5c206cf01cb3407ca83368a2c7479da5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42
 Flat. Jet Dispensing & Printing Technology Copyright, 2004 © Multimedia Studio Budapest- HUNGARY
Flat. Jet Dispensing & Printing Technology Copyright, 2004 © Multimedia Studio Budapest- HUNGARY
 Flat. Jet • Liquid dispensing • High Throughput Printing
Flat. Jet • Liquid dispensing • High Throughput Printing
 Objective • The development of the technology is motivated by the gap between production rate of a conventional offset and the digital systems. • Other ink-jet developers are searching solutions to reduce the ejected ink quantity – our aiming was opposite – the high flow rate.
Objective • The development of the technology is motivated by the gap between production rate of a conventional offset and the digital systems. • Other ink-jet developers are searching solutions to reduce the ejected ink quantity – our aiming was opposite – the high flow rate.
 The aimed resolution • The theoretical limit of the human eye’s resolution is 1’ angle – it means that from 3 meter viewing distance, 1 mm size details can hardly be distinguished. • Our basic objective was to find solution to produce images for large distance observation with as high throughput as possible.
The aimed resolution • The theoretical limit of the human eye’s resolution is 1’ angle – it means that from 3 meter viewing distance, 1 mm size details can hardly be distinguished. • Our basic objective was to find solution to produce images for large distance observation with as high throughput as possible.
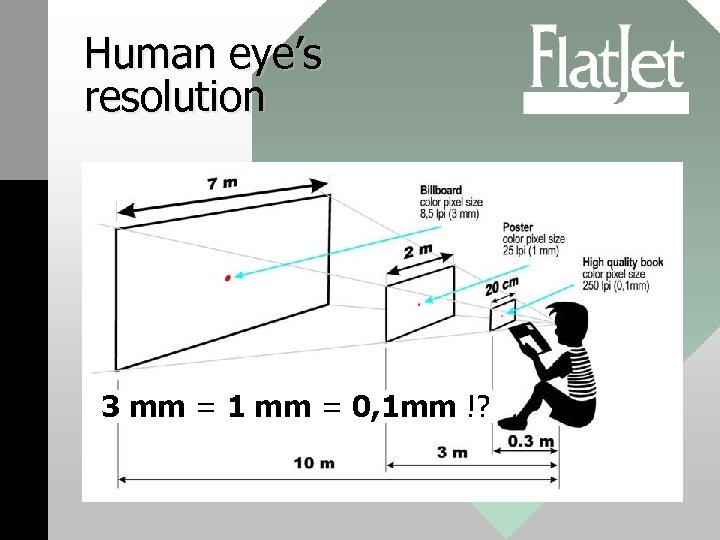 Human eye’s resolution 3 mm = 1 mm = 0, 1 mm !?
Human eye’s resolution 3 mm = 1 mm = 0, 1 mm !?
 The result • simple robust construction, possibility of low production costs • very low & extremely high liquid flow • Possibility of media-wide operating large -format digital systems • Individually replaceable printing elements
The result • simple robust construction, possibility of low production costs • very low & extremely high liquid flow • Possibility of media-wide operating large -format digital systems • Individually replaceable printing elements
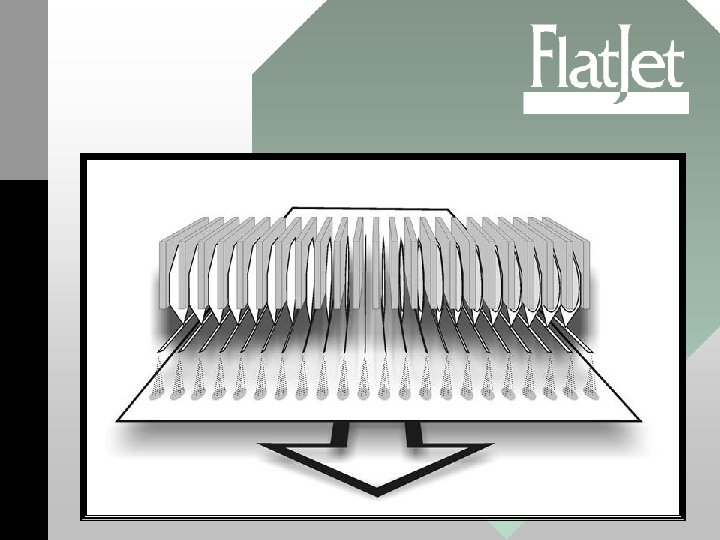
 Simple and easy to manufacture • Flat. Jet is assembled of a metal plate and tube, and a piezo-ceramic disc • Simple and relatively robust mechanical construction • Conventional materials and manufacturing
Simple and easy to manufacture • Flat. Jet is assembled of a metal plate and tube, and a piezo-ceramic disc • Simple and relatively robust mechanical construction • Conventional materials and manufacturing
