a6f3a23a1fa066e7d2b63fb4f348c498.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42

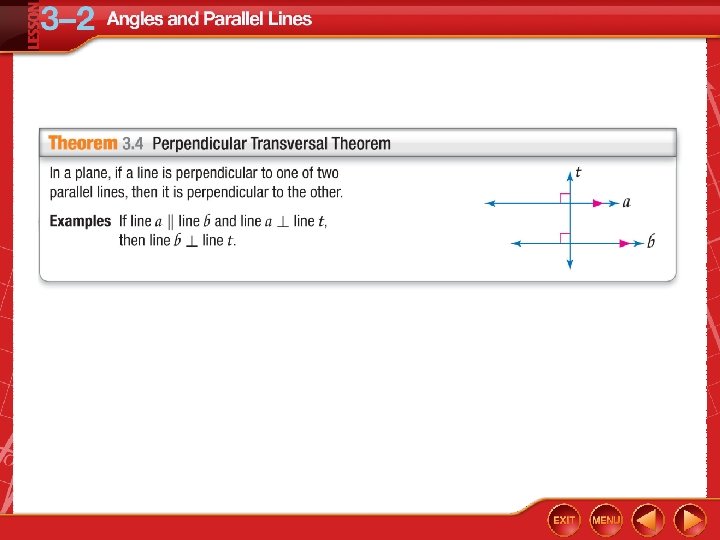
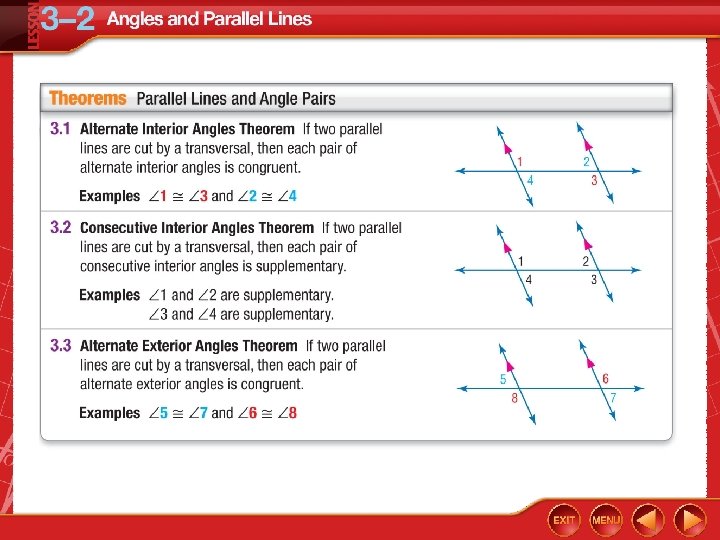
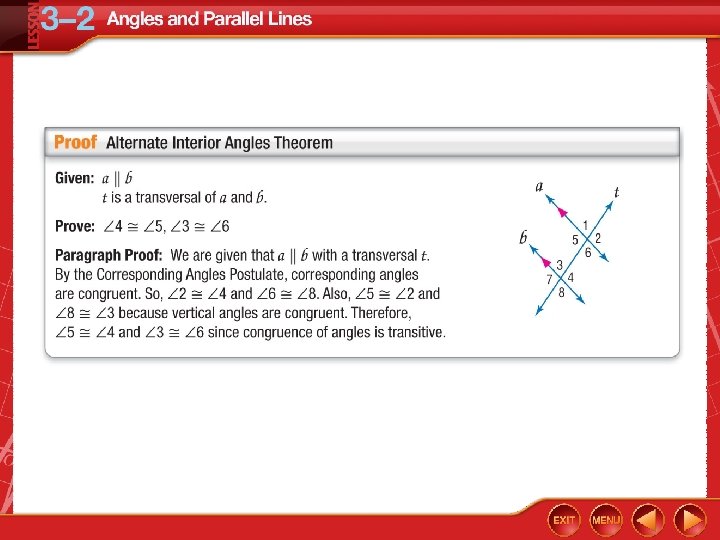
 Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 3– 1) CCSS Then/Now Postulate 3. 1: Corresponding Angles Postulate Example 1: Use Corresponding Angles Postulate Theorems: Parallel Lines and Angle Pairs Proof: Alternate Interior Angles Theorem Example 2: Real-World Example: Use Theorems about Parallel Lines Example 3: Find Values of Variables Theorem 3. 4: Perpendicular Transversal Theorem
Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 3– 1) CCSS Then/Now Postulate 3. 1: Corresponding Angles Postulate Example 1: Use Corresponding Angles Postulate Theorems: Parallel Lines and Angle Pairs Proof: Alternate Interior Angles Theorem Example 2: Real-World Example: Use Theorems about Parallel Lines Example 3: Find Values of Variables Theorem 3. 4: Perpendicular Transversal Theorem
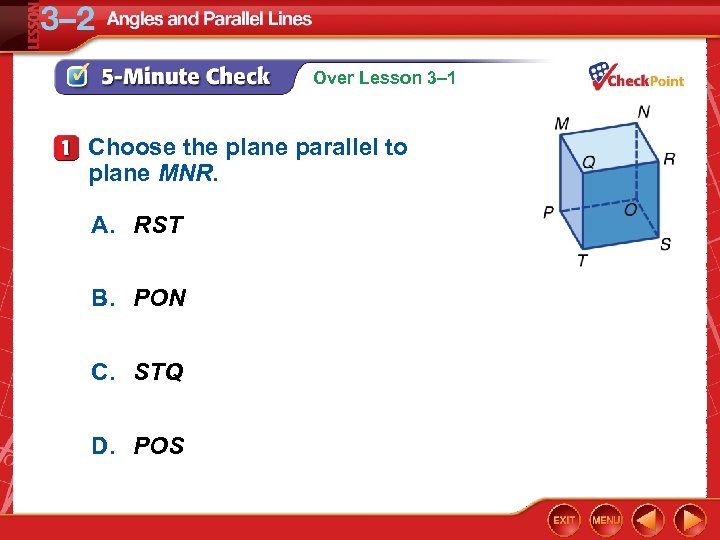 Over Lesson 3– 1 Choose the plane parallel to plane MNR. A. RST B. PON C. STQ D. POS
Over Lesson 3– 1 Choose the plane parallel to plane MNR. A. RST B. PON C. STQ D. POS
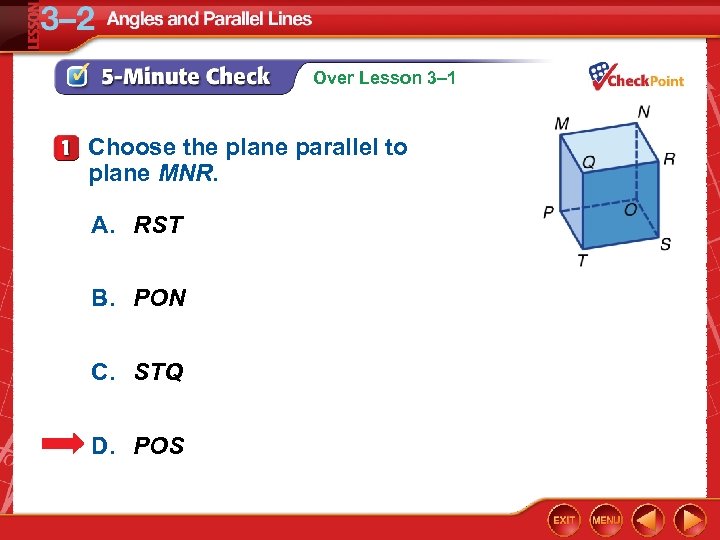 Over Lesson 3– 1 Choose the plane parallel to plane MNR. A. RST B. PON C. STQ D. POS
Over Lesson 3– 1 Choose the plane parallel to plane MNR. A. RST B. PON C. STQ D. POS
 Over Lesson 3– 1 Choose the segment skew to MP. ___ A. PM ___ B. TS ___ C. PO ___ D. MQ
Over Lesson 3– 1 Choose the segment skew to MP. ___ A. PM ___ B. TS ___ C. PO ___ D. MQ
