Finding your topic.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Finding your topic Lecture 3
Finding your topic Lecture 3
 Outline • What is a good topic? • The process of finding a good topic – Discovering your topic – Exploring your topic area – Refining your topic
Outline • What is a good topic? • The process of finding a good topic – Discovering your topic – Exploring your topic area – Refining your topic
 What is a good topic? • A good topic involves your listeners – They lean forward in their seats – They nod and smile appropriately – At the end, they break out in applause – They want to ask you questions
What is a good topic? • A good topic involves your listeners – They lean forward in their seats – They nod and smile appropriately – At the end, they break out in applause – They want to ask you questions
 What is a good topic? • A good topic involves you – You’re enthusiastic – Your face shows your involvement – Your voice expresses your feelings – Your gestures reinforce your meaning – “This is important!”, “This is interesting!”, “This will make a difference in your lives”
What is a good topic? • A good topic involves you – You’re enthusiastic – Your face shows your involvement – Your voice expresses your feelings – Your gestures reinforce your meaning – “This is important!”, “This is interesting!”, “This will make a difference in your lives”
 What is a good topic? • A good topic is one you can manage – Whether you can acquire the knowledge you will need to speak responsibly – Select a topic you know something about – Develop a manageable part of it for presentation
What is a good topic? • A good topic is one you can manage – Whether you can acquire the knowledge you will need to speak responsibly – Select a topic you know something about – Develop a manageable part of it for presentation
 The process of finding a good topic • The discovery phase – uncover promising topic areas • The exploration phase – focus on specific speech topics within these areas • The refinement phase – identify the general and specific purposes of speeches / write a thesis statement
The process of finding a good topic • The discovery phase – uncover promising topic areas • The exploration phase – focus on specific speech topics within these areas • The refinement phase – identify the general and specific purposes of speeches / write a thesis statement
 Discovering your topic • “What can I talk about? I don’t know anything. I’m not even interested in very much. Am I hopeless? ” – Brainstorming – Interest charts – Media prompts
Discovering your topic • “What can I talk about? I don’t know anything. I’m not even interested in very much. Am I hopeless? ” – Brainstorming – Interest charts – Media prompts
 Discovering your topic • Brainstorming – Free associations – Write down the first idea that comes to you – Let you mind wander
Discovering your topic • Brainstorming – Free associations – Write down the first idea that comes to you – Let you mind wander
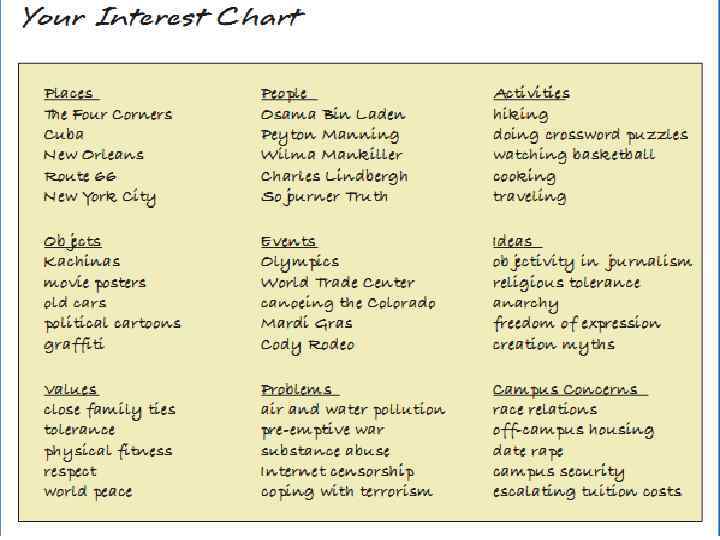
 Discovering your topic • Interest charts – What places do you find interesting? – What people do you find fascinating? – What activities do you enjoy? – What things do you find interesting? – What events stand out in your mind? – What ideas do you find intriguing?
Discovering your topic • Interest charts – What places do you find interesting? – What people do you find fascinating? – What activities do you enjoy? – What things do you find interesting? – What events stand out in your mind? – What ideas do you find intriguing?
