 Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river River Channel: § wider and deeper § Volume of water greater than that in upper course. § Gradient is less than upstream portion of the river course.
Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river River Channel: § wider and deeper § Volume of water greater than that in upper course. § Gradient is less than upstream portion of the river course.
 Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river River Valley : § More open V shape and wider valley floor. § Lateral erosion of river more dominant. § Weathering and mass wasting of valley sides.
Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river River Valley : § More open V shape and wider valley floor. § Lateral erosion of river more dominant. § Weathering and mass wasting of valley sides.
 Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river Work of river : § Vertical erosion is reduced. § Increased volume of load and water in the river is used mainly for lateral erosion. § Some energy is also used for transportation. § Some deposition also occurs.
Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river Work of river : § Vertical erosion is reduced. § Increased volume of load and water in the river is used mainly for lateral erosion. § Some energy is also used for transportation. § Some deposition also occurs.
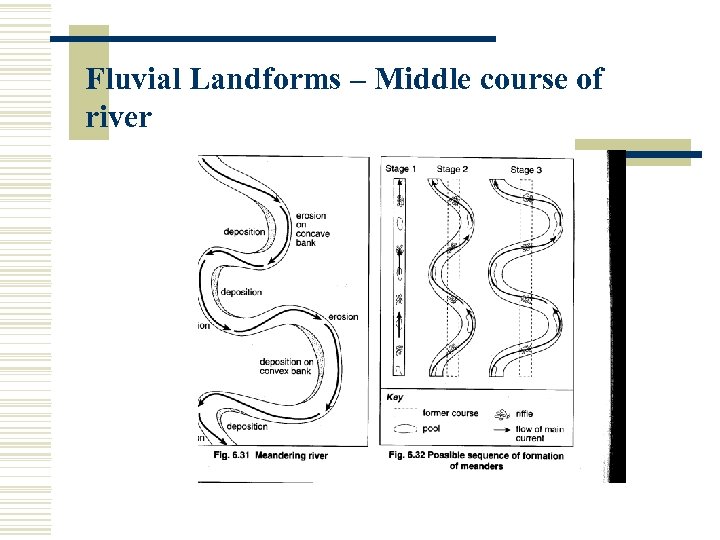
 Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river Meanders, river cliffs and slip-off slopes How meanders begin to form is uncertain. They appear to have their origins in times of flood and in relatively straight sections where pools and riffles develop.
Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river Meanders, river cliffs and slip-off slopes How meanders begin to form is uncertain. They appear to have their origins in times of flood and in relatively straight sections where pools and riffles develop.
 Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river
Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river
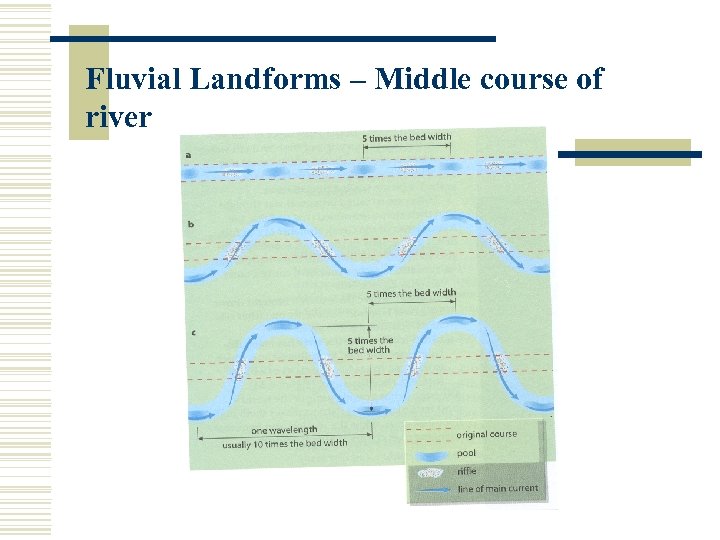
 Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river Pools: areas of deeper water. Riffles: areas of shallow water. Spacing between pools and rivers usually very regular: 5 x – 6 x of river width
Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river Pools: areas of deeper water. Riffles: areas of shallow water. Spacing between pools and rivers usually very regular: 5 x – 6 x of river width
 Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river There is less friction in pools. Thus, river flows faster and has more erosive power. Increased friction in the riffles slows water down and more deposition takes place. Continuous erosion in the pools and deposition in the river accentuates the slight bends of a river.
Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river There is less friction in pools. Thus, river flows faster and has more erosive power. Increased friction in the riffles slows water down and more deposition takes place. Continuous erosion in the pools and deposition in the river accentuates the slight bends of a river.
 Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river
Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river
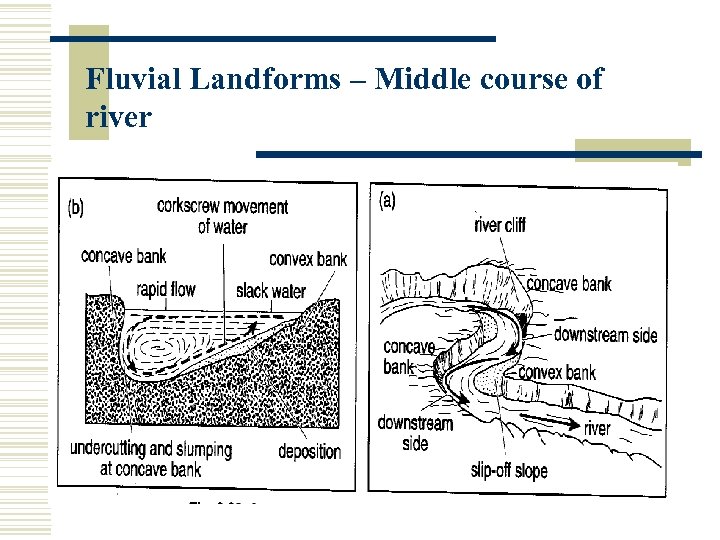
 Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river There exists a series secondary flow of water in a river, other than the main flow. One of these is called the helicoidal flow – cockscrew movement of water.
Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river There exists a series secondary flow of water in a river, other than the main flow. One of these is called the helicoidal flow – cockscrew movement of water.
 Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river Difference in velocity across the channel causes unequal pressure distribution. Current from the concave bank descends downwards, undercutting and eroding the river side. Eroded material carried along the bed and up the convex bank where it is deposited.
Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river Difference in velocity across the channel causes unequal pressure distribution. Current from the concave bank descends downwards, undercutting and eroding the river side. Eroded material carried along the bed and up the convex bank where it is deposited.
 Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river This current represents a cockscrew movement of water because it continues downstream and repeats the series of rotations.
Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river This current represents a cockscrew movement of water because it continues downstream and repeats the series of rotations.
 Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river As erosion continues to undercut the concave bank, eroded materials slump down into the river, forming a steep river cliff.
Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river As erosion continues to undercut the concave bank, eroded materials slump down into the river, forming a steep river cliff.
 Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river Continuous deposition on the convex bank makes it shallow and deposition takes place. These deposits on the convex bank build up into a gently sloping slip-off slope.
Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river Continuous deposition on the convex bank makes it shallow and deposition takes place. These deposits on the convex bank build up into a gently sloping slip-off slope.
 Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river
Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river
 Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river The channel has an asymmetrical crosssection. Continued erosion on the concave banks and deposition on the convex banks cause the meanders to migrate laterally.
Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river The channel has an asymmetrical crosssection. Continued erosion on the concave banks and deposition on the convex banks cause the meanders to migrate laterally.
 Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river
Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river
 Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river References: 1. Chong, M. (2001) Aspects of Physical Geography, Singapore: Pekoe Books. 2. Waugh, D. (2000) Geography – An Integrated Approach, UK: Nelson
Fluvial Landforms – Middle course of river References: 1. Chong, M. (2001) Aspects of Physical Geography, Singapore: Pekoe Books. 2. Waugh, D. (2000) Geography – An Integrated Approach, UK: Nelson