0803708c64ca089d9d7996e6868fb434.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24

Flexible Biochemical Manufacturing: Strategic Considerations April 18, 2002 Robert Bottome 1
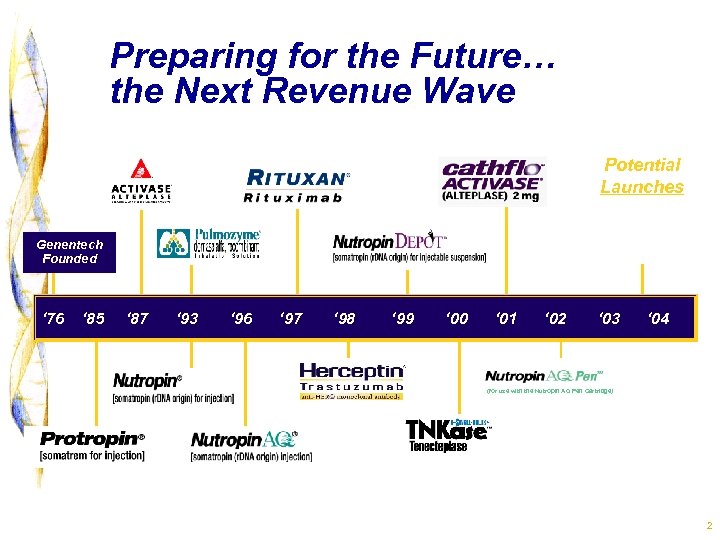
Preparing for the Future… the Next Revenue Wave Potential Launches Xolair Xanelim Avastin Genentech Founded ‘ 76 ‘ 85 ‘ 87 ‘ 93 ‘ 96 ‘ 97 ‘ 98 ‘ 99 ‘ 00 ‘ 01 ‘ 02 ‘ 03 ‘ 04 (for use with the Nutropin AQ Pen Cartridge) 2

