867e92f8c73433c90b9318eb2c861334.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 72
 First trimester screening The Danish Experiences Vårmötet 2007 Lennart Friis-Hansen Dept. of Clinical Biochemistry Rigshospitalet Univeristy of Copenhagen Denmark Borås, Mayr 11 h, 2007
First trimester screening The Danish Experiences Vårmötet 2007 Lennart Friis-Hansen Dept. of Clinical Biochemistry Rigshospitalet Univeristy of Copenhagen Denmark Borås, Mayr 11 h, 2007
 First trimester screening in Denmark Historical overview of the Prenatal screening in Denmark – Early 1970 s First antenatal diagnosis of DS – 1978 Introduction of national guidelines for when offer karyotyping All women > 35 years Women with known risk factors: 4 Previous birth of a child with karyotype anomalies 4 Carrier state of a known disease, e. g. thalassemia, CF, – 1980 Screening for NTD using MS-AFP and ultrasound – 1990 Screening for DS using MS-AFP, HCG and u. E 3 as part of trials in parts of Denmark 2
First trimester screening in Denmark Historical overview of the Prenatal screening in Denmark – Early 1970 s First antenatal diagnosis of DS – 1978 Introduction of national guidelines for when offer karyotyping All women > 35 years Women with known risk factors: 4 Previous birth of a child with karyotype anomalies 4 Carrier state of a known disease, e. g. thalassemia, CF, – 1980 Screening for NTD using MS-AFP and ultrasound – 1990 Screening for DS using MS-AFP, HCG and u. E 3 as part of trials in parts of Denmark 2
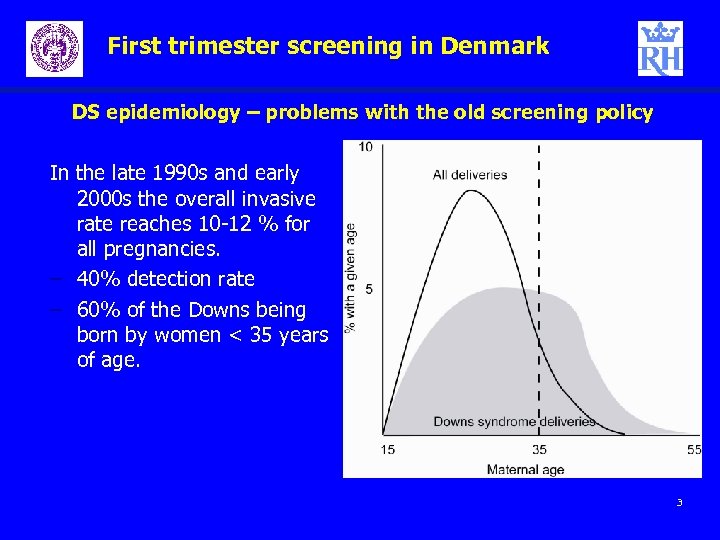 First trimester screening in Denmark DS epidemiology – problems with the old screening policy In the late 1990 s and early 2000 s the overall invasive rate reaches 10 -12 % for all pregnancies. – 40% detection rate – 60% of the Downs being born by women < 35 years of age. 3
First trimester screening in Denmark DS epidemiology – problems with the old screening policy In the late 1990 s and early 2000 s the overall invasive rate reaches 10 -12 % for all pregnancies. – 40% detection rate – 60% of the Downs being born by women < 35 years of age. 3
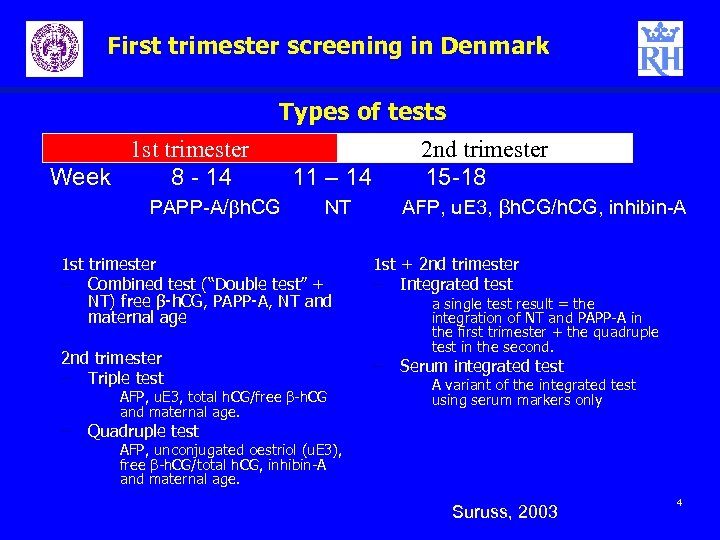 First trimester screening in Denmark Types of tests 1 st trimester Week 8 - 14 PAPP-A/bh. CG 11 – 14 NT 2 nd trimester 15 -18 AFP, u. E 3, βh. CG/h. CG, inhibin-A 1 st trimester – Combined test (“Double test” + NT) free β-h. CG, PAPP-A, NT and maternal age 1 st + 2 nd trimester – Integrated test 2 nd trimester – Triple test – Serum integrated test AFP, u. E 3, total h. CG/free β-h. CG and maternal age. a single test result = the integration of NT and PAPP-A in the first trimester + the quadruple test in the second. A variant of the integrated test using serum markers only – Quadruple test AFP, unconjugated oestriol (u. E 3), free β-h. CG/total h. CG, inhibin-A and maternal age. Suruss, 2003 4
First trimester screening in Denmark Types of tests 1 st trimester Week 8 - 14 PAPP-A/bh. CG 11 – 14 NT 2 nd trimester 15 -18 AFP, u. E 3, βh. CG/h. CG, inhibin-A 1 st trimester – Combined test (“Double test” + NT) free β-h. CG, PAPP-A, NT and maternal age 1 st + 2 nd trimester – Integrated test 2 nd trimester – Triple test – Serum integrated test AFP, u. E 3, total h. CG/free β-h. CG and maternal age. a single test result = the integration of NT and PAPP-A in the first trimester + the quadruple test in the second. A variant of the integrated test using serum markers only – Quadruple test AFP, unconjugated oestriol (u. E 3), free β-h. CG/total h. CG, inhibin-A and maternal age. Suruss, 2003 4
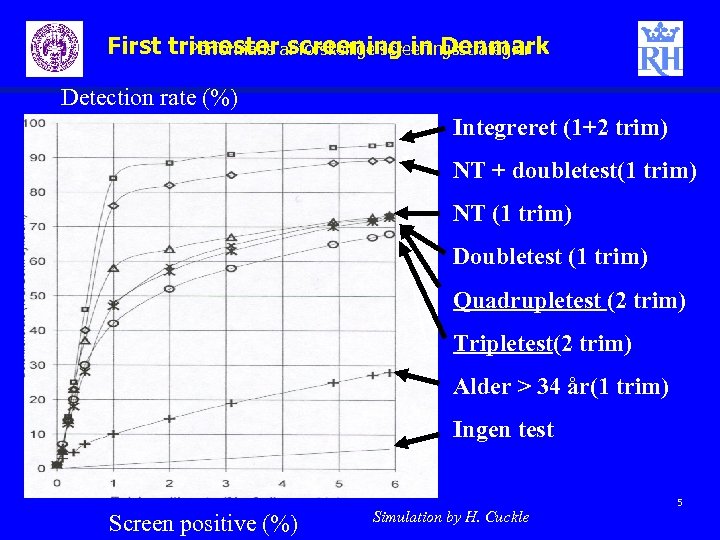 First trimester screening in Denmark Performans af forskellige screeningsstrategier Detection rate (%) Integreret (1+2 trim) NT + doubletest(1 trim) NT (1 trim) Doubletest (1 trim) Quadrupletest (2 trim) Tripletest(2 trim) Alder > 34 år(1 trim) Ingen test Screen positive (%) Simulation by H. Cuckle 5
First trimester screening in Denmark Performans af forskellige screeningsstrategier Detection rate (%) Integreret (1+2 trim) NT + doubletest(1 trim) NT (1 trim) Doubletest (1 trim) Quadrupletest (2 trim) Tripletest(2 trim) Alder > 34 år(1 trim) Ingen test Screen positive (%) Simulation by H. Cuckle 5
 First trimester screening in Denmark Types of tests 1 st trimester Week 8 - 14 PAPP-A/bh. CG 11 – 14 NT 2 nd trimester 15 - 20 AFP, u. E 3, βh. CG/h. CG, inhibin-A Why 1 st trimester screening is preferred – Faster result -> the pregnant women have less time in which to worry – If needed abortion can be performed almost within limits for “free abortion” – High % of attendance because: Pregnant women want to see the baby – they accept the NT as part of “seeing the baby”. However, once they’ve seen it, they are less likely to come back. – (Programs combining 1 st and 2 nd trimester screening suffer from patients not attending the 2 nd trimester screening. ) 6