 The head
The head
 The liquid transfer • From pico-liter range ejection up to 50 microliters/s continuous flow
The liquid transfer • From pico-liter range ejection up to 50 microliters/s continuous flow
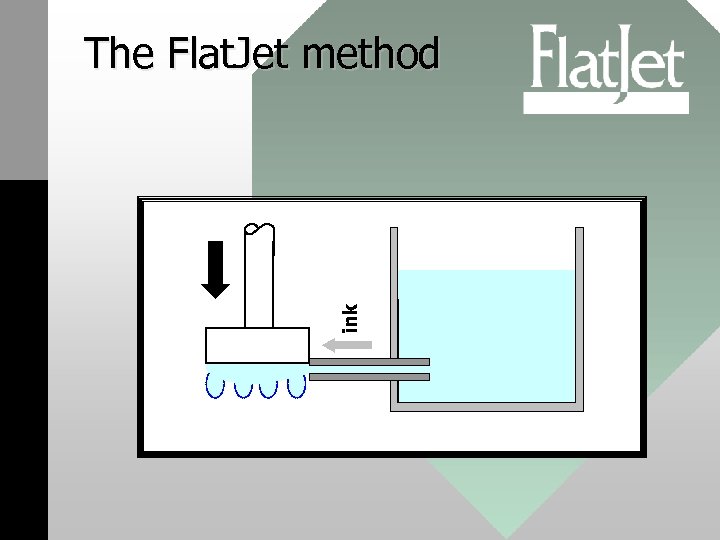 ink The Flat. Jet method
ink The Flat. Jet method
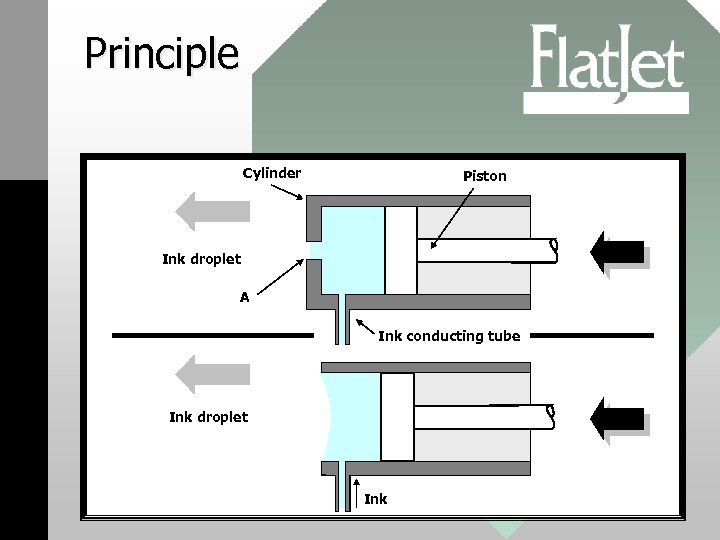 Principle Cylinder Piston Ink droplet A Ink conducting tube Ink droplet Ink
Principle Cylinder Piston Ink droplet A Ink conducting tube Ink droplet Ink
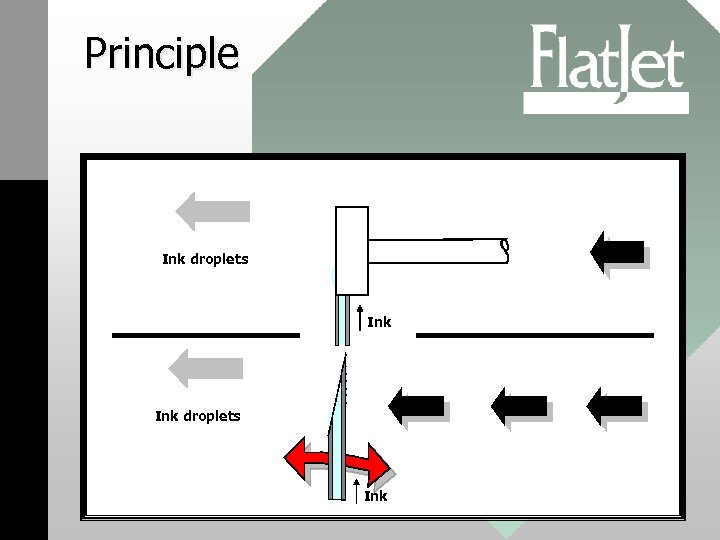 Principle Ink droplets Ink
Principle Ink droplets Ink
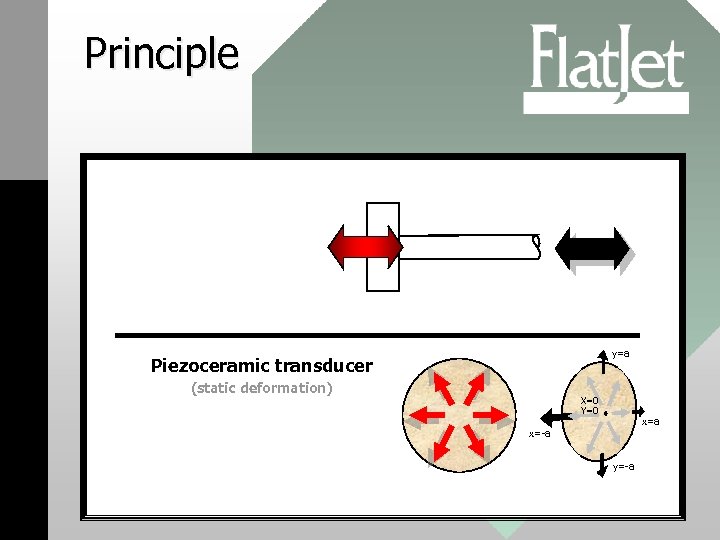 Principle y=a Piezoceramic transducer (static deformation) X=0 Y=0 x=a x=-a y=-a
Principle y=a Piezoceramic transducer (static deformation) X=0 Y=0 x=a x=-a y=-a
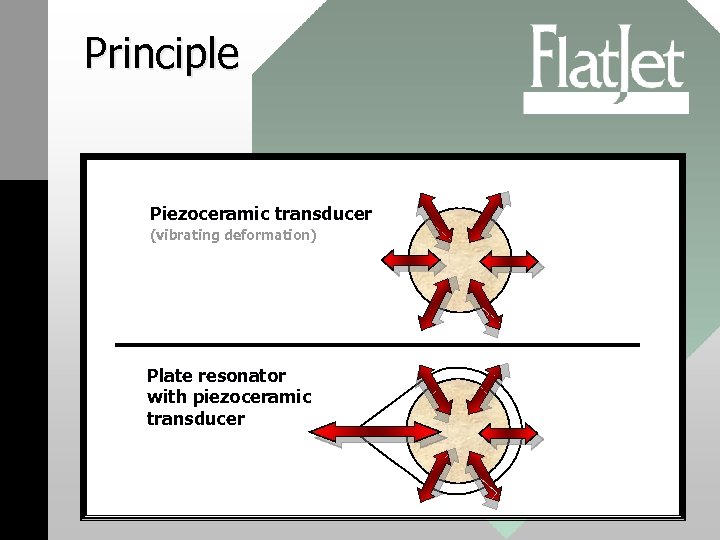 Principle Piezoceramic transducer (vibrating deformation) Plate resonator with piezoceramic transducer
Principle Piezoceramic transducer (vibrating deformation) Plate resonator with piezoceramic transducer
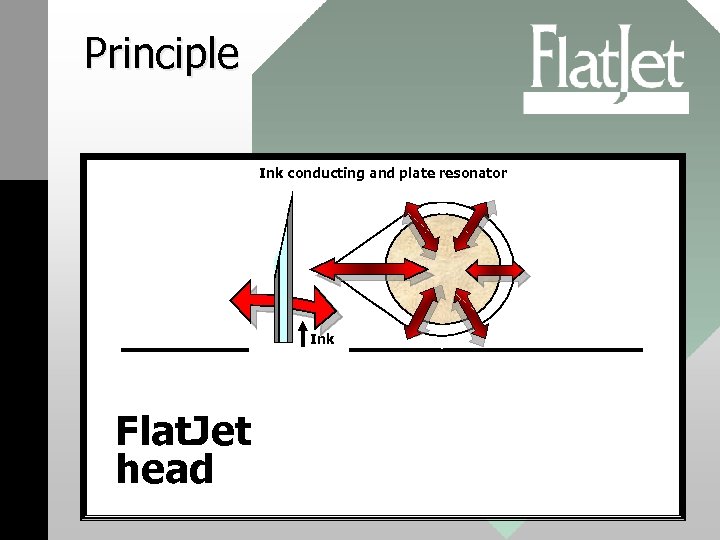 Principle Ink conducting and plate resonator Ink Flat. Jet head
Principle Ink conducting and plate resonator Ink Flat. Jet head
