98786fa95488bd7212b20ff161caedd4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 78
 Flora & Fauna CLIMATE CHANGE As it affects the flora and fauna of Virginia’s coastal regions
Flora & Fauna CLIMATE CHANGE As it affects the flora and fauna of Virginia’s coastal regions
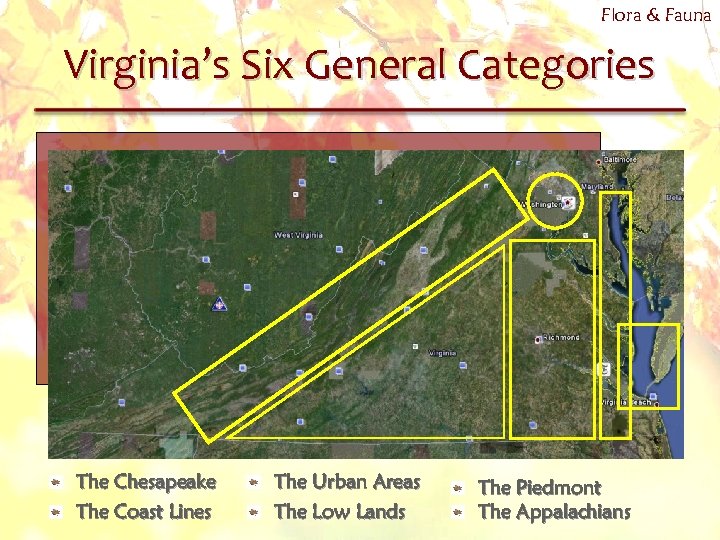 Flora & Fauna Virginia’s Six General Categories The Chesapeake The Coast Lines The Urban Areas The Low Lands The Piedmont The Appalachians
Flora & Fauna Virginia’s Six General Categories The Chesapeake The Coast Lines The Urban Areas The Low Lands The Piedmont The Appalachians
 Flora & Fauna Virginia’s Coastline: A Lot to Lose 112 miles of coastline 4, 475 m² of coastal waters 374 m² land lies 5 feet above sea level IPCC conservative sea level rise = 2 feet (2100) Rise could reach
Flora & Fauna Virginia’s Coastline: A Lot to Lose 112 miles of coastline 4, 475 m² of coastal waters 374 m² land lies 5 feet above sea level IPCC conservative sea level rise = 2 feet (2100) Rise could reach
 Flora & Fauna Premise #1 90% confidence that anthropogenic fossil fuel burning has increased global mean temperature (IPCC AR 4) Ocean surface waters 90% of Earth’s total increased heat uptake (IPCC AR 4 Chpt. 5) Increased SST result in thermal expansion and sea level rise Sea level rise will directly impact coastal flora and fauna
Flora & Fauna Premise #1 90% confidence that anthropogenic fossil fuel burning has increased global mean temperature (IPCC AR 4) Ocean surface waters 90% of Earth’s total increased heat uptake (IPCC AR 4 Chpt. 5) Increased SST result in thermal expansion and sea level rise Sea level rise will directly impact coastal flora and fauna
 Flora & Fauna Premise #2 90% confidence : observed global warming Atmospheric Warming: - altered regional climates - increased occurrence of extreme weather - increased runoff intensity - increased erosion - changes in disease prevalence by region - specific Virginia habitat losses
Flora & Fauna Premise #2 90% confidence : observed global warming Atmospheric Warming: - altered regional climates - increased occurrence of extreme weather - increased runoff intensity - increased erosion - changes in disease prevalence by region - specific Virginia habitat losses
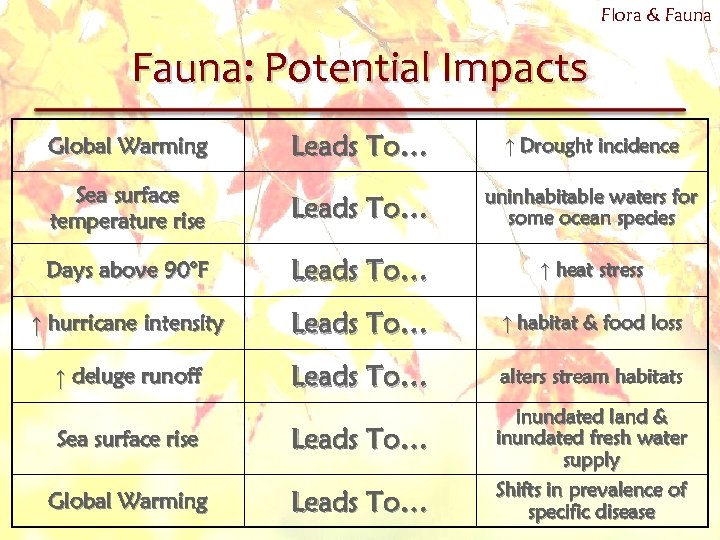 Flora & Fauna: Potential Impacts Leads To… ↑ Drought incidence Sea surface temperature rise Leads To… uninhabitable waters for some ocean species Days above 90°F Leads To… ↑ heat stress ↑ hurricane intensity Leads To… ↑ habitat & food loss ↑ deluge runoff Leads To… alters stream habitats Global Warming Sea surface rise Leads To… Global Warming Leads To… inundated land & inundated fresh water supply Shifts in prevalence of specific disease
Flora & Fauna: Potential Impacts Leads To… ↑ Drought incidence Sea surface temperature rise Leads To… uninhabitable waters for some ocean species Days above 90°F Leads To… ↑ heat stress ↑ hurricane intensity Leads To… ↑ habitat & food loss ↑ deluge runoff Leads To… alters stream habitats Global Warming Sea surface rise Leads To… Global Warming Leads To… inundated land & inundated fresh water supply Shifts in prevalence of specific disease
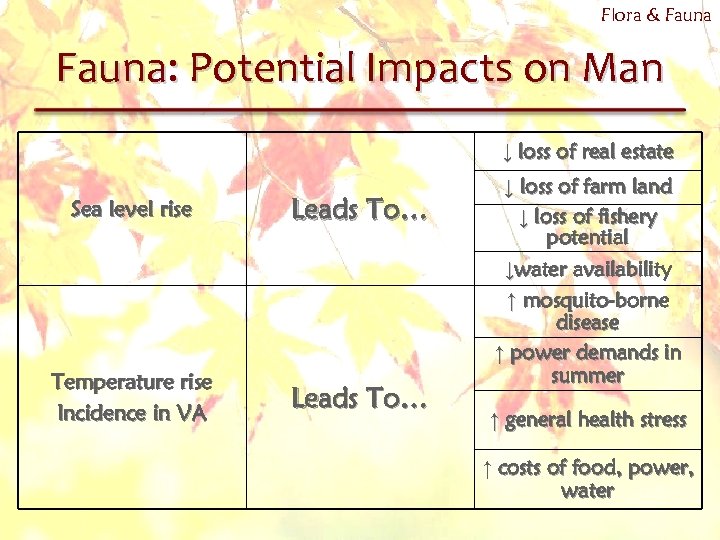 Flora & Fauna: Potential Impacts on Man ↓ loss of real estate Sea level rise Leads To… Temperature rise Incidence in VA Leads To… ↓ loss of farm land ↓ loss of fishery potential ↓water availability ↑ mosquito-borne disease ↑ power demands in summer ↑ general health stress ↑ costs of food, power, water
Flora & Fauna: Potential Impacts on Man ↓ loss of real estate Sea level rise Leads To… Temperature rise Incidence in VA Leads To… ↓ loss of farm land ↓ loss of fishery potential ↓water availability ↑ mosquito-borne disease ↑ power demands in summer ↑ general health stress ↑ costs of food, power, water
 Fauna Specifically: What is at Risk? Flora & Fauna Fish Species: IUCN red listed Brook Trout Migratory birds: thousands stop in VA marshes Amphibians flooded/ faster water breeding waters endanger success Reptiles flooding endangers Fur-bearers loss of prey species (amphibians, reptiles and birds) endangers
Fauna Specifically: What is at Risk? Flora & Fauna Fish Species: IUCN red listed Brook Trout Migratory birds: thousands stop in VA marshes Amphibians flooded/ faster water breeding waters endanger success Reptiles flooding endangers Fur-bearers loss of prey species (amphibians, reptiles and birds) endangers
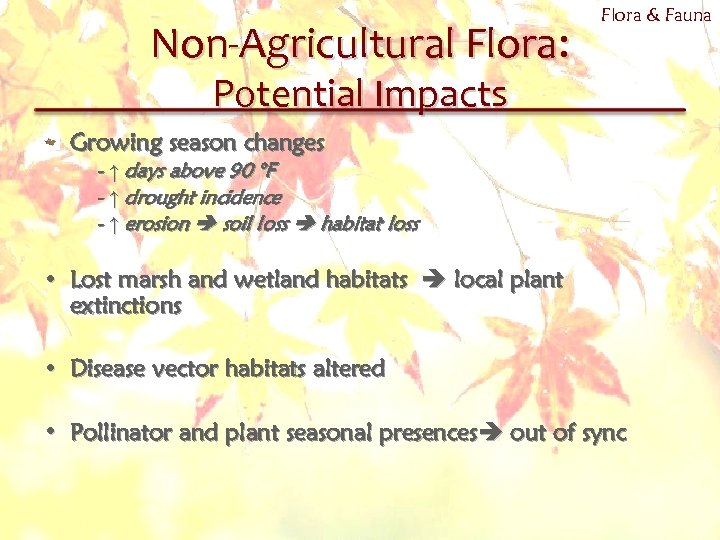 Non-Agricultural Flora: Flora & Fauna Potential Impacts Growing season changes - ↑ days above 90 °F - ↑ drought incidence - ↑ erosion soil loss habitat loss • Lost marsh and wetland habitats local plant extinctions • Disease vector habitats altered • Pollinator and plant seasonal presences out of sync
Non-Agricultural Flora: Flora & Fauna Potential Impacts Growing season changes - ↑ days above 90 °F - ↑ drought incidence - ↑ erosion soil loss habitat loss • Lost marsh and wetland habitats local plant extinctions • Disease vector habitats altered • Pollinator and plant seasonal presences out of sync
 Non Agricultural Flora Specifically: What is at Risk? Loblolly pine Bald cypress Swamp oaks Tapelos Atlantic white cedar Flora & Fauna
