5ad77ac94d8dd69cc4fd130fd7bb5510.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34

First-principles Calculation of Zr-alloys based on e-Infrastructure Yang Chen(1), Xushan Zhao(1), Yuqin Liu(2) , Maoyou Chu(1), Jianyun Shen(1) General Research Institute for Nonferrous Metals (2) China University of Geosciences Beijing

Introduction of GRINM • 1. the largest R&D institution in the field of nonferrous metals industry in China • 2. more than 5, 000 projects have been carried out in GRINM Since establishment • 3. research areas microelectronic 、 photoelectronic materials、rare and precious metals, rare earth materials, energy technology and materials

Our group Research fields: • 1. Thermodynamics of phase diagram, diffusion and interfacial reaction, computational simulation of materials. • 2. Mainly on the Titanium and Zirconium Alloys. Research condition for compution: 1. 100 CPUs can be used 2. Soft-package: VASP, Wien 2 k

Outline 1. Background 2. The Soft package 3. Arrange the application on grid euchina 4. Test of Our application on grid 5. Conclusions
1. Background Nuclear Power Stations being and to be Constructed Current: 9000 MW 2020: 86000 MW
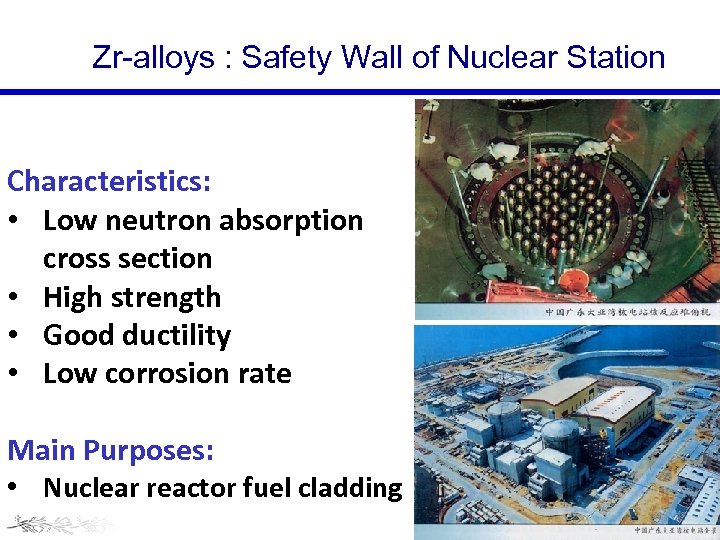
Zr-alloys : Safety Wall of Nuclear Station Characteristics: • Low neutron absorption cross section • High strength • Good ductility • Low corrosion rate Main Purposes: • Nuclear reactor fuel cladding
Shortage of domestic Zr-alloy 1. Most nuclear reactors constructed by ANP(French), Western house(USA) 2. The fuel cladding should be replace every 18 months 3. Demand: 1000 t/Year Current situation: Domestic Zr-alloy can’t satisfy the high quality requirement in Nuclear reactor
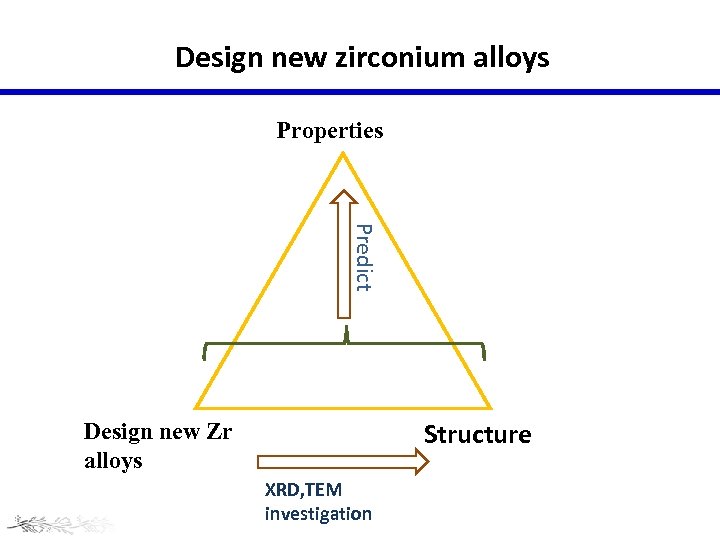
Design new zirconium alloys Properties Predict Structure Design new Zr alloys XRD, TEM investigation