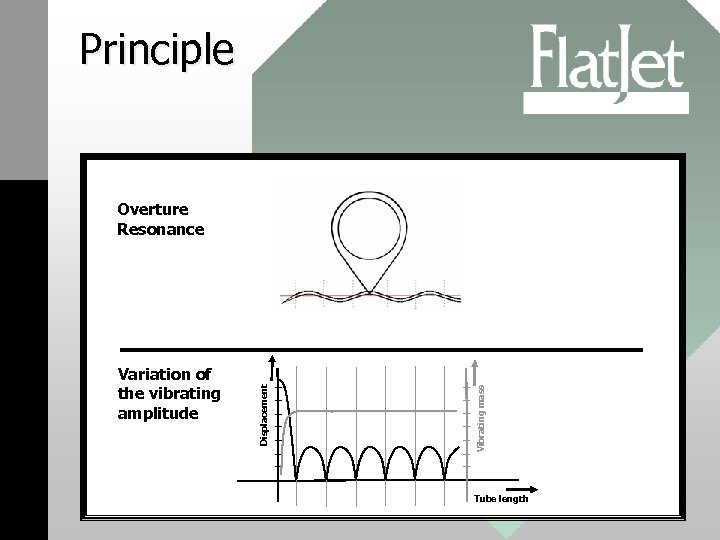 Principle Vibrating mass Variation of the vibrating amplitude Displacement Overture Resonance Tube length
Principle Vibrating mass Variation of the vibrating amplitude Displacement Overture Resonance Tube length
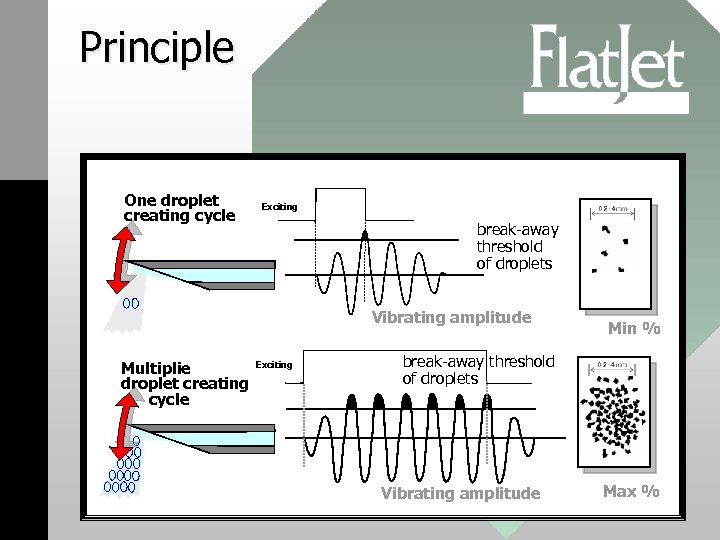 Principle One droplet creating cycle Exciting break-away threshold of droplets Vibrating amplitude Multiplie droplet creating cycle Exciting Min % break-away threshold of droplets Vibrating amplitude Max %
Principle One droplet creating cycle Exciting break-away threshold of droplets Vibrating amplitude Multiplie droplet creating cycle Exciting Min % break-away threshold of droplets Vibrating amplitude Max %
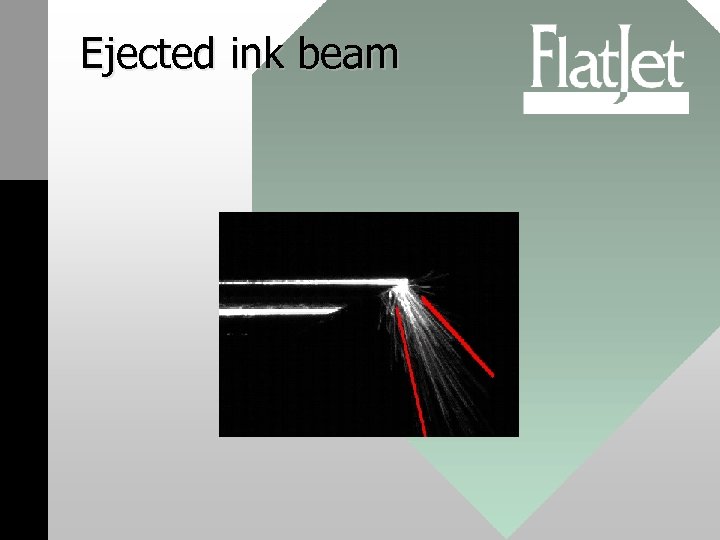 Ejected ink beam
Ejected ink beam
 Ejection process Microscopic shot with high speed camera, with shifted exposure phases
Ejection process Microscopic shot with high speed camera, with shifted exposure phases
 Ejection process
Ejection process
 Extent of deformation at the tip Microscopic shot with stroboscopic backight, shifted phase
Extent of deformation at the tip Microscopic shot with stroboscopic backight, shifted phase