 Over Lesson 3– 1 Choose the segment skew to MP. ___ A. PM ___ B. TS ___ C. PO ___ D. MQ
Over Lesson 3– 1 Choose the segment skew to MP. ___ A. PM ___ B. TS ___ C. PO ___ D. MQ
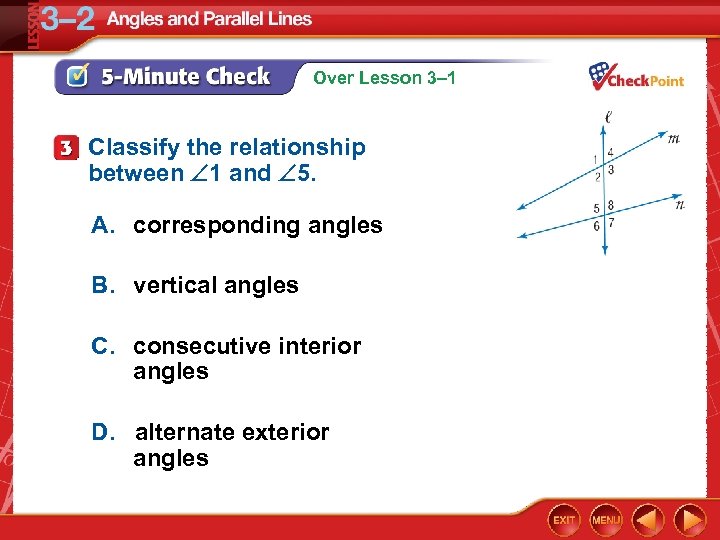 Over Lesson 3– 1 Classify the relationship between 1 and 5. A. corresponding angles B. vertical angles C. consecutive interior angles D. alternate exterior angles
Over Lesson 3– 1 Classify the relationship between 1 and 5. A. corresponding angles B. vertical angles C. consecutive interior angles D. alternate exterior angles
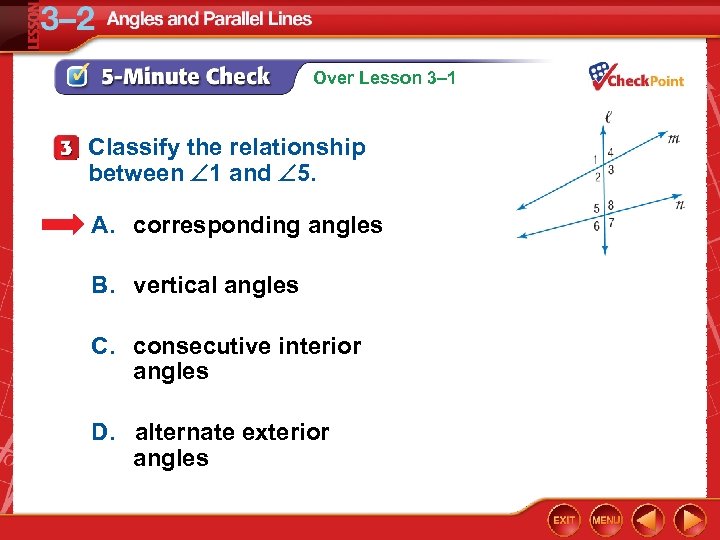 Over Lesson 3– 1 Classify the relationship between 1 and 5. A. corresponding angles B. vertical angles C. consecutive interior angles D. alternate exterior angles
Over Lesson 3– 1 Classify the relationship between 1 and 5. A. corresponding angles B. vertical angles C. consecutive interior angles D. alternate exterior angles
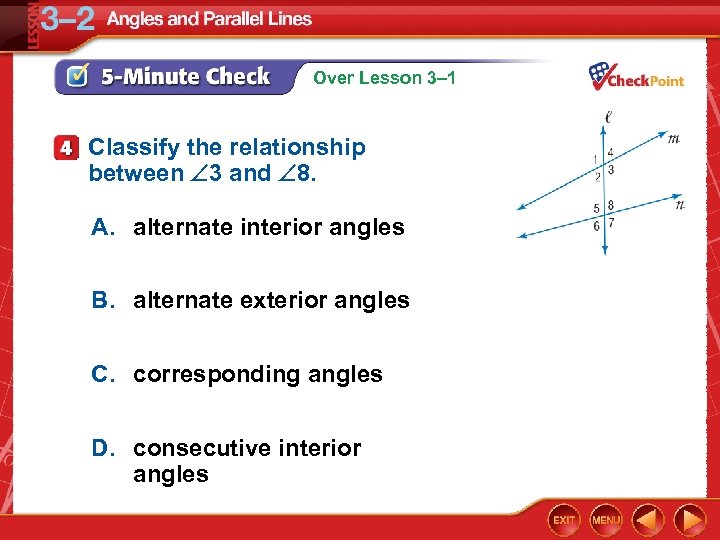 Over Lesson 3– 1 Classify the relationship between 3 and 8. A. alternate interior angles B. alternate exterior angles C. corresponding angles D. consecutive interior angles
Over Lesson 3– 1 Classify the relationship between 3 and 8. A. alternate interior angles B. alternate exterior angles C. corresponding angles D. consecutive interior angles
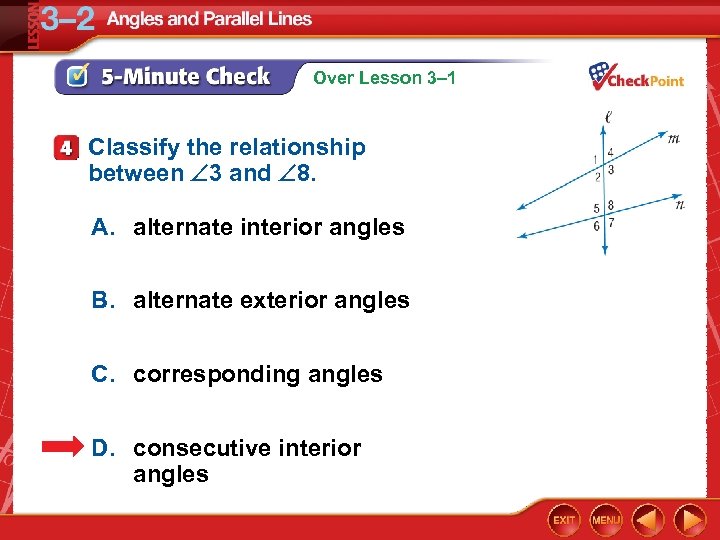 Over Lesson 3– 1 Classify the relationship between 3 and 8. A. alternate interior angles B. alternate exterior angles C. corresponding angles D. consecutive interior angles
