews which focus on timing and systems level issues n There are technical design reviews which are related to specifications and performance n Action reviews from FMEA’s/test results are addressed in design review www. quality-one. com 61
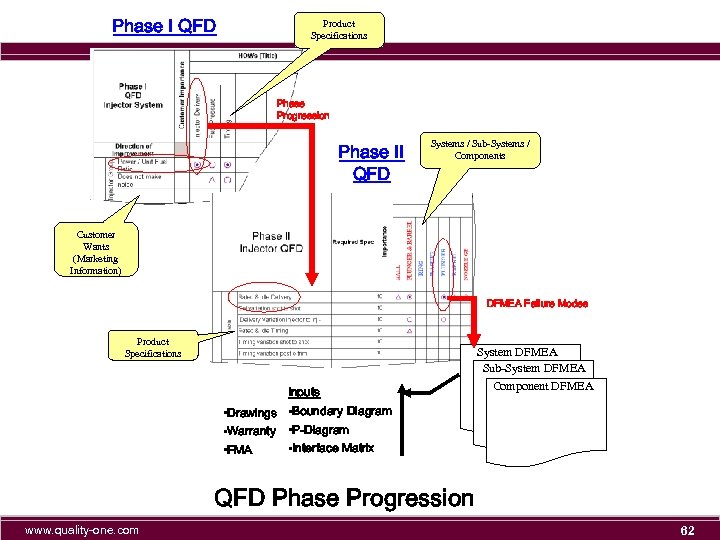
Phase I QFD Product Specifications Phase Progression Phase II QFD Systems / Sub-Systems / Components Customer Wants (Marketing Information) DFMEA Failure Modes Product Specifications System DFMEA Sub-System DFMEA Inputs Component DFMEA • Drawings • Boundary Diagram • Warranty • P-Diagram • Interface Matrix • FMA QFD Phase Progression www. quality-one. com 62
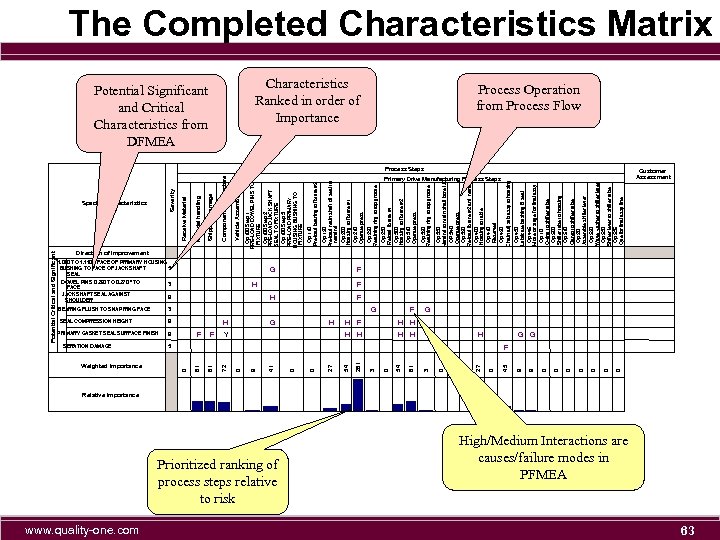
Weighted Importance www. quality-one. com Prioritized ranking of process steps relative to risk H H 27 5 H F G 9 0 0 0 0 G 9 45 Shipping Damage Primary Drive Manufacturing Process Steps Op 430 Lubricate bushing & seal Op 445 Move or stage for final assy Op 10 O-ring to shifter tube Op 500 Shifter tube to housing Op 510 Clamp to shifter tube Op 20 Assemble shifter lever Op 520 Wave washer to shifter lever Op 530 Shifter lever to shifter tube Op 535 Que for final assy line Op 420 Chain adj sub assy to housing Op 330 Mandrel to main shaft bore I. D. OP 340 Operate press Op 350 Re-load fixture #2 and mandrel Op 400 Housing to table Op 410 Reserved Op 320 Retaining ring to top groove Op 230 Reload fixture #1 Op 300 Housing to fixture #2 Op 310 Operate press Op 220 Retaining ring to top groove Op 120 Pre-load main shaft oil seal to mandrel Op 200 Housing to fixture #1 Op 210 Operate press Op 110 Pre-load bearing to fixture #2 Op 100 Step 1 PRE-LOAD DOWEL PINS TO FIXTURE Op 100 Step 2 PRE-LOAD JACK SHAFT SEAL TO FIXTURE Op 100 Step 3 PRE-LOAD PRIMARY HOUSING BUSHING TO FIXTURE Vehicle Assembly Component Manufacture Characteristics Ranked in order of Importance 0 H H 0 F 0 H 0 G 81 F 3 3 54 H 0 H 261 G 3 Y H H H 54 F G 27 F 0 H 0 1. 090 TO 1. 110 " FACE OF PRIMARY HOUSING 5 BUSHING TO FACE OF JACK SHAFT SEAL DOWEL PINS 0. 260 TO 0. 