Abstract n The strategic value of the SSF Biochemical manufacturing facility à Flexibility • Ability to rapidly reconfigure shrinks development timelines • Maximizes return on asset à à n Offsets the risk, limitations à à n Proximity to Development organization Able to make any known biotech molecule High cost of living Disaster risk Multi-product, mixed facility (GMP and clinical) inspection risks Challenge to continuous improvement and standardization efforts The De-coupled paradigm enabled à Engaged, dedicated cross-trained technicians 3
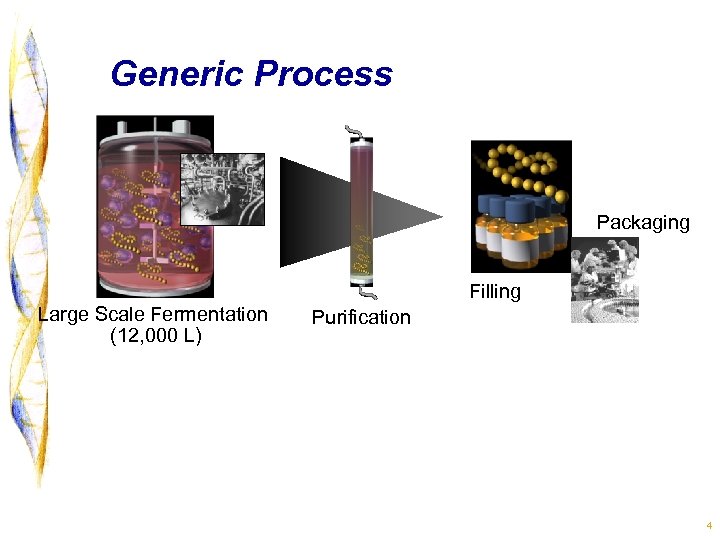
Generic Process Packaging Filling Large Scale Fermentation (12, 000 L) Purification 4
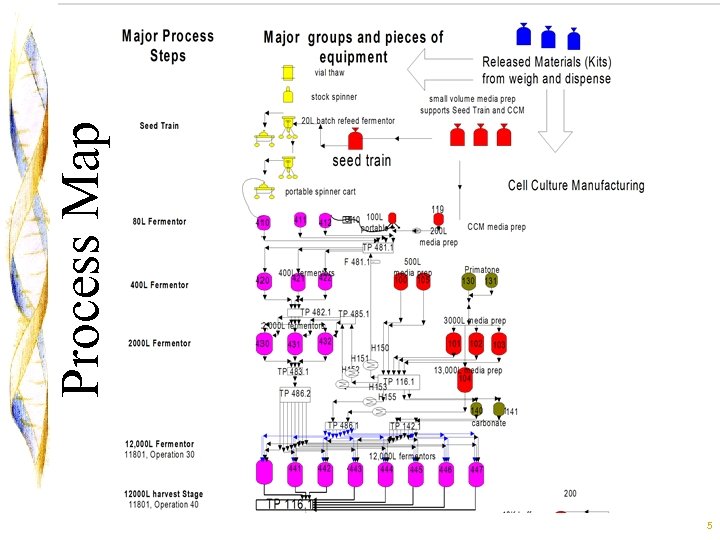
5 Process Map
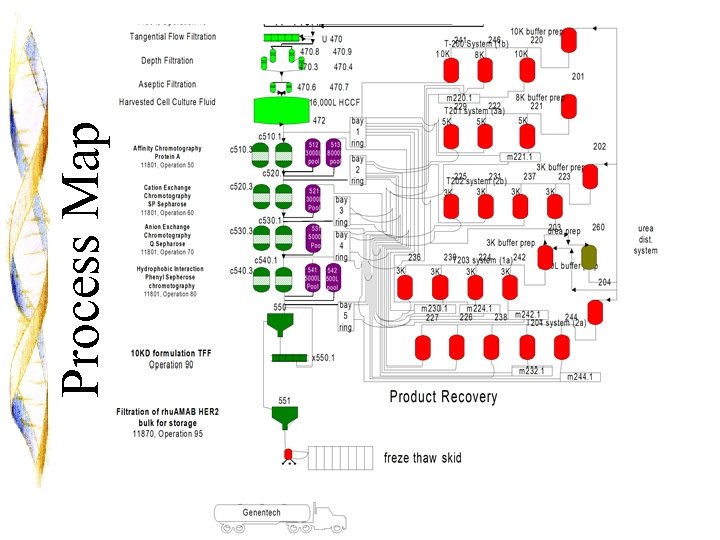
6 Process Map
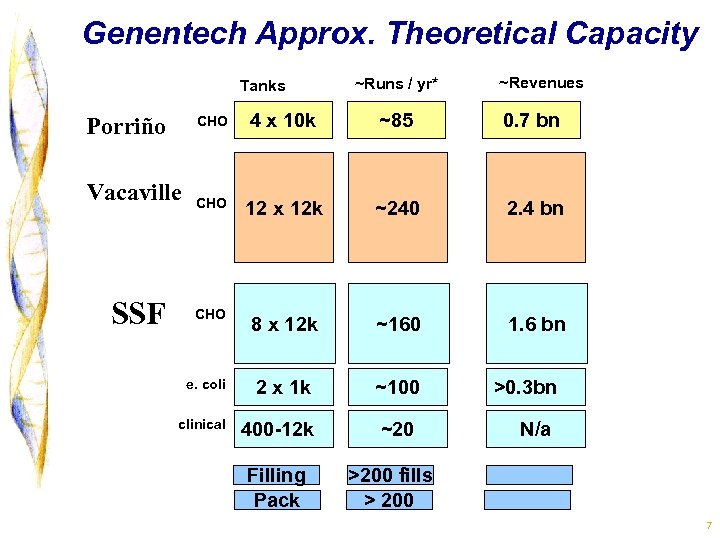
Genentech Approx. Theoretical Capacity Tanks ~Revenues CHO 4 x 10 k ~85 0. 7 bn CHO 12 x 12 k ~240 2. 4 bn CHO 8 x 12 k ~160 1. 6 bn e. coli 2 x 1 k ~100 clinical 400 -12 k ~20 Porriño Vacaville SSF ~Runs / yr* Filling Pack >0. 3 bn N/a >200 fills > 200 7

B 3 A/3 B Fermentation 8

Portable Skids Used to Purify Growth Hormone 9

Top of Buffer Prep 10

Bottom of Pool tanks, chrom skid is behind you 11

Today’s Situation at SSF: Challenges n Current LRP says 7 years, à Development Org moved to revise to 9 years as realistic; à PPC and EC held line at 7 years n Development Operating Team Productivity Initiative has set a timeline compression goal à down to 5. 5 years 12

