02c2a824f9b706d9e75bb2598a4c870b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47
 Five Top Priorities Radiation technology and applications Yuhui Dong Multidisciplinary Research Center Program Review, Beijing October 22, 2013
Five Top Priorities Radiation technology and applications Yuhui Dong Multidisciplinary Research Center Program Review, Beijing October 22, 2013
 Outline • Description of the goals • Recent status • Development strategy • Summary
Outline • Description of the goals • Recent status • Development strategy • Summary
 On the 1 -3 -5 strategic plan of IHEP • To position IHEP to be one of world’s leading high energy physics research centers and a world-class, large, comprehensively multidisciplinary research base.
On the 1 -3 -5 strategic plan of IHEP • To position IHEP to be one of world’s leading high energy physics research centers and a world-class, large, comprehensively multidisciplinary research base.
 The goals • Operating large (user) facilities for multidisciplinary study • Developing cutting-edge experimental methods • Performing research on the frontiers of sciences Large, comprehensively multi-disciplinary research center based on user facilities.
The goals • Operating large (user) facilities for multidisciplinary study • Developing cutting-edge experimental methods • Performing research on the frontiers of sciences Large, comprehensively multi-disciplinary research center based on user facilities.
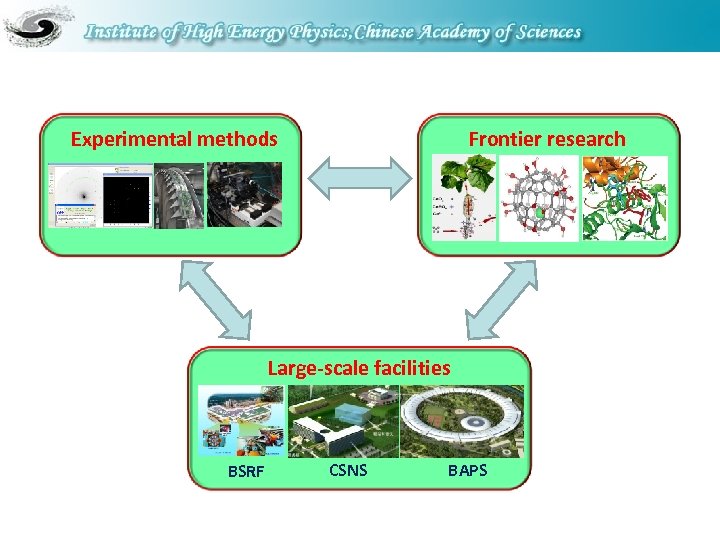 Experimental methods Frontier research Large-scale facilities BSRF CSNS BAPS
Experimental methods Frontier research Large-scale facilities BSRF CSNS BAPS
 The consideration in development • The reasonable development strategy depends on: ü The existing basis ü Opportunities for development • The foundation of IHEP in accelerator-based large facilities • Development in cutting-edge methods and frontier research
The consideration in development • The reasonable development strategy depends on: ü The existing basis ü Opportunities for development • The foundation of IHEP in accelerator-based large facilities • Development in cutting-edge methods and frontier research
 Large facilities The explosive growth of research in China evokes the imminence demand for large (user) facilities (SR and neutron). Only SSRF can not satisfy this requirement, especially the north of China. The growth of structure biology teams in mainland China IHEP is one of the pioneer in the field of SR and spallation neutron source. The accumulation on experimental methods and detectors allows us to construct and operate more powerful facilities.
Large facilities The explosive growth of research in China evokes the imminence demand for large (user) facilities (SR and neutron). Only SSRF can not satisfy this requirement, especially the north of China. The growth of structure biology teams in mainland China IHEP is one of the pioneer in the field of SR and spallation neutron source. The accumulation on experimental methods and detectors allows us to construct and operate more powerful facilities.
 Frontier research • Not only the role of “test center”: the frontier research needs cutting-edge methods • The “in-house” research and cooperation will guide the development of facilities and methods • Ø Ø Ø The criteria for selecting the research fields: Importance Distinguishing features: facility-based Synthetically studies Unreplacibility and promoting the developments of facilities
Frontier research • Not only the role of “test center”: the frontier research needs cutting-edge methods • The “in-house” research and cooperation will guide the development of facilities and methods • Ø Ø Ø The criteria for selecting the research fields: Importance Distinguishing features: facility-based Synthetically studies Unreplacibility and promoting the developments of facilities
 Recent Status • BSRF (in operation), CSNS (in construction), BAPS (R&D) • The research fields established: Ø Protein Life Science and Technology Ø Environmental Health Ø Biological effects of nano-materials
Recent Status • BSRF (in operation), CSNS (in construction), BAPS (R&D) • The research fields established: Ø Protein Life Science and Technology Ø Environmental Health Ø Biological effects of nano-materials
 Development strategy • Facilities and methods Ø BAPS Ø CSNS • Research Ø Synergy: The mechanism of nanomedicine, the immigration/transformation/controlling of meavy metal pollutions Ø Growing point: radiochemistry and nuclear materials
Development strategy • Facilities and methods Ø BAPS Ø CSNS • Research Ø Synergy: The mechanism of nanomedicine, the immigration/transformation/controlling of meavy metal pollutions Ø Growing point: radiochemistry and nuclear materials
 Development in large facilities • We have solid foundation in construction/operation of large-scale facilities. • The requirement for large user facilities in China. • The goal of “world-class, large, comprehensively multidisciplinary research base” mainly depends on the large user facilities, which are guided by the “inhouse” research and cooperation with other teams.