First-principles methodology First-princples methodlogy in material design: Based on structure of the Material, We can : 1. Calculate the structure and electronic properties 2. Obtain thermodynamic properties 3. Simulate the material transformation and Failure in service ………

Part 1: Thermodynamic properties
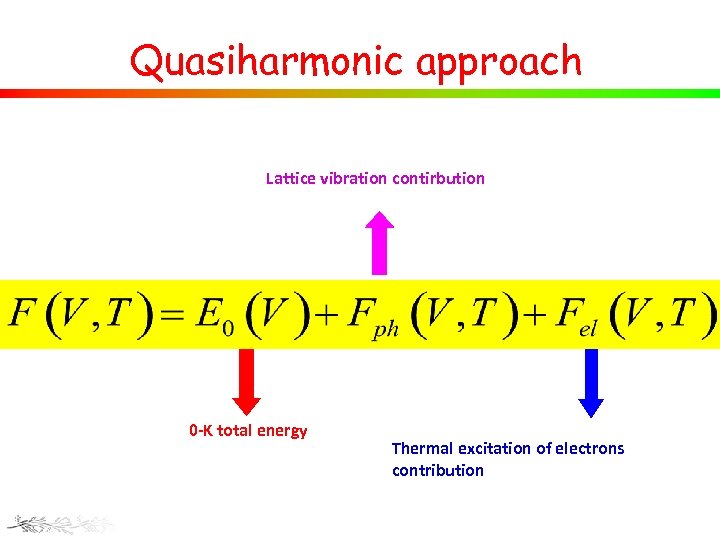
Quasiharmonic approach Lattice vibration contirbution 0 -K total energy Thermal excitation of electrons contribution
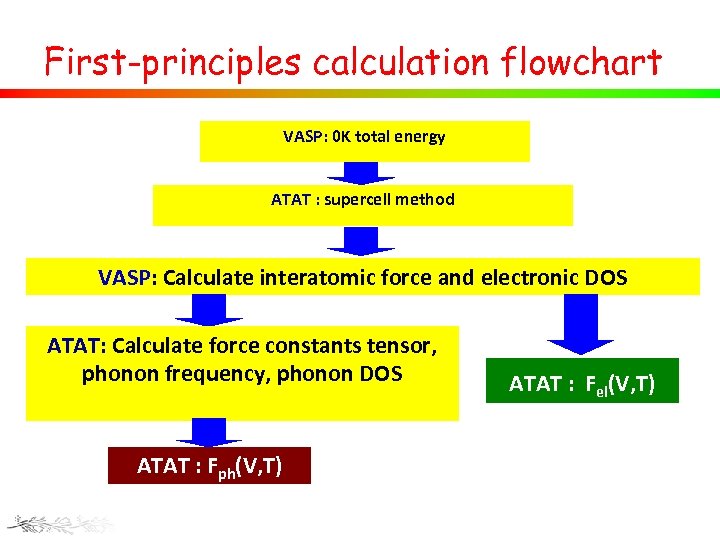
First-principles calculation flowchart VASP: 0 K total energy ATAT : supercell method VASP: Calculate interatomic force and electronic DOS ATAT: Calculate force constants tensor, phonon frequency, phonon DOS ATAT : Fph(V, T) ATAT : Fel(V, T)
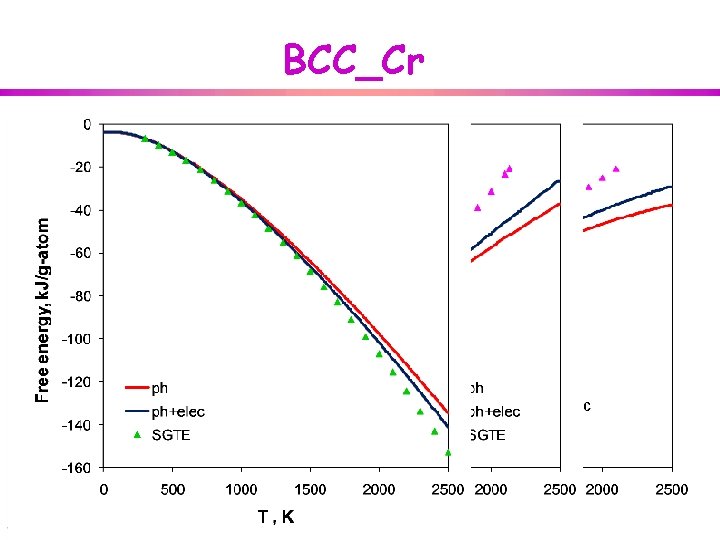
BCC_Cr