Non Agricultural Flora Specifically: What is at Risk? Loblolly pine Bald cypress Swamp oaks Tapelos Atlantic white cedar Flora & Fauna
 What Can be Done? Flora & Fauna Near term Mediation of Impacts Increase living shoreline buffers Restore dune and wetlands Institute measures to limit loss corridors, land preservation Monitor biodiversity for trends toward loss Consider sea level rise in long term planning of road, home, business, utility construction Consider extreme weather event likelihood in zoning and building code actions Close coal burning plants
What Can be Done? Flora & Fauna Near term Mediation of Impacts Increase living shoreline buffers Restore dune and wetlands Institute measures to limit loss corridors, land preservation Monitor biodiversity for trends toward loss Consider sea level rise in long term planning of road, home, business, utility construction Consider extreme weather event likelihood in zoning and building code actions Close coal burning plants
 What else can be done? Flora & Fauna Policy changes: reduce direct impacts Introduce threatened species to new habitats when feasible Initiate a moratorium on building, road and utility construction in low lying areas Develop green energy sources to reduce emissions Cap road construction but expand mass transit
What else can be done? Flora & Fauna Policy changes: reduce direct impacts Introduce threatened species to new habitats when feasible Initiate a moratorium on building, road and utility construction in low lying areas Develop green energy sources to reduce emissions Cap road construction but expand mass transit
 Flora & Fauna What More Can Be Done? A Gigaton Saved is a Kilawatt Earned Pass legislation to ban HOA restrictions on clotheslines Regulate lawn mower emissions Restrict median mowing of state roads to areas necessitated by safety concerns
Flora & Fauna What More Can Be Done? A Gigaton Saved is a Kilawatt Earned Pass legislation to ban HOA restrictions on clotheslines Regulate lawn mower emissions Restrict median mowing of state roads to areas necessitated by safety concerns
 What Else Can We Do? Flora & Fauna Recognize True Consumptive Costs Require billing for all energy production, agricultural and commercial externalities to cover all warming adaptation and mitigation costs That is: Tax CO² emissions (~sales tax) for all goods and services with exemptions as needed for low income residents
What Else Can We Do? Flora & Fauna Recognize True Consumptive Costs Require billing for all energy production, agricultural and commercial externalities to cover all warming adaptation and mitigation costs That is: Tax CO² emissions (~sales tax) for all goods and services with exemptions as needed for low income residents
 Flora & Fauna The Chesapeake Bay
Flora & Fauna The Chesapeake Bay
 Flora & Fauna The Chesapeake Bay • The mouth of the Bay is located near Virginia Beach, Virginia. The Bay extends along almost 100 miles of Virginia’s coastline, fed by the Potomac and Rappahannock rivers. • The average depth is a surprisingly shallow 21 ft. This makes the Bay especially susceptible to the impacts of sea -level rise. • It supports over 3, 600 species of plants and animals, harbors over one million waterfowl every winter, and is a permanent home to over 29 avian species.
Flora & Fauna The Chesapeake Bay • The mouth of the Bay is located near Virginia Beach, Virginia. The Bay extends along almost 100 miles of Virginia’s coastline, fed by the Potomac and Rappahannock rivers. • The average depth is a surprisingly shallow 21 ft. This makes the Bay especially susceptible to the impacts of sea -level rise. • It supports over 3, 600 species of plants and animals, harbors over one million waterfowl every winter, and is a permanent home to over 29 avian species.
 Flora & Fauna Potential Impacts • An increase in sea-level is not just inevitable for the Chesapeake Bay, it has already been observed. Since 1900, the sea-level has increased by 1 ft, and is predicted to rise another 2 ft by 2100. • An increase in temperature has also been observed in the area. Since 1960, the temperature has risen by almost 2 o, and is expected to warm another 5 o to 9 o by the end of this century. • It is very likely that an impact of climate change on the Bay would include increased precipitation. This would decrease the water quality by inundating the Bay with nutrients and sediments, while at the same time decreasing salinity. • A significant change of any one of these factors would greatly shift species distribution in the Bay.
Flora & Fauna Potential Impacts • An increase in sea-level is not just inevitable for the Chesapeake Bay, it has already been observed. Since 1900, the sea-level has increased by 1 ft, and is predicted to rise another 2 ft by 2100. • An increase in temperature has also been observed in the area. Since 1960, the temperature has risen by almost 2 o, and is expected to warm another 5 o to 9 o by the end of this century. • It is very likely that an impact of climate change on the Bay would include increased precipitation. This would decrease the water quality by inundating the Bay with nutrients and sediments, while at the same time decreasing salinity. • A significant change of any one of these factors would greatly shift species distribution in the Bay.