Development in large facilities • We have solid foundation in construction/operation of large-scale facilities. • The requirement for large user facilities in China. • The goal of “world-class, large, comprehensively multidisciplinary research base” mainly depends on the large user facilities, which are guided by the “inhouse” research and cooperation with other teams.
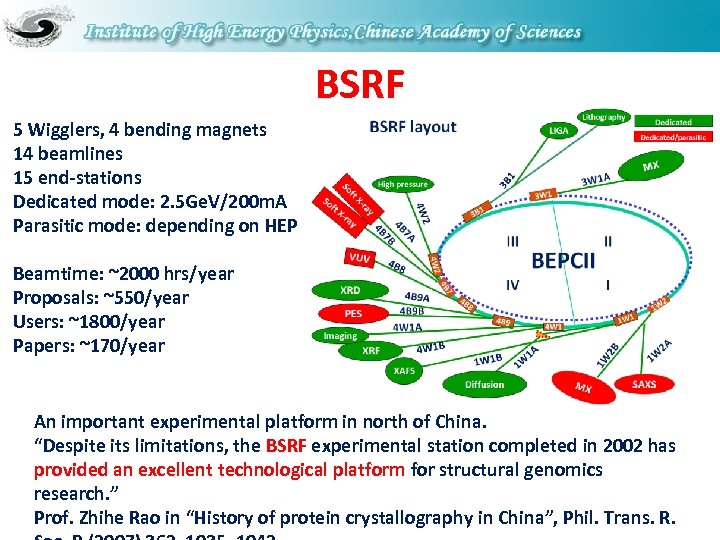 BSRF 5 Wigglers, 4 bending magnets 14 beamlines 15 end-stations Dedicated mode: 2. 5 Ge. V/200 m. A Parasitic mode: depending on HEP Beamtime: ~2000 hrs/year Proposals: ~550/year Users: ~1800/year Papers: ~170/year An important experimental platform in north of China. “Despite its limitations, the BSRF experimental station completed in 2002 has provided an excellent technological platform for structural genomics research. ” Prof. Zhihe Rao in “History of protein crystallography in China”, Phil. Trans. R.
BSRF 5 Wigglers, 4 bending magnets 14 beamlines 15 end-stations Dedicated mode: 2. 5 Ge. V/200 m. A Parasitic mode: depending on HEP Beamtime: ~2000 hrs/year Proposals: ~550/year Users: ~1800/year Papers: ~170/year An important experimental platform in north of China. “Despite its limitations, the BSRF experimental station completed in 2002 has provided an excellent technological platform for structural genomics research. ” Prof. Zhihe Rao in “History of protein crystallography in China”, Phil. Trans. R.
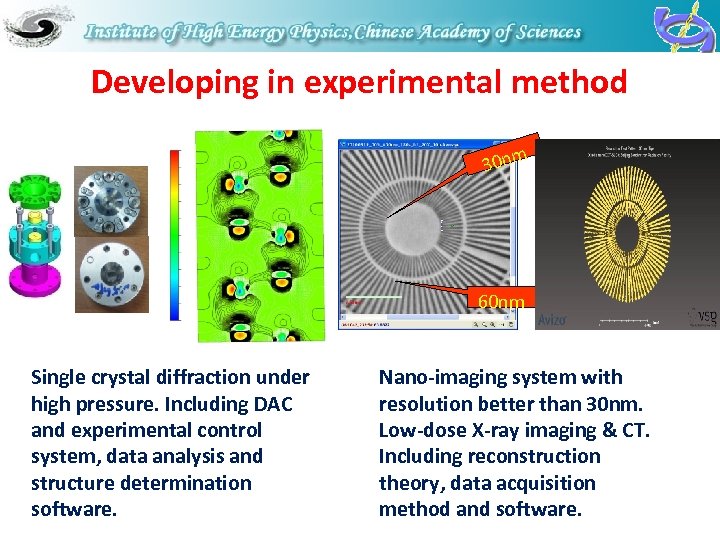 Developing in experimental method 30 nm 60 nm Single crystal diffraction under high pressure. Including DAC and experimental control system, data analysis and structure determination software. Nano-imaging system with resolution better than 30 nm. Low-dose X-ray imaging & CT. Including reconstruction theory, data acquisition method and software.