Part 2. First-principles elastic constants
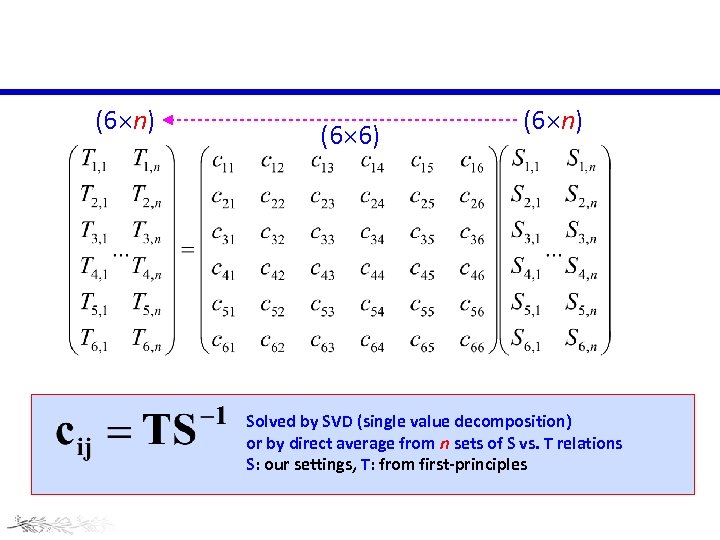
(6 n) (6 6) (6 n) Solved by SVD (single value decomposition) or by direct average from n sets of S vs. T relations S: our settings, T: from first-principles
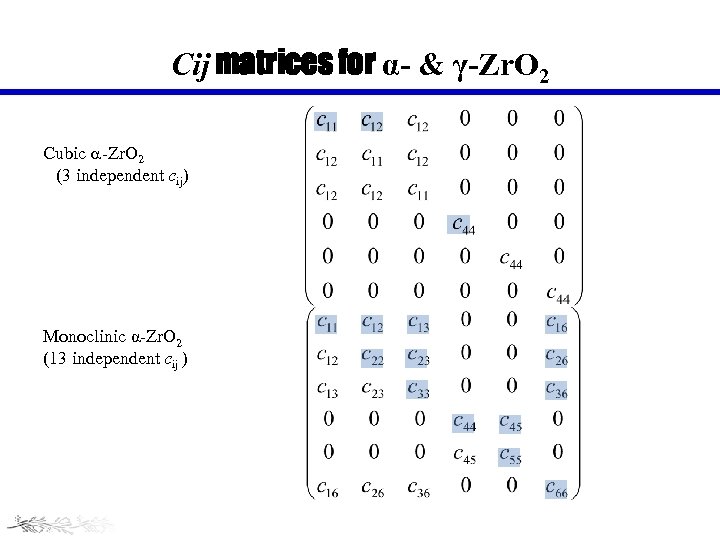
Cij matrices for α- & γ-Zr. O 2 Cubic -Zr. O 2 (3 independent cij) Monoclinic α-Zr. O 2 (13 independent cij )
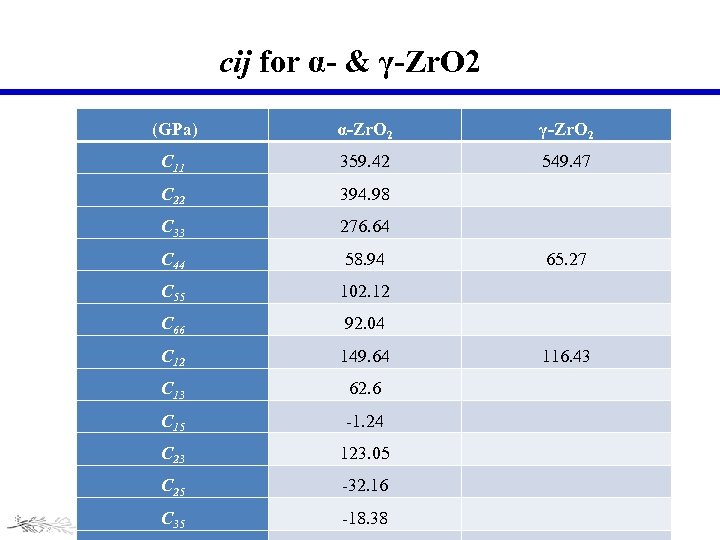
cij for α- & γ-Zr. O 2 (GPa) α-Zr. O 2 γ-Zr. O 2 C 11 359. 42 549. 47 C 22 394. 98 C 33 276. 64 C 44 58. 94 65. 27 C 55 102. 12 C 66 92. 04 C 12 149. 64 116. 43 C 13 62. 6 C 15 -1. 24 C 23 123. 05 C 25 -32. 16 C 35 -18. 38

