aerodynamics.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 FLIGHT & AERODYNAMICS
FLIGHT & AERODYNAMICS
 Progress in aviation industry develops rapidly nowadays. With the help of pilots observations, discoveries and engineering taught people learned to create an innovation types of aircraft wings and construction which helps to fly on the different altitudes and modes of flight.
Progress in aviation industry develops rapidly nowadays. With the help of pilots observations, discoveries and engineering taught people learned to create an innovation types of aircraft wings and construction which helps to fly on the different altitudes and modes of flight.
 Flight is the process by which an object moves either through the air, or movement beyond earth's atmosphere (as in the case of spaceflight).
Flight is the process by which an object moves either through the air, or movement beyond earth's atmosphere (as in the case of spaceflight).
 Aerodynamics is a branch of dynamics concerned with studying the motion of air, particularly when it interacts with a moving object. Aerodynamics is a subfield of fluid dynamics and gas dynamics, with much theory shared between them.
Aerodynamics is a branch of dynamics concerned with studying the motion of air, particularly when it interacts with a moving object. Aerodynamics is a subfield of fluid dynamics and gas dynamics, with much theory shared between them.
 Science of wings A wing is a surface used to produce lift for flight through the air or another gaseous or fluid medium.
Science of wings A wing is a surface used to produce lift for flight through the air or another gaseous or fluid medium.
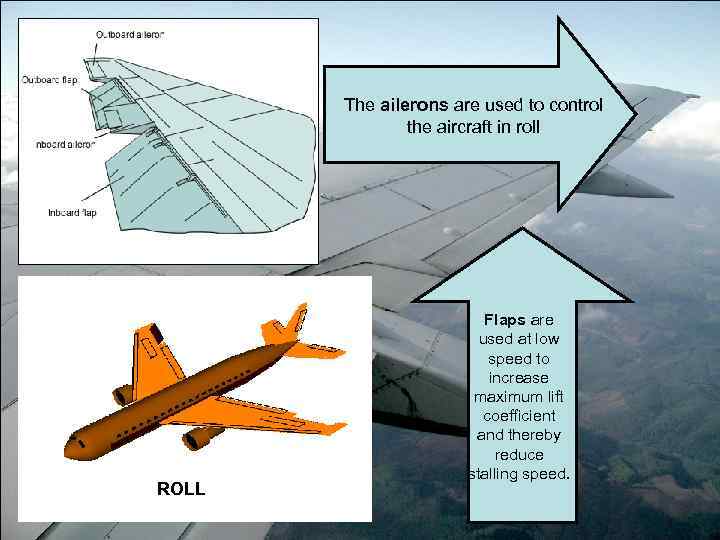 The ailerons are used to control the aircraft in roll ROLL Flaps are used at low speed to increase maximum lift coefficient and thereby reduce stalling speed.
The ailerons are used to control the aircraft in roll ROLL Flaps are used at low speed to increase maximum lift coefficient and thereby reduce stalling speed.
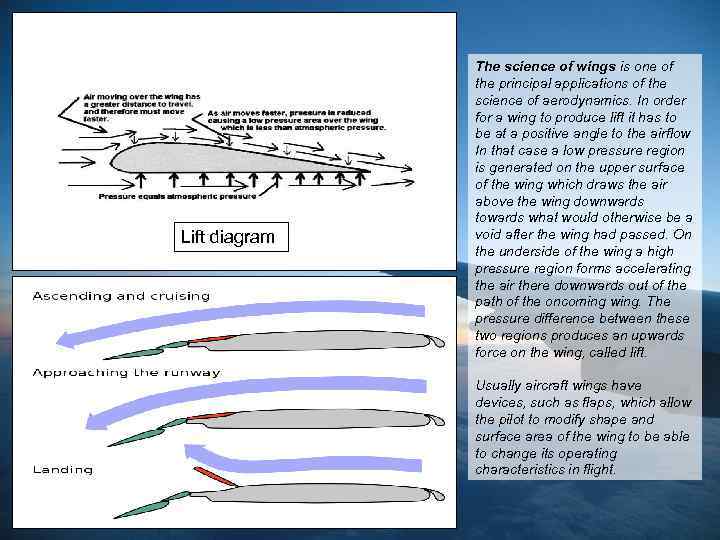 Lift diagram The science of wings is one of the principal applications of the science of aerodynamics. In order for a wing to produce lift it has to be at a positive angle to the airflow In that case a low pressure region is generated on the upper surface of the wing which draws the air above the wing downwards towards what would otherwise be a void after the wing had passed. On the underside of the wing a high pressure region forms accelerating the air there downwards out of the path of the oncoming wing. The pressure difference between these two regions produces an upwards force on the wing, called lift. Usually aircraft wings have devices, such as flaps, which allow the pilot to modify shape and surface area of the wing to be able to change its operating characteristics in flight.