Over Lesson 3– 1 Classify the relationship between 3 and 8. A. alternate interior angles B. alternate exterior angles C. corresponding angles D. consecutive interior angles
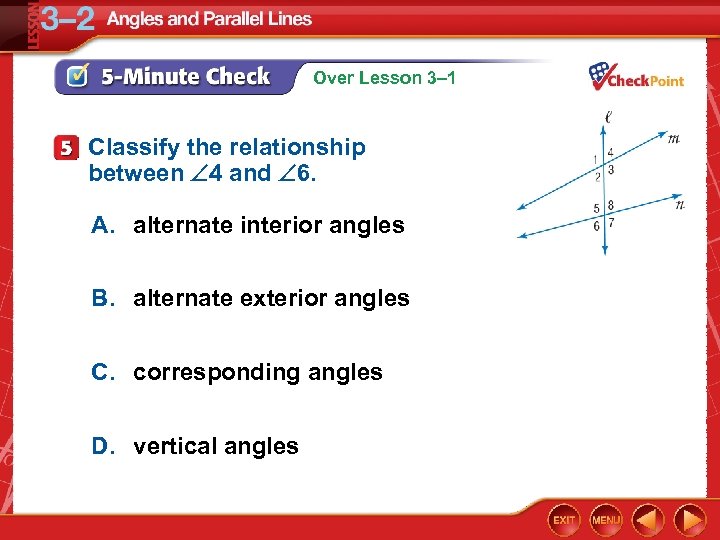 Over Lesson 3– 1 Classify the relationship between 4 and 6. A. alternate interior angles B. alternate exterior angles C. corresponding angles D. vertical angles
Over Lesson 3– 1 Classify the relationship between 4 and 6. A. alternate interior angles B. alternate exterior angles C. corresponding angles D. vertical angles
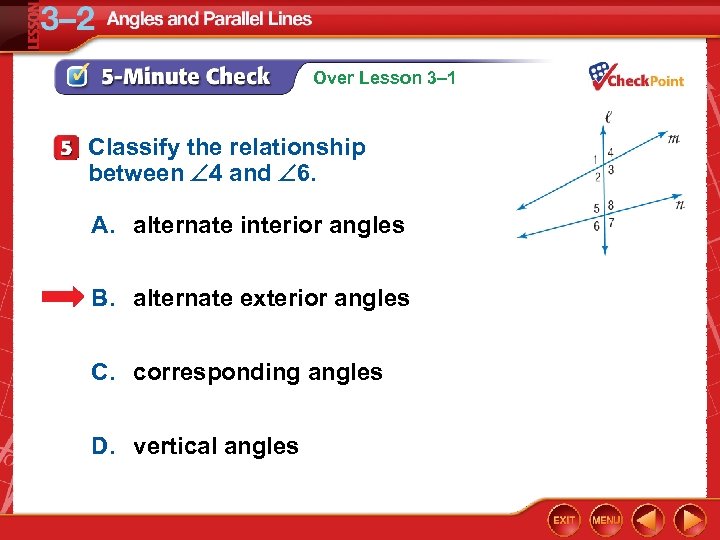 Over Lesson 3– 1 Classify the relationship between 4 and 6. A. alternate interior angles B. alternate exterior angles C. corresponding angles D. vertical angles
Over Lesson 3– 1 Classify the relationship between 4 and 6. A. alternate interior angles B. alternate exterior angles C. corresponding angles D. vertical angles
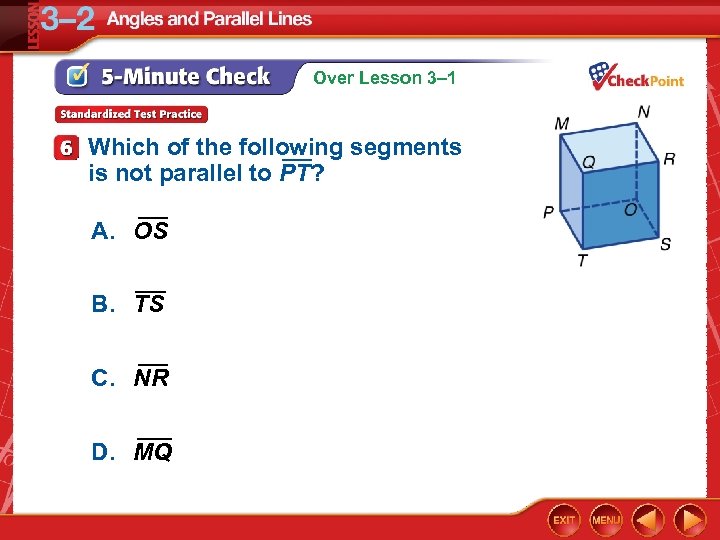 Over Lesson 3– 1 Which of the following segments is not parallel to PT? A. OS B. TS C. NR D. MQ
Over Lesson 3– 1 Which of the following segments is not parallel to PT? A. OS B. TS C. NR D. MQ
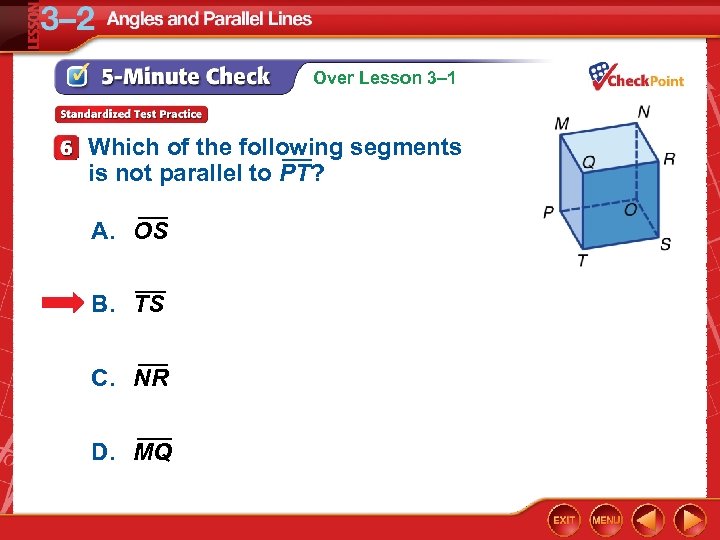 Over Lesson 3– 1 Which of the following segments is not parallel to PT? A. OS B. TS C. NR D. MQ
Over Lesson 3– 1 Which of the following segments is not parallel to PT? A. OS B. TS C. NR D. MQ
 Content Standards G. CO. 1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance around a circular arc. G. CO. 9 Prove theorems about lines and angles. Mathematical Practices 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 3 Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others.