First trimester screening in Denmark Types of tests 1 st trimester Week 8 - 14 PAPP-A/bh. CG 11 – 14 NT 2 nd trimester 15 - 20 AFP, u. E 3, βh. CG/h. CG, inhibin-A Why 1 st trimester screening is preferred – Faster result -> the pregnant women have less time in which to worry – If needed abortion can be performed almost within limits for “free abortion” – High % of attendance because: Pregnant women want to see the baby – they accept the NT as part of “seeing the baby”. However, once they’ve seen it, they are less likely to come back. – (Programs combining 1 st and 2 nd trimester screening suffer from patients not attending the 2 nd trimester screening. ) 6
 First trimester screening in Denmark Initial questions from the Danish National board of health – Can foreign programs be copied? – can their performance be achieved? 7
First trimester screening in Denmark Initial questions from the Danish National board of health – Can foreign programs be copied? – can their performance be achieved? 7
 First trimester screening in Denmark 1 st Trimester screening trials in Denmark Copenhagen first trimester study (HS) (1997 -2001) (Wøjdeman et al. , 2005) Intervention study – by NT only – NT was measured in 8622 singleton pregnancies (97. 5% of the screened cases) GA 10 + 3 and 13 + 6 weeks. DR for DS with NT alone 75%, FPR 1. 8%. – beta-h. CG and PAPP-A were analyzed in 6441 cases. DR 73%, FPRs of 8. 8% – the combined test (NT + biochemistry) DR 91%, FPR 2. 1% – Low beta-h. CG and PAPP-A values (below 0. 4 Mo. M) were observed in 0. 5% of the women including all cases of triploidy and trisomy 18 and 13. Skejby study (Schøidt et al. , 2006) Intervention study by Double + NT – 881 had the full test. – Screen positive = 34. – CVS with aneuploidy = 11 (6 trisomy-21, 5 others). – FPR = 3. 2%. Positive Predictive Value (PPV) = 17. 6% for T-21. Bent Nørgaard-Pedersen and Michael Chistriansen, both Statens Serum Institut 8
First trimester screening in Denmark 1 st Trimester screening trials in Denmark Copenhagen first trimester study (HS) (1997 -2001) (Wøjdeman et al. , 2005) Intervention study – by NT only – NT was measured in 8622 singleton pregnancies (97. 5% of the screened cases) GA 10 + 3 and 13 + 6 weeks. DR for DS with NT alone 75%, FPR 1. 8%. – beta-h. CG and PAPP-A were analyzed in 6441 cases. DR 73%, FPRs of 8. 8% – the combined test (NT + biochemistry) DR 91%, FPR 2. 1% – Low beta-h. CG and PAPP-A values (below 0. 4 Mo. M) were observed in 0. 5% of the women including all cases of triploidy and trisomy 18 and 13. Skejby study (Schøidt et al. , 2006) Intervention study by Double + NT – 881 had the full test. – Screen positive = 34. – CVS with aneuploidy = 11 (6 trisomy-21, 5 others). – FPR = 3. 2%. Positive Predictive Value (PPV) = 17. 6% for T-21. Bent Nørgaard-Pedersen and Michael Chistriansen, both Statens Serum Institut 8
 First trimester screening in Denmark ”Fetal Diagnostics and Risk Evaluation” A report from Danish National Board of Health, April 1 st 2003 Antenatal care in Denmark 2004/5 -> • Week 8 -10 (-12) GP (confirmatory) pregnancy testing, general information about the pregnancy and information 1 st trimester scrrening program for DS • Week 8 -10 (-12) Blood sampling for biochemistry performed at GP or at the hospital • Week 11 -13+6 NT (maybe one-stop) • If screen positive CVS/AC • Week 18 -20 malformation screening by ultrasound 9
First trimester screening in Denmark ”Fetal Diagnostics and Risk Evaluation” A report from Danish National Board of Health, April 1 st 2003 Antenatal care in Denmark 2004/5 -> • Week 8 -10 (-12) GP (confirmatory) pregnancy testing, general information about the pregnancy and information 1 st trimester scrrening program for DS • Week 8 -10 (-12) Blood sampling for biochemistry performed at GP or at the hospital • Week 11 -13+6 NT (maybe one-stop) • If screen positive CVS/AC • Week 18 -20 malformation screening by ultrasound 9
 First trimester screening in Denmark National guidelines for quality assurance of the 1 st trimester screening – Ultrasound Certification of sonographers Continuous monitoring (>500 scan/year) Each centre should handle at least 1, 000 deliveries per year – Biochemistry Internal & external quality control Minimal number of test required 4 > 5, 000 tests/year -> the laboratory can operate independently 4 < 5, 000 tests/year -> the laboratory can only operate if they collaborate with a another laboratory on quality assurance – Screening program performance Screen positive rates should be monitored False negative rates should be monitored A National center for monitoring the quality of the program should be established 10
First trimester screening in Denmark National guidelines for quality assurance of the 1 st trimester screening – Ultrasound Certification of sonographers Continuous monitoring (>500 scan/year) Each centre should handle at least 1, 000 deliveries per year – Biochemistry Internal & external quality control Minimal number of test required 4 > 5, 000 tests/year -> the laboratory can operate independently 4 < 5, 000 tests/year -> the laboratory can only operate if they collaborate with a another laboratory on quality assurance – Screening program performance Screen positive rates should be monitored False negative rates should be monitored A National center for monitoring the quality of the program should be established 10
