c72ea774cff8a68786af0f552735db19.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 FLIPPED CLASSROOM ACTIVITY CONSTRUCTOR – USING EXISTING CONTENT
FLIPPED CLASSROOM ACTIVITY CONSTRUCTOR – USING EXISTING CONTENT
 Financial Mathematics - An Introduction A. Muthulakshmi PSG College of Technology
Financial Mathematics - An Introduction A. Muthulakshmi PSG College of Technology
 Course Outcome • Upon completion of the course the students will be able to understand the different financial terminologies such as money market instruments, bonds, stocks and derivatives.
Course Outcome • Upon completion of the course the students will be able to understand the different financial terminologies such as money market instruments, bonds, stocks and derivatives.
 Overview Ø Introduction Ø Periodic Compounding Ø Continuous Compounding Ø Return
Overview Ø Introduction Ø Periodic Compounding Ø Continuous Compounding Ø Return
 A. Muthulakshmi Periodic, Continuous Compounding and Return MATHEMATICAL FINANCE MATHEMATICS UG STUDENTS PSG COLLEGE OF TCHNOLOGY, COIMBATORE, TN 5
A. Muthulakshmi Periodic, Continuous Compounding and Return MATHEMATICAL FINANCE MATHEMATICS UG STUDENTS PSG COLLEGE OF TCHNOLOGY, COIMBATORE, TN 5
 Introduction What is Financial Mathematics? Financial Mathematics is a Mathematical tool to study problems arising in Finance These includes: ü Probability and Statistics ü Stochastic Processes ü Optimization ü Economics ü Numerical Analysis ü Partial Differential Equations and others
Introduction What is Financial Mathematics? Financial Mathematics is a Mathematical tool to study problems arising in Finance These includes: ü Probability and Statistics ü Stochastic Processes ü Optimization ü Economics ü Numerical Analysis ü Partial Differential Equations and others
 Introduction…. . The scope of the word “Finance” could be very broad, but here we understand in terms of ‘Investment of Money for the purpose of receiving more money (Hopefully!!) at sometime in future’ Financial Mathematics = Investment Science/Investment Theory
Introduction…. . The scope of the word “Finance” could be very broad, but here we understand in terms of ‘Investment of Money for the purpose of receiving more money (Hopefully!!) at sometime in future’ Financial Mathematics = Investment Science/Investment Theory
 Introduction…. . ØInvestment as an art form has always been there but it developed as Science/Theory in late 50’s , 60’s and early 70’s due to pioneering work of üFisher Black üMyron Scholes üRobert Merton ØMerton and Scholes: Nobel prize in Economics (1997)
Introduction…. . ØInvestment as an art form has always been there but it developed as Science/Theory in late 50’s , 60’s and early 70’s due to pioneering work of üFisher Black üMyron Scholes üRobert Merton ØMerton and Scholes: Nobel prize in Economics (1997)
 Introduction…. . ØFinancial Market deals the trading of financial assets (simply called assets) Market ØAsset: It is a financial instrument that can be bought environment where the or sold. trade takes place Cash Instrument There are two types: (Bonds, loans, deposits, Risk free (Bank deposits, bonds etc) Financial issued by Government, etc) Instrument Risky (Stocks) Tradable asset of any kind Derivative Instrument (contracts, options, etc)
Introduction…. . ØFinancial Market deals the trading of financial assets (simply called assets) Market ØAsset: It is a financial instrument that can be bought environment where the or sold. trade takes place Cash Instrument There are two types: (Bonds, loans, deposits, Risk free (Bank deposits, bonds etc) Financial issued by Government, etc) Instrument Risky (Stocks) Tradable asset of any kind Derivative Instrument (contracts, options, etc)