Content Standards G. CO. 1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance around a circular arc. G. CO. 9 Prove theorems about lines and angles. Mathematical Practices 1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 3 Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others.
 You named angle pairs formed by parallel lines and transversals. • Use theorems to determine the relationships between specific pairs of angles. • Use algebra to find angle measurements.
You named angle pairs formed by parallel lines and transversals. • Use theorems to determine the relationships between specific pairs of angles. • Use algebra to find angle measurements.

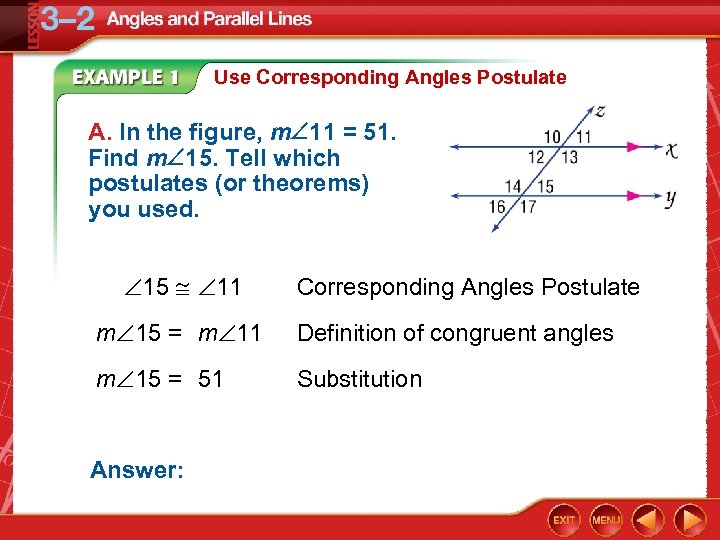 Use Corresponding Angles Postulate A. In the figure, m 11 = 51. Find m 15. Tell which postulates (or theorems) you used. 15 11 Corresponding Angles Postulate m 15 = m 11 Definition of congruent angles m 15 = 51 Substitution Answer:
Use Corresponding Angles Postulate A. In the figure, m 11 = 51. Find m 15. Tell which postulates (or theorems) you used. 15 11 Corresponding Angles Postulate m 15 = m 11 Definition of congruent angles m 15 = 51 Substitution Answer:
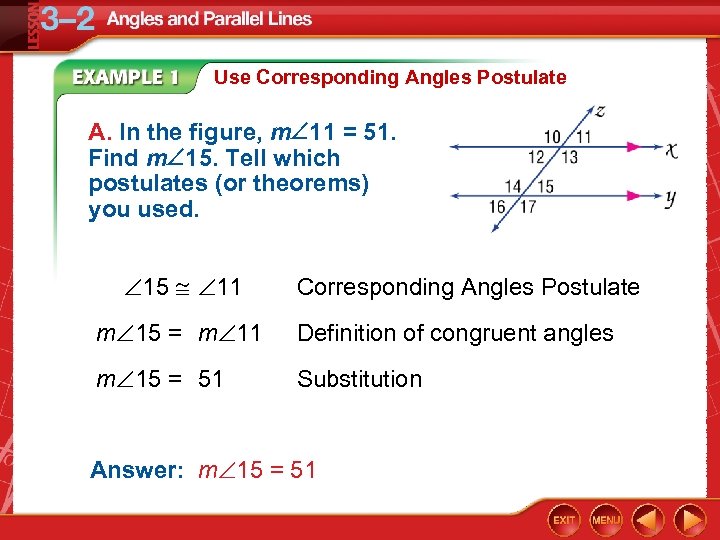 Use Corresponding Angles Postulate A. In the figure, m 11 = 51. Find m 15. Tell which postulates (or theorems) you used. 15 11 Corresponding Angles Postulate m 15 = m 11 Definition of congruent angles m 15 = 51 Substitution Answer: m 15 = 51
Use Corresponding Angles Postulate A. In the figure, m 11 = 51. Find m 15. Tell which postulates (or theorems) you used. 15 11 Corresponding Angles Postulate m 15 = m 11 Definition of congruent angles m 15 = 51 Substitution Answer: m 15 = 51
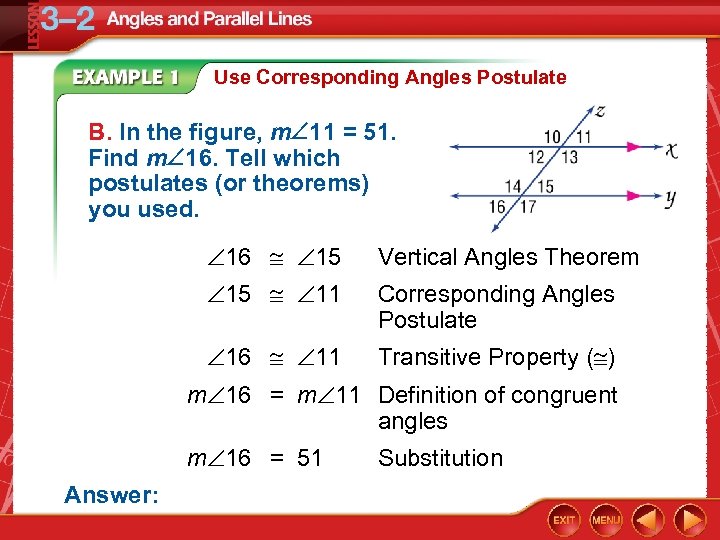 Use Corresponding Angles Postulate B. In the figure, m 11 = 51. Find m 16. Tell which postulates (or theorems) you used. 16 15 Vertical Angles Theorem 15 11 Corresponding Angles Postulate 16 11 Transitive Property ( ) m 16 = m 11 Definition of congruent angles m 16 = 51 Answer: Substitution
