5da7367a8165001426ac72528f9498a7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21

Flow sorting – a brief overview Ian Titley Haematology Oncology Leukaemia Research Fund Institute of Cancer Research London

Flow sorting - a form of fluorescence microscopy whereby single cells in liquid suspension can be identified and physically separated from each other according to unique characteristics

History of cell sorter 1 st prototype at Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) in 1965 developed by Mack J Fulwyler by “joining” Coulter volume sensing (invented by Wallace and Joseph Coulter) with the newly invented ink-jet printer technology. Biologist Leonard Herzenberg at Stanford University was the first to recognise the utility for this technology to biological applications. With colleagues from the Genetics Dept Instrument Research group and using Fulwyler’s plans developed a machine to sort fluorescently labelled cells. The 1969 instrument had a mercury arc lamp as light source and in 1972 an argon ion laser. Funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) allowed Herzenberg and the Stanford engineers to interest the medical products company Becton Dickinson (BD) to convert their prototypes into the first commercial instruments, the FACS (Fluorescence Activated Cell Sorter) in 1975. Smithsonian Institute Archives – Video History Collection http: //www. si. edu/archives/ihd/videocatalog/9554. htm
Electrostatic Mechanical “Lab-on-chip”

http: //www. cardiff. ac. uk/medicine/haematology/cytonetuk/introduction_to_fcm/cell_sorting. htm

BD Vantage. SE Di. Va option Dako. Cytomation Mo. Flo Beckman Coulter Epics Altra Hypersort BD FACSAria

Sorting into a 96 well plate (Taken from BD FACSAria brochure)

Electrostatic Pros Fast (? x 104 cellssec-1) Multiparameter High purity 4 -way Cons Expensive to buy and run Needs trained operator Aerosol – biohazard
Electrostatic Mechanical “Lab-on-chip”

http: //www. cardiff. ac. uk/medicine/haematology/cytonetuk/introduction_to_fcm/cell_sorting. htm
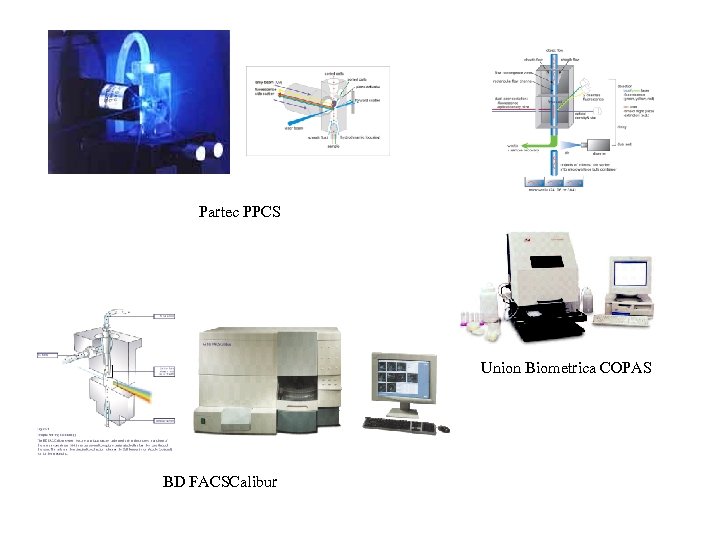
Partec PPCS Union Biometrica COPAS BD FACSCalibur

Mechanical Pros “Cheaper” No aerosol Easier to use Multiparameter Cons Slow (? x 102 cellssec-1) 1(2) way sorting “Dilute” sorted sample
Electrostatic Mechanical “Lab-on-chip”

Gawad, S. , Heuschkel, M. , Leung-Ki, Y. , Iuzzolino, R. , Schild, Lerch, Ph. & Renaud, Ph. Fabrication of a microfluidic cell ananlyzer in a microchannel using impedance spectroscopy in IEEE-EMBS Conference on Microtechnologies in Medicine & Biology 297 -301 (Lyon, France, 2000).
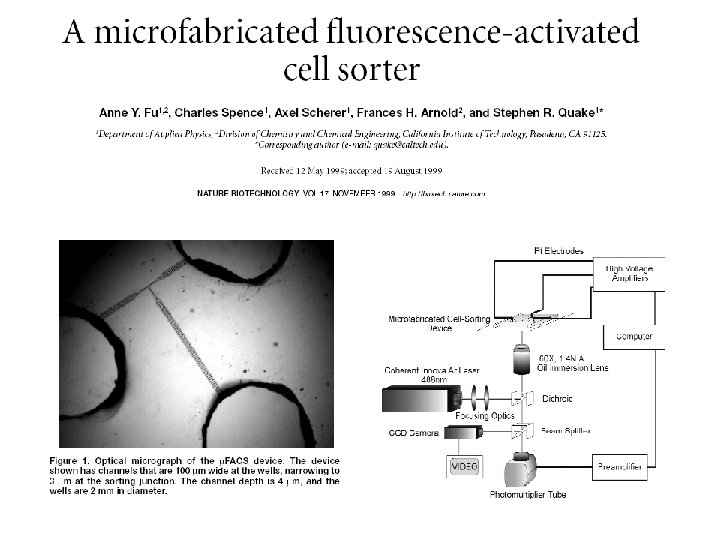
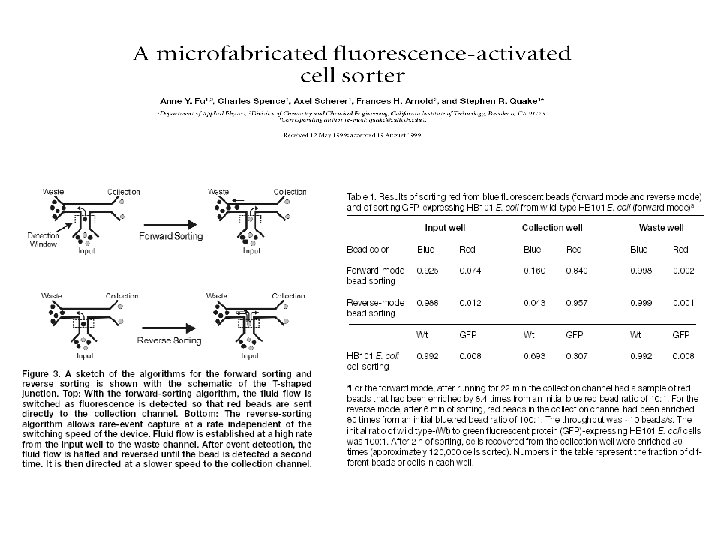

Useful texts Flow cytometry: a practical approach MG Ormerod IRL Press Practical flow cytometry HM Shapiro Wiley. Liss Current protocols in flow cytometry Ed JP Robinson et al Wiley

Some cell sorting web resources Terry Hoy et al Cardiff University http: //www. cardiff. ac. uk/medicine/haematology/cytonetuk/introduction_to_fcm/cell_sorting. htm Royal Microscopical Society http: //www. rms. org. uk/cyto. shtml Derek Davies et al London Research Institute http: //science. cancerresearchuk. org/sci/facs/fac_labinfo/flow_sorting/? version=1 Cytometry E-mail archive Purdue USA http: //www. cyto. purdue. edu/hmarchiv/index. htm
5da7367a8165001426ac72528f9498a7.ppt