 Flora & Fauna: What is at Risk? • • There are over 350 species of fish that call the Chesapeake Bay home. A decrease in salinity from higher precipitation would decrease the number of species that would be able to travel into the Bay from marine environments, who require a certain salinity. The runoff of sediment into the Bay from increased precipitation would also limit the habitat of the abundant freshwater species. (Atlantic/Shortnose Sturgeon) Increased water levels would inundate regions of the Bay, eliminating swamps and marshes that are home to many species of reptile and amphibian. (Red Bellied Turtle) Elevated water levels would limit the habitat of many mammalian species, in addition to pushing them further into the state. Many mammals live the marsh environments of the Bay, and would need to migrate inland to avoid this. (Red Fox, White-tailed deer) Many migratory birds inhabit the Chesapeake Bay during the winter, and an increase in temperature would force them out of this region. In addition, many species inhabit the swamp areas, and would need to evacuate their already threatened habitat. (Bald Eagle, Great Blue Heron)
Flora & Fauna: What is at Risk? • • There are over 350 species of fish that call the Chesapeake Bay home. A decrease in salinity from higher precipitation would decrease the number of species that would be able to travel into the Bay from marine environments, who require a certain salinity. The runoff of sediment into the Bay from increased precipitation would also limit the habitat of the abundant freshwater species. (Atlantic/Shortnose Sturgeon) Increased water levels would inundate regions of the Bay, eliminating swamps and marshes that are home to many species of reptile and amphibian. (Red Bellied Turtle) Elevated water levels would limit the habitat of many mammalian species, in addition to pushing them further into the state. Many mammals live the marsh environments of the Bay, and would need to migrate inland to avoid this. (Red Fox, White-tailed deer) Many migratory birds inhabit the Chesapeake Bay during the winter, and an increase in temperature would force them out of this region. In addition, many species inhabit the swamp areas, and would need to evacuate their already threatened habitat. (Bald Eagle, Great Blue Heron)
 Flora & Fauna Flora: What is at Risk? • An increase in temperature from climate change would be detrimental to most, if not all of the many types of underwater grasses in the Bay. Eelgrass is an especially important component to the Chesapeake Bay ecosystem. It provides shelter for many species, and as serves as food for others. Eelgrass prefers the high salinity waters of the lower Bay, so an increase in sea-level or precipitation would limit its environment. An above average stretch of warm weather was experienced in 2005, and as a result huge swaths of eelgrass were killed. Any further increase in temperature would permanently force out this important vegetation. • An increase in water level would force out many species of flora in the Bay region that live in marsh environments or near shallow stream banks. (Sweet Magnolia, Coontail)
Flora & Fauna Flora: What is at Risk? • An increase in temperature from climate change would be detrimental to most, if not all of the many types of underwater grasses in the Bay. Eelgrass is an especially important component to the Chesapeake Bay ecosystem. It provides shelter for many species, and as serves as food for others. Eelgrass prefers the high salinity waters of the lower Bay, so an increase in sea-level or precipitation would limit its environment. An above average stretch of warm weather was experienced in 2005, and as a result huge swaths of eelgrass were killed. Any further increase in temperature would permanently force out this important vegetation. • An increase in water level would force out many species of flora in the Bay region that live in marsh environments or near shallow stream banks. (Sweet Magnolia, Coontail)
 Flora & Fauna Solutions • It will be difficult for those inhabitants near the shorelines to avoid the effects of water level rise. It might be necessary for those affected to relocate, including both homeowners and businesses. • As in the coastal areas, it will be necessary to consider water level rise in building future infrastructure. • Homeowners and businesses located on shorelines will need to adjust their structure to adapt to higher water levels. This would be preferable to invading the already threatened areas of natural habitat. Long Term: • The most important policy changes to be made are those which reduce carbon emissions. • This can be done by giving commuters in the area more choices when it comes to transportation options, such as carpooling, telecommuting and investing in mass transit. Investments should be made in creating modern and efficient transit. • Residential and business areas need to be built more compactly to avoid sprawl. Incentives to build more “green” structures should be offered, as well as those willing to update older buildings. • Residential energy use must also be reduced. This can be done simply by improving insulation, replacing windows, and using compact fluorescent lighting. • An immensely beneficial change would simply be to increase the amount of energy that comes from renewable sources to the region.
Flora & Fauna Solutions • It will be difficult for those inhabitants near the shorelines to avoid the effects of water level rise. It might be necessary for those affected to relocate, including both homeowners and businesses. • As in the coastal areas, it will be necessary to consider water level rise in building future infrastructure. • Homeowners and businesses located on shorelines will need to adjust their structure to adapt to higher water levels. This would be preferable to invading the already threatened areas of natural habitat. Long Term: • The most important policy changes to be made are those which reduce carbon emissions. • This can be done by giving commuters in the area more choices when it comes to transportation options, such as carpooling, telecommuting and investing in mass transit. Investments should be made in creating modern and efficient transit. • Residential and business areas need to be built more compactly to avoid sprawl. Incentives to build more “green” structures should be offered, as well as those willing to update older buildings. • Residential energy use must also be reduced. This can be done simply by improving insulation, replacing windows, and using compact fluorescent lighting. • An immensely beneficial change would simply be to increase the amount of energy that comes from renewable sources to the region.
 Flora & Fauna References: http: //www. chesapeakebay. net/factsandfigures. aspx? menuitem=14582 Chesapeake Bay Program: Facts and Figures http: //www. chesapeakebay. net/climatechange. aspx? menuitem=16860 The Impacts of Climate Change on the Chesapeake Bay http: //www. cbf. org/Document. Doc? id=140 The Chesapeake Bay Foundation’s Report on Climate Change http: //www. chesapeakebay. net/bfg_fish. aspx? menuitem=14340 The Fish Species of the Chesapeake Bay http: //www. chesapeakebay. net/bfg_reptphib. aspx? menuitem=14344 Reptile Species http: //www. chesapeakebay. net/bfg_birds. aspx? menuitem=14339 Avian Species http: //www. chesapeakebay. net/bfg_mammals. aspx? menuitem=14342 Mammalian Species http: //www. chesapeakebay. net/baygrasses. aspx? menuitem=14621 Underwater Bay Grasses
Flora & Fauna References: http: //www. chesapeakebay. net/factsandfigures. aspx? menuitem=14582 Chesapeake Bay Program: Facts and Figures http: //www. chesapeakebay. net/climatechange. aspx? menuitem=16860 The Impacts of Climate Change on the Chesapeake Bay http: //www. cbf. org/Document. Doc? id=140 The Chesapeake Bay Foundation’s Report on Climate Change http: //www. chesapeakebay. net/bfg_fish. aspx? menuitem=14340 The Fish Species of the Chesapeake Bay http: //www. chesapeakebay. net/bfg_reptphib. aspx? menuitem=14344 Reptile Species http: //www. chesapeakebay. net/bfg_birds. aspx? menuitem=14339 Avian Species http: //www. chesapeakebay. net/bfg_mammals. aspx? menuitem=14342 Mammalian Species http: //www. chesapeakebay. net/baygrasses. aspx? menuitem=14621 Underwater Bay Grasses
 Virginia’s Cities: Flora & Fauna The Dangers of the Urban Heat Island What is the Urban Heat Island effect? What are the causes of this effect? What are the results of the Urban Heat Island? The demand for air conditioning increases greenhouse gas emissions from power plants Increased days of 100 degrees Devastating effects on surrounding wildlife and plantlife What is the urban heat island effect? by Jane Mc. Grath
Virginia’s Cities: Flora & Fauna The Dangers of the Urban Heat Island What is the Urban Heat Island effect? What are the causes of this effect? What are the results of the Urban Heat Island? The demand for air conditioning increases greenhouse gas emissions from power plants Increased days of 100 degrees Devastating effects on surrounding wildlife and plantlife What is the urban heat island effect? by Jane Mc. Grath
 Virginia’s Urban Areas: Flora & Fauna Some Background 95 counties and 39 independent cities Virginia has 11 Metropolitan Statistical Areas Richmond - population of over 1. 2 million people. Virginia Beach - most populous city in the Commonwealth Fairfax County is the most populous locality in Virginia, with over one million residents. Tysons Corner - Virginia's largest office market. Loudoun County - the fastest-growing county in the United States highest median household income: $107, 207 (as of 2007) Roanoke - the largest Metropolitan Statistical Area in western Virginia.
Virginia’s Urban Areas: Flora & Fauna Some Background 95 counties and 39 independent cities Virginia has 11 Metropolitan Statistical Areas Richmond - population of over 1. 2 million people. Virginia Beach - most populous city in the Commonwealth Fairfax County is the most populous locality in Virginia, with over one million residents. Tysons Corner - Virginia's largest office market. Loudoun County - the fastest-growing county in the United States highest median household income: $107, 207 (as of 2007) Roanoke - the largest Metropolitan Statistical Area in western Virginia.