 Local speed and acceleration at the tip • At 200 k. Hz frequency the periodical speed of the tip surface is about 6 m/s • The acceleration at the dead point exceeds the 1. 000 g
Local speed and acceleration at the tip • At 200 k. Hz frequency the periodical speed of the tip surface is about 6 m/s • The acceleration at the dead point exceeds the 1. 000 g
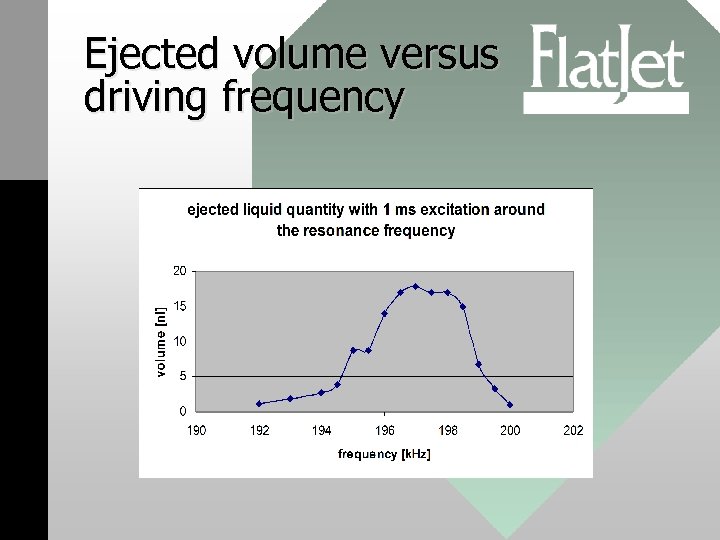 Ejected volume versus driving frequency
Ejected volume versus driving frequency
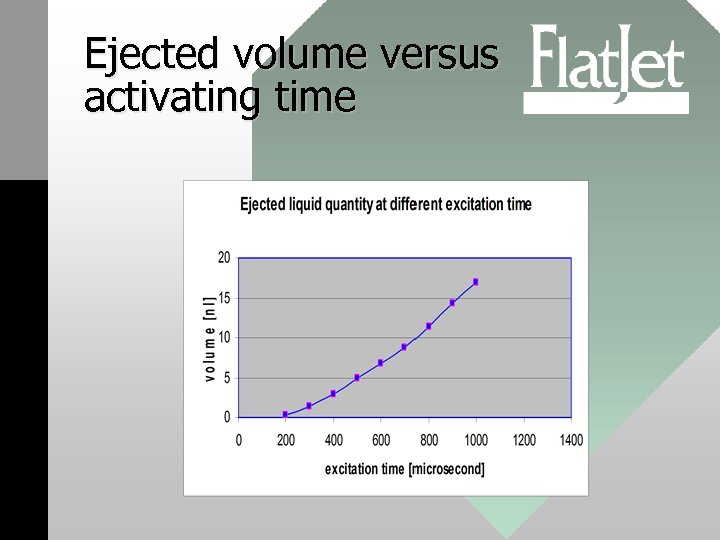 Ejected volume versus activating time
Ejected volume versus activating time
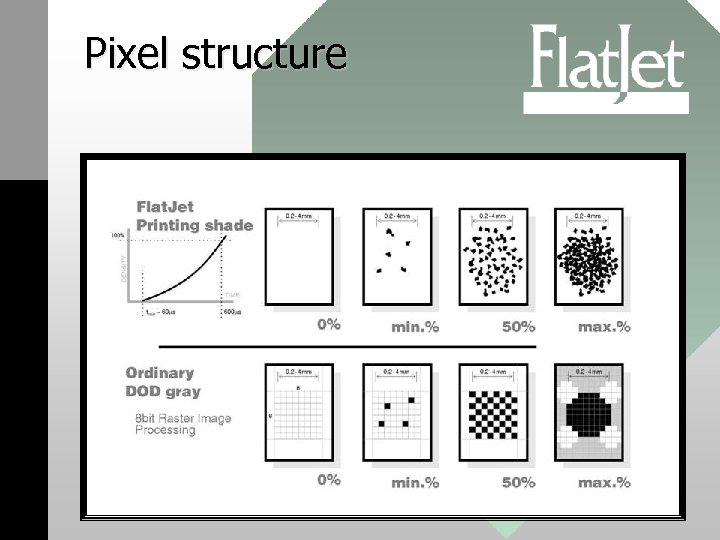 Pixel structure
Pixel structure
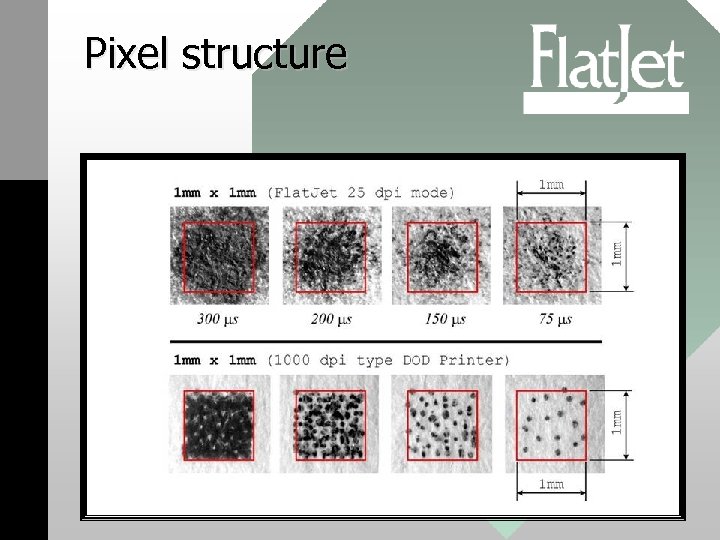 Pixel structure
Pixel structure
 Color mode Flat. Jet Raster color
Color mode Flat. Jet Raster color
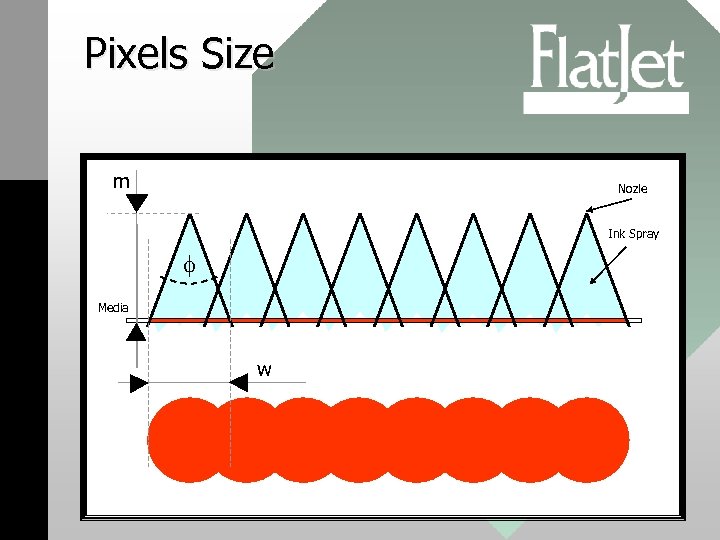 Pixels Size m Nozle Ink Spray f Media w
Pixels Size m Nozle Ink Spray f Media w
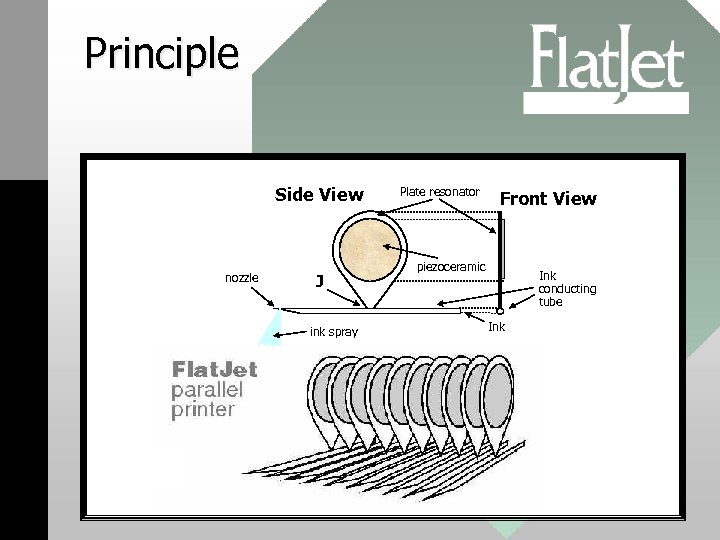 Principle Side View nozzle J ink spray Plate resonator Front View piezoceramic Ink conducting tube Ink
Principle Side View nozzle J ink spray Plate resonator Front View piezoceramic Ink conducting tube Ink
 64 head test printing bar
64 head test printing bar
 Planed media-wide printer
Planed media-wide printer