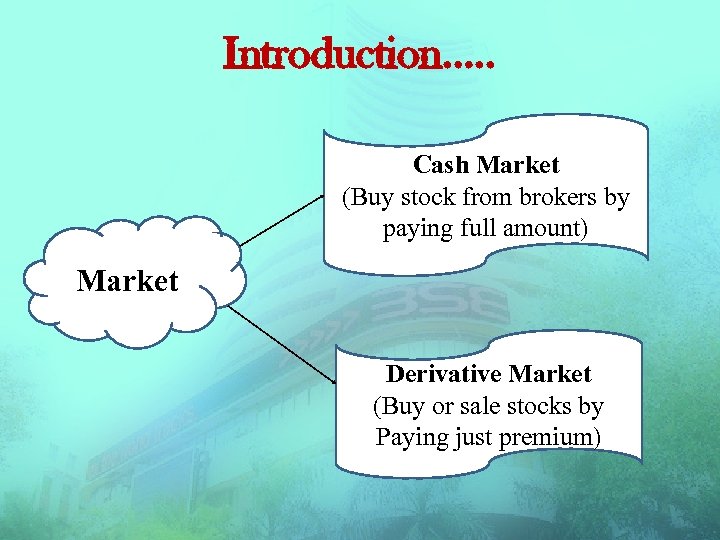 Introduction…. . Cash Market (Buy stock from brokers by paying full amount) Market Derivative Market (Buy or sale stocks by Paying just premium)
Introduction…. . Cash Market (Buy stock from brokers by paying full amount) Market Derivative Market (Buy or sale stocks by Paying just premium)
 Introduction…. . Some Notations Ø Time Horizon: Single period model, i. e. , time scale to be two instants only Two time instants (Single period) A(0): Price of one Bond at T=0 A(1): Price of one Bond at T=1 S(0): Price of one share of stock at T=0 S(1): Price of one share of stock at T=1 Note: ü Bond is risk free so A(0) and A(1) are known. Both are deterministic ü Stock is risky. S(0) is known (deterministic) but S(1) is a random variable
Introduction…. . Some Notations Ø Time Horizon: Single period model, i. e. , time scale to be two instants only Two time instants (Single period) A(0): Price of one Bond at T=0 A(1): Price of one Bond at T=1 S(0): Price of one share of stock at T=0 S(1): Price of one share of stock at T=1 Note: ü Bond is risk free so A(0) and A(1) are known. Both are deterministic ü Stock is risky. S(0) is known (deterministic) but S(1) is a random variable
 Introduction…. . Some Notations ü Rate of return for bond ü Rate of return for stock is deterministic but is a random variable
Introduction…. . Some Notations ü Rate of return for bond ü Rate of return for stock is deterministic but is a random variable
 Simple Interest Ø The initial deposit is called the principal (P). If ‘r’ is the annual simple interest rate offered by a bank then the interest earned on P is ‘r. P’, and so the principal grows to P+r. P. Ø The value of the investment becomes V(1) = P+r. P = (1+r)P V(2) = (1+2 r)P In general, V(t) = (1+tr)P
Simple Interest Ø The initial deposit is called the principal (P). If ‘r’ is the annual simple interest rate offered by a bank then the interest earned on P is ‘r. P’, and so the principal grows to P+r. P. Ø The value of the investment becomes V(1) = P+r. P = (1+r)P V(2) = (1+2 r)P In general, V(t) = (1+tr)P
 Simple Interest Ø If interest is calculated on daily basis, then the interest earned in one day is . After ‘n’ days the interest becomes . So, the value of investment after n days is In general, V(t) = (1+tr)P V(0) = P and the factor (1+tr) is called growth factor
Simple Interest Ø If interest is calculated on daily basis, then the interest earned in one day is . After ‘n’ days the interest becomes . So, the value of investment after n days is In general, V(t) = (1+tr)P V(0) = P and the factor (1+tr) is called growth factor
 Simple Interest • K(0, 1) = r • The return over one year from the initial time ‘ 0’ = rate of interest
Simple Interest • K(0, 1) = r • The return over one year from the initial time ‘ 0’ = rate of interest
 Periodic Compounding Ø The interest earned is added to the principal amount periodically. Ø In case of monthly compounding, the first interest payment is . The principal will grow to after one month. The investment for second month is and the principal will grow to
Periodic Compounding Ø The interest earned is added to the principal amount periodically. Ø In case of monthly compounding, the first interest payment is . The principal will grow to after one month. The investment for second month is and the principal will grow to
 Periodic Compounding… Ø So, after n months, the investment becomes and after t years, it is Ø Instead of monthly compounding, if the time between two consecutive interest payment is years, then the initial principal P becomes Ø Growth factor is