Lift diagram The science of wings is one of the principal applications of the science of aerodynamics. In order for a wing to produce lift it has to be at a positive angle to the airflow In that case a low pressure region is generated on the upper surface of the wing which draws the air above the wing downwards towards what would otherwise be a void after the wing had passed. On the underside of the wing a high pressure region forms accelerating the air there downwards out of the path of the oncoming wing. The pressure difference between these two regions produces an upwards force on the wing, called lift. Usually aircraft wings have devices, such as flaps, which allow the pilot to modify shape and surface area of the wing to be able to change its operating characteristics in flight.
 forward wing A swept wing is a wing angled beyond the spanwise axis, generally used to delay the drag rise caused by fluid compressibility. Unusual variants of this design feature are forward sweep, variable sweep wings , and pivoting wings. Pivoting wing Variable wing
forward wing A swept wing is a wing angled beyond the spanwise axis, generally used to delay the drag rise caused by fluid compressibility. Unusual variants of this design feature are forward sweep, variable sweep wings , and pivoting wings. Pivoting wing Variable wing
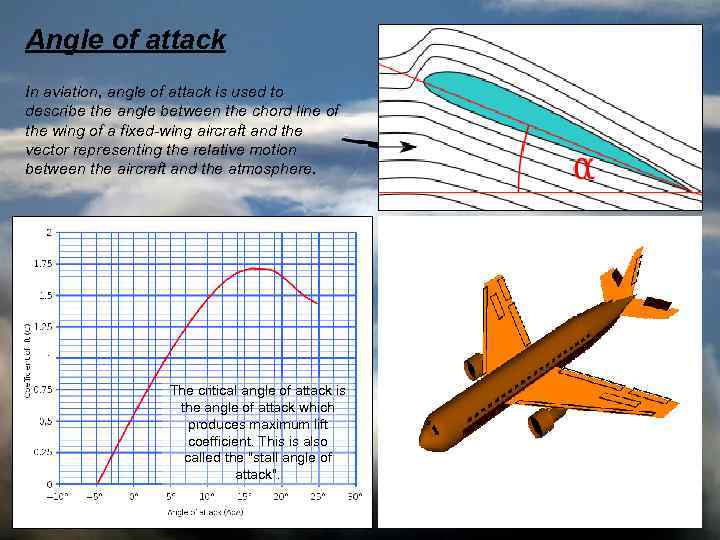 Angle of attack In aviation, angle of attack is used to describe the angle between the chord line of the wing of a fixed-wing aircraft and the vector representing the relative motion between the aircraft and the atmosphere. The critical angle of attack is the angle of attack which produces maximum lift coefficient. This is also called the "stall angle of attack".
Angle of attack In aviation, angle of attack is used to describe the angle between the chord line of the wing of a fixed-wing aircraft and the vector representing the relative motion between the aircraft and the atmosphere. The critical angle of attack is the angle of attack which produces maximum lift coefficient. This is also called the "stall angle of attack".