 Application fields • Printing on ordinary materials • Printing on special materials • Different applications – Chemical, Pharmaceutical or Microbiological dispensers – Moisturizers
Application fields • Printing on ordinary materials • Printing on special materials • Different applications – Chemical, Pharmaceutical or Microbiological dispensers – Moisturizers
 Printing on ordinary materials • Industrial media-wide large-format ink-jet printing • Low cost media, low cost inks & low operating costs • Wide variety of media & inks • Computer to print technology
Printing on ordinary materials • Industrial media-wide large-format ink-jet printing • Low cost media, low cost inks & low operating costs • Wide variety of media & inks • Computer to print technology
 Printing on special materials • Ceramics • Wallpaper • Glass • Corrugated paper • Wood • Leather • Concrete • Plastics • Metals • …etc.
Printing on special materials • Ceramics • Wallpaper • Glass • Corrugated paper • Wood • Leather • Concrete • Plastics • Metals • …etc.
 First Industrial Application • Zimmer Gmb. H (A) Chromotex Textile Printer
First Industrial Application • Zimmer Gmb. H (A) Chromotex Textile Printer
 First Industrial Application • Zimmer Gmb. H (A) Chromotex Textile Printer
First Industrial Application • Zimmer Gmb. H (A) Chromotex Textile Printer