Developing in experimental method 30 nm 60 nm Single crystal diffraction under high pressure. Including DAC and experimental control system, data analysis and structure determination software. Nano-imaging system with resolution better than 30 nm. Low-dose X-ray imaging & CT. Including reconstruction theory, data acquisition method and software.
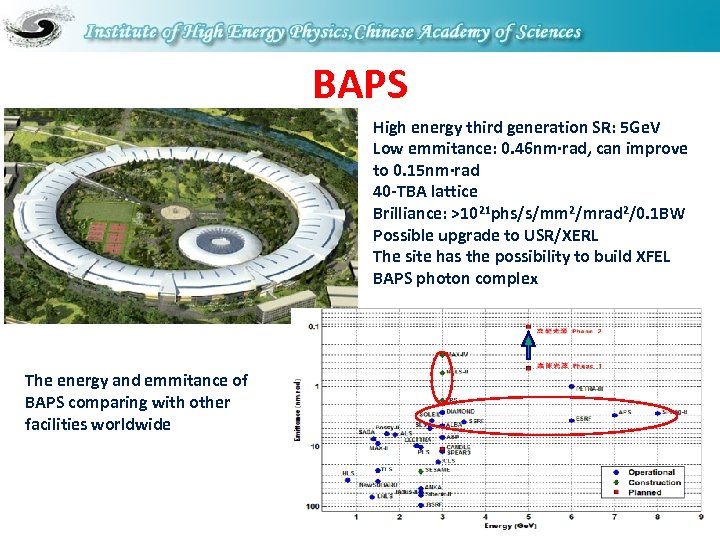 BAPS High energy third generation SR: 5 Ge. V Low emmitance: 0. 46 nm·rad, can improve to 0. 15 nm·rad 40 -TBA lattice Brilliance: >1021 phs/s/mm 2/mrad 2/0. 1 BW Possible upgrade to USR/XERL The site has the possibility to build XFEL BAPS photon complex The energy and emmitance of BAPS comparing with other facilities worldwide
BAPS High energy third generation SR: 5 Ge. V Low emmitance: 0. 46 nm·rad, can improve to 0. 15 nm·rad 40 -TBA lattice Brilliance: >1021 phs/s/mm 2/mrad 2/0. 1 BW Possible upgrade to USR/XERL The site has the possibility to build XFEL BAPS photon complex The energy and emmitance of BAPS comparing with other facilities worldwide
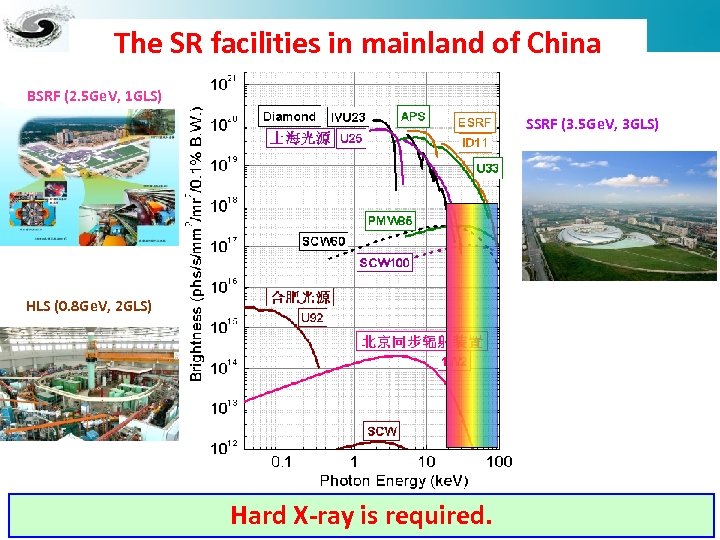 The SR facilities in mainland of China BSRF (2. 5 Ge. V, 1 GLS) SSRF (3. 5 Ge. V, 3 GLS) HLS (0. 8 Ge. V, 2 GLS) Hard X-ray is required.
The SR facilities in mainland of China BSRF (2. 5 Ge. V, 1 GLS) SSRF (3. 5 Ge. V, 3 GLS) HLS (0. 8 Ge. V, 2 GLS) Hard X-ray is required.