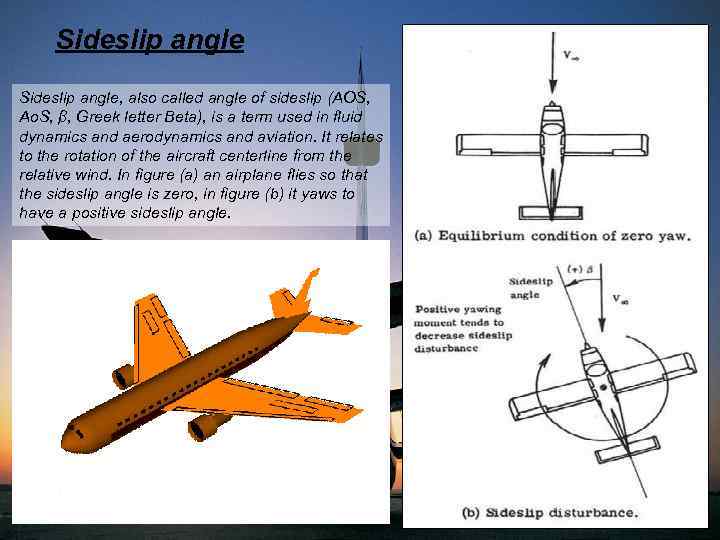 Sideslip angle, also called angle of sideslip (AOS, Ao. S, β, Greek letter Beta), is a term used in fluid dynamics and aerodynamics and aviation. It relates to the rotation of the aircraft centerline from the relative wind. In figure (a) an airplane flies so that the sideslip angle is zero, in figure (b) it yaws to have a positive sideslip angle.
Sideslip angle, also called angle of sideslip (AOS, Ao. S, β, Greek letter Beta), is a term used in fluid dynamics and aerodynamics and aviation. It relates to the rotation of the aircraft centerline from the relative wind. In figure (a) an airplane flies so that the sideslip angle is zero, in figure (b) it yaws to have a positive sideslip angle.
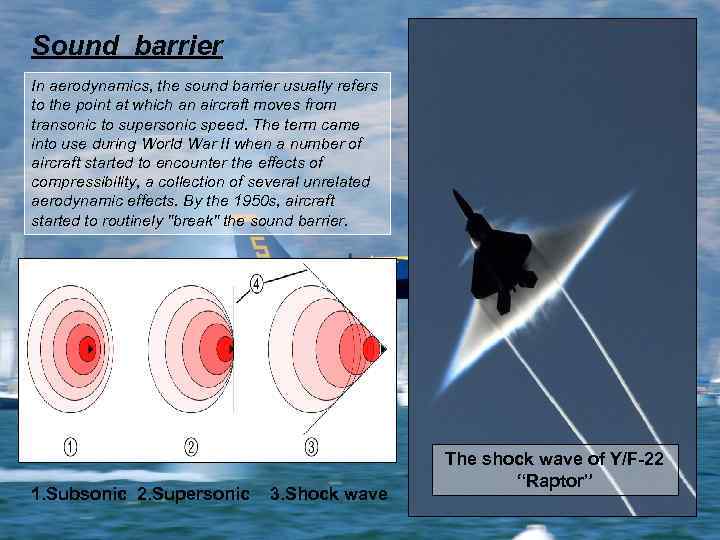 Sound barrier In aerodynamics, the sound barrier usually refers to the point at which an aircraft moves from transonic to supersonic speed. The term came into use during World War II when a number of aircraft started to encounter the effects of compressibility, a collection of several unrelated aerodynamic effects. By the 1950 s, aircraft started to routinely "break" the sound barrier. 1. Subsonic 2. Supersonic 3. Shock wave The shock wave of Y/F-22 “Raptor”
Sound barrier In aerodynamics, the sound barrier usually refers to the point at which an aircraft moves from transonic to supersonic speed. The term came into use during World War II when a number of aircraft started to encounter the effects of compressibility, a collection of several unrelated aerodynamic effects. By the 1950 s, aircraft started to routinely "break" the sound barrier. 1. Subsonic 2. Supersonic 3. Shock wave The shock wave of Y/F-22 “Raptor”
 AEROBATICS Aerobatics is the practice of maneuvers involving aircraft flying attitudes that are not used in normal flight. On the aerobatic festivals pilots show all features of its aircraft flying almost beyond the physical laws.