Use Corresponding Angles Postulate B. In the figure, m 11 = 51. Find m 16. Tell which postulates (or theorems) you used. 16 15 Vertical Angles Theorem 15 11 Corresponding Angles Postulate 16 11 Transitive Property ( ) m 16 = m 11 Definition of congruent angles m 16 = 51 Answer: Substitution
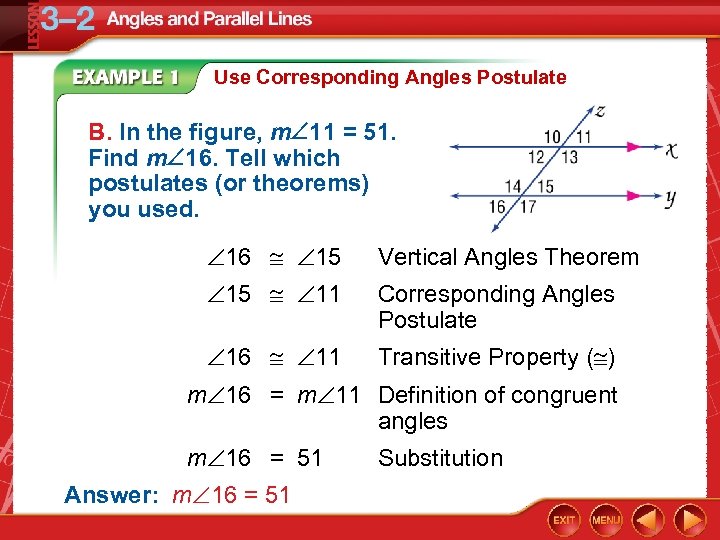 Use Corresponding Angles Postulate B. In the figure, m 11 = 51. Find m 16. Tell which postulates (or theorems) you used. 16 15 Vertical Angles Theorem 15 11 Corresponding Angles Postulate 16 11 Transitive Property ( ) m 16 = m 11 Definition of congruent angles m 16 = 51 Answer: m 16 = 51 Substitution
Use Corresponding Angles Postulate B. In the figure, m 11 = 51. Find m 16. Tell which postulates (or theorems) you used. 16 15 Vertical Angles Theorem 15 11 Corresponding Angles Postulate 16 11 Transitive Property ( ) m 16 = m 11 Definition of congruent angles m 16 = 51 Answer: m 16 = 51 Substitution
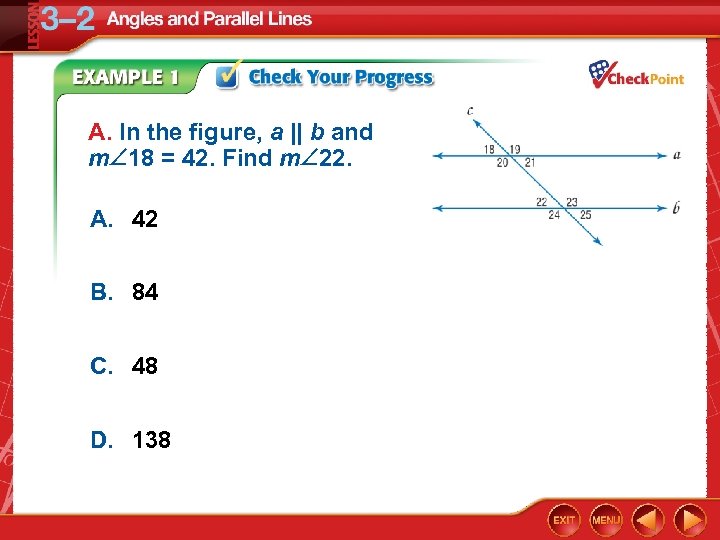 A. In the figure, a || b and m 18 = 42. Find m 22. A. 42 B. 84 C. 48 D. 138
A. In the figure, a || b and m 18 = 42. Find m 22. A. 42 B. 84 C. 48 D. 138
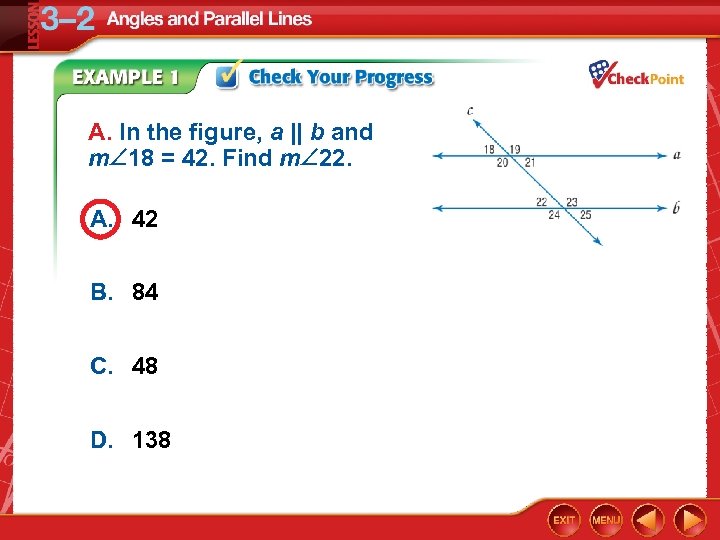 A. In the figure, a || b and m 18 = 42. Find m 22. A. 42 B. 84 C. 48 D. 138
A. In the figure, a || b and m 18 = 42. Find m 22. A. 42 B. 84 C. 48 D. 138
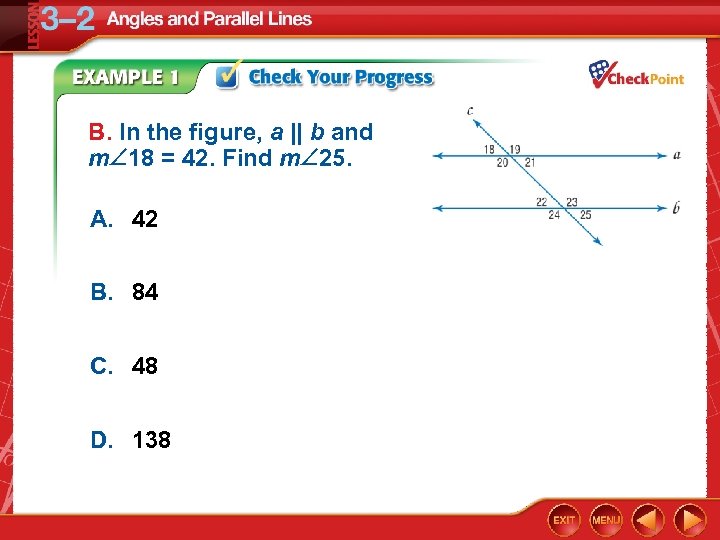 B. In the figure, a || b and m 18 = 42. Find m 25. A. 42 B. 84 C. 48 D. 138
B. In the figure, a || b and m 18 = 42. Find m 25. A. 42 B. 84 C. 48 D. 138
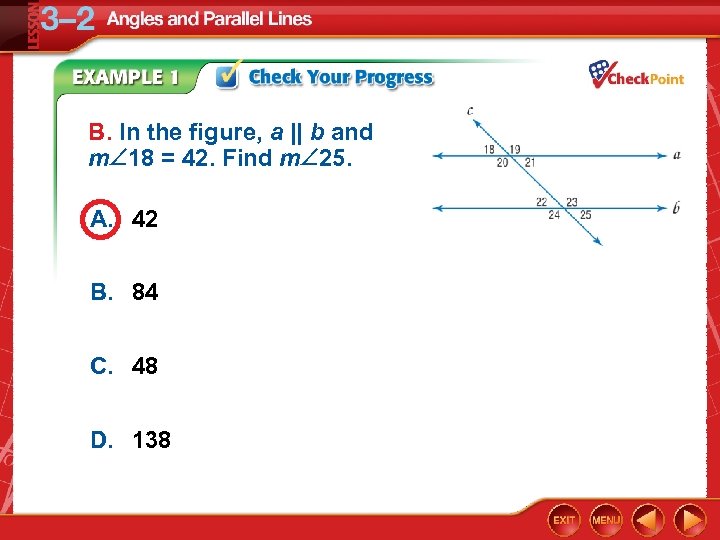 B. In the figure, a || b and m 18 = 42. Find m 25. A. 42 B. 84 C. 48 D. 138
B. In the figure, a || b and m 18 = 42. Find m 25. A. 42 B. 84 C. 48 D. 138