 First trimester screening in Denmark Implementation of 1. trimester screening NT + biochemistry Copy the FMF program to the very point => – known screen positive rates – Known detection rates 11
First trimester screening in Denmark Implementation of 1. trimester screening NT + biochemistry Copy the FMF program to the very point => – known screen positive rates – Known detection rates 11
 First trimester screening in Denmark Implementation of 1. trimester screening NT + biochemistry The sonography followed FMF guidelines – NT had already been established at several centers Major Departments of Fetal medicine performing the NT had all been trained by the Fetal Medicine Foundattion, London, all sonographers were already FMF-certified. – NT QC All sonographers are FMF certified – Software All Departments of Fetal medicine were using the Astraia software (FMF approved) 12
First trimester screening in Denmark Implementation of 1. trimester screening NT + biochemistry The sonography followed FMF guidelines – NT had already been established at several centers Major Departments of Fetal medicine performing the NT had all been trained by the Fetal Medicine Foundattion, London, all sonographers were already FMF-certified. – NT QC All sonographers are FMF certified – Software All Departments of Fetal medicine were using the Astraia software (FMF approved) 12
 First trimester screening in Denmark Implementation of 1. trimester screening NT + biochemistry Biochemistry – Exclusively performed at Depts. of Clinical biochemistry It was decided to follow the FMF standards and only use FMF certified platforms because only data generate using these platforms can be entered into the Astraia software 4 Brahms Kryptor 4 Perkin Elmer Delphia Systems – QC Internal and external controls. All Depts. Of Clinical biochemistry are participating in the UKNEQAS 1. trimester QC program Monitor screenpostive rate Monitor medians Mo. M 13
First trimester screening in Denmark Implementation of 1. trimester screening NT + biochemistry Biochemistry – Exclusively performed at Depts. of Clinical biochemistry It was decided to follow the FMF standards and only use FMF certified platforms because only data generate using these platforms can be entered into the Astraia software 4 Brahms Kryptor 4 Perkin Elmer Delphia Systems – QC Internal and external controls. All Depts. Of Clinical biochemistry are participating in the UKNEQAS 1. trimester QC program Monitor screenpostive rate Monitor medians Mo. M 13
 First trimester screening in Denmark Implementation of 1. trimester screening NT + biochemistry Risk estimation All centers performing NT sonography use the Astraia software Biochemical data generated using FMF approved platforms can be entered directly into Astraia could be used for risk estimation Astraia could be used for quality assurance. 14
First trimester screening in Denmark Implementation of 1. trimester screening NT + biochemistry Risk estimation All centers performing NT sonography use the Astraia software Biochemical data generated using FMF approved platforms can be entered directly into Astraia could be used for risk estimation Astraia could be used for quality assurance. 14
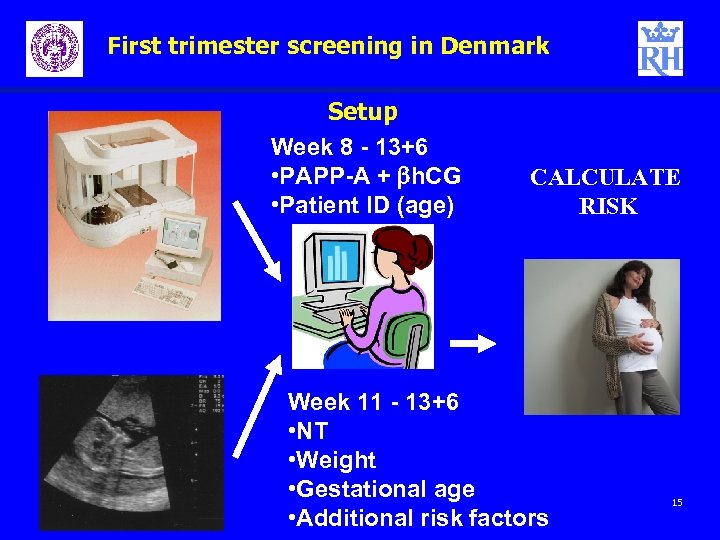 First trimester screening in Denmark Setup Week 8 - 13+6 • PAPP-A + bh. CG • Patient ID (age) CALCULATE RISK Week 11 - 13+6 • NT • Weight • Gestational age • Additional risk factors 15
First trimester screening in Denmark Setup Week 8 - 13+6 • PAPP-A + bh. CG • Patient ID (age) CALCULATE RISK Week 11 - 13+6 • NT • Weight • Gestational age • Additional risk factors 15
 First trimester screening in Denmark Challenges - 1 – Astraia The window for which biochemistry is accepted in Astraia 4 Expanded from 10+0 – 13+6 to 8+0 – 13+6 in 2005 Inability of Astraia to communicate with the Hospital Laboratory Information Management System 4 All data have to be manually entered into Astraia. This is associated with a great risk for typing mistakes. 4 Astraia are currently working on making the necessary changes – deadline? 16
First trimester screening in Denmark Challenges - 1 – Astraia The window for which biochemistry is accepted in Astraia 4 Expanded from 10+0 – 13+6 to 8+0 – 13+6 in 2005 Inability of Astraia to communicate with the Hospital Laboratory Information Management System 4 All data have to be manually entered into Astraia. This is associated with a great risk for typing mistakes. 4 Astraia are currently working on making the necessary changes – deadline? 16
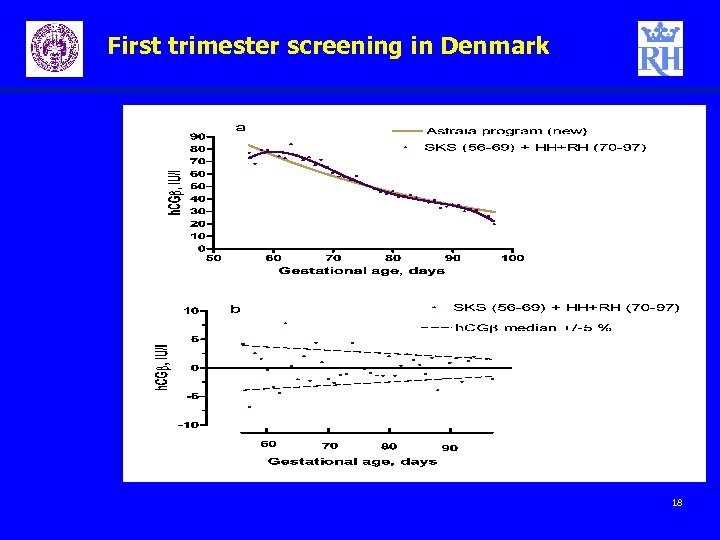
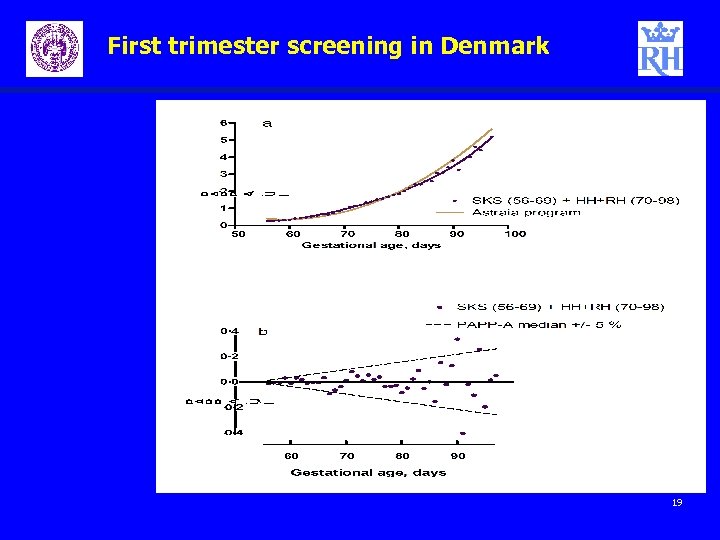
 First trimester screening in Denmark Challenges - 2 – Default medians – can they be used Initial study 1500 samples analyzed at Hvidovre and Rigshospitalet -> Yes Follow-up 20000 samples analyzed at Hvidovre and Rigshospitalet -> Yes but ability to modify medians would be preferable 17
First trimester screening in Denmark Challenges - 2 – Default medians – can they be used Initial study 1500 samples analyzed at Hvidovre and Rigshospitalet -> Yes Follow-up 20000 samples analyzed at Hvidovre and Rigshospitalet -> Yes but ability to modify medians would be preferable 17