Periodic Compounding… Ø So, after n months, the investment becomes and after t years, it is Ø Instead of monthly compounding, if the time between two consecutive interest payment is years, then the initial principal P becomes Ø Growth factor is
 Periodic Compounding… Ø The present value or discounted value of V(t) is Ø For ‘n’ years ,
Periodic Compounding… Ø The present value or discounted value of V(t) is Ø For ‘n’ years ,
 Periodic Compounding… Ø Eg: How long it will take to double the capital attracting interest at 3% compounded daily? V(t) = 2 P t = 23 years 39 days (approximately)
Periodic Compounding… Ø Eg: How long it will take to double the capital attracting interest at 3% compounded daily? V(t) = 2 P t = 23 years 39 days (approximately)
 Continuous Compounding Also,
Continuous Compounding Also,
 Continuous Compounding… Eg: Given that the future value of Rs. 950 subject to continuous compounding will be Rs. 1000 after half a year. What is the interest rate? r= 10. 26% (approximately)
Continuous Compounding… Eg: Given that the future value of Rs. 950 subject to continuous compounding will be Rs. 1000 after half a year. What is the interest rate? r= 10. 26% (approximately)
 Return The return on a deposit attracting interest compounded periodically In particular, For m =1 K(0, 1) = r; K(1, 2) = r
Return The return on a deposit attracting interest compounded periodically In particular, For m =1 K(0, 1) = r; K(1, 2) = r
 QUIZ I Let S(0) = Price of one share of a stock at t = 0 Let S(1) = Price of one share of a stock at t = 1 Let B(0) = Price of one bond at t = 0, Let B(1) = Price of one bond at t = 1 01 Rate of return of an asset ………………. . 02 Rate of return of a stock ……. . ……………. . II Let an investor hold ‘x’ shares of stock and ‘y’ units of bond at t = 0, and P: (x, y) is a Portfolio, then 03 04 III The value of P at t = 0 is VP(0) = ……………. . Rate of return of Portfolio is ……………. …… Let B(0) = 200, B(1) = 210, S(0) = 160 and. What is the expected return on the stock? Consider the portfolio P: (50, 60), then determine the expected return and the risk for the given portfolio.
QUIZ I Let S(0) = Price of one share of a stock at t = 0 Let S(1) = Price of one share of a stock at t = 1 Let B(0) = Price of one bond at t = 0, Let B(1) = Price of one bond at t = 1 01 Rate of return of an asset ………………. . 02 Rate of return of a stock ……. . ……………. . II Let an investor hold ‘x’ shares of stock and ‘y’ units of bond at t = 0, and P: (x, y) is a Portfolio, then 03 04 III The value of P at t = 0 is VP(0) = ……………. . Rate of return of Portfolio is ……………. …… Let B(0) = 200, B(1) = 210, S(0) = 160 and. What is the expected return on the stock? Consider the portfolio P: (50, 60), then determine the expected return and the risk for the given portfolio.
 Web links: • http: //www. math. cornell. edu/~mec/Summer 2008/spulido/Deriv atives. html • http: //www. diffen. com/difference/Forward_Contract_vs_Future s_Contract • http: //www. investopedia. com/articles/optioninvestor/07/options _beat_market. asp • https: //www. aaii. com/journal/article/the-role-of-risk-free-assetsin-your-long-term- portfolio. touch
Web links: • http: //www. math. cornell. edu/~mec/Summer 2008/spulido/Deriv atives. html • http: //www. diffen. com/difference/Forward_Contract_vs_Future s_Contract • http: //www. investopedia. com/articles/optioninvestor/07/options _beat_market. asp • https: //www. aaii. com/journal/article/the-role-of-risk-free-assetsin-your-long-term- portfolio. touch