 Flora & Fauna Premise Expansion of Washington, D. C. suburbs into Northern Virginia has created an urban heat island Mostly caused by more absorption of solar radiation in densely populated areas 15 counties received failing grades for air quality - Fairfax County having the worst in the state Effects of Air Quality on Flora and Fauna climate change and urban growth impacts on headwater streams, ecosystem structure and services will be more costly than climate change alone. Virginia's Cities and Towns
Flora & Fauna Premise Expansion of Washington, D. C. suburbs into Northern Virginia has created an urban heat island Mostly caused by more absorption of solar radiation in densely populated areas 15 counties received failing grades for air quality - Fairfax County having the worst in the state Effects of Air Quality on Flora and Fauna climate change and urban growth impacts on headwater streams, ecosystem structure and services will be more costly than climate change alone. Virginia's Cities and Towns
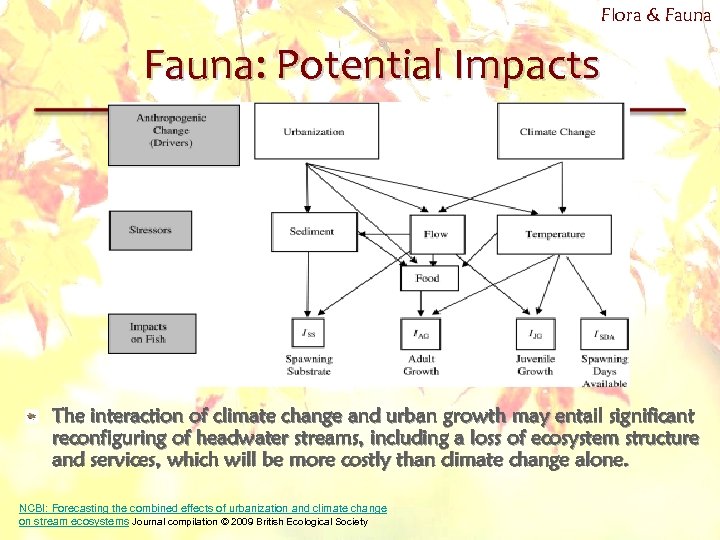 Flora & Fauna: Potential Impacts The interaction of climate change and urban growth may entail significant reconfiguring of headwater streams, including a loss of ecosystem structure and services, which will be more costly than climate change alone. NCBI: Forecasting the combined effects of urbanization and climate change on stream ecosystems Journal compilation © 2009 British Ecological Society
Flora & Fauna: Potential Impacts The interaction of climate change and urban growth may entail significant reconfiguring of headwater streams, including a loss of ecosystem structure and services, which will be more costly than climate change alone. NCBI: Forecasting the combined effects of urbanization and climate change on stream ecosystems Journal compilation © 2009 British Ecological Society
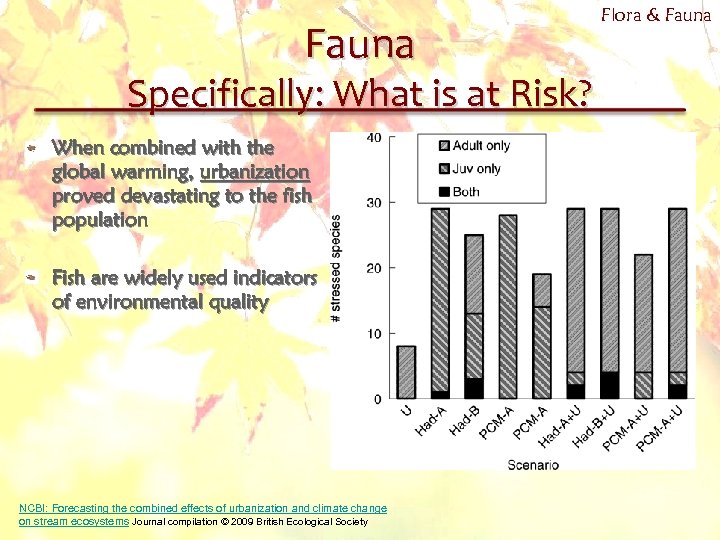 Fauna Specifically: What is at Risk? When combined with the global warming, urbanization proved devastating to the fish population Fish are widely used indicators of environmental quality NCBI: Forecasting the combined effects of urbanization and climate change on stream ecosystems Journal compilation © 2009 British Ecological Society Flora & Fauna
Fauna Specifically: What is at Risk? When combined with the global warming, urbanization proved devastating to the fish population Fish are widely used indicators of environmental quality NCBI: Forecasting the combined effects of urbanization and climate change on stream ecosystems Journal compilation © 2009 British Ecological Society Flora & Fauna
 Non-Agricultural Flora: Flora & Fauna Urban Impacts Urban development… Diminishes the resilience of freshwater ecosystems to climate variability. Storms are sharply increased scours stream banks, decreases the reproductive success of aquatic insects and of fish that lay eggs near the edges of streams increases the input of sediments, nutrients and toxic chemicals into rivers, streams, lakes and estuaries. Sediments reduce water clarity, smother bottom organisms, and clog waterways; excessive inputs of nutrients create toxic chemicals that affect plants and animals. NCBI: Climate change and ecosystems of the Mid-Atlantic Region
Non-Agricultural Flora: Flora & Fauna Urban Impacts Urban development… Diminishes the resilience of freshwater ecosystems to climate variability. Storms are sharply increased scours stream banks, decreases the reproductive success of aquatic insects and of fish that lay eggs near the edges of streams increases the input of sediments, nutrients and toxic chemicals into rivers, streams, lakes and estuaries. Sediments reduce water clarity, smother bottom organisms, and clog waterways; excessive inputs of nutrients create toxic chemicals that affect plants and animals. NCBI: Climate change and ecosystems of the Mid-Atlantic Region
 What Can be Done? Flora & Fauna Encourage Individual Homeowners to… Plant shade trees: reduce your annual heating and cooling costs by an average of 40 percent. Deciduous on the South: loose leaves in Winter; Reflect sun in Summer Convert to compact fluorescent bulbs: Would prevent more than 13 billion pounds of carbon dioxide from being emitted. Become a Green Tag subscriber: Options for homeowners to buy electricity from clean, renewable sources Act locally: Contact your mayor and ask that he sign the U. S. Mayors Climate Protection Agreement, committing your city or town to meet or beat the global warming pollution reductions National Wildlife Federation
What Can be Done? Flora & Fauna Encourage Individual Homeowners to… Plant shade trees: reduce your annual heating and cooling costs by an average of 40 percent. Deciduous on the South: loose leaves in Winter; Reflect sun in Summer Convert to compact fluorescent bulbs: Would prevent more than 13 billion pounds of carbon dioxide from being emitted. Become a Green Tag subscriber: Options for homeowners to buy electricity from clean, renewable sources Act locally: Contact your mayor and ask that he sign the U. S. Mayors Climate Protection Agreement, committing your city or town to meet or beat the global warming pollution reductions National Wildlife Federation
 What else can be done? Flora & Fauna Policy changes: reduce direct impacts “Where land is not already heavily developed, land preservation [programs] could be used to protect headwater streams. ” More aggressive efforts to reduce sediment and pollutant loads, Urbanization combined with climate change will be more environmentally costly than either impact alone. Minimizing costs by reassessing the importance of urban streams, as well as the adequacy of [programs] to protect them Proactive policy and/or management actions are needed to advance conservation and should have high priority in future ubranized regions
What else can be done? Flora & Fauna Policy changes: reduce direct impacts “Where land is not already heavily developed, land preservation [programs] could be used to protect headwater streams. ” More aggressive efforts to reduce sediment and pollutant loads, Urbanization combined with climate change will be more environmentally costly than either impact alone. Minimizing costs by reassessing the importance of urban streams, as well as the adequacy of [programs] to protect them Proactive policy and/or management actions are needed to advance conservation and should have high priority in future ubranized regions
 Flora & Fauna Conclusion to VA’s Urban Areas
Flora & Fauna Conclusion to VA’s Urban Areas
 Flora & Fauna Piedmont Region
Flora & Fauna Piedmont Region
 Endangered Species: Flora & Fauna Piedmont Region of Virginia • There are many threatened and endangered plant and animal species in Virginia alone. • Many of these endangered species lie in the piedmont region of VA. • These species are threatened and endangered because of loss of habitat and food resources, changes in climate, and human population expansion.
Endangered Species: Flora & Fauna Piedmont Region of Virginia • There are many threatened and endangered plant and animal species in Virginia alone. • Many of these endangered species lie in the piedmont region of VA. • These species are threatened and endangered because of loss of habitat and food resources, changes in climate, and human population expansion.
 Flora & Fauna Shenandoah Salamander • Is only found on north facing talus slopes on three mountain tops inside the Shenandoah National Park. • It’s natural habitat are temperate forests and rocky areas. • Breeding occurs in the fall and spring where the eggs are laid under rocks in their natural talus habitats.
Flora & Fauna Shenandoah Salamander • Is only found on north facing talus slopes on three mountain tops inside the Shenandoah National Park. • It’s natural habitat are temperate forests and rocky areas. • Breeding occurs in the fall and spring where the eggs are laid under rocks in their natural talus habitats.
 Flora & Fauna Reasons for Endangerment • Climate change is a major factor in the survival of these amphibians. • Rising temperatures. • Confined habitat. Limited to the Shenandoah National Forrest. • Defoliation of trees by invasive moths
Flora & Fauna Reasons for Endangerment • Climate change is a major factor in the survival of these amphibians. • Rising temperatures. • Confined habitat. Limited to the Shenandoah National Forrest. • Defoliation of trees by invasive moths
 Flora & Fauna Roanoke Logperch
Flora & Fauna Roanoke Logperch
 Flora & Fauna Roanoke Logperch • Lives only in the Roanoke, Smith and Nottoway rivers within the piedmont region. • Needs clear, silt-free water for living and breeding. • Eats, lives, and breeds in low streams and rivers in gravel beds. • Their feeding habits rely on loosely embedded gravel.
Flora & Fauna Roanoke Logperch • Lives only in the Roanoke, Smith and Nottoway rivers within the piedmont region. • Needs clear, silt-free water for living and breeding. • Eats, lives, and breeds in low streams and rivers in gravel beds. • Their feeding habits rely on loosely embedded gravel.