 First trimester screening in Denmark 18
First trimester screening in Denmark 18
 First trimester screening in Denmark 19
First trimester screening in Denmark 19
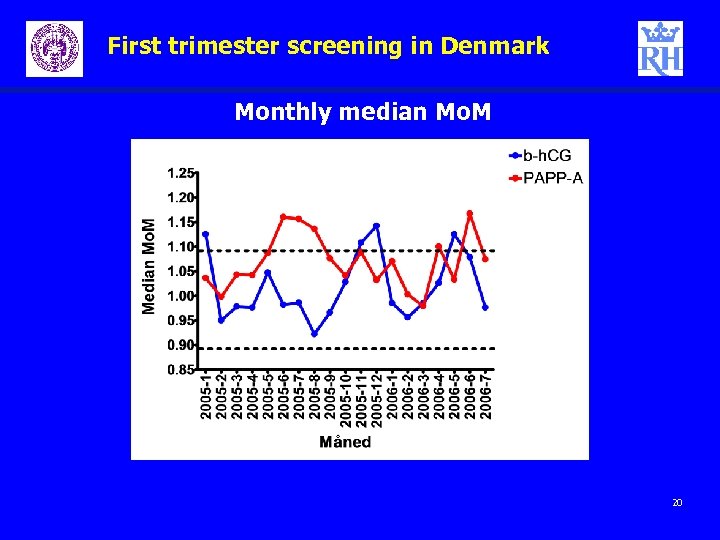 First trimester screening in Denmark Monthly median Mo. M 20
First trimester screening in Denmark Monthly median Mo. M 20
 First trimester screening in Denmark Conclusion Medians – Medians can be used during start up phase of a first triemster program. – The bigger Danish centres would like to be able to individualise the Kryptor medians (scheduled to take place with the next Astraia update) – The Delphia Express medians needed a major adjustment (which has taken place) 21
First trimester screening in Denmark Conclusion Medians – Medians can be used during start up phase of a first triemster program. – The bigger Danish centres would like to be able to individualise the Kryptor medians (scheduled to take place with the next Astraia update) – The Delphia Express medians needed a major adjustment (which has taken place) 21
 First trimester screening in Denmark Challenges - 3 – Pre-analytical – can samples be sent by mail to the laboratories Pilot experiment Compare medians 22
First trimester screening in Denmark Challenges - 3 – Pre-analytical – can samples be sent by mail to the laboratories Pilot experiment Compare medians 22
 First trimester screening in Denmark Summer temperatures in Denmark 23
First trimester screening in Denmark Summer temperatures in Denmark 23
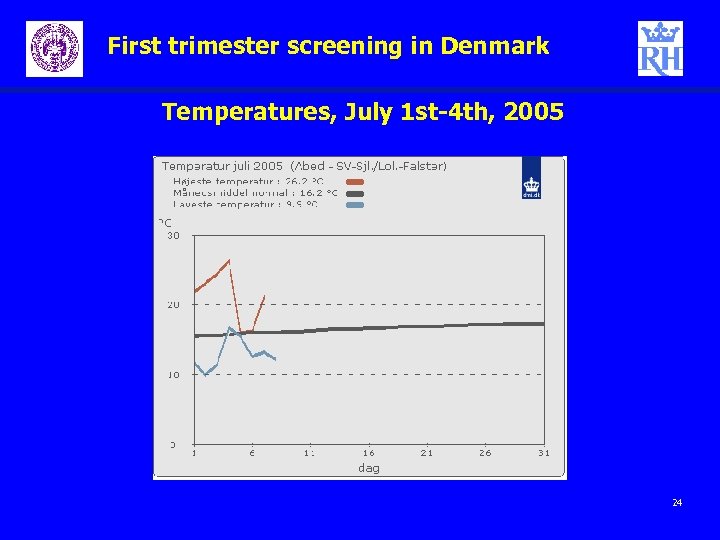 First trimester screening in Denmark Temperatures, July 1 st-4 th, 2005 24
First trimester screening in Denmark Temperatures, July 1 st-4 th, 2005 24
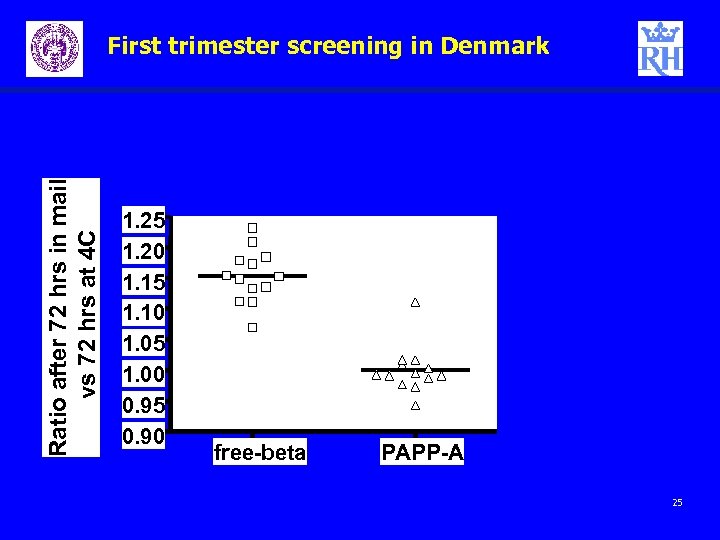 Ratio after 72 hrs in mail vs 72 hrs at 4 C First trimester screening in Denmark 1. 25 1. 20 1. 15 1. 10 1. 05 1. 00 0. 95 0. 90 free-beta PAPP-A 25
Ratio after 72 hrs in mail vs 72 hrs at 4 C First trimester screening in Denmark 1. 25 1. 20 1. 15 1. 10 1. 05 1. 00 0. 95 0. 90 free-beta PAPP-A 25
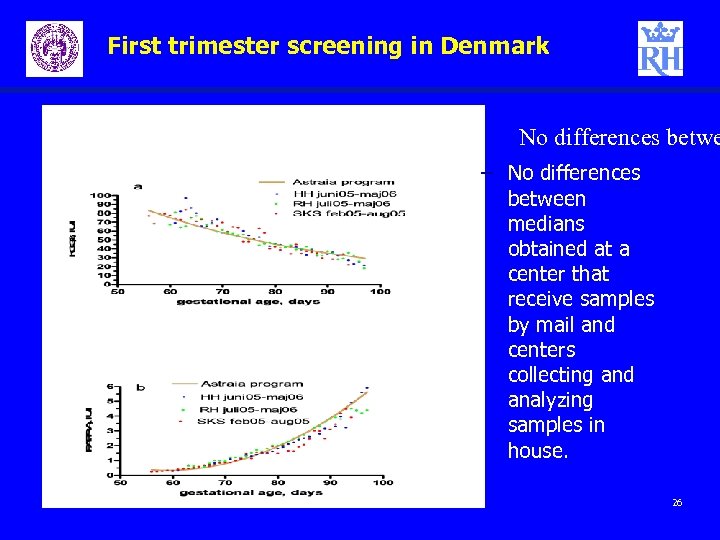 First trimester screening in Denmark No differences betwe – No differences between medians obtained at a center that receive samples by mail and centers collecting and analyzing samples in house. 26
First trimester screening in Denmark No differences betwe – No differences between medians obtained at a center that receive samples by mail and centers collecting and analyzing samples in house. 26
 First trimester screening in Denmark Conclusions transport – Sending the samples to the laboratories using mail does not affect medians. – However, care should be taken to avoid exposing samples to high temperatures. 27
First trimester screening in Denmark Conclusions transport – Sending the samples to the laboratories using mail does not affect medians. – However, care should be taken to avoid exposing samples to high temperatures. 27
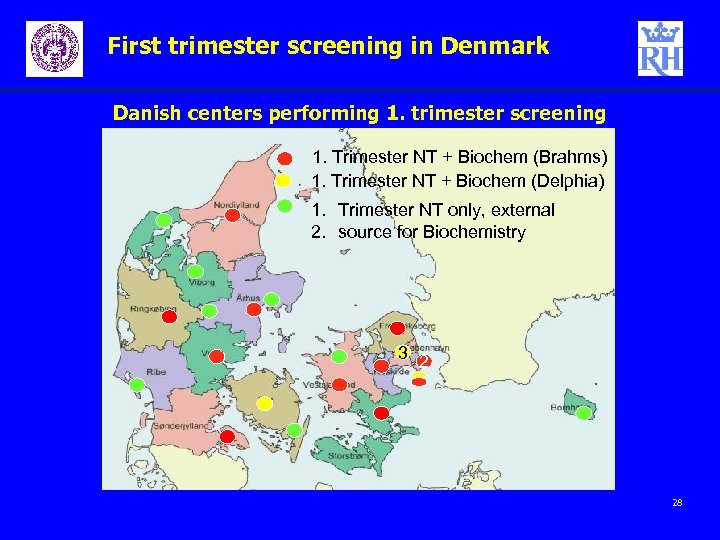 First trimester screening in Denmark Danish centers performing 1. trimester screening 1. Trimester NT + Biochem (Brahms) 1. Trimester NT + Biochem (Delphia) 1. Trimester NT only, external 2. source for Biochemistry 3 2 28
First trimester screening in Denmark Danish centers performing 1. trimester screening 1. Trimester NT + Biochem (Brahms) 1. Trimester NT + Biochem (Delphia) 1. Trimester NT only, external 2. source for Biochemistry 3 2 28
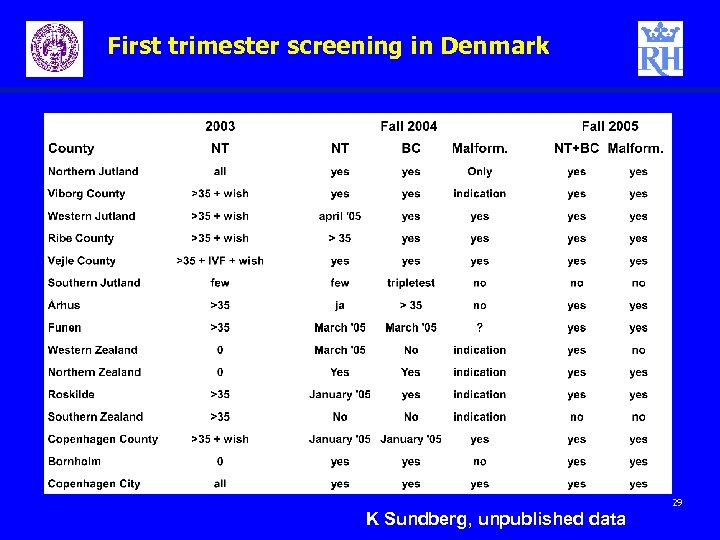 First trimester screening in Denmark 29 K Sundberg, unpublished data
First trimester screening in Denmark 29 K Sundberg, unpublished data
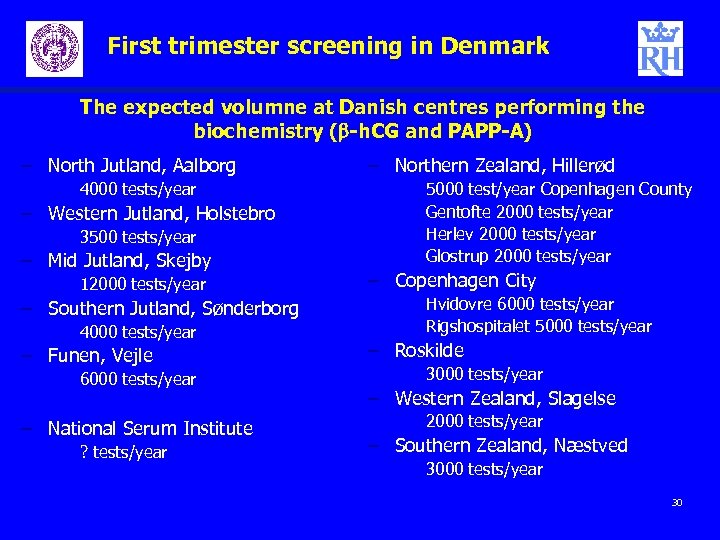 First trimester screening in Denmark The expected volumne at Danish centres performing the biochemistry (b-h. CG and PAPP-A) – North Jutland, Aalborg 4000 tests/year – Western Jutland, Holstebro 3500 tests/year – Mid Jutland, Skejby 12000 tests/year – Southern Jutland, Sønderborg 4000 tests/year – Funen, Vejle 6000 tests/year – National Serum Institute ? tests/year – Northern Zealand, Hillerød 5000 test/year Copenhagen County Gentofte 2000 tests/year Herlev 2000 tests/year Glostrup 2000 tests/year – Copenhagen City Hvidovre 6000 tests/year Rigshospitalet 5000 tests/year – Roskilde 3000 tests/year – Western Zealand, Slagelse 2000 tests/year – Southern Zealand, Næstved 3000 tests/year 30
First trimester screening in Denmark The expected volumne at Danish centres performing the biochemistry (b-h. CG and PAPP-A) – North Jutland, Aalborg 4000 tests/year – Western Jutland, Holstebro 3500 tests/year – Mid Jutland, Skejby 12000 tests/year – Southern Jutland, Sønderborg 4000 tests/year – Funen, Vejle 6000 tests/year – National Serum Institute ? tests/year – Northern Zealand, Hillerød 5000 test/year Copenhagen County Gentofte 2000 tests/year Herlev 2000 tests/year Glostrup 2000 tests/year – Copenhagen City Hvidovre 6000 tests/year Rigshospitalet 5000 tests/year – Roskilde 3000 tests/year – Western Zealand, Slagelse 2000 tests/year – Southern Zealand, Næstved 3000 tests/year 30