2. The soft package Ø A package for performing ab-initio quantum-mechanical molecular dynamics (MD).

Installation of VASP Minimum requirements 1. FORTRAN 90 Compiler(Intel Fortran, PGI Fortran) 2. Math library (Intel MKL, -Atlas…. . ) 3. MPI Library for parallel work(MPICH, OPENMPI……. )
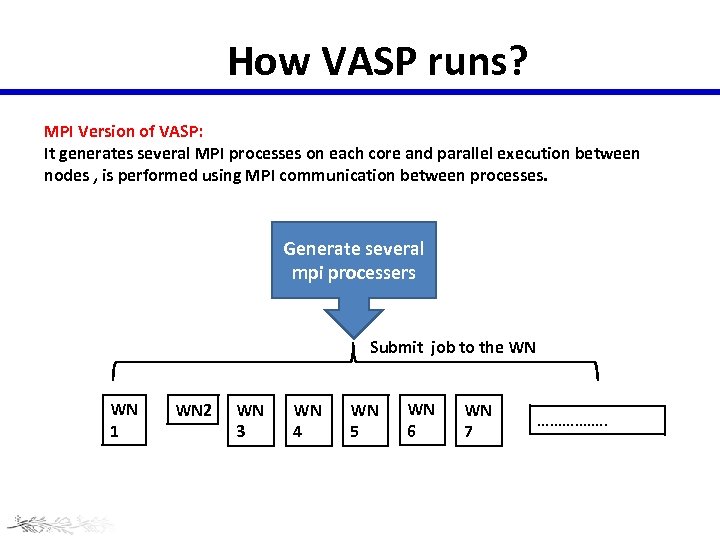
How VASP runs? MPI Version of VASP: It generates several MPI processes on each core and parallel execution between nodes , is performed using MPI communication between processes. Generate several mpi processers Submit job to the WN WN 1 WN 2 WN 3 WN 4 WN 5 WN 6 WN 7 ……………. .
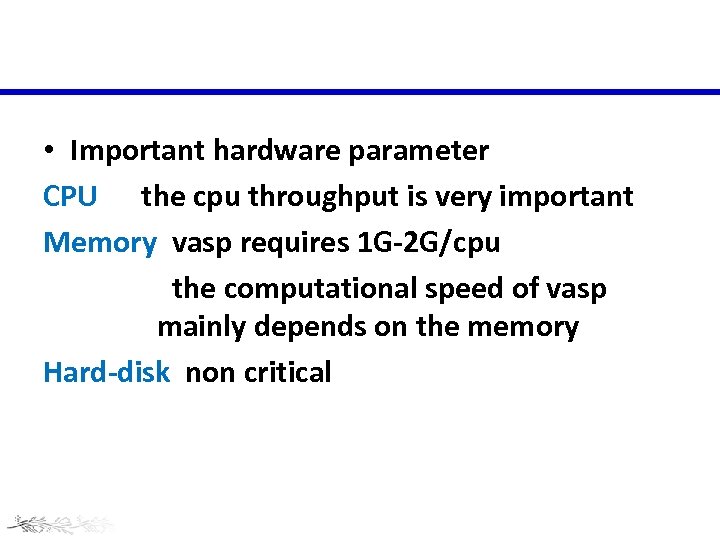
• Important hardware parameter CPU the cpu throughput is very important Memory vasp requires 1 G-2 G/cpu the computational speed of vasp mainly depends on the memory Hard-disk non critical
Demand of Hardware One Single job: • 20~30*CPU with 2 GB Memory • Cost: 2 -7 days depend on the accuracy required • One calculation always >10 jobs Some remarks: 1. Clusters are suitable for parallel applications (100~200 CPUs ) 2. When Big system and high accuracy is required! More CPUs needed
3. Arrange the application on grid euchina • • • EUChina. GRID partners Beihang University, Beijing (China) CNIC (China) IHEP, Beijing (China) Peking University, Beijing (China) GRnet (Greece) Consortium GARR (Italy) Department of Biology, Università di Roma 3 (Italy) INFN (Italy) Jagiellonian University in Krakow (Poland) CERN (Switzerland)