 Flora & Fauna Logperch Endangerment • Decades of development beginning in the 1970’s • 1989 species placed on the federal endangered list. • In-stream dam removal, and bridge expansion. • Cloudy, contaminated, or murky water • Receding streams and rivers
Flora & Fauna Logperch Endangerment • Decades of development beginning in the 1970’s • 1989 species placed on the federal endangered list. • In-stream dam removal, and bridge expansion. • Cloudy, contaminated, or murky water • Receding streams and rivers
 Flora & Fauna Smooth Coneflower
Flora & Fauna Smooth Coneflower
 Smooth Cone Flower Endangerment Flora & Fauna • Smooth coneflower is a perennial herb • Listed as endangered. • Can be only found in the piedmont regions of four states: Virginia, North and South Carolina, and Georgia. • Was once found in eight states. • Grows in sunny, open areas usually alongside roads and highways. • Endangered because of uprooting by humans.
Smooth Cone Flower Endangerment Flora & Fauna • Smooth coneflower is a perennial herb • Listed as endangered. • Can be only found in the piedmont regions of four states: Virginia, North and South Carolina, and Georgia. • Was once found in eight states. • Grows in sunny, open areas usually alongside roads and highways. • Endangered because of uprooting by humans.
 Flora & Fauna What we can do, about land use, water quality, and wetlands protection? • • Education of: Landscape conservation Carbon foot printing Habitat destruction and fragmentation Pollution and habitat changes due to industry and development Support local government changes for air quality protection programs. Energy conservation and efficiency by recycling and buying renewable resources. • Opposing new nuclear and coal-fueled power plants in North Anna and Wise and Surry counties • Expansion of public transportation, and encourage car pooling
Flora & Fauna What we can do, about land use, water quality, and wetlands protection? • • Education of: Landscape conservation Carbon foot printing Habitat destruction and fragmentation Pollution and habitat changes due to industry and development Support local government changes for air quality protection programs. Energy conservation and efficiency by recycling and buying renewable resources. • Opposing new nuclear and coal-fueled power plants in North Anna and Wise and Surry counties • Expansion of public transportation, and encourage car pooling
 Flora & Fauna What we can do, about land use, water quality, and wetlands protection? • Oppose new road projects like the Meadow Creek parkway, and Eastern Connector trail that will go through public parks. • Support land use planning guidelines that protect open spaces, residential planning and development in rural areas that will discourage deforestation. • Protect our local water supply by; restoring and dredging the Rivanna Reservoir, support stream buffering, oppose confined livestock raising. • Preservation of native species and ecosystems, opposing pesticide use in the Shenandoah National Park • Support the use of organic solutions for pest control. • Environmentally friendly lawn care with natural fertilizers, composting, and self mulching mowers. • Encourage sustainable local organic agriculture.
Flora & Fauna What we can do, about land use, water quality, and wetlands protection? • Oppose new road projects like the Meadow Creek parkway, and Eastern Connector trail that will go through public parks. • Support land use planning guidelines that protect open spaces, residential planning and development in rural areas that will discourage deforestation. • Protect our local water supply by; restoring and dredging the Rivanna Reservoir, support stream buffering, oppose confined livestock raising. • Preservation of native species and ecosystems, opposing pesticide use in the Shenandoah National Park • Support the use of organic solutions for pest control. • Environmentally friendly lawn care with natural fertilizers, composting, and self mulching mowers. • Encourage sustainable local organic agriculture.
 Flora & Fauna Resources • • • Endangered. Specie. com http: //www. endangeredspecie. com/states/va. htm Managing Land in the Piedmont of Virginia for the Benefit of Birds and Other Wildlife. Faren Wolter, Stephen Capel, David Pashley, Susan Heath. 2008 Threatened, Endangered, Sensetive, and other species of ceoncern in Virginia. http: //www. virginiaplaces. org/natural/especies. html Spring belongs to the Roanoke Logperch. http: //www. roanoke. com/news/roanoke/wb/198464 Protecting Wildlife Habitat. Piedmont Environmental Council. http: //www. pecva. org Piedmont Group of the Sierra Club Environmental Agenda 2009. http: //virginia. sierraclub. org Efforts to Save Endangered Species. http: //www. clemson. edu/hort/sctop/bsec 13. php U. S. Fish and Wildlife Service. http: //www. fws. gov American Bird Conservatory. http: //www. abcbirds. org Virginia Department of Game and Inland Fisheries. http: //www. dgif. virginia. gov
Flora & Fauna Resources • • • Endangered. Specie. com http: //www. endangeredspecie. com/states/va. htm Managing Land in the Piedmont of Virginia for the Benefit of Birds and Other Wildlife. Faren Wolter, Stephen Capel, David Pashley, Susan Heath. 2008 Threatened, Endangered, Sensetive, and other species of ceoncern in Virginia. http: //www. virginiaplaces. org/natural/especies. html Spring belongs to the Roanoke Logperch. http: //www. roanoke. com/news/roanoke/wb/198464 Protecting Wildlife Habitat. Piedmont Environmental Council. http: //www. pecva. org Piedmont Group of the Sierra Club Environmental Agenda 2009. http: //virginia. sierraclub. org Efforts to Save Endangered Species. http: //www. clemson. edu/hort/sctop/bsec 13. php U. S. Fish and Wildlife Service. http: //www. fws. gov American Bird Conservatory. http: //www. abcbirds. org Virginia Department of Game and Inland Fisheries. http: //www. dgif. virginia. gov
 Appalachia: Already in Peril Flora & Fauna • The Appalachian Mountain range extends from Alabama to Canada • National Lands – Shenandoah National Park (almost 200, 000 acres) – George Washington and Jefferson National Forests (1, 646, 328 acres) Drew, Mc. Afee’s Knob, Appalachian Trail
Appalachia: Already in Peril Flora & Fauna • The Appalachian Mountain range extends from Alabama to Canada • National Lands – Shenandoah National Park (almost 200, 000 acres) – George Washington and Jefferson National Forests (1, 646, 328 acres) Drew, Mc. Afee’s Knob, Appalachian Trail
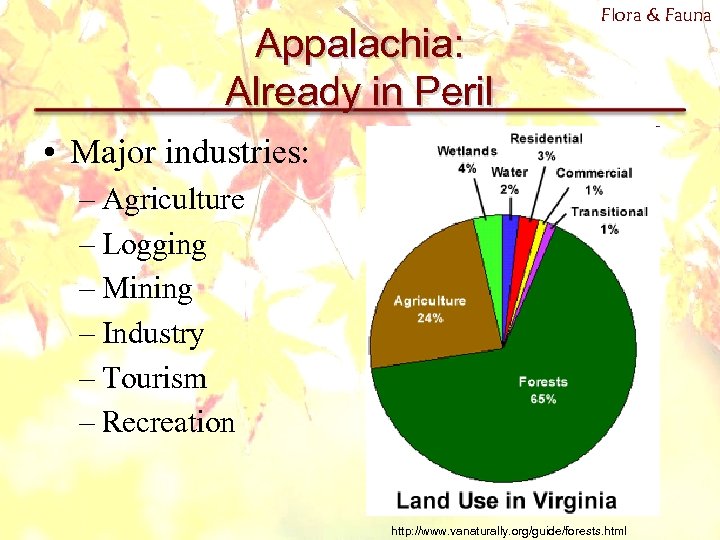 Appalachia: Already in Peril Flora & Fauna • Major industries: – Agriculture – Logging – Mining – Industry – Tourism – Recreation http: //www. vanaturally. org/guide/forests. html
Appalachia: Already in Peril Flora & Fauna • Major industries: – Agriculture – Logging – Mining – Industry – Tourism – Recreation http: //www. vanaturally. org/guide/forests. html
 Appalachia: Already in Peril Flora & Fauna • Appalachia, despite having almost 1, 850, 000 acres of nationally protected land is already in a precariously fragile environmental state • From 1993 -2008 Appalachia has already experienced a 2* F increase in temperature • Projections tell of 5*-8* F increases for the region during the next century • The negative impacts of Global Warming may unfortunately push many threatened species over the edge • As crucial links in food weds are lost, the stability of entire ecosystems can be jeopardized
Appalachia: Already in Peril Flora & Fauna • Appalachia, despite having almost 1, 850, 000 acres of nationally protected land is already in a precariously fragile environmental state • From 1993 -2008 Appalachia has already experienced a 2* F increase in temperature • Projections tell of 5*-8* F increases for the region during the next century • The negative impacts of Global Warming may unfortunately push many threatened species over the edge • As crucial links in food weds are lost, the stability of entire ecosystems can be jeopardized
 Flora & Fauna Endangered Species • Around 520 threatened, endangered or Special Concern Species of fauna are found in VA. • There are 28 Endangered species of flora & fauna in VA. • In Appalachia endangered species include: (VA Department of game and fisheries) (US Fish and Wildlife Service) – Fauna: bats, salamanders, fish, Isopods, bivalves – Flora: Flowers, lichen www. fws. gov
Flora & Fauna Endangered Species • Around 520 threatened, endangered or Special Concern Species of fauna are found in VA. • There are 28 Endangered species of flora & fauna in VA. • In Appalachia endangered species include: (VA Department of game and fisheries) (US Fish and Wildlife Service) – Fauna: bats, salamanders, fish, Isopods, bivalves – Flora: Flowers, lichen www. fws. gov
 Flora & Fauna Environmental Degradation in Appalachia • Habitat destruction and degradation • • • – Deforestation (Development & logging) – Mountain top removal (Coal mining) Air pollution (Highway 81) Acid Rain Water contamination/Increased H O temperature 2 www. coal-is-dirty. com – Bioaccumulation of toxins – Decreased dissolved O 2 • Invasive Spices www. kokudzu. com http: //site. wellthysolutions. com http: //www. virginia. org/images/Shenbig. gif
Flora & Fauna Environmental Degradation in Appalachia • Habitat destruction and degradation • • • – Deforestation (Development & logging) – Mountain top removal (Coal mining) Air pollution (Highway 81) Acid Rain Water contamination/Increased H O temperature 2 www. coal-is-dirty. com – Bioaccumulation of toxins – Decreased dissolved O 2 • Invasive Spices www. kokudzu. com http: //site. wellthysolutions. com http: //www. virginia. org/images/Shenbig. gif
 Flora & Fauna Premise #1 90% confidence that anthropogenic fossil fuel burning has increased global mean temperature (IPCC AR 4) Increase in local temperatures will lead to the retreat of ecosystems Northward and to higher elevations Reduction in the number and severity of cold days, along with the reduction of snowfall will lead to an increase in the water temper in creeks and rivers Warmer temperature earlier in the spring and through later in the Fall have thrown off rhythmical predator prey equilibriums.