 First trimester screening in Denmark Regimes at the centers – One stop Samples drawn and NT performed at the same day at the hospital in weeks 11 -13+6 (Copenhagen County) – Two stop Samples drawn at the GP in weeks 8 -10, NT 11 -13+6 at the Hospital (most hospitals) Samples drawn at the hospital in weeks 8 -13+6, NT 1113+6 at the Hospital (Hvidovre and Rigshospitalet) – Risk calculation Only the final risk is calculated. An independent risk based on PAPP-A and b-h. CG is NOT calculated 31
First trimester screening in Denmark Regimes at the centers – One stop Samples drawn and NT performed at the same day at the hospital in weeks 11 -13+6 (Copenhagen County) – Two stop Samples drawn at the GP in weeks 8 -10, NT 11 -13+6 at the Hospital (most hospitals) Samples drawn at the hospital in weeks 8 -13+6, NT 1113+6 at the Hospital (Hvidovre and Rigshospitalet) – Risk calculation Only the final risk is calculated. An independent risk based on PAPP-A and b-h. CG is NOT calculated 31
 First trimester screening in Denmark How the pregnant women choose Accept to be screened Yes > 80% RH Accept having a CVS if screen positive Yes - CVS Wants a diagnostic despite a low risk estimate Few Choses abortion after the fetus has been found to carry trisomi 21 All but one! 32
First trimester screening in Denmark How the pregnant women choose Accept to be screened Yes > 80% RH Accept having a CVS if screen positive Yes - CVS Wants a diagnostic despite a low risk estimate Few Choses abortion after the fetus has been found to carry trisomi 21 All but one! 32
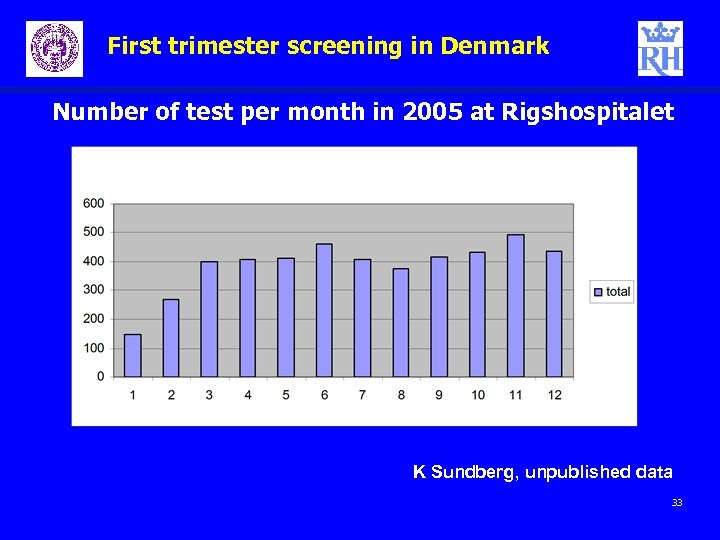 First trimester screening in Denmark Number of test per month in 2005 at Rigshospitalet K Sundberg, unpublished data 33
First trimester screening in Denmark Number of test per month in 2005 at Rigshospitalet K Sundberg, unpublished data 33
 First trimester screening in Denmark Reasons for not enroling in the first trimester screening Percentage not enroling 6% - 8% • Late bookers • Ethnic minorities • Unaware of the screening program • Don’t wish to be screened (few) K Sundberg, unpublished data 34
First trimester screening in Denmark Reasons for not enroling in the first trimester screening Percentage not enroling 6% - 8% • Late bookers • Ethnic minorities • Unaware of the screening program • Don’t wish to be screened (few) K Sundberg, unpublished data 34
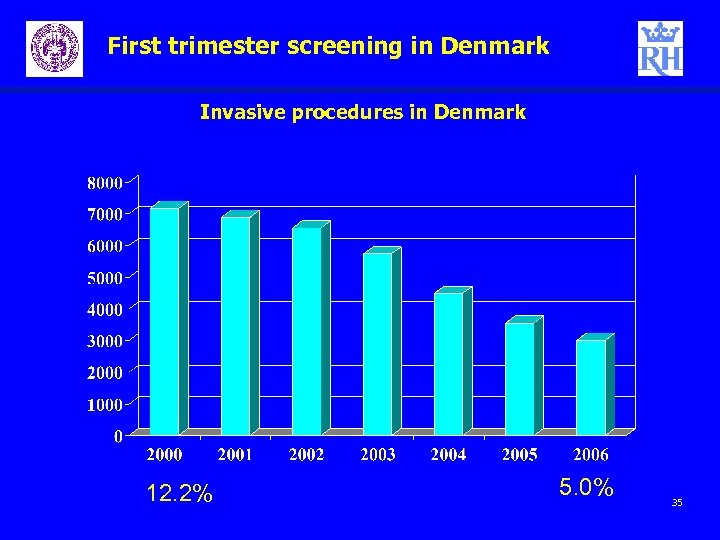 First trimester screening in Denmark Invasive procedures in Denmark 12. 2% 5. 0% 35
First trimester screening in Denmark Invasive procedures in Denmark 12. 2% 5. 0% 35
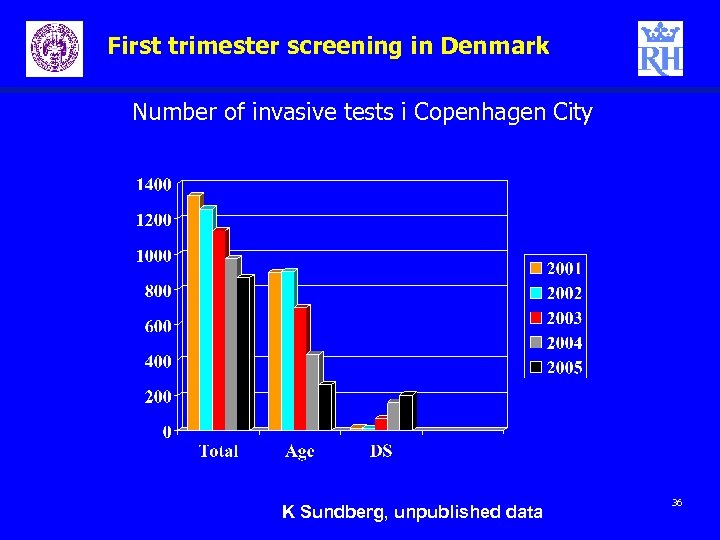 First trimester screening in Denmark Number of invasive tests i Copenhagen City K Sundberg, unpublished data 36
First trimester screening in Denmark Number of invasive tests i Copenhagen City K Sundberg, unpublished data 36
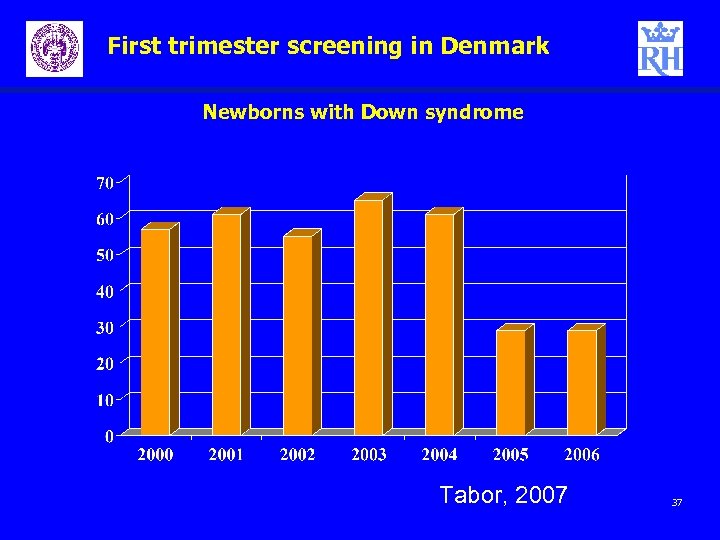 First trimester screening in Denmark Newborns with Down syndrome Tabor, 2007 37
First trimester screening in Denmark Newborns with Down syndrome Tabor, 2007 37
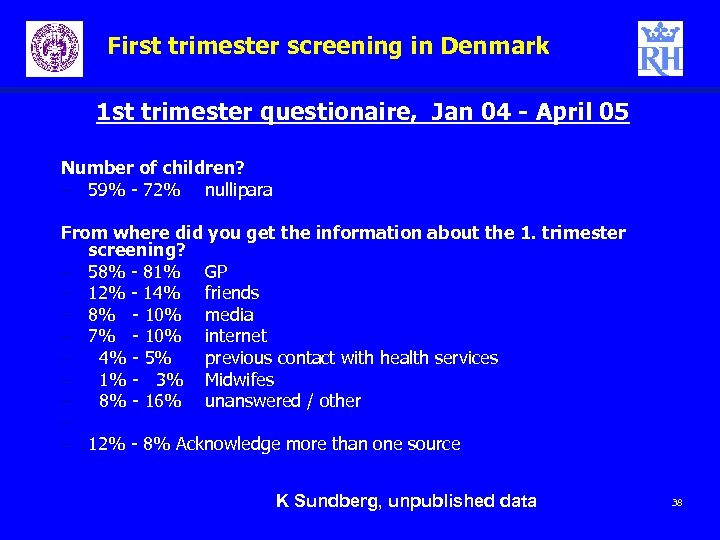 First trimester screening in Denmark 1 st trimester questionaire, Jan 04 - April 05 Number of children? – 59% - 72% nullipara From where did you get the information about the 1. trimester screening? – 58% - 81% GP – 12% - 14% friends – 8% - 10% media – 7% - 10% internet – 4% - 5% previous contact with health services – 1% - 3% Midwifes – 8% - 16% unanswered / other – – 12% - 8% Acknowledge more than one source K Sundberg, unpublished data 38
First trimester screening in Denmark 1 st trimester questionaire, Jan 04 - April 05 Number of children? – 59% - 72% nullipara From where did you get the information about the 1. trimester screening? – 58% - 81% GP – 12% - 14% friends – 8% - 10% media – 7% - 10% internet – 4% - 5% previous contact with health services – 1% - 3% Midwifes – 8% - 16% unanswered / other – – 12% - 8% Acknowledge more than one source K Sundberg, unpublished data 38
 First trimester screening in Denmark Future tasks – Establishment of a national QC database which will pair data from Astraia 4 NT data 4 Biochemistry data The Danish Cytogenetic Central register (DCCR) National patient register (LPR) which includes data from the Danish newborn register and the Danish abortion register – Better information to the pregnant women 39
First trimester screening in Denmark Future tasks – Establishment of a national QC database which will pair data from Astraia 4 NT data 4 Biochemistry data The Danish Cytogenetic Central register (DCCR) National patient register (LPR) which includes data from the Danish newborn register and the Danish abortion register – Better information to the pregnant women 39
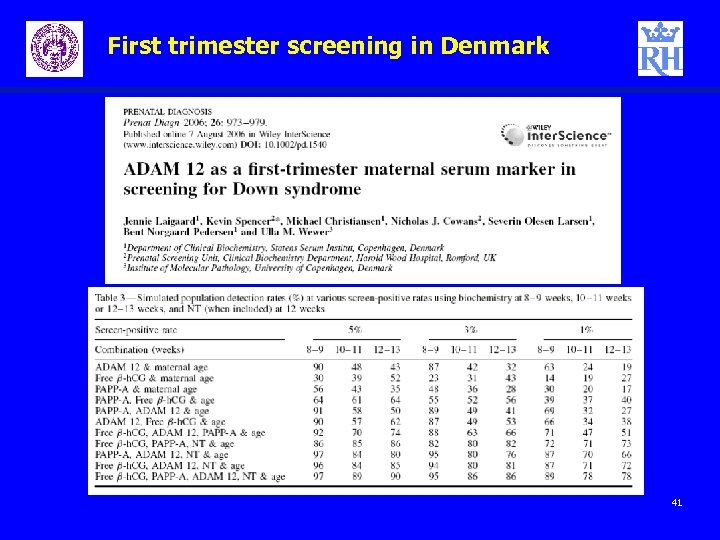
 First trimester screening in Denmark New markers and new strategies – ADAM 12 – Contingent testing – Repeated measurement 40
First trimester screening in Denmark New markers and new strategies – ADAM 12 – Contingent testing – Repeated measurement 40
 First trimester screening in Denmark 41
First trimester screening in Denmark 41
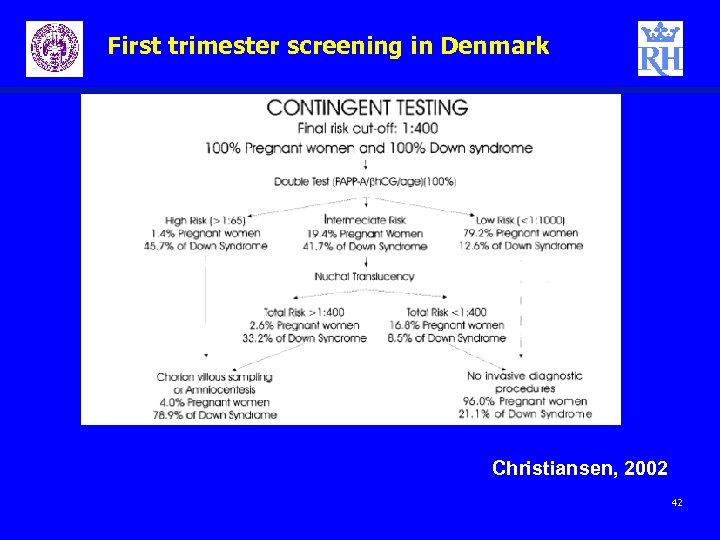 First trimester screening in Denmark Christiansen, 2002 42
First trimester screening in Denmark Christiansen, 2002 42