We arranged our application on UI(lcg 003) provided by IHEP Ø Install Fortran compiler for linux Ø Compile Math Kernel Library Ø Install VASP program

4. Test Our Application on Grid
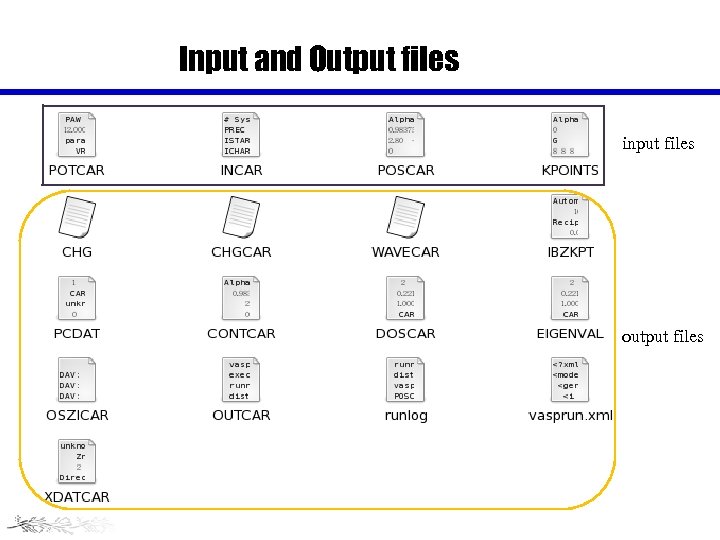
Input and Output files input files output files

Extra required files: jdl, wrapper and hook The JDL: Ø A fully extensible language Ø Support a certain set of attributes Ø Schedule and submit our job
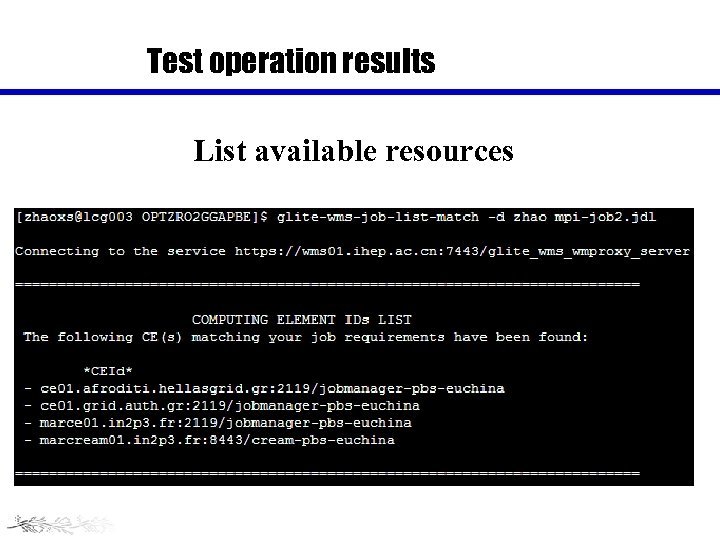
Test operation results List available resources
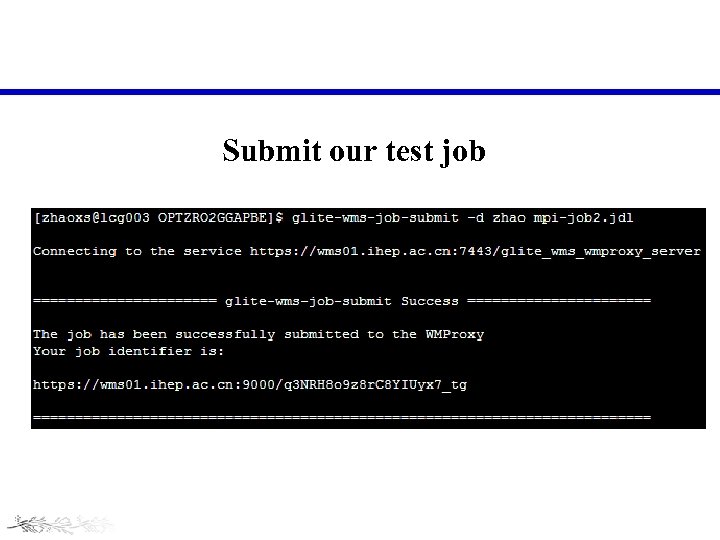
Submit our test job