Flora & Fauna Premise #1 90% confidence that anthropogenic fossil fuel burning has increased global mean temperature (IPCC AR 4) Increase in local temperatures will lead to the retreat of ecosystems Northward and to higher elevations Reduction in the number and severity of cold days, along with the reduction of snowfall will lead to an increase in the water temper in creeks and rivers Warmer temperature earlier in the spring and through later in the Fall have thrown off rhythmical predator prey equilibriums.
 Flora & Fauna Premise #2 • 90% confidence : observed global warming • Atmospheric Warming: - altered regional climates - increased occurrence of extreme weather - increased runoff intensity - increased erosion - changes in disease prevalence by region - specific Virginia habitat losses http: //veganverve. files. wordpress. com/2008/08/cows. jpg
Flora & Fauna Premise #2 • 90% confidence : observed global warming • Atmospheric Warming: - altered regional climates - increased occurrence of extreme weather - increased runoff intensity - increased erosion - changes in disease prevalence by region - specific Virginia habitat losses http: //veganverve. files. wordpress. com/2008/08/cows. jpg
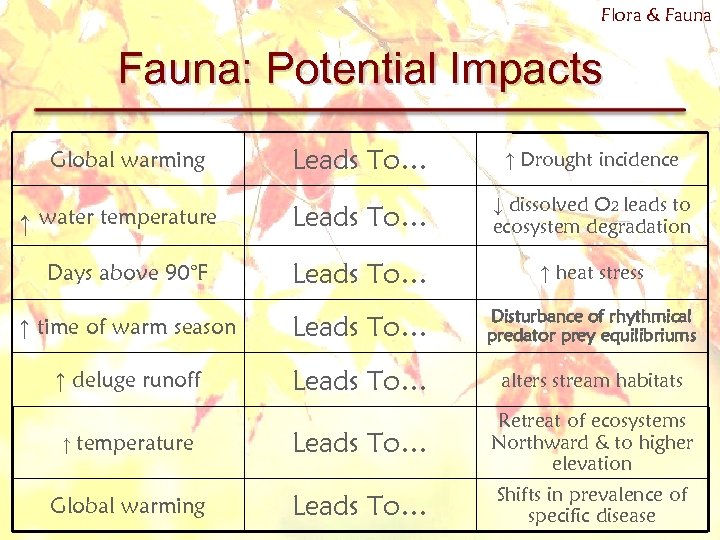 Flora & Fauna: Potential Impacts Leads To… ↑ Drought incidence Leads To… ↓ dissolved O 2 leads to ecosystem degradation Leads To… ↑ heat stress ↑ time of warm season Leads To… Disturbance of rhythmical predator prey equilibriums ↑ deluge runoff Leads To… alters stream habitats ↑ temperature Leads To… Retreat of ecosystems Northward & to higher elevation Global warming Leads To… Shifts in prevalence of specific disease Global warming ↑ water temperature Days above 90°F
Flora & Fauna: Potential Impacts Leads To… ↑ Drought incidence Leads To… ↓ dissolved O 2 leads to ecosystem degradation Leads To… ↑ heat stress ↑ time of warm season Leads To… Disturbance of rhythmical predator prey equilibriums ↑ deluge runoff Leads To… alters stream habitats ↑ temperature Leads To… Retreat of ecosystems Northward & to higher elevation Global warming Leads To… Shifts in prevalence of specific disease Global warming ↑ water temperature Days above 90°F
 Flora & Fauna: Potential Impacts on Man • Rising Temperature leads to: – Increase of mosquito-borne diseases – Increased power demands in summer – Increased general health stress – Increased cost of food, water and power • More floods →runoff → water pollution → environmental degradation → increased disease → financial burden
Flora & Fauna: Potential Impacts on Man • Rising Temperature leads to: – Increase of mosquito-borne diseases – Increased power demands in summer – Increased general health stress – Increased cost of food, water and power • More floods →runoff → water pollution → environmental degradation → increased disease → financial burden
 Flora & Fauna Specifically: What is at Risk? Fish Species: Many endangered and threatened fish species are found in Appalachia Birds: Endangered and threatened birds living and travel through the mountains Amphibians flooded/ faster/polluted water breeding waters endanger success Reptiles flooding, disease, and invasive predators reduce survival Fur-bearers loss of prey species (amphibians, reptiles and birds) imbalance of natural equilibriums endanger larger ecosystem stability
Flora & Fauna Specifically: What is at Risk? Fish Species: Many endangered and threatened fish species are found in Appalachia Birds: Endangered and threatened birds living and travel through the mountains Amphibians flooded/ faster/polluted water breeding waters endanger success Reptiles flooding, disease, and invasive predators reduce survival Fur-bearers loss of prey species (amphibians, reptiles and birds) imbalance of natural equilibriums endanger larger ecosystem stability
 Flora & Fauna Non-Agricultural Flora: Potential Impacts Growing season changes - ↑ days above 90 °F - ↑ drought incidence - ↑ erosion soil loss habitat loss Less snow cover and fewer light rains stress on spring plants may lead to local plant extinctions or extirpations Disease vector habitats altered Pollinator and plant seasonal presences out of sync
Flora & Fauna Non-Agricultural Flora: Potential Impacts Growing season changes - ↑ days above 90 °F - ↑ drought incidence - ↑ erosion soil loss habitat loss Less snow cover and fewer light rains stress on spring plants may lead to local plant extinctions or extirpations Disease vector habitats altered Pollinator and plant seasonal presences out of sync
 Flora & Fauna Non Agricultural Flora Specifically: What is at Risk? Swamp pink (Helonias bullata) Virginia spirea (Spiraea Virginiana) Small-whorled pogonia (Isotria medoloides) www. fws. gov
Flora & Fauna Non Agricultural Flora Specifically: What is at Risk? Swamp pink (Helonias bullata) Virginia spirea (Spiraea Virginiana) Small-whorled pogonia (Isotria medoloides) www. fws. gov
 Flora & Fauna High Risk ecosystems in Appalachia • Unique Caves • Mountain Creeks and Streams • Biologically Historic Rivers • Mountain Forests • Highland Valleys
Flora & Fauna High Risk ecosystems in Appalachia • Unique Caves • Mountain Creeks and Streams • Biologically Historic Rivers • Mountain Forests • Highland Valleys
 Flora & Fauna Unique Caves • Cave stay at the average temperature of an area year round thus there is very little temperature change • Caves create very isolated ecosystems that often aid to the rise of genetically divergent unique species that can only be found in a single cave or specific to a particular region • Highly specialized= vulnerable to change • These factors led me to fear that cave ecosystems may be severely hit by GW
Flora & Fauna Unique Caves • Cave stay at the average temperature of an area year round thus there is very little temperature change • Caves create very isolated ecosystems that often aid to the rise of genetically divergent unique species that can only be found in a single cave or specific to a particular region • Highly specialized= vulnerable to change • These factors led me to fear that cave ecosystems may be severely hit by GW
 Flora & Fauna Bats • Bats are often keystone species and therefore can be critical to a healthy ecosystem • Positive Roles – Eat insects – Pollinators – Seed dispersers http: //www. netcore. ca/~peleetom/Bats%20 in%20 sunset%202. jpg
Flora & Fauna Bats • Bats are often keystone species and therefore can be critical to a healthy ecosystem • Positive Roles – Eat insects – Pollinators – Seed dispersers http: //www. netcore. ca/~peleetom/Bats%20 in%20 sunset%202. jpg
 Flora & Fauna Bats • Unfortunately bats are facing hardship from many sides whose negative effects may be amplified by GW. – Human Disturbances – Habitat Loss & Degradation (flooding from dams) – Cave Commercialization and Improper Gating – White-Nose Syndrome
Flora & Fauna Bats • Unfortunately bats are facing hardship from many sides whose negative effects may be amplified by GW. – Human Disturbances – Habitat Loss & Degradation (flooding from dams) – Cave Commercialization and Improper Gating – White-Nose Syndrome
 Flora & Fauna Endangered Bats in VA – Indiana Bat • (Myotis sodalis) – Virginia Big-Eared Bat • (Corynorhinus townsendii virginiaus) – Grey Bat • (Myotis grisescens) www. fws. gov www. scenic-suffolk. co. uk/2008/04/bats. html http: //greenupgrader. com
Flora & Fauna Endangered Bats in VA – Indiana Bat • (Myotis sodalis) – Virginia Big-Eared Bat • (Corynorhinus townsendii virginiaus) – Grey Bat • (Myotis grisescens) www. fws. gov www. scenic-suffolk. co. uk/2008/04/bats. html http: //greenupgrader. com