Today’s Situation at SSF: Challenges n Compliance Challenges: à à Simultaneous Multi-product Licensure (“ 4 plants”); Mixed plant / Multiple Flow Paths: • Research, Clinical, Marketed • Inter-path tensions, validation, asset management • Highly utilized critical constraint utilities n Complex Manufacturing Plant: à Mixture of • Old & New, Traditional & State-of-the-art • Fully automated, Semi-automated and Manual – Manual valves lead to errors à Inconsistencies burden technicians • Controls, automation / HMI’s à Low standardization complicates improvement efforts • Poorly defined labor model, takt times • Not all skids equipped with comparable defenses Footnotes: Slides 52 -53 13
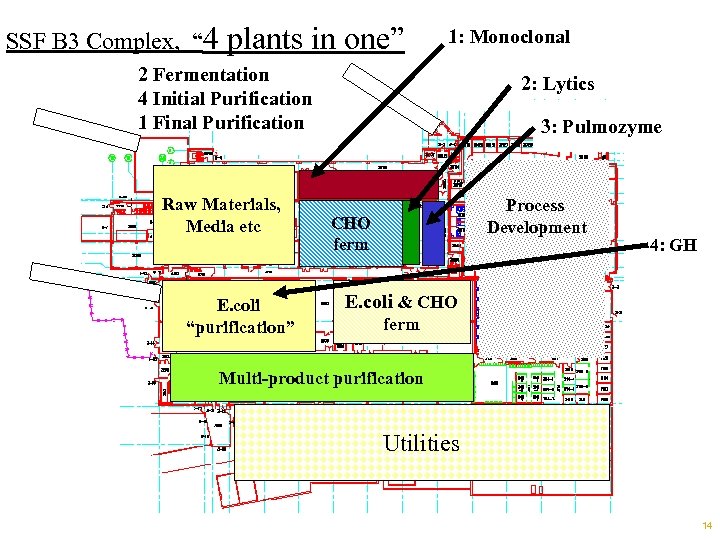
SSF B 3 Complex, “ 4 plants in one” 1: Monoclonal 2 Fermentation 4 Initial Purification 1 Final Purification Raw Materials, Media etc E. coli “purification” 2: Lytics 3: Pulmozyme Process Development CHO ferm 4: GH E. coli & CHO ferm Multi-product purification Utilities 14

Changeover n As plant ramped up production volume and variety of products (t. PA and Pulmozyme to Antibodies) à Original arbitrary window of 21 days between campaigns inadequate • Pressure to do more in the same amount of time • Effort to decrease change-over – 3 weeks to 2 weeks, pilot – Equipment, process start up varies by product – Optimize changeover by combining low overlap product » Activase to c 2 b 8 in one day » Eliminate overlap, focus on single shared asset » Pulmozyme uses everything, high overlap » 10 days current max 15
16

Lost Product Scenario’s n ‘Cracked’ Manual Valve à Product flowing to drain, masked • Detected late n Non standard skid design à Buffer made and held, not transferred • Salt collected in dead leg à Pumped onto column through pool filter • Not around through buffer filter n Non standard automation à ‘Acknowledge’ has dwell on some not others • Technician left room, and product pumped to floor n Inconsistent mixing à Variety of vessel sizes, impeller lengths, mixing times 17

Today’s Situation at SSF: Challenges n Optimize fit: Process vs Plant à To what degree does the ‘ideal’ process have to be sub-optimized to match the constraints in the plant • Can we successfully challenge these constraints? à Cost control • Can we learn everything we need at 1000 L vs 12 K? à QC test and validation • Standard tests, uniform turn-around times • Validation philosophy to enable reliable manufacturing 18

Today’s Situation at SSF: Strengths n n n Only site capable of producing all products Strategic back-up to other sites Sole supplier for Pulmozyme, Lytics and Growth Hormone Only site for E. coli production Production of Clinical Material & Launching pad for Development projects Flexible: best Development time 5. 5 years (Pulmozyme) Can schedule complex Development campaigns & changes etc. n Flexible = competitive advantage (e. g. Enbrel) 19