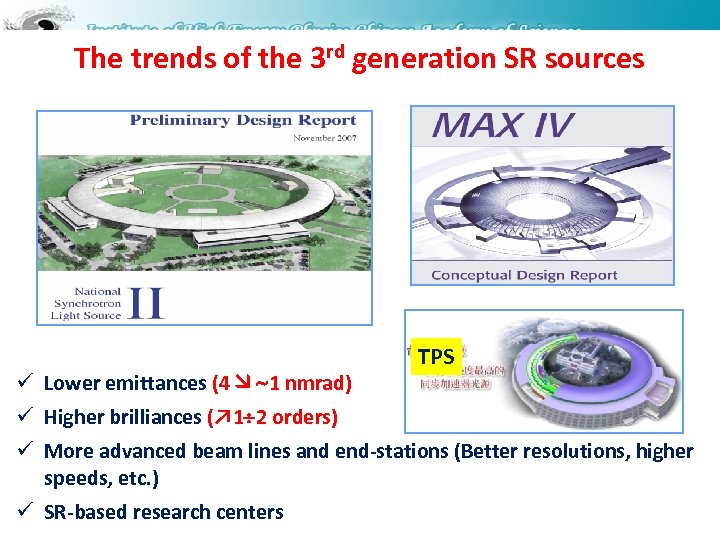 The trends of the 3 rd generation SR sources ü Lower emittances (4 1 nmrad) TPS ü Higher brilliances (↗ 1 2 orders) ü More advanced beam lines and end-stations (Better resolutions, higher speeds, etc. ) ü SR-based research centers 16
The trends of the 3 rd generation SR sources ü Lower emittances (4 1 nmrad) TPS ü Higher brilliances (↗ 1 2 orders) ü More advanced beam lines and end-stations (Better resolutions, higher speeds, etc. ) ü SR-based research centers 16
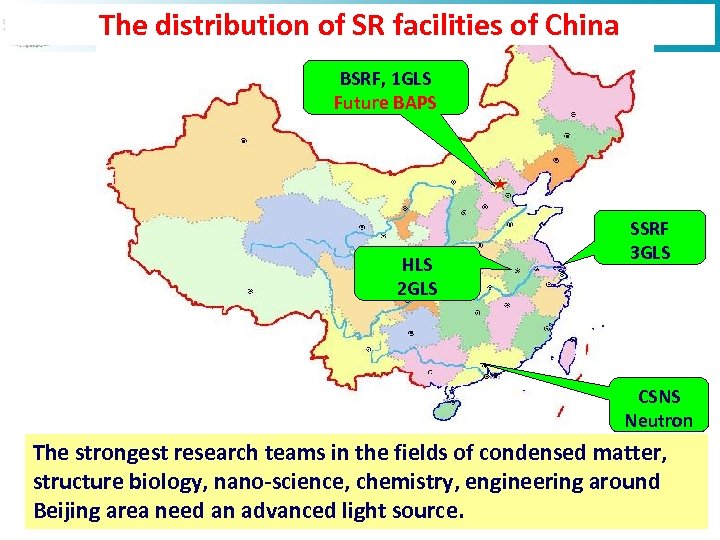 The distribution of SR facilities of China BSRF, 1 GLS Future BAPS HLS 2 GLS SSRF 3 GLS CSNS Neutron The strongest research teams in the fields of condensed matter, structure biology, nano-science, chemistry, engineering around Beijing area need an advanced light source. 17
The distribution of SR facilities of China BSRF, 1 GLS Future BAPS HLS 2 GLS SSRF 3 GLS CSNS Neutron The strongest research teams in the fields of condensed matter, structure biology, nano-science, chemistry, engineering around Beijing area need an advanced light source. 17
 Next SR facility in mainland of China • The imminence demand for SR facility requires a high-energy, low-emittance SR facility around Beijing area • Beijing Advanced Photo Source (BAPS) • 5 Ge. V, <0. 5 nmrad (bare lattice) SR machine • Higher energy for hard X-ray • Low emittance for high brilliance
Next SR facility in mainland of China • The imminence demand for SR facility requires a high-energy, low-emittance SR facility around Beijing area • Beijing Advanced Photo Source (BAPS) • 5 Ge. V, <0. 5 nmrad (bare lattice) SR machine • Higher energy for hard X-ray • Low emittance for high brilliance
 The plan of BAPS construction • • Now in the phase of R&D will start in 2014. Construction will start in 2016 or 2017. Commissioning in 2020 or 2021. • The preliminary research has started supported by IHEP.
The plan of BAPS construction • • Now in the phase of R&D will start in 2014. Construction will start in 2016 or 2017. Commissioning in 2020 or 2021. • The preliminary research has started supported by IHEP.