 Flora & Fauna Threatened Cave-Isopods • Endangered Isopod, Lee County cave, – (Lirceus usdagalun) • Threatened Isopod, Madison Cave, – (Antrolana lira) www. dcr. virginia. gov
Flora & Fauna Threatened Cave-Isopods • Endangered Isopod, Lee County cave, – (Lirceus usdagalun) • Threatened Isopod, Madison Cave, – (Antrolana lira) www. dcr. virginia. gov
 Flora & Fauna Mountain Creeks and Rivers • Mountain streams are often know for there biodiversity • The New River is one of the oldest rivers in the world, geologically speaking Cascades, VA, Leigh Knudsen
Flora & Fauna Mountain Creeks and Rivers • Mountain streams are often know for there biodiversity • The New River is one of the oldest rivers in the world, geologically speaking Cascades, VA, Leigh Knudsen
 Flora & Fauna Mountain Creeks and Rivers • Unfortunately many creeks and rivers in Appalachia already suffer from environmental degradation – Pollution from industrial factories – Pollution from Mountain Top Removal and other mining operations – Pollution from agriculture – Silt buildup from erosion – Introduction of invasive species
Flora & Fauna Mountain Creeks and Rivers • Unfortunately many creeks and rivers in Appalachia already suffer from environmental degradation – Pollution from industrial factories – Pollution from Mountain Top Removal and other mining operations – Pollution from agriculture – Silt buildup from erosion – Introduction of invasive species
 Flora & Fauna Mountain Creeks and Rivers • As the temperature of Appalachia continues to increase, water temperature will also rise due to less cold weather and less snow • Warmer water is not able have the same concentration levels of dissolved oxygen • Warmer than usual water temperatures are detrimental to the health of the ecosystems because the lack of oxygen will lead to the death of some animals • Unpolluted warm water re-entering rivers from power plants often leads dead-zones downstream
Flora & Fauna Mountain Creeks and Rivers • As the temperature of Appalachia continues to increase, water temperature will also rise due to less cold weather and less snow • Warmer water is not able have the same concentration levels of dissolved oxygen • Warmer than usual water temperatures are detrimental to the health of the ecosystems because the lack of oxygen will lead to the death of some animals • Unpolluted warm water re-entering rivers from power plants often leads dead-zones downstream
 Flora & Fauna Mountain Creeks and Rivers • Many of the threatened and endangered species in the creeks and rivers of Appalachia are filter feeders • Filter feeders help to clean natural pollutants from the ecosystem • Unfortunately filter feeders are not able to process most industrial pollutants and when they are eaten the pollutants get passes up the food-chain along with the energy • The concentration of pollutants accrues by a factor of about 10 with each progressive level of the chain reaching potential toxic levels for human consumption – Ex: Mercury Poising from diets high in top predators like tuna
Flora & Fauna Mountain Creeks and Rivers • Many of the threatened and endangered species in the creeks and rivers of Appalachia are filter feeders • Filter feeders help to clean natural pollutants from the ecosystem • Unfortunately filter feeders are not able to process most industrial pollutants and when they are eaten the pollutants get passes up the food-chain along with the energy • The concentration of pollutants accrues by a factor of about 10 with each progressive level of the chain reaching potential toxic levels for human consumption – Ex: Mercury Poising from diets high in top predators like tuna
 Flora & Fauna Threatened and Endangered Species in the Rivers • Endangered Freshwater Mussel, oyster (Epioblasms capsaeformis) • Endangered Freshwater Mussels Pearlymussel: birdwing (Coradilla caelata), cracking (Hemistena lata), dromedary (Dromus dromas), littlewing (Pegias fabula) www. fws. gov
Flora & Fauna Threatened and Endangered Species in the Rivers • Endangered Freshwater Mussel, oyster (Epioblasms capsaeformis) • Endangered Freshwater Mussels Pearlymussel: birdwing (Coradilla caelata), cracking (Hemistena lata), dromedary (Dromus dromas), littlewing (Pegias fabula) www. fws. gov
 Flora & Fauna Threatened and Endangered Species in the Rivers • Endangered Freshwater Mussel Combshell, Cumberlandian (Epioblasma brevidens) • Endangered Fish Darter, duskytail Entire (Etheostoma percnurum) • Endangered Freshwater Mollusks Fanshell (Cyprogenia stegaria) www. fws. gov www. conservationfisheries. org www. fws. gov
Flora & Fauna Threatened and Endangered Species in the Rivers • Endangered Freshwater Mussel Combshell, Cumberlandian (Epioblasma brevidens) • Endangered Fish Darter, duskytail Entire (Etheostoma percnurum) • Endangered Freshwater Mollusks Fanshell (Cyprogenia stegaria) www. fws. gov www. conservationfisheries. org www. fws. gov
 Flora & Fauna Threatened and Endangered Species in the Rivers • Endangered Freshwater Mussel Purple Bean, (Villosa perpurpurea) • Threatened Fish Chub, slender (Erimystax cahni) • Threatened Fish Chub, spotfin Entire (Cyprinella monacha) www. conservationfisheries. org www. outdooralabama. com www. fws. gov
Flora & Fauna Threatened and Endangered Species in the Rivers • Endangered Freshwater Mussel Purple Bean, (Villosa perpurpurea) • Threatened Fish Chub, slender (Erimystax cahni) • Threatened Fish Chub, spotfin Entire (Cyprinella monacha) www. conservationfisheries. org www. outdooralabama. com www. fws. gov
 Flora & Fauna Threatened and Endangered Species in the Rivers • Threatened Fish Madtom, yellowfin (Noturus flavipinnis) • Endangered Freshwater Mussel Monkeyface, Appalachian (Ouadrula sparsa) • Endangered Freshwater Mussel Monkeyface, Cumberland (Ouadrula intermedia) www. tolweb. org www. fws. gov
Flora & Fauna Threatened and Endangered Species in the Rivers • Threatened Fish Madtom, yellowfin (Noturus flavipinnis) • Endangered Freshwater Mussel Monkeyface, Appalachian (Ouadrula sparsa) • Endangered Freshwater Mussel Monkeyface, Cumberland (Ouadrula intermedia) www. tolweb. org www. fws. gov
 Flora & Fauna Threatened and Endangered Species in the Rivers • Endangered Bivalve -Pigtoe, finerayed (Fusconaia cunelus) -Pigtoe, rough (Pleurobema plenum) -Pigtoe, shiny (Fusconaia cor) www. fws. gov
Flora & Fauna Threatened and Endangered Species in the Rivers • Endangered Bivalve -Pigtoe, finerayed (Fusconaia cunelus) -Pigtoe, rough (Pleurobema plenum) -Pigtoe, shiny (Fusconaia cor) www. fws. gov
 Flora & Fauna Forests • Forest help to protect a healthy ecosystem – Help absorb rain which reduces flooding and erosion – Decreases runoff which can harm stream ecosystems – Reduce air pollution – Shade – Micro ecosystems http: //www. vanaturally. org/guide/forests. html
Flora & Fauna Forests • Forest help to protect a healthy ecosystem – Help absorb rain which reduces flooding and erosion – Decreases runoff which can harm stream ecosystems – Reduce air pollution – Shade – Micro ecosystems http: //www. vanaturally. org/guide/forests. html
 Flora & Fauna Deforestation • Number one cause of deforestation in VA is urban and community development. – Loss of 68, 000 acres every year • As of 2001 forests in Virginia counted for $30. 5 billion dollars annually to the economy. • In 2001 389 million cubic feet of forests were harvested. • Logging operations have gotten better at replanting areas, unfortunately to cut costs monoculture fast growing pines replace the original diverse ecosystems.