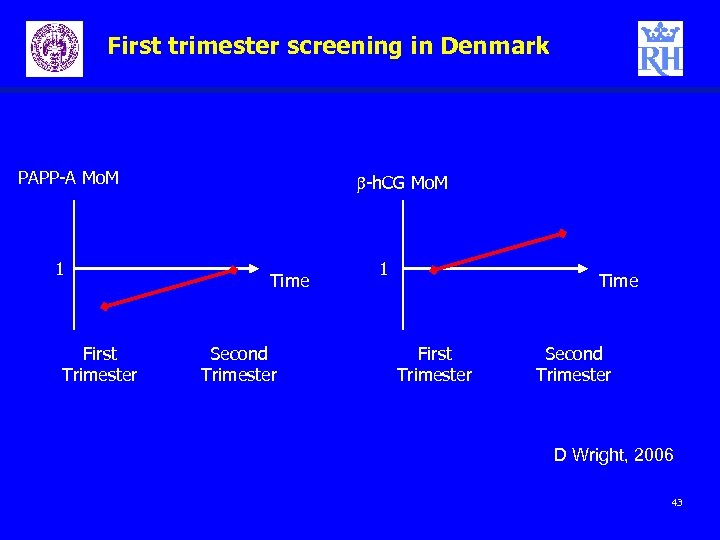 First trimester screening in Denmark PAPP-A Mo. M 1 First Trimester b-h. CG Mo. M Time Second Trimester 1 Time First Trimester Second Trimester D Wright, 2006 43
First trimester screening in Denmark PAPP-A Mo. M 1 First Trimester b-h. CG Mo. M Time Second Trimester 1 Time First Trimester Second Trimester D Wright, 2006 43
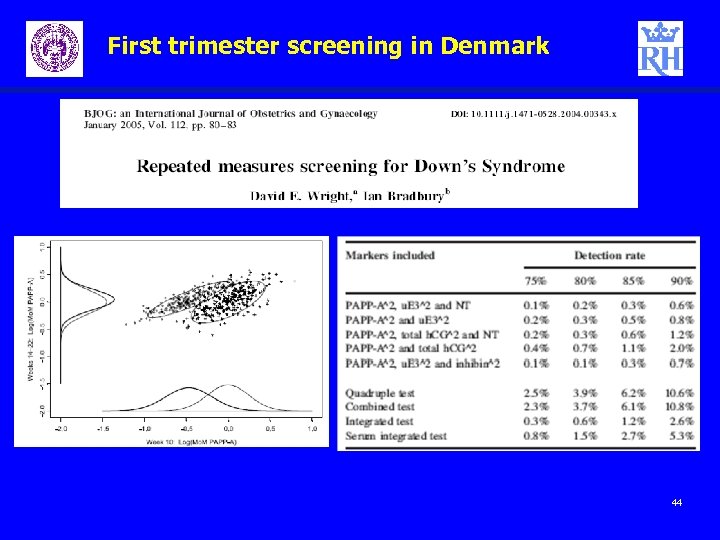 First trimester screening in Denmark 44
First trimester screening in Denmark 44
 First trimester screening in Denmark Conclusions – It has been possible to offer all pregnant women first trimester screening in Denmark by Duplicating an existing well proven program (for instance the FMF program) Having well educated staff 4 Nuchal translucency 4 Biochemistry Adhering to the strict quality control rules (e. g. the rules set up by the FMF) 4 Nuchal translucency 4 Biochemistry Choosing components that work well together 4 Software 4 Analytical platform 45
First trimester screening in Denmark Conclusions – It has been possible to offer all pregnant women first trimester screening in Denmark by Duplicating an existing well proven program (for instance the FMF program) Having well educated staff 4 Nuchal translucency 4 Biochemistry Adhering to the strict quality control rules (e. g. the rules set up by the FMF) 4 Nuchal translucency 4 Biochemistry Choosing components that work well together 4 Software 4 Analytical platform 45
 First trimester screening in Denmark Acknowlegdements – Karin Sundberg, Rigshospitalet – Ann Tabor, Rigshospitalet – Connie Jørgensen, Rigshospitalet – Niels Tørring, Skejby Hospital – Steen Sørensen, Hvidovre Hospital 46
First trimester screening in Denmark Acknowlegdements – Karin Sundberg, Rigshospitalet – Ann Tabor, Rigshospitalet – Connie Jørgensen, Rigshospitalet – Niels Tørring, Skejby Hospital – Steen Sørensen, Hvidovre Hospital 46
 First trimester screening in Denmark Thank you for your attention 47
First trimester screening in Denmark Thank you for your attention 47
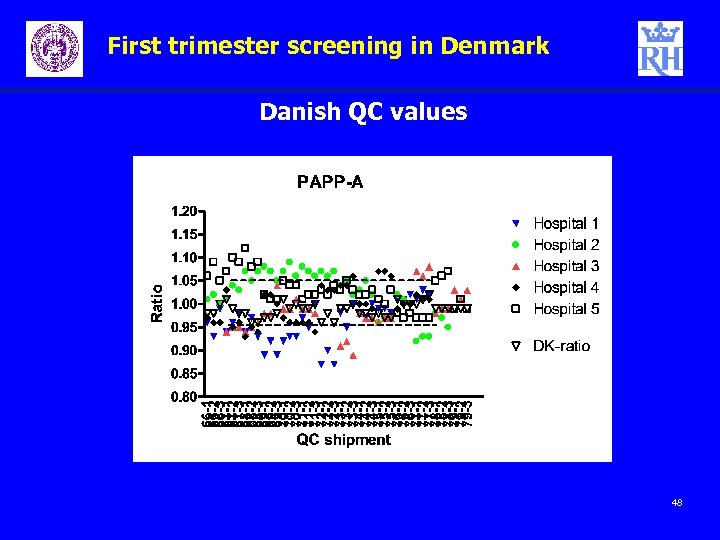 First trimester screening in Denmark Danish QC values 48
First trimester screening in Denmark Danish QC values 48
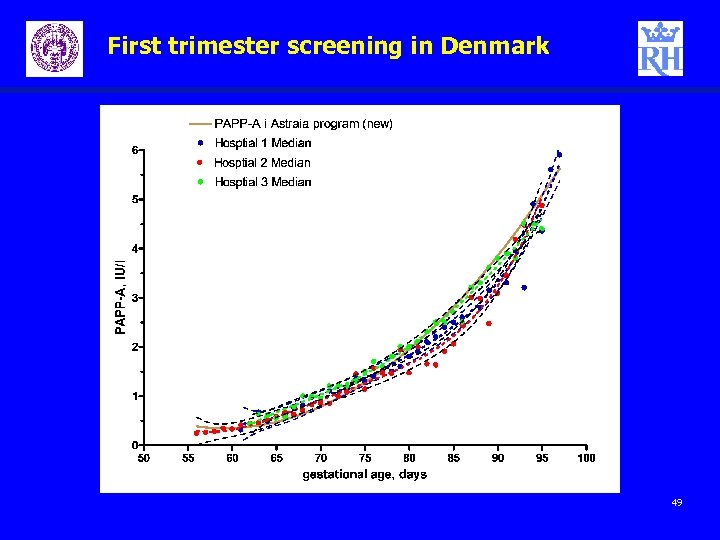 First trimester screening in Denmark 49
First trimester screening in Denmark 49
 First trimester screening in Denmark Outline – How it was Prevention oriented, age determined – The new policy Informed Choice – Implementation Choice of program to chose Choice of analytical platform – Status 2006 Where are we in Denmark – New markers and new strategies 50
First trimester screening in Denmark Outline – How it was Prevention oriented, age determined – The new policy Informed Choice – Implementation Choice of program to chose Choice of analytical platform – Status 2006 Where are we in Denmark – New markers and new strategies 50
 First trimester screening in Denmark Outline – How it was Prevention oriented, age determined – The new policy Informed Choice – Implementation Choice of program to chose Choice of analytical platform – Status 2006 Where are we in Denmark – New markers and new strategies 51
First trimester screening in Denmark Outline – How it was Prevention oriented, age determined – The new policy Informed Choice – Implementation Choice of program to chose Choice of analytical platform – Status 2006 Where are we in Denmark – New markers and new strategies 51
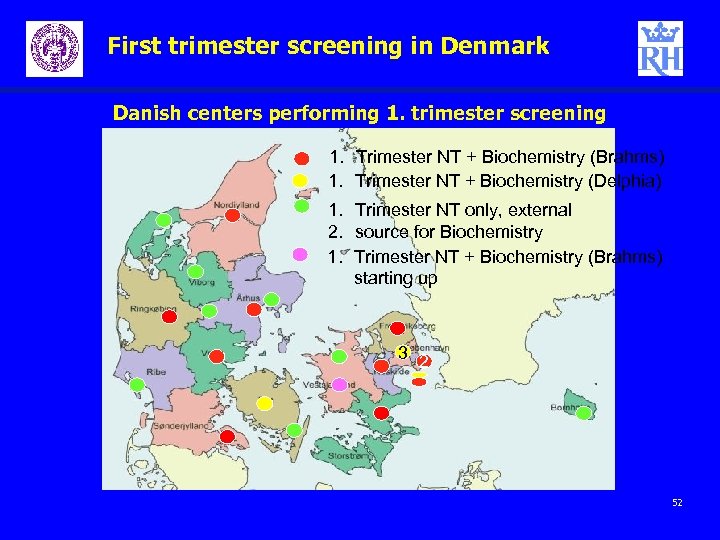 First trimester screening in Denmark Danish centers performing 1. trimester screening 1. Trimester NT + Biochemistry (Brahms) 1. Trimester NT + Biochemistry (Delphia) 1. Trimester NT only, external 2. source for Biochemistry 1. Trimester NT + Biochemistry (Brahms) starting up 3 2 52
First trimester screening in Denmark Danish centers performing 1. trimester screening 1. Trimester NT + Biochemistry (Brahms) 1. Trimester NT + Biochemistry (Delphia) 1. Trimester NT only, external 2. source for Biochemistry 1. Trimester NT + Biochemistry (Brahms) starting up 3 2 52
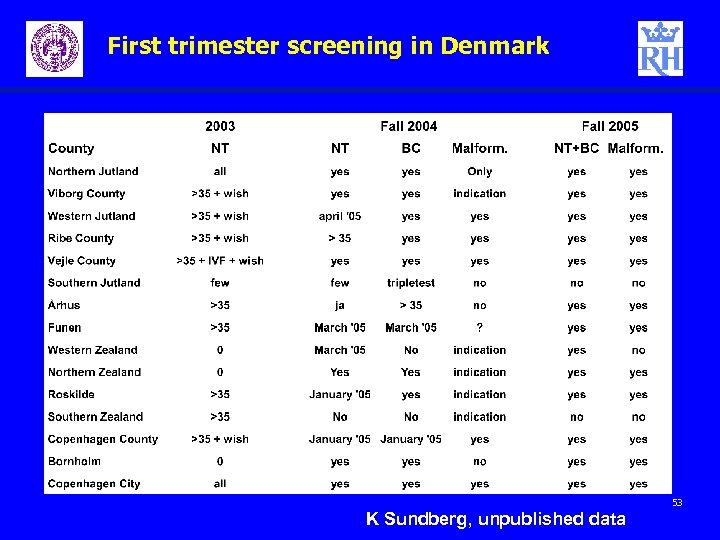 First trimester screening in Denmark 53 K Sundberg, unpublished data
First trimester screening in Denmark 53 K Sundberg, unpublished data
 First trimester screening in Denmark Performance – 4% screen positive rate – Due to the low number of undected DS, the detection rate is difficult to estimate at present. However it seems to be between 80 -95%, but numbers are still to small to allow for a proper evaluation at the different centers. 54
First trimester screening in Denmark Performance – 4% screen positive rate – Due to the low number of undected DS, the detection rate is difficult to estimate at present. However it seems to be between 80 -95%, but numbers are still to small to allow for a proper evaluation at the different centers. 54
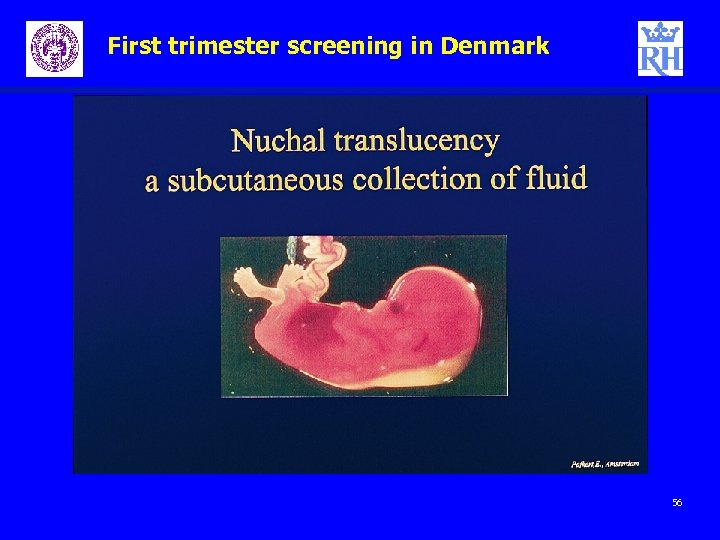
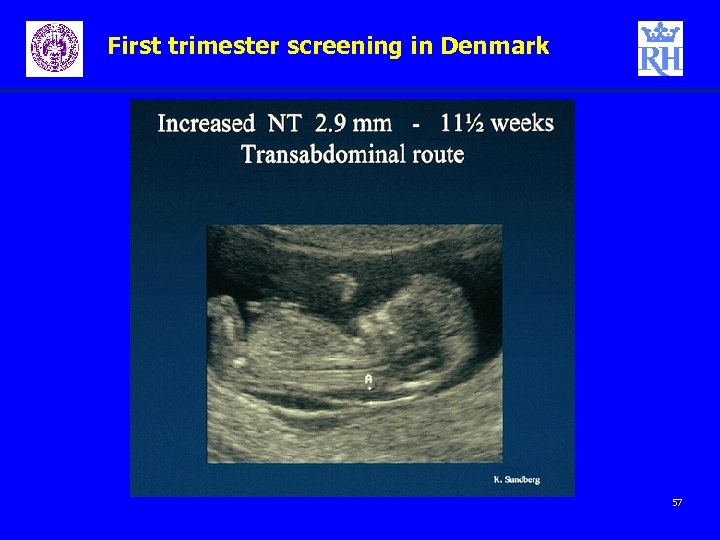
 First trimester screening in Denmark – – ) NT Biochemical markers Nick Wald introduces the Mo. Ms (multiples of meadian 55
First trimester screening in Denmark – – ) NT Biochemical markers Nick Wald introduces the Mo. Ms (multiples of meadian 55