AEROBATICS Aerobatics is the practice of maneuvers involving aircraft flying attitudes that are not used in normal flight. On the aerobatic festivals pilots show all features of its aircraft flying almost beyond the physical laws.
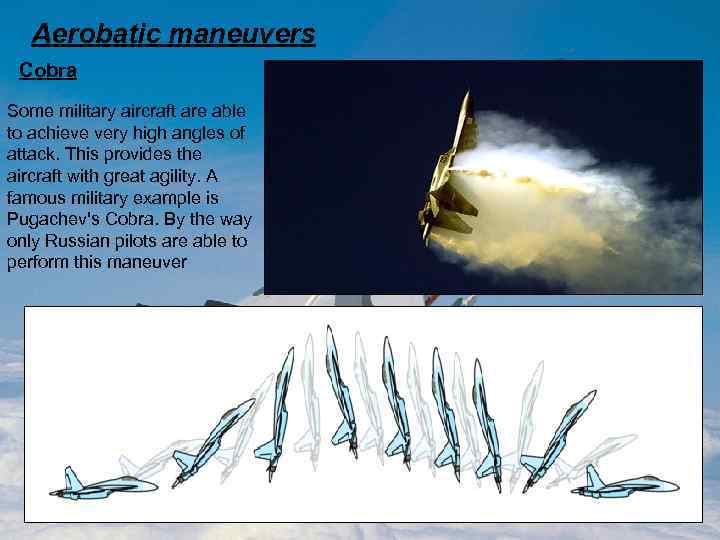 Aerobatic maneuvers Cobra Some military aircraft are able to achieve very high angles of attack. This provides the aircraft with great agility. A famous military example is Pugachev's Cobra. By the way only Russian pilots are able to perform this maneuver
Aerobatic maneuvers Cobra Some military aircraft are able to achieve very high angles of attack. This provides the aircraft with great agility. A famous military example is Pugachev's Cobra. By the way only Russian pilots are able to perform this maneuver
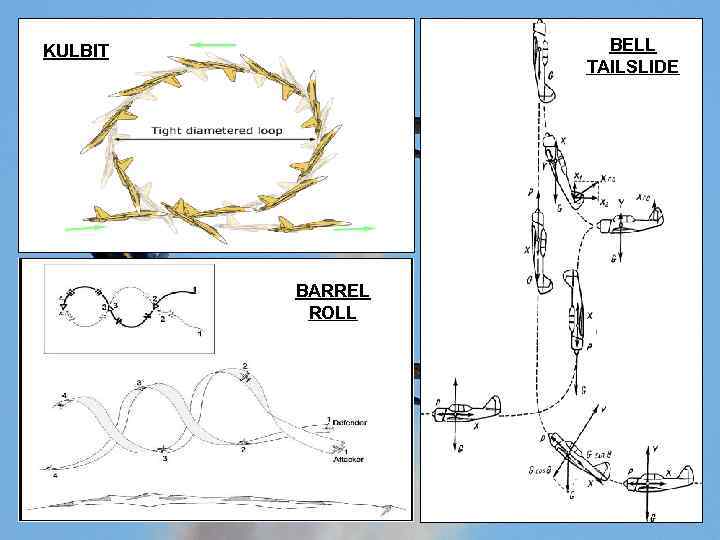 BELL TAILSLIDE KULBIT BARREL ROLL
BELL TAILSLIDE KULBIT BARREL ROLL
 Combine maneuvering barrel roll fountain loop
Combine maneuvering barrel roll fountain loop
 THE END
THE END