Flora & Fauna Deforestation • Number one cause of deforestation in VA is urban and community development. – Loss of 68, 000 acres every year • As of 2001 forests in Virginia counted for $30. 5 billion dollars annually to the economy. • In 2001 389 million cubic feet of forests were harvested. • Logging operations have gotten better at replanting areas, unfortunately to cut costs monoculture fast growing pines replace the original diverse ecosystems.
 Flora & Fauna Minerals • Around 35 million short tons of Coal was produced a year in VA from 1970 -1997 • Mountain Top removal destroys microenvironment and the burning of coal produces emissions of GHGs. www. ilovemountains. org
Flora & Fauna Minerals • Around 35 million short tons of Coal was produced a year in VA from 1970 -1997 • Mountain Top removal destroys microenvironment and the burning of coal produces emissions of GHGs. www. ilovemountains. org
 Flora & Fauna What Can be Done? Near term Mediation of Impacts Reduce further deforestation by better development planning try to reduce sprawl Regulate Logging industry enforce real sustainable forestry prevent monocultures Institute measures to limit loss corridors, land preservation Fund research and monitoring efforts to baselines and trends for biodiversity Consider taxing industrial transportation within and throughout VA Consider extreme weather event likelihood in zoning and building code actions Close coal burning plants
Flora & Fauna What Can be Done? Near term Mediation of Impacts Reduce further deforestation by better development planning try to reduce sprawl Regulate Logging industry enforce real sustainable forestry prevent monocultures Institute measures to limit loss corridors, land preservation Fund research and monitoring efforts to baselines and trends for biodiversity Consider taxing industrial transportation within and throughout VA Consider extreme weather event likelihood in zoning and building code actions Close coal burning plants
 What Can be Done? Flora & Fauna Policy changes: reduce direct impacts • Subsidize conversion to sustainable agriculture, which has soon success in some small farms in the region • Invest in Ecotourism – – Recreation and travel Appalachian Trail Blue Ridge Parkway George Washington and Jefferson National Forests • Support NGOs – Western Virginia Land Trust – Sierra Club • Cap and trade for CO 2 emissions • Imposing taxes on energy usage • Charging electric at rates that fluctuate to represent production costs.
What Can be Done? Flora & Fauna Policy changes: reduce direct impacts • Subsidize conversion to sustainable agriculture, which has soon success in some small farms in the region • Invest in Ecotourism – – Recreation and travel Appalachian Trail Blue Ridge Parkway George Washington and Jefferson National Forests • Support NGOs – Western Virginia Land Trust – Sierra Club • Cap and trade for CO 2 emissions • Imposing taxes on energy usage • Charging electric at rates that fluctuate to represent production costs.
 Flora & Fauna What else can be done? Policy changes: reduce direct impacts Streamline the process for species to be granted endangered or threatened status and protection Adequately fund and enforce the Endangered Species Act of 1973 Introduce threatened species to new feasible habitats, so long as this would not further cause environmental damage Develop green energy sources to reduce emissions Wind turbines have already proven to be profitable in nearby regions in Appalachia Cap road construction but expand mass transit
Flora & Fauna What else can be done? Policy changes: reduce direct impacts Streamline the process for species to be granted endangered or threatened status and protection Adequately fund and enforce the Endangered Species Act of 1973 Introduce threatened species to new feasible habitats, so long as this would not further cause environmental damage Develop green energy sources to reduce emissions Wind turbines have already proven to be profitable in nearby regions in Appalachia Cap road construction but expand mass transit
 Flora & Fauna And What More Can Be Done? A Gigaton Saved is a Kilawatt Earned • Pass legislation to ban HOA restrictions on clotheslines • Regulate lawn mower emissions • Restrict median mowing of state roads to areas necessitated by safety concerns
Flora & Fauna And What More Can Be Done? A Gigaton Saved is a Kilawatt Earned • Pass legislation to ban HOA restrictions on clotheslines • Regulate lawn mower emissions • Restrict median mowing of state roads to areas necessitated by safety concerns
 Flora & Fauna What Else Can We Do? Recognize True Consumptive Costs Require billing for all energy production, agricultural and commercial externalities to cover all warming adaptation and mitigation costs That is: Tax CO² emissions (~sales tax) for all goods and services with exemptions as needed for low income residents
Flora & Fauna What Else Can We Do? Recognize True Consumptive Costs Require billing for all energy production, agricultural and commercial externalities to cover all warming adaptation and mitigation costs That is: Tax CO² emissions (~sales tax) for all goods and services with exemptions as needed for low income residents
 Flora & Fauna Works Cited • • • • US Fish & Wildlife Service www. fws. gov University of Michigan Museum of Zoology http: //animaldiversity. ummz. umich. edu NY State Department of Environmental Conservation www. dec. ny. gov Virginia Sustainable Building Network www. vsbn. org VA Department of Environmental Quality www. deq. virginia. gov VA Department of Conservation and Recreation www. dcr. virginia. gov Conservation Fisheries www. conservationfisheries. org Outdoor Alabama www. outdooralabama. com Tree of Life Web Project http: //tolweb. org Animal Pictures Archive www. animalpicturesarchive. com I Love Mountains www. ilovemountains. org Coal is Dirty www. coal-is-dirty. com Google Images – – – – Highway 81 http: //www. virginia. org/images/Shenbig. gif Kudzu www. kokudzu. com Water contamination http: //sitewellthysolutions. com VA Big-Eared Bat www. scenic-suffolk. co. uk/2008/04/bats. html Grey Bat http: //greenupgrader. com/wp-content/uploads/2009/05/greybat. jpg Bats http: //www. netcore. ca/~peleetom/Bats%20 in%20 sunset%202. jpg Runoff http: //veganverve. files. wordpress. com/2008/08/cows. jpg
Flora & Fauna Works Cited • • • • US Fish & Wildlife Service www. fws. gov University of Michigan Museum of Zoology http: //animaldiversity. ummz. umich. edu NY State Department of Environmental Conservation www. dec. ny. gov Virginia Sustainable Building Network www. vsbn. org VA Department of Environmental Quality www. deq. virginia. gov VA Department of Conservation and Recreation www. dcr. virginia. gov Conservation Fisheries www. conservationfisheries. org Outdoor Alabama www. outdooralabama. com Tree of Life Web Project http: //tolweb. org Animal Pictures Archive www. animalpicturesarchive. com I Love Mountains www. ilovemountains. org Coal is Dirty www. coal-is-dirty. com Google Images – – – – Highway 81 http: //www. virginia. org/images/Shenbig. gif Kudzu www. kokudzu. com Water contamination http: //sitewellthysolutions. com VA Big-Eared Bat www. scenic-suffolk. co. uk/2008/04/bats. html Grey Bat http: //greenupgrader. com/wp-content/uploads/2009/05/greybat. jpg Bats http: //www. netcore. ca/~peleetom/Bats%20 in%20 sunset%202. jpg Runoff http: //veganverve. files. wordpress. com/2008/08/cows. jpg