 First trimester screening in Denmark 56
First trimester screening in Denmark 56
 First trimester screening in Denmark 57
First trimester screening in Denmark 57
 First trimester screening in Denmark The general idea – Chromosome aberrations and/or developmental abnormalities lead to altered secretions of peptides/proteins from the placenta – The maternal plasma concentration of these analytes can be measured – These results can be used for Screening Diagnosis 58
First trimester screening in Denmark The general idea – Chromosome aberrations and/or developmental abnormalities lead to altered secretions of peptides/proteins from the placenta – The maternal plasma concentration of these analytes can be measured – These results can be used for Screening Diagnosis 58
 First trimester screening in Denmark PAPP-A – IGF 4 BP protease – Secreted by the trophoblast – Released directly into maternal serum (not present in amniotic fluid) – Detectable at ~6 wks of pregnancy – Doubles every 6 days – Increases to plateau at 14 wks – Decreased levels in Downs (0. 3 -0. 4 Mo. M) 59
First trimester screening in Denmark PAPP-A – IGF 4 BP protease – Secreted by the trophoblast – Released directly into maternal serum (not present in amniotic fluid) – Detectable at ~6 wks of pregnancy – Doubles every 6 days – Increases to plateau at 14 wks – Decreased levels in Downs (0. 3 -0. 4 Mo. M) 59
 First trimester screening in Denmark Low Levels of PAPP-A – Trisomy 21 – Other chromosome abnormalities Trisomy 18 Trisomy 13 – Aneuploidy – Impending fetal death – Impaired fetal wellbeing Preterm labour Low birth weight 60
First trimester screening in Denmark Low Levels of PAPP-A – Trisomy 21 – Other chromosome abnormalities Trisomy 18 Trisomy 13 – Aneuploidy – Impending fetal death – Impaired fetal wellbeing Preterm labour Low birth weight 60
 First trimester screening in Denmark Free b-subunit h. CG – – · – – Glycoprotein hormone Secreted by placental trophoblast b subunit derived by elastase activity on total HCG Detectable 10 days post ovulation Initially doubles every 1. 5 – 2 days Peaks at 8 -10 weeks (FTS performed at 10 -14 weeks) Increased levels in Downs (2. 0 -2. 5 Mo. M) 61
First trimester screening in Denmark Free b-subunit h. CG – – · – – Glycoprotein hormone Secreted by placental trophoblast b subunit derived by elastase activity on total HCG Detectable 10 days post ovulation Initially doubles every 1. 5 – 2 days Peaks at 8 -10 weeks (FTS performed at 10 -14 weeks) Increased levels in Downs (2. 0 -2. 5 Mo. M) 61
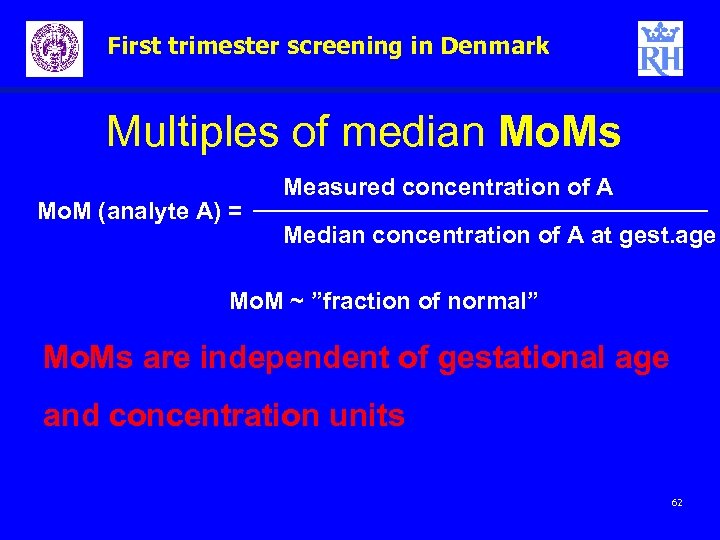 First trimester screening in Denmark Multiples of median Mo. Ms Measured concentration of A _________________ Mo. M (analyte A) = Median concentration of A at gest. age Mo. M ~ ”fraction of normal” Mo. Ms are independent of gestational age and concentration units 62
First trimester screening in Denmark Multiples of median Mo. Ms Measured concentration of A _________________ Mo. M (analyte A) = Median concentration of A at gest. age Mo. M ~ ”fraction of normal” Mo. Ms are independent of gestational age and concentration units 62
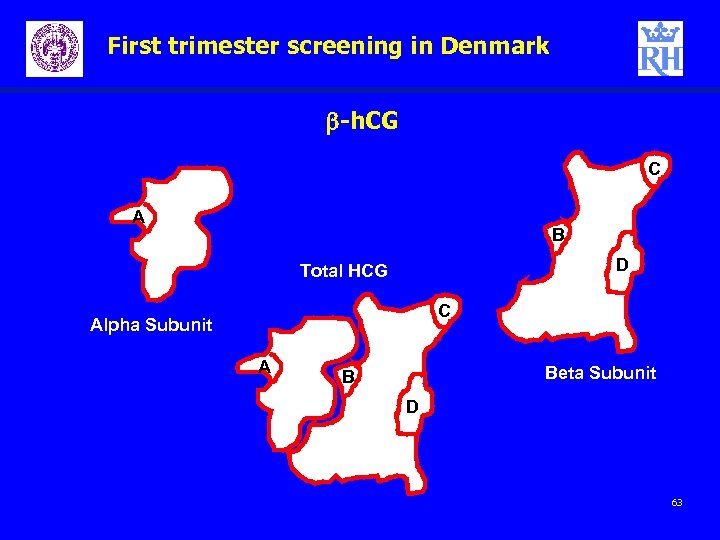 First trimester screening in Denmark b-h. CG C A B D Total HCG C Alpha Subunit A Beta Subunit B D 63
First trimester screening in Denmark b-h. CG C A B D Total HCG C Alpha Subunit A Beta Subunit B D 63
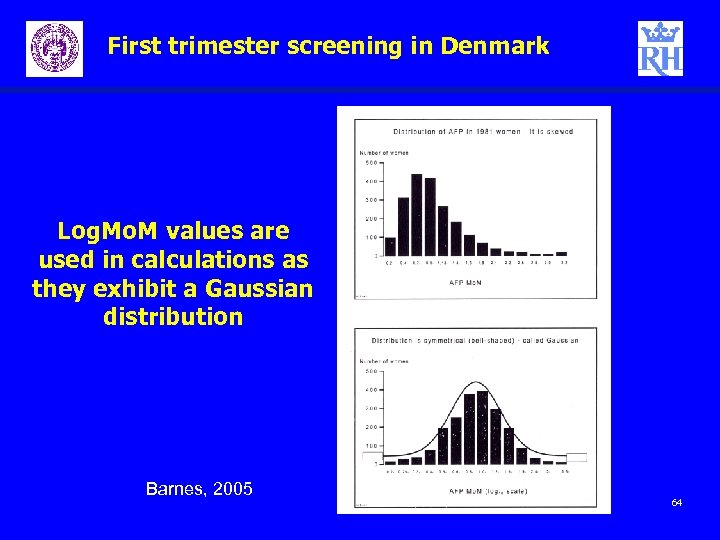 First trimester screening in Denmark Log. Mo. M values are used in calculations as they exhibit a Gaussian distribution Barnes, 2005 64
First trimester screening in Denmark Log. Mo. M values are used in calculations as they exhibit a Gaussian distribution Barnes, 2005 64
 First trimester screening in Denmark Factors influencing marker performance – – – – Maternal weight Smoking Diabetes mellitus Twins Ethnicity Mode of conception Parity 65
First trimester screening in Denmark Factors influencing marker performance – – – – Maternal weight Smoking Diabetes mellitus Twins Ethnicity Mode of conception Parity 65
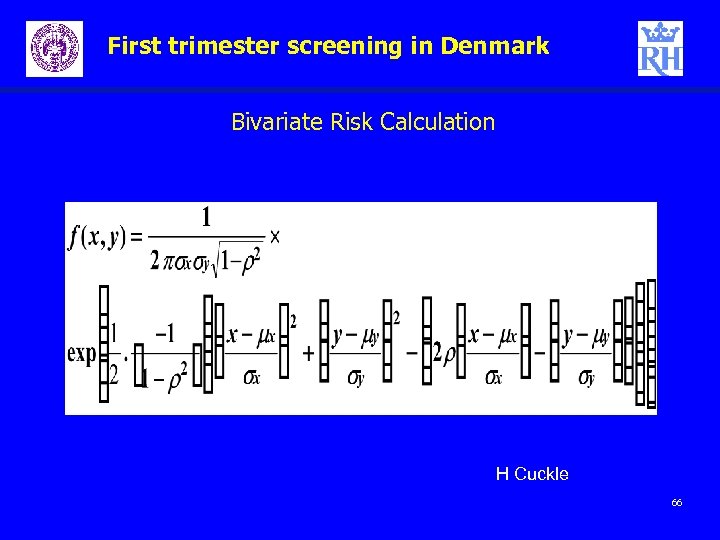 First trimester screening in Denmark Bivariate Risk Calculation H Cuckle 66
First trimester screening in Denmark Bivariate Risk Calculation H Cuckle 66
 First trimester screening in Denmark Implementation of 1. trimester screening NT + biochemistry The sonography follows FMF guidelines – NT performed at centers with trained sonographers and doctors Major Departments of Fetal medicine performing the NT had all been trained by the Fetal Medicine Foundattion, London, all sonographers were already FMF-certified. – Software All Departments of Fetal medicine were using the Astraia software. (All FMF approved) – NT QC All sonographers are FMF certified 67
First trimester screening in Denmark Implementation of 1. trimester screening NT + biochemistry The sonography follows FMF guidelines – NT performed at centers with trained sonographers and doctors Major Departments of Fetal medicine performing the NT had all been trained by the Fetal Medicine Foundattion, London, all sonographers were already FMF-certified. – Software All Departments of Fetal medicine were using the Astraia software. (All FMF approved) – NT QC All sonographers are FMF certified 67