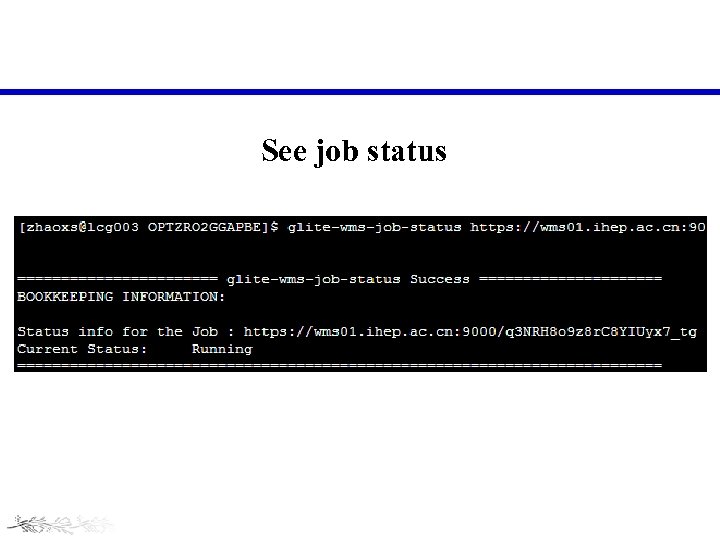
See job status
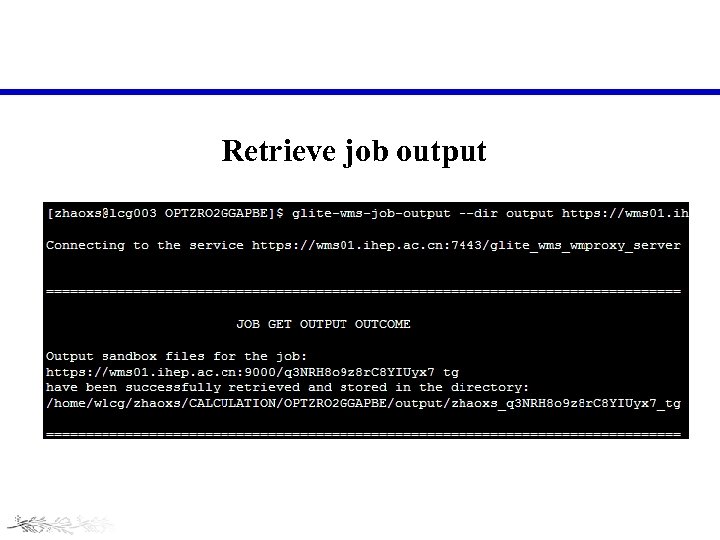
Retrieve job output

5. Conclusion

• 1. our application runs sucessfully on the euchina grid • 2. more than 200 CPU*2 G memory we can use • Tips: • 1. the efficiency is low when use >10 CPUs (MPI communication efficiency)

Thanks to: EPIKH Project Institute of High Energy Physics Special thanks to: Prof. Si. Jin Qian (PKU) 马兰馨老师 Dr. Fargetta Marco (INFN) 许冬老师 Dr. Fabrizio Pistagna (INFN) 伍文静老师 Dr. Andre Cortelleses (INFN) 朱威老师
5ad77ac94d8dd69cc4fd130fd7bb5510.ppt