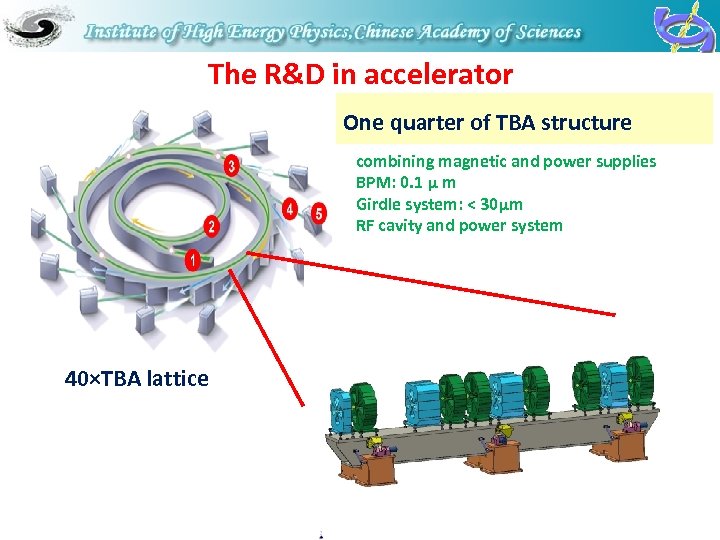 The R&D in accelerator One quarter of TBA structure combining magnetic and power supplies BPM: 0. 1 μ m Girdle system: < 30μm RF cavity and power system 40×TBA lattice 20
The R&D in accelerator One quarter of TBA structure combining magnetic and power supplies BPM: 0. 1 μ m Girdle system: < 30μm RF cavity and power system 40×TBA lattice 20
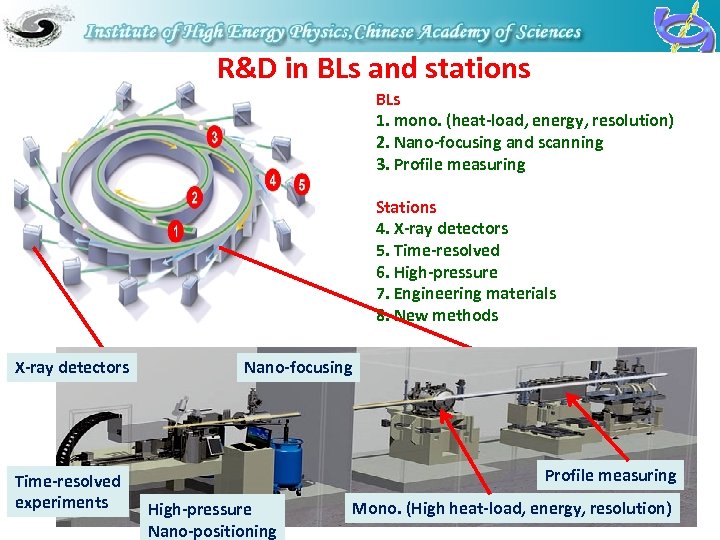 R&D in BLs and stations BLs 1. mono. (heat-load, energy, resolution) 2. Nano-focusing and scanning 3. Profile measuring Stations 4. X-ray detectors 5. Time-resolved 6. High-pressure 7. Engineering materials 8. New methods X-ray detectors Time-resolved experiments Nano-focusing Profile measuring High-pressure Nano-positioning 21 Mono. (High heat-load, energy, resolution)
R&D in BLs and stations BLs 1. mono. (heat-load, energy, resolution) 2. Nano-focusing and scanning 3. Profile measuring Stations 4. X-ray detectors 5. Time-resolved 6. High-pressure 7. Engineering materials 8. New methods X-ray detectors Time-resolved experiments Nano-focusing Profile measuring High-pressure Nano-positioning 21 Mono. (High heat-load, energy, resolution)
 The research in Laboratory of X-ray optics and technology X-ray imaging: theory and application X-ray modulation X-ray detector Micro and Nano X-ray optic X-ray source X-ray Metrology
The research in Laboratory of X-ray optics and technology X-ray imaging: theory and application X-ray modulation X-ray detector Micro and Nano X-ray optic X-ray source X-ray Metrology
 The team of BAPS Ø The Project Manager Department is organized in July 2012 • Manager: JIANG Xiaoming • Deputy manager: WANG Jiuqing, QIN Qing, DONG Yuhui • Chief engineer: SHENG Weifan, CHENG Jian, XU Gang • Chief economic manager: DENG Hu • Division manager: QIN Qing(Partial time), HU Tiandou Hu – 2 divisions (accelerator/BL&station), 18 systems – Now 53. 5 members (FTE) – 50 -60 members will be recruited in future
The team of BAPS Ø The Project Manager Department is organized in July 2012 • Manager: JIANG Xiaoming • Deputy manager: WANG Jiuqing, QIN Qing, DONG Yuhui • Chief engineer: SHENG Weifan, CHENG Jian, XU Gang • Chief economic manager: DENG Hu • Division manager: QIN Qing(Partial time), HU Tiandou Hu – 2 divisions (accelerator/BL&station), 18 systems – Now 53. 5 members (FTE) – 50 -60 members will be recruited in future
 Dr. JIANG Xiaoming, manager, vice director of IHEP Ph. D in USTC; postdoc. in IHEP; Alexander von Humboldt fellow Synchrotron radiation Dr. WANG Jiuqing, deputy manager, vice director of IHEP Ph. D in IHEP; JSPS fellow at KEK in Japan Accelerator Dr. QIN Qing, deputy manager, assistant director of IHEP Ph. D in IHEP; Supported by “ 100 -Talents Program “of Chinese Academy of Sciences in 2012 Accelerator
Dr. JIANG Xiaoming, manager, vice director of IHEP Ph. D in USTC; postdoc. in IHEP; Alexander von Humboldt fellow Synchrotron radiation Dr. WANG Jiuqing, deputy manager, vice director of IHEP Ph. D in IHEP; JSPS fellow at KEK in Japan Accelerator Dr. QIN Qing, deputy manager, assistant director of IHEP Ph. D in IHEP; Supported by “ 100 -Talents Program “of Chinese Academy of Sciences in 2012 Accelerator
 CSNS • Complementary to light source • Neutron: nuclear density, easily detecting light atoms. Suitable for magnetic properties research.