270 " TO 3 FACE JACK SHAFT SEAL AGAINST 9 SHOULDER 41 9 Material handling Potential Significant and Critical Characteristics from DFMEA 9 9 0 PRIMARY GASKET SEAL SURFACE FINISH 81 SEAL COMPRESSION HEIGHT 72 BEARING FLUSH TO SNAP RING FACE Receive Material Severity Special Characteristics Matrix 81 SERATION DAMAGE 0 Potential Critical and Significant The Completed Characteristics Matrix Process Operation from Process Flow Process Steps Customer Assessment Direction of Improvement F F F G Relative Importance High/Medium Interactions are causes/failure modes in PFMEA 63
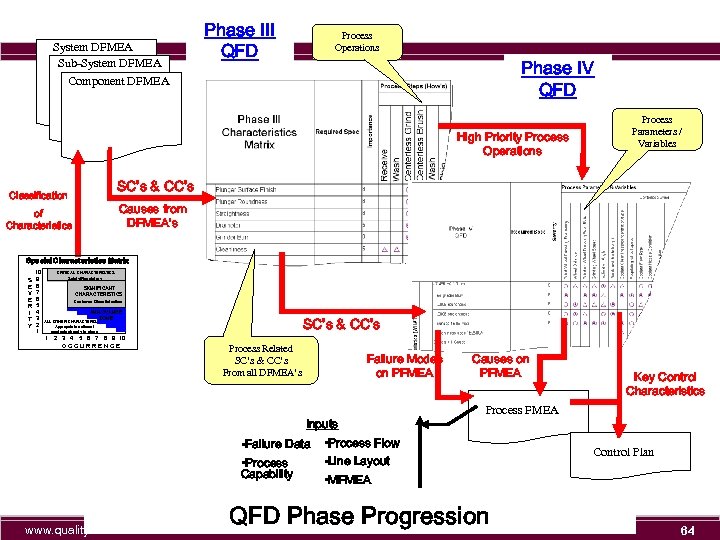
System DFMEA Sub-System DFMEA Phase III QFD Process Operations Phase IV QFD Component DFMEA High Priority Process Operations Process Parameters / Variables SC’s & CC’s Classification Causes from DFMEA’s of Characteristics Special Characteristics Matrix S E V E R I T Y 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 CRITICAL CHARACTERISTICS Safety/Regulatory SIGNIFICANT CHARACTERISTICS Customer Dissatisfaction ANNOYANCE ZONE SC’s & CC’s ALL OTHER CHARACTERISTICS Appropriate actions / controls already in place 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 OCCURRENCE Process Related SC’s & CC’s From all DFMEA’s Failure Modes on PFMEA Inputs • Failure Data • Process Capability www. quality-one. com Causes on PFMEA Key Control Characteristics Process FMEA • Process Flow • Line Layout • MFMEA QFD Phase Progression Control Plan 64

Summary n. FMEA can be used creatively in continuous processing. n. Linking key customer requirements to process outputs instead of standard product grade is valuable. n. Future customer requirements will drive new and modified processes to achieve specialty results as a normal practice www. quality-one. com 65

Training and Facilitation n. Fmea benefits certainly outweigh the obvious difficulty in developing them. n. To maintain efficiency, FMEA must be deployed with several methods of varying degrees of intensity. n. Methods to consider Computer based training Pin point Facilitation for Family groups. Database approach to legacy www. quality-one. com 66
4a3b59ba51e3a0f6f52ed67d77da7fa4.ppt