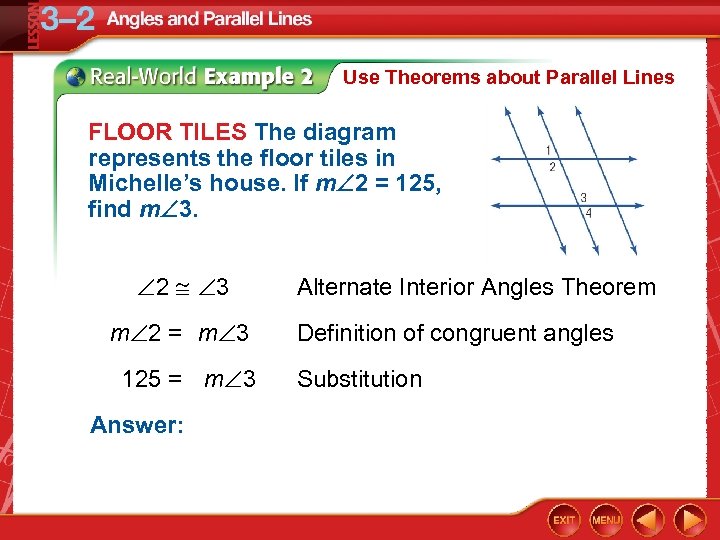 Use Theorems about Parallel Lines FLOOR TILES The diagram represents the floor tiles in Michelle’s house. If m 2 = 125, find m 3. 2 3 m 2 = m 3 125 = m 3 Answer: Alternate Interior Angles Theorem Definition of congruent angles Substitution
Use Theorems about Parallel Lines FLOOR TILES The diagram represents the floor tiles in Michelle’s house. If m 2 = 125, find m 3. 2 3 m 2 = m 3 125 = m 3 Answer: Alternate Interior Angles Theorem Definition of congruent angles Substitution
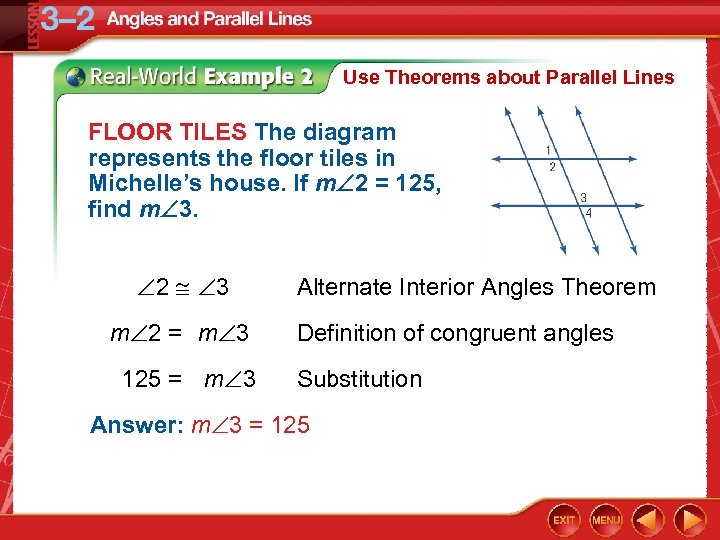 Use Theorems about Parallel Lines FLOOR TILES The diagram represents the floor tiles in Michelle’s house. If m 2 = 125, find m 3. 2 3 m 2 = m 3 125 = m 3 Alternate Interior Angles Theorem Definition of congruent angles Substitution Answer: m 3 = 125
Use Theorems about Parallel Lines FLOOR TILES The diagram represents the floor tiles in Michelle’s house. If m 2 = 125, find m 3. 2 3 m 2 = m 3 125 = m 3 Alternate Interior Angles Theorem Definition of congruent angles Substitution Answer: m 3 = 125
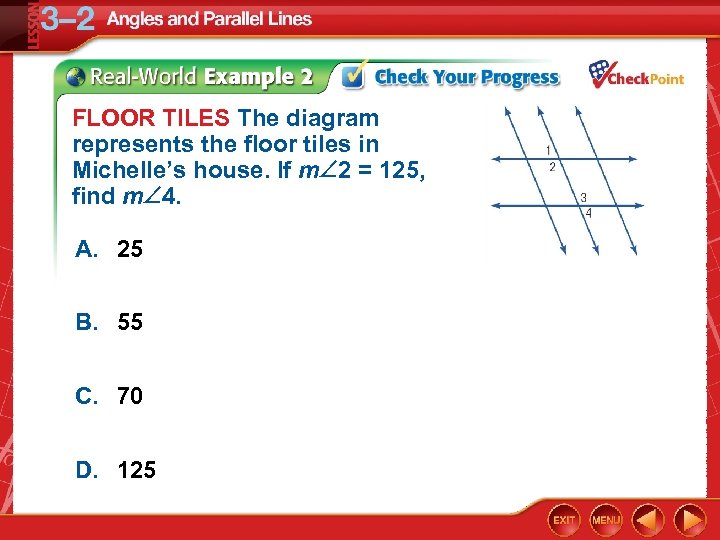 FLOOR TILES The diagram represents the floor tiles in Michelle’s house. If m 2 = 125, find m 4. A. 25 B. 55 C. 70 D. 125
FLOOR TILES The diagram represents the floor tiles in Michelle’s house. If m 2 = 125, find m 4. A. 25 B. 55 C. 70 D. 125
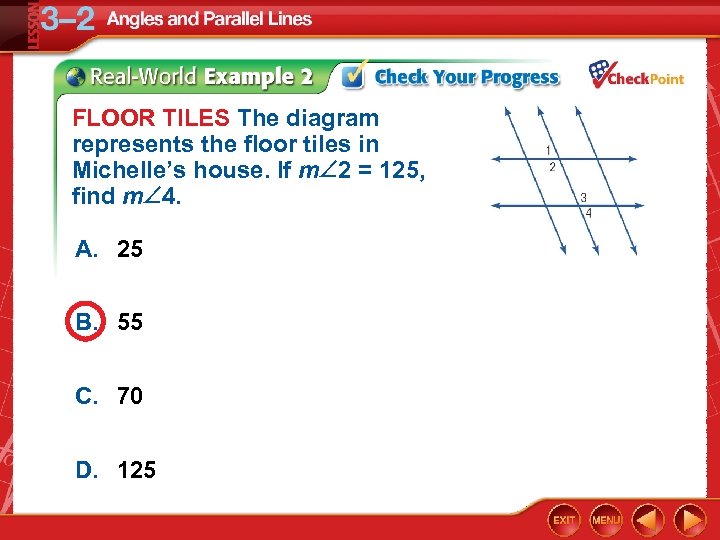 FLOOR TILES The diagram represents the floor tiles in Michelle’s house. If m 2 = 125, find m 4. A. 25 B. 55 C. 70 D. 125
FLOOR TILES The diagram represents the floor tiles in Michelle’s house. If m 2 = 125, find m 4. A. 25 B. 55 C. 70 D. 125
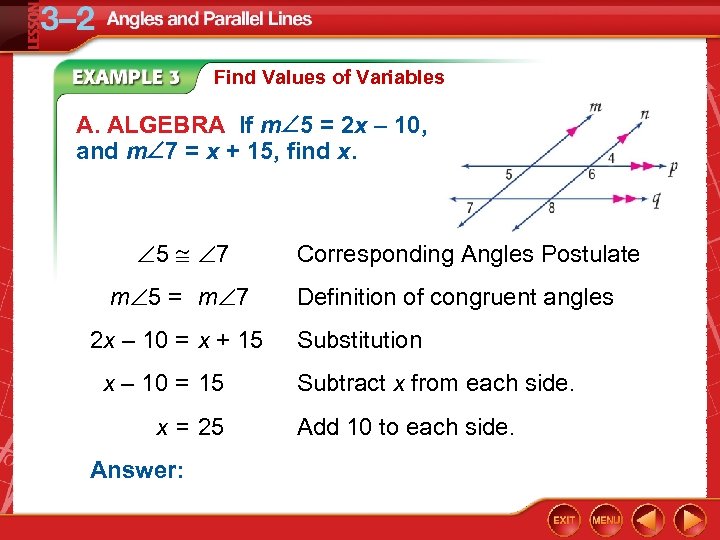 Find Values of Variables A. ALGEBRA If m 5 = 2 x – 10, and m 7 = x + 15, find x. 5 7 m 5 = m 7 2 x – 10 = x + 15 x – 10 = 15 x = 25 Answer: Corresponding Angles Postulate Definition of congruent angles Substitution Subtract x from each side. Add 10 to each side.