CSNS • Complementary to light source • Neutron: nuclear density, easily detecting light atoms. Suitable for magnetic properties research.
 The possible application fields of CSNS • Condensed matter physics: neutron scattering/diffraction • Nano science: SANS • Life science: neutron scattering/diffraction, high resolution reflection • Chemistry, materials, environmental sciences, etc. • Cooperation with users, developments for instrumentation and experimental methods.
The possible application fields of CSNS • Condensed matter physics: neutron scattering/diffraction • Nano science: SANS • Life science: neutron scattering/diffraction, high resolution reflection • Chemistry, materials, environmental sciences, etc. • Cooperation with users, developments for instrumentation and experimental methods.
 Development in Research • In addition to operate large facilities (SR based: BAPS; Neutron: CSNS) and develop cutting-edge experimental methods • Performing research on the frontiers of sciences • Guiding the development of facilities
Development in Research • In addition to operate large facilities (SR based: BAPS; Neutron: CSNS) and develop cutting-edge experimental methods • Performing research on the frontiers of sciences • Guiding the development of facilities
 Biological effects of nano-materials • • • Established in November 2001. One of several earliest teams in the world. Supporting from SR and nuclear analysis platforms. Cooperating with other teams. The leading position in Nanotoxicology, nanotherapy.
Biological effects of nano-materials • • • Established in November 2001. One of several earliest teams in the world. Supporting from SR and nuclear analysis platforms. Cooperating with other teams. The leading position in Nanotoxicology, nanotherapy.
 Curing cancers by imprisoning ~ 1 nm Before therapy 2 weeks tumor Fibrotic layer New strategy: Prison caner cells, not kill cancer cells Can avoid to stimulate cancer cells becoming more aggressive. Drug development Mechanism
Curing cancers by imprisoning ~ 1 nm Before therapy 2 weeks tumor Fibrotic layer New strategy: Prison caner cells, not kill cancer cells Can avoid to stimulate cancer cells becoming more aggressive. Drug development Mechanism
 The first textbook of Nanotoxicology Published in 2007, edited by Dr. ZHAO Yuliang, scientists from 11 countries involved. Reprinted several times during 2008 -2012. . 8002 , 81. tpe. S Chairmen of IUTOX 2007年 9月被Nature Prof. Kai Savolainen, 选为有号召力的人物 “ This textbook made a significant contribution in …. . Y L Zhao, H S Nalwa edited American Scientific Publishers, 2007
The first textbook of Nanotoxicology Published in 2007, edited by Dr. ZHAO Yuliang, scientists from 11 countries involved. Reprinted several times during 2008 -2012. . 8002 , 81. tpe. S Chairmen of IUTOX 2007年 9月被Nature Prof. Kai Savolainen, 选为有号召力的人物 “ This textbook made a significant contribution in …. . Y L Zhao, H S Nalwa edited American Scientific Publishers, 2007
 Series review papers in the field of nanotoxicology Nature Nanotechnology 2 Account of Chemical Research 6 Chemical Society Review 2 Advanced Materials 2 Biotechnology Advance 2 Small 6 (IF=31. 17) (IF=21. 84) (IF=26. 58) (IF=14. 78) (IF=10. 32) (IF=8. 349)
Series review papers in the field of nanotoxicology Nature Nanotechnology 2 Account of Chemical Research 6 Chemical Society Review 2 Advanced Materials 2 Biotechnology Advance 2 Small 6 (IF=31. 17) (IF=21. 84) (IF=26. 58) (IF=14. 78) (IF=10. 32) (IF=8. 349)
 Research plan: Biological effects of nano-materials Biological effects Positive Negative Nanomedicine -diagnosis and therapy- Nanomedicine for tumor Toxicity Bio Nano Tech Safety Standard & methodology Nano surface tech
Research plan: Biological effects of nano-materials Biological effects Positive Negative Nanomedicine -diagnosis and therapy- Nanomedicine for tumor Toxicity Bio Nano Tech Safety Standard & methodology Nano surface tech
 Dr. Yuliang ZHAO Founder and director of CAS Key Laboratory for Biomedical Effects of Nanomaterials and Nanosafety committee for OECD, United Nations Environmental Program (UNEP), European Commission, National Research Council of Canada Dr. Xueyun GAO Ph. D. from University of Science and Technology of China (2003); Research scientist, Department of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, and Department of Chemistry, the City University of New York Dr. Baoyun SUN Ph. D. Peking University; Department of Chemistry, Nagoya University, postdoctoral fellow (JSPS) and a researcher (JST); Leibniz Institute for Solid State and Materials Research, Germany