 First trimester screening in Denmark The challanges – Pre-analytical – Astraia The window for which biochemistry is accepted in Astraia Inability of Astraia to communicate with the Hospital Laboratory Information Management System Medians 68
First trimester screening in Denmark The challanges – Pre-analytical – Astraia The window for which biochemistry is accepted in Astraia Inability of Astraia to communicate with the Hospital Laboratory Information Management System Medians 68
 First trimester screening in Denmark The biochemists 10 wishes 1. Reproducibility of values over time (no drift) 2. Reproducibility of values over time (no drift) 3. Reproducibility of values over time (no drift) 4. Reproducibility of values over time (no drift) 5. Reproducibility of values over time (no drift) 6. Reproducibility of values over time (no drift) 7. Precision 8. Robustness 9. High specificity – no interference 10. Documentation 69
First trimester screening in Denmark The biochemists 10 wishes 1. Reproducibility of values over time (no drift) 2. Reproducibility of values over time (no drift) 3. Reproducibility of values over time (no drift) 4. Reproducibility of values over time (no drift) 5. Reproducibility of values over time (no drift) 6. Reproducibility of values over time (no drift) 7. Precision 8. Robustness 9. High specificity – no interference 10. Documentation 69
 First trimester screening in Denmark Reasons for not enroling in the first trimester screening Number of women not enroling in the first trimester screening: 6% - 8% Reasons • Late bookers • Ethnic minorities • Unaware of the screening program • Don’t wish to be screened (few) K Sundberg, unpublished data 70
First trimester screening in Denmark Reasons for not enroling in the first trimester screening Number of women not enroling in the first trimester screening: 6% - 8% Reasons • Late bookers • Ethnic minorities • Unaware of the screening program • Don’t wish to be screened (few) K Sundberg, unpublished data 70
 First trimester screening in Denmark Transport of blood samples to the laboratories – unexpected help from the Royal Danish Mail Most counties in Denmark are currently implementing systems where the samples will be picked up at the GPs (This is not because the National Health Care wants to reduced the pre-analytical errors but because they can save money – sending blood samples by mail has become too expensive). 71
First trimester screening in Denmark Transport of blood samples to the laboratories – unexpected help from the Royal Danish Mail Most counties in Denmark are currently implementing systems where the samples will be picked up at the GPs (This is not because the National Health Care wants to reduced the pre-analytical errors but because they can save money – sending blood samples by mail has become too expensive). 71
 First trimester screening in Denmark How to handle the changes in the medians – – The Astraia database generates a new set of medians from data collected in it. Fourthermore there is a mimgenererer nye medianer baseret på de data som er indtastet i Astraia databasen ud fra de krav vi har opstillet (f. eks 200 pr. uge i de forudgående 6 måneder. Det vil gøre det umuligt at dele medianer mellem 2 centre fordi medianen udelukkende kan genereres ud fra data i den enkelte database. At Astraia genererer medianer ud fra indtastede medianer, som et var i den gamle version. Dvs. at man blot indtaster en medianværdi for hver enkelt gestationsuge 8+3, 9+3, 10+3 etc. Og at Astraia så selv genererer den nye median. Det er et ”åbent system” hvor der ikke er krav til datamængde, og hvor medianer kan deles mellem centre. Og hvor det også vil være muligt at generere DPC Immulite medianer hvis det er det som man har lyst til!! Data is sent to London (Kevin) or Germany (Roland). From these data they generate a new set of medians. Probelms FMF has the rights to the risk module in Astraia. What will they accept. 72
First trimester screening in Denmark How to handle the changes in the medians – – The Astraia database generates a new set of medians from data collected in it. Fourthermore there is a mimgenererer nye medianer baseret på de data som er indtastet i Astraia databasen ud fra de krav vi har opstillet (f. eks 200 pr. uge i de forudgående 6 måneder. Det vil gøre det umuligt at dele medianer mellem 2 centre fordi medianen udelukkende kan genereres ud fra data i den enkelte database. At Astraia genererer medianer ud fra indtastede medianer, som et var i den gamle version. Dvs. at man blot indtaster en medianværdi for hver enkelt gestationsuge 8+3, 9+3, 10+3 etc. Og at Astraia så selv genererer den nye median. Det er et ”åbent system” hvor der ikke er krav til datamængde, og hvor medianer kan deles mellem centre. Og hvor det også vil være muligt at generere DPC Immulite medianer hvis det er det som man har lyst til!! Data is sent to London (Kevin) or Germany (Roland). From these data they generate a new set of medians. Probelms FMF has the rights to the risk module in Astraia. What will they accept. 72