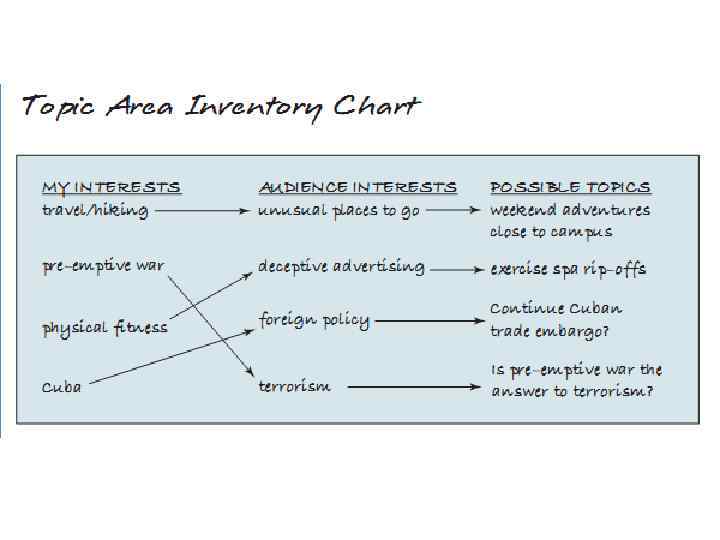
 Discovering your topic • Media prompts – Newspapers – Magazines – Electronic media – Headlines – Advertisements – Pictures
Discovering your topic • Media prompts – Newspapers – Magazines – Electronic media – Headlines – Advertisements – Pictures
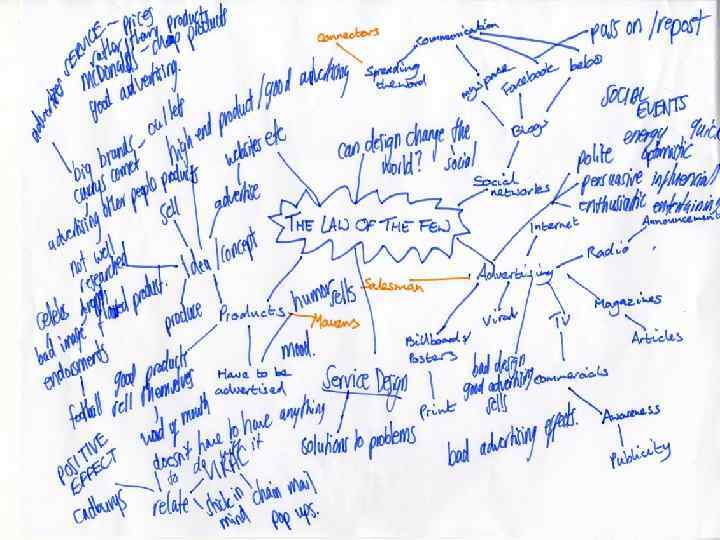
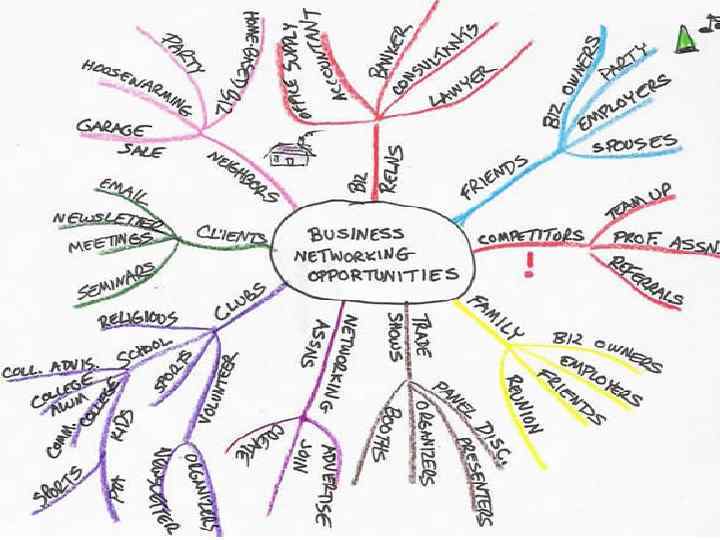
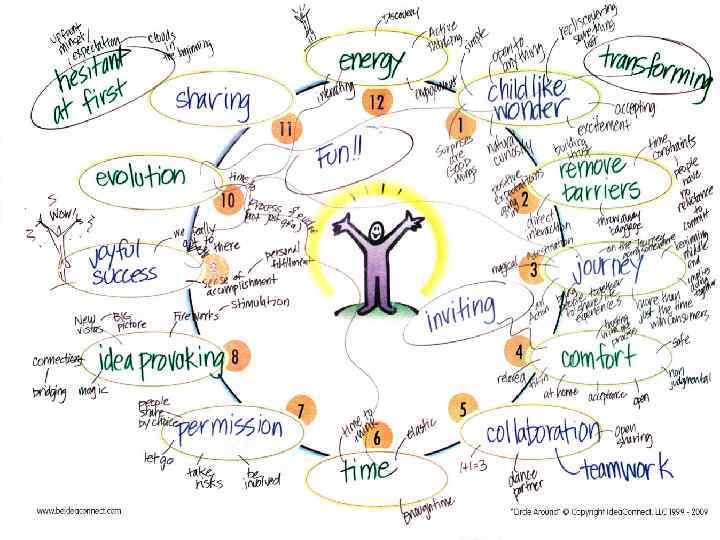
 Exploring your topic area • Mind mapping • Topic analysis
Exploring your topic area • Mind mapping • Topic analysis
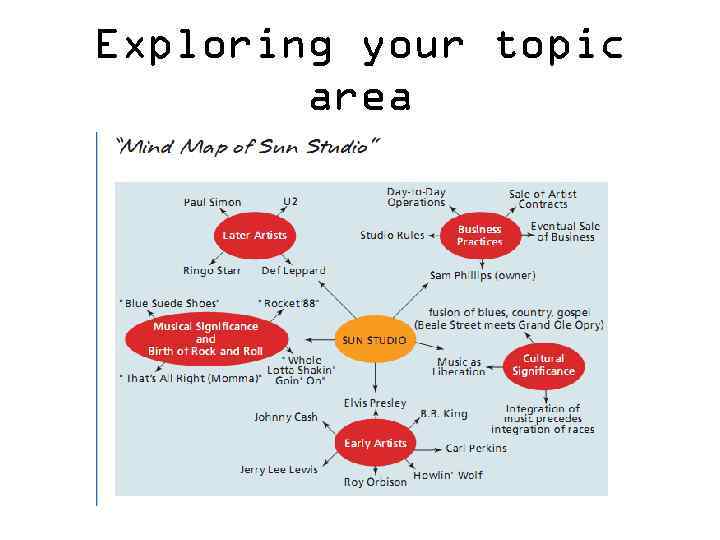 Exploring your topic area
Exploring your topic area
 Exploring your topic area • Topic analysis I keep six honest serving-men (They taught me all I knew): Their names are What and Why and When And How and Where and Who Rudyard Kipling
Exploring your topic area • Topic analysis I keep six honest serving-men (They taught me all I knew): Their names are What and Why and When And How and Where and Who Rudyard Kipling

 Exploring your topic area • Selecting a topic – Does the topic fit the assignment – Could I give a speech on this topic in the time available? – Why would I want to speak on that topic? – Could I interest my listeners in this topic?
Exploring your topic area • Selecting a topic – Does the topic fit the assignment – Could I give a speech on this topic in the time available? – Why would I want to speak on that topic? – Could I interest my listeners in this topic?
 Refining your topic • Consider the general purpose of your speech • Determine your specific objectives • Prepare a clearly worded thesis statement
Refining your topic • Consider the general purpose of your speech • Determine your specific objectives • Prepare a clearly worded thesis statement
 Refining your topic • General purpose – the speaker’s overall intention to inform or persuade listeners, or to celebrate some person or occasion. – To inform – To persuade – To celebrate
Refining your topic • General purpose – the speaker’s overall intention to inform or persuade listeners, or to celebrate some person or occasion. – To inform – To persuade – To celebrate