Find Values of Variables A. ALGEBRA If m 5 = 2 x – 10, and m 7 = x + 15, find x. 5 7 m 5 = m 7 2 x – 10 = x + 15 x – 10 = 15 x = 25 Answer: Corresponding Angles Postulate Definition of congruent angles Substitution Subtract x from each side. Add 10 to each side.
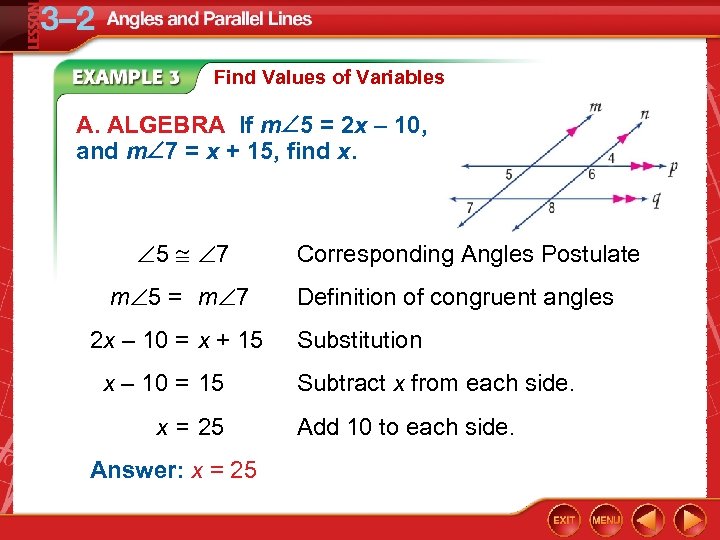 Find Values of Variables A. ALGEBRA If m 5 = 2 x – 10, and m 7 = x + 15, find x. 5 7 m 5 = m 7 2 x – 10 = x + 15 x – 10 = 15 x = 25 Answer: x = 25 Corresponding Angles Postulate Definition of congruent angles Substitution Subtract x from each side. Add 10 to each side.
Find Values of Variables A. ALGEBRA If m 5 = 2 x – 10, and m 7 = x + 15, find x. 5 7 m 5 = m 7 2 x – 10 = x + 15 x – 10 = 15 x = 25 Answer: x = 25 Corresponding Angles Postulate Definition of congruent angles Substitution Subtract x from each side. Add 10 to each side.
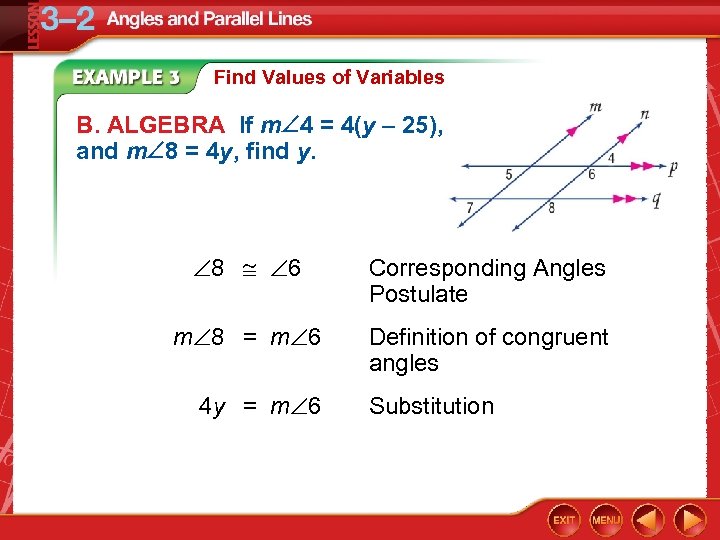 Find Values of Variables B. ALGEBRA If m 4 = 4(y – 25), and m 8 = 4 y, find y. 8 6 Corresponding Angles Postulate m 8 = m 6 Definition of congruent angles 4 y = m 6 Substitution
Find Values of Variables B. ALGEBRA If m 4 = 4(y – 25), and m 8 = 4 y, find y. 8 6 Corresponding Angles Postulate m 8 = m 6 Definition of congruent angles 4 y = m 6 Substitution
 Find Values of Variables m 6 + m 4 = 180 Supplement Theorem 4 y + 4(y – 25) = 180 Substitution 4 y + 4 y – 100 = 180 Distributive Property 8 y = 280 y = 35 Answer: Add 100 to each side. Divide each side by 8.
Find Values of Variables m 6 + m 4 = 180 Supplement Theorem 4 y + 4(y – 25) = 180 Substitution 4 y + 4 y – 100 = 180 Distributive Property 8 y = 280 y = 35 Answer: Add 100 to each side. Divide each side by 8.