Dr. Yuliang ZHAO Founder and director of CAS Key Laboratory for Biomedical Effects of Nanomaterials and Nanosafety committee for OECD, United Nations Environmental Program (UNEP), European Commission, National Research Council of Canada Dr. Xueyun GAO Ph. D. from University of Science and Technology of China (2003); Research scientist, Department of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, and Department of Chemistry, the City University of New York Dr. Baoyun SUN Ph. D. Peking University; Department of Chemistry, Nagoya University, postdoctoral fellow (JSPS) and a researcher (JST); Leibniz Institute for Solid State and Materials Research, Germany
 Environmental Health Research • Research on two major pollutants, i. e. heavy metal mercury and air fine particulate matter (including nanoparticles) • Identification of environmental risk sources, emission characteristics, migration, biological effects, key control technology, environmental remediation and related therapeutics • SR & Nuclear analytical techniques
Environmental Health Research • Research on two major pollutants, i. e. heavy metal mercury and air fine particulate matter (including nanoparticles) • Identification of environmental risk sources, emission characteristics, migration, biological effects, key control technology, environmental remediation and related therapeutics • SR & Nuclear analytical techniques
 Research in future • Research platform on metallomics by integrating advanced analytic techniques from other research groups at IHEP • Develop novel methods for quantitative analysis of proteins • Single cell/single particle element analysis • Transformation and migration of mercury, pollution management, environmental remediation and solutions for related health problem and environmental technology
Research in future • Research platform on metallomics by integrating advanced analytic techniques from other research groups at IHEP • Develop novel methods for quantitative analysis of proteins • Single cell/single particle element analysis • Transformation and migration of mercury, pollution management, environmental remediation and solutions for related health problem and environmental technology
 Dr. Zhiyong ZHANG Ph. D. from Peking University in 1997 Applications of nuclear analytical techniques, rare earth chemistry Dr. Weiyue FENG Ph. D. from IHEP in 1998 Application of nuclear analytical techniques in the study of chemical biology and metallomics/metalloprotein; biological and toxicological study of nanomaterials. Dr. Yi HU Ph. D. from National University of Singapore, postdoc. at Harvard Medical School and Brigham & Women’s Hospital Chemical Biology
Dr. Zhiyong ZHANG Ph. D. from Peking University in 1997 Applications of nuclear analytical techniques, rare earth chemistry Dr. Weiyue FENG Ph. D. from IHEP in 1998 Application of nuclear analytical techniques in the study of chemical biology and metallomics/metalloprotein; biological and toxicological study of nanomaterials. Dr. Yi HU Ph. D. from National University of Singapore, postdoc. at Harvard Medical School and Brigham & Women’s Hospital Chemical Biology
 Protein Life Science and Technology • Established in 2008 • Research on the methods for structure determination: automation, new methods in SR and XFEL • Structures of the proteins related to DNA repair, drugresistance of pathogens • Cooperation in the mechanism of biological effects of nanoparticles and heavy ions
Protein Life Science and Technology • Established in 2008 • Research on the methods for structure determination: automation, new methods in SR and XFEL • Structures of the proteins related to DNA repair, drugresistance of pathogens • Cooperation in the mechanism of biological effects of nanoparticles and heavy ions
 Research in future • Methodological research Ø SR-based: ab initio phasing, weak anomalous scattering, synergy of PX and SAXS, automation Ø XFEL-based: nano-crystallography, single particle • Structural biology Ø Proteins/complexes related to biological effects of nanomaterials and heavy ions Ø DNA repairs Ø Drug-resistance
Research in future • Methodological research Ø SR-based: ab initio phasing, weak anomalous scattering, synergy of PX and SAXS, automation Ø XFEL-based: nano-crystallography, single particle • Structural biology Ø Proteins/complexes related to biological effects of nanomaterials and heavy ions Ø DNA repairs Ø Drug-resistance
 Dr. Yuhui DONG Ph. D. from IHEP in 1995; postdoc. IPHY, Trento univ. Italy, “ 100 -talent project” of CAS in 2001 Crystallography, structure biology Deputy manager of BAPS R&D Dr. Quansheng LIU Ph. D. from Shanghai Institute of Biochemistry, CAS. Postdoc in University of Massachusetts Amherst. Research Fellow in Sloan-Kettering Institute, Skirball Institute, NYU Medical Center. “ 100 Talent Program” of CAS in 2010. Dr. Yong GONG Ph. D from Peking Union Medical College. 2000 -2002, Postdoc in Johns Hopkins University, USA. ; Professor, National Laboratory of Biomacromolecules, Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Dr. Yuhui DONG Ph. D. from IHEP in 1995; postdoc. IPHY, Trento univ. Italy, “ 100 -talent project” of CAS in 2001 Crystallography, structure biology Deputy manager of BAPS R&D Dr. Quansheng LIU Ph. D. from Shanghai Institute of Biochemistry, CAS. Postdoc in University of Massachusetts Amherst. Research Fellow in Sloan-Kettering Institute, Skirball Institute, NYU Medical Center. “ 100 Talent Program” of CAS in 2010. Dr. Yong GONG Ph. D from Peking Union Medical College. 2000 -2002, Postdoc in Johns Hopkins University, USA. ; Professor, National Laboratory of Biomacromolecules, Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