 Patents EU)(DE)(GB)(FR)(AT)(IT)(BE)(NL)(ES)(CH)(CA)(AU)(JP)
Patents EU)(DE)(GB)(FR)(AT)(IT)(BE)(NL)(ES)(CH)(CA)(AU)(JP)
 Hopes and Expectations • A NEW TECHNOLOGY CAN SUCCEED IF IT IS QUICKER OR BETTER OR CHEAPER • THE FLATJET CAN BE QUICKER & BETTER & CHEAPER
Hopes and Expectations • A NEW TECHNOLOGY CAN SUCCEED IF IT IS QUICKER OR BETTER OR CHEAPER • THE FLATJET CAN BE QUICKER & BETTER & CHEAPER
 QUICKER • Possible 1 sq. meter per second printing speed • The printing width can be increased without limits
QUICKER • Possible 1 sq. meter per second printing speed • The printing width can be increased without limits
 BETTER • High tone / color resolution (possibly 256 shade in a pixel) • High color saturation pigmented inks • Environmentally friendly water based inks • High tolerance in ink parameters (viscosity up to 15 m. Pas)
BETTER • High tone / color resolution (possibly 256 shade in a pixel) • High color saturation pigmented inks • Environmentally friendly water based inks • High tolerance in ink parameters (viscosity up to 15 m. Pas)
 CHEAPER • Low cost media • Low cost inks • Low operating costs • Quick return of investment
CHEAPER • Low cost media • Low cost inks • Low operating costs • Quick return of investment