 Refining your topic • Specific purpose – the speaker’s particular goal or the response that the speaker wishes to evoke. • Topic: • General purpose: Music therapy To inform • Specific purpose: To inform my audience about the benefits of music therapy for people with psychological and cognitive disabilities
Refining your topic • Specific purpose – the speaker’s particular goal or the response that the speaker wishes to evoke. • Topic: • General purpose: Music therapy To inform • Specific purpose: To inform my audience about the benefits of music therapy for people with psychological and cognitive disabilities
 Refining your topic • Testing your specific purpose statement – Does the specific purpose promise new information or fresh advice? – Can you satisfy your specific purpose statement in the time allotted? – Have you avoided double-focus traps? – Have you avoided the triviality trap? – Have you avoided the technicality trap?
Refining your topic • Testing your specific purpose statement – Does the specific purpose promise new information or fresh advice? – Can you satisfy your specific purpose statement in the time allotted? – Have you avoided double-focus traps? – Have you avoided the triviality trap? – Have you avoided the technicality trap?
 Refining your topic • Thesis statement – is sometimes called a “central idea” and summarizes in a single sentence the message of your speech.
Refining your topic • Thesis statement – is sometimes called a “central idea” and summarizes in a single sentence the message of your speech.
 Refining your topic • Music therapy • To inform • To explain the benefits of music therapy for people with psychological or cognitive disabilities • Music therapy developed as a formal mode of treatment during the twentieth century, utilizes a number of methods, and is explained by several theories that account for its success
Refining your topic • Music therapy • To inform • To explain the benefits of music therapy for people with psychological or cognitive disabilities • Music therapy developed as a formal mode of treatment during the twentieth century, utilizes a number of methods, and is explained by several theories that account for its success