Today’s Situation at SSF: Strengths n CHO processes remarkably similar à à Ferm; Purification = 3 chromatographies and 1 formulation Resins and membranes standardized • Long lead times, high expense n Decoupled à Concurrent processing possible • Build buffers to cushion impact of process variability • Changeover begins before routing complete n Redundant à Parallel paths available • Equipment availability issues NOTE: Vacaville plant is tightly coupled and highly automated—one large routing with few parallel paths available. Changeovers take weeks (e. g. recipes need to be re-written for each product); problems become preemptive outages. 20
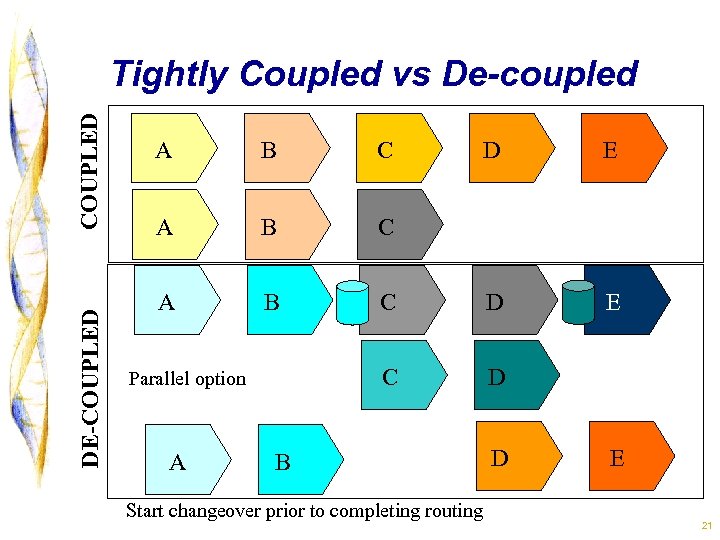
DE-COUPLED Tightly Coupled vs De-coupled A B C A B A E C D E C Parallel option D D B Start changeover prior to completing routing D E 21
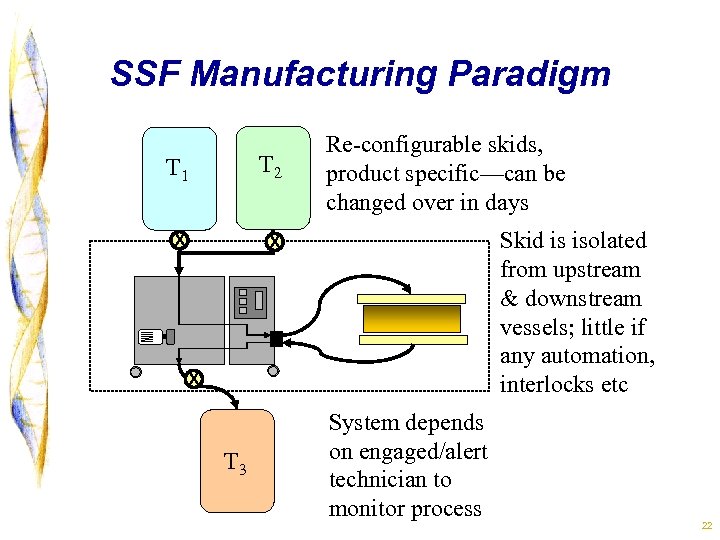
SSF Manufacturing Paradigm T 1 T 2 x Re-configurable skids, product specific—can be changed over in days x Skid is isolated from upstream & downstream vessels; little if any automation, interlocks etc x T 3 System depends on engaged/alert technician to monitor process 22

Technician Engagement n Recruitment and Retention à à n Wear & Tear issues à à à n Transport Parts, tools Automation design for support Ownership à à n Career path Cross-trained vs silo’d Recognition Mastery Readiness rituals 23

Aspects of Flexibility n Product Range à Excellent, able to make all molecules • Optimum for Dnase and Activase • Less ideal for others n Mobility à Higher in some areas • Final was designed for flexibility – Central core, ample floor space n Uniformity of Performance à Variable / vulnerable • Utility constraints • Latent errors—automation needs to support operator – Not mask failures 24
0803708c64ca089d9d7996e6868fb434.ppt