 Find Values of Variables m 6 + m 4 = 180 Supplement Theorem 4 y + 4(y – 25) = 180 Substitution 4 y + 4 y – 100 = 180 Distributive Property 8 y = 280 Add 100 to each side. y = 35 Divide each side by 8. Answer: y = 35
Find Values of Variables m 6 + m 4 = 180 Supplement Theorem 4 y + 4(y – 25) = 180 Substitution 4 y + 4 y – 100 = 180 Distributive Property 8 y = 280 Add 100 to each side. y = 35 Divide each side by 8. Answer: y = 35
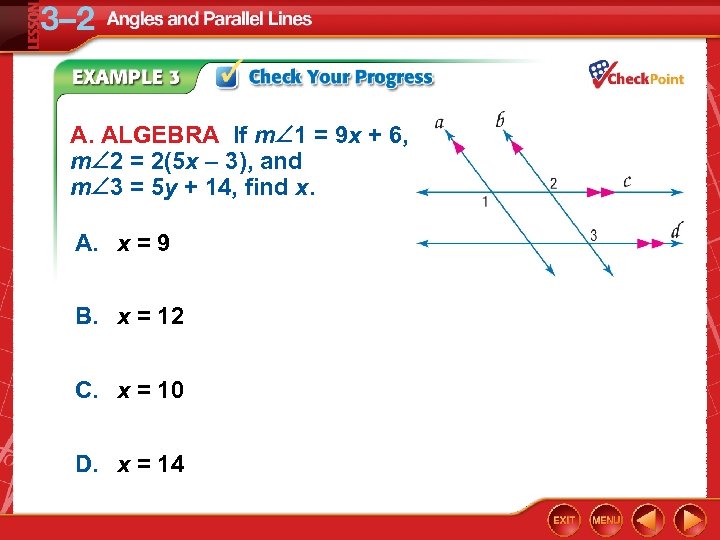 A. ALGEBRA If m 1 = 9 x + 6, m 2 = 2(5 x – 3), and m 3 = 5 y + 14, find x. A. x = 9 B. x = 12 C. x = 10 D. x = 14
A. ALGEBRA If m 1 = 9 x + 6, m 2 = 2(5 x – 3), and m 3 = 5 y + 14, find x. A. x = 9 B. x = 12 C. x = 10 D. x = 14
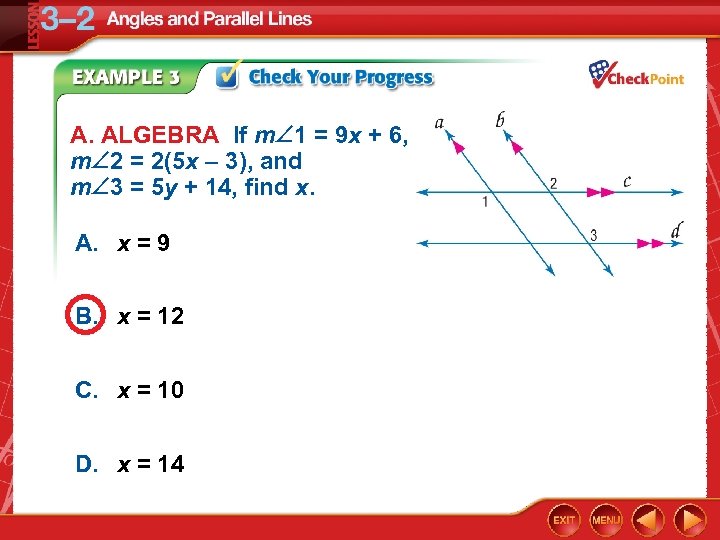 A. ALGEBRA If m 1 = 9 x + 6, m 2 = 2(5 x – 3), and m 3 = 5 y + 14, find x. A. x = 9 B. x = 12 C. x = 10 D. x = 14
A. ALGEBRA If m 1 = 9 x + 6, m 2 = 2(5 x – 3), and m 3 = 5 y + 14, find x. A. x = 9 B. x = 12 C. x = 10 D. x = 14
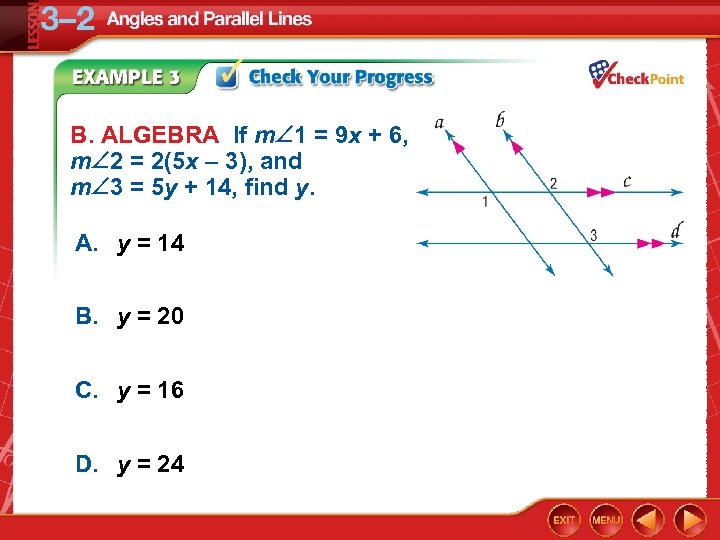 B. ALGEBRA If m 1 = 9 x + 6, m 2 = 2(5 x – 3), and m 3 = 5 y + 14, find y. A. y = 14 B. y = 20 C. y = 16 D. y = 24
B. ALGEBRA If m 1 = 9 x + 6, m 2 = 2(5 x – 3), and m 3 = 5 y + 14, find y. A. y = 14 B. y = 20 C. y = 16 D. y = 24
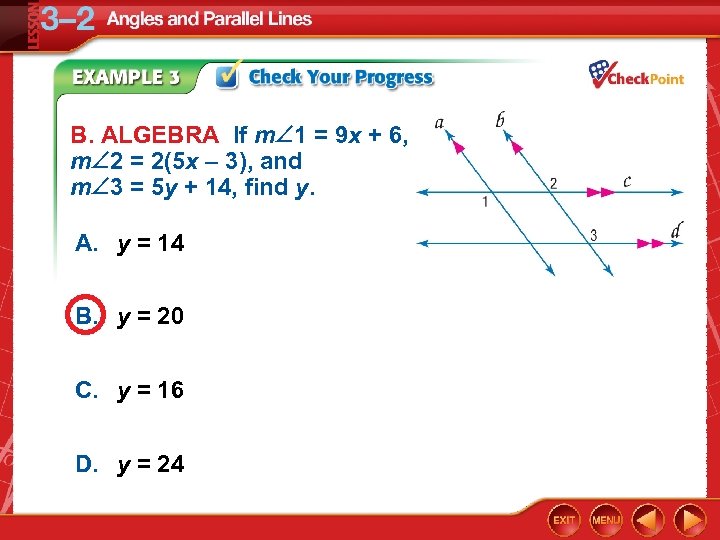 B. ALGEBRA If m 1 = 9 x + 6, m 2 = 2(5 x – 3), and m 3 = 5 y + 14, find y. A. y = 14 B. y = 20 C. y = 16 D. y = 24
B. ALGEBRA If m 1 = 9 x + 6, m 2 = 2(5 x – 3), and m 3 = 5 y + 14, find y. A. y = 14 B. y = 20 C. y = 16 D. y = 24