 The long-term goals of research • The teams of biological effects of nano-materials and nano-safety, environmental health and safety, Protein Life Science and Technology, collaborate in: Ø Mechanism of anticancer nanomedicine with high efficiency and low toxicity; Ø The immigration, transformation, and controlling of heavy ion pollution (especially Hg).
The long-term goals of research • The teams of biological effects of nano-materials and nano-safety, environmental health and safety, Protein Life Science and Technology, collaborate in: Ø Mechanism of anticancer nanomedicine with high efficiency and low toxicity; Ø The immigration, transformation, and controlling of heavy ion pollution (especially Hg).
 Radiochemistry • Established 2011 • In response to the recent rapid development of the nuclear power industry and the increasing demand for nuclear energy in the future. • Nano-tech. • Fuel recycling
Radiochemistry • Established 2011 • In response to the recent rapid development of the nuclear power industry and the increasing demand for nuclear energy in the future. • Nano-tech. • Fuel recycling
 Manpower (FTE) Current In next 5 years Prof. All BAPS 7. 5 53. 5+10 14 120+30 CSNS 2 5 15 50+20 In-house research. 7 37+25 10 45+35 Totally 753 research papers (SCI) published during 2008 -2013.
Manpower (FTE) Current In next 5 years Prof. All BAPS 7. 5 53. 5+10 14 120+30 CSNS 2 5 15 50+20 In-house research. 7 37+25 10 45+35 Totally 753 research papers (SCI) published during 2008 -2013.
 Challenges (1) • Keep the position in research • Some research teams (e. g. Biological effects of nano -materials) have been the leaders in their fields. How to keep this superiority in the highly competitive environment? • The continuously improvement of user facilities? ü Cooperation of different teams, for more comprehensive research. ü Supporting from new facilities (instruments & methods)
Challenges (1) • Keep the position in research • Some research teams (e. g. Biological effects of nano -materials) have been the leaders in their fields. How to keep this superiority in the highly competitive environment? • The continuously improvement of user facilities? ü Cooperation of different teams, for more comprehensive research. ü Supporting from new facilities (instruments & methods)
 Challenges (2) • Reasonable growth in manpower • Need to expand the teams for future development, for adapting the more comprehensive research and facility developments. • Not only the staff for specific research projects, but also similar to development of facilities, since “facilities” & “research” work as a team. ü Recruitment or training ü “Mission-orientated” instead of “projectorientated”
Challenges (2) • Reasonable growth in manpower • Need to expand the teams for future development, for adapting the more comprehensive research and facility developments. • Not only the staff for specific research projects, but also similar to development of facilities, since “facilities” & “research” work as a team. ü Recruitment or training ü “Mission-orientated” instead of “projectorientated”
 Challenges (3) • Enlarge space for future development • The site of Yuquan Road is not suitable for future expansion (especially the sizes of laboratory and office). ü The new sites of CSNS and BAPS. ü Research centers around user facilities.
Challenges (3) • Enlarge space for future development • The site of Yuquan Road is not suitable for future expansion (especially the sizes of laboratory and office). ü The new sites of CSNS and BAPS. ü Research centers around user facilities.
 Summary • We have solid foundation in large facilities. • BAPS and CSNS will promote us to the top level in user facilities. • The frontier research based on the facilities will reinforce our strength in facilities. • Cooperation between research teams with different backgrounds is essential.
Summary • We have solid foundation in large facilities. • BAPS and CSNS will promote us to the top level in user facilities. • The frontier research based on the facilities will reinforce our strength in facilities. • Cooperation between research teams with different backgrounds is essential.
 Thanks for your attention !
Thanks for your attention !


