fb3a6f82a2fd415b6ccefff663620b89.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13

FINANCIAL SERVICES Institute of International Bankers Enterprise Risk Management October 29, 2007

Agenda § Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) Industry Drivers § ERM Framework: Key Elements § Primary Benefits of ERM Programs § Key Considerations for FBOs § ERM Challenges and Critical Success Factors 1

Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) Industry Drivers Keep Us Out of Expanding Trouble Increasing Impact of Regulatory Scrutiny Make Our Business Improved New Better Risks to Risk/Return Recognize Decisioning Extreme Events and Activism Increased Risk Interaction Criminal Indictment s Bigger Fines and Settlements Irrecoverable Ratings Downgrades Irreparable Reputational Damage goal and Manage Optimizing Risk-Taking Capacity Aggregate Risk Reporting and Value Management Development of Consistent Risk Appetite Linking Strategy to Risk and Optimizing Use of Capital Effective Use of Risk Mitigation All too confusing and overdone… Must do it… Except when we get in trouble But how do we do it better? 2
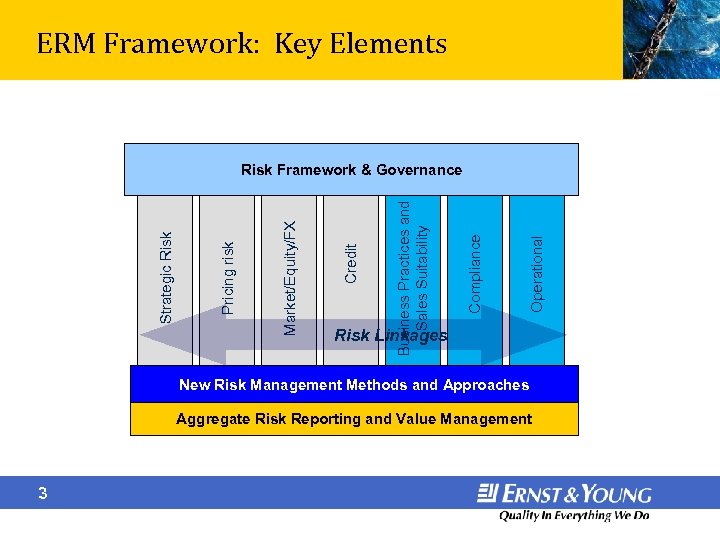
ERM Framework: Key Elements Operational Compliance Business Practices and Sales Suitability Credit Market/Equity/FX Pricing risk Strategic Risk Framework & Governance Risk Linkages New Risk Management Methods and Approaches Aggregate Risk Reporting and Value Management 3

ERM Framework: Risk Framework and Governance § Defining the approach/philosophy to risk ― Role of the center, the CRO and risk committees Risk Linkages ― Role of existing risk silos and infrastructure New Risk Management Methods and Approaches ― Defining risk taking, risk owner, risk champion, controlling, Aggregate Risk Reporting and Value monitoring, measurement, management, oversight and assurance Management roles and accountability ― Risk responsibility matrix ― Delegation of authority ― Governance, reporting lines and information/reporting § Risk appetite and limit structure § Incentive alignment ― Linkages to performance measurement and people effectiveness § Strategic value linkage ― Define how risk information will be used in decision making (e. g. , pricing, capital allocation) 4 Operational Compliance Credit Business Practices and Sales Suitability Market/equity/FX Pricing risk Strategic Risk § Organizational and governance structure Risk Framework & Governance
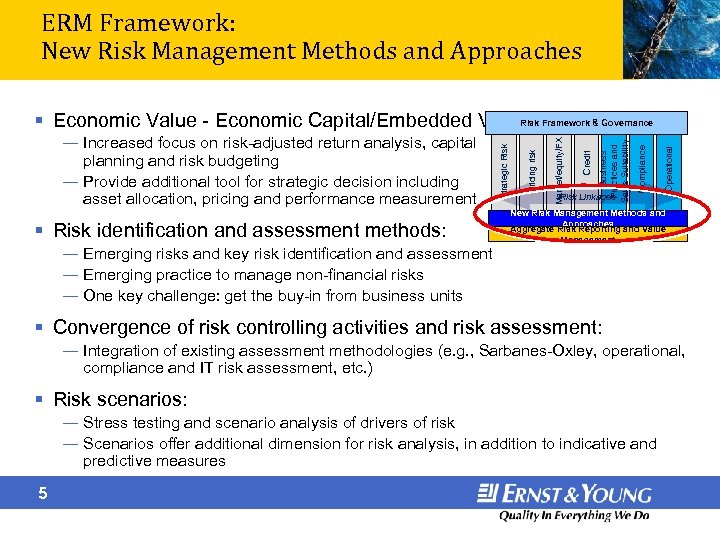
ERM Framework: New Risk Management Methods and Approaches § Risk identification and assessment methods: ― Emerging risks and key risk identification and assessment ― Emerging practice to manage non-financial risks ― One key challenge: get the buy-in from business units Operational Risk Linkages Compliance Business Practices and Sales Suitability Credit Market/equity/FX Pricing risk ― Increased focus on risk-adjusted return analysis, capital planning and risk budgeting ― Provide additional tool for strategic decision including asset allocation, pricing and performance measurement Strategic Risk § Economic Value - Economic Capital/Embedded Value: Framework & Governance New Risk Management Methods and Approaches Aggregate Risk Reporting and Value Management § Convergence of risk controlling activities and risk assessment: ― Integration of existing assessment methodologies (e. g. , Sarbanes-Oxley, operational, compliance and IT risk assessment, etc. ) § Risk scenarios: ― Stress testing and scenario analysis of drivers of risk ― Scenarios offer additional dimension for risk analysis, in addition to indicative and predictive measures 5

ERM Framework: Aggregate Risk Reporting and Value Management § Reporting of ERM: § Limits monitoring and escalation: Operational Risk Linkages Compliance Business Practices and Sales Suitability Credit Market/equity/FX Pricing risk Strategic Risk – Effort to aggregate existing risk reporting packages to develop comprehensive view of risks – Non-financial risks are added to risk reporting – More forward-looking measures help assess potential impact on organization Risk Framework & Governance New Risk Management Methods and Approaches Aggregate Risk Reporting and Value Management – Reporting of limits or other policy breaches – Escalating procedures define roles, authority and accountability § Linkage to strategic decision making process: – Strengthening linkage between risk reporting, performance measurement, and strategy – Making decision based on value creation and/or risk-adjusted performance measures, linking top line revenues and risk § Linkage to tactical decision making processes: – Strengthening linkage between holistic view of risks and key decision-making processes – Revising new product development, product pricing, investments/asset allocation, credit risk management, ALM and operational optimization 6

ERM Framework: Risk Linkages § Correlation and correlation breakage: Operational Compliance Business Practices and Sales Suitability Credit Market/equity/FX Pricing risk – Alignment of management-level and corporate-level governance structures – Assign ownership for risk monitoring Strategic Risk Framework § Improve linkage between risk classes and risk organizations: & Governance Risk Linkages New Risk Management Methods and Approaches Aggregate Risk Reporting and Value Management – Correlation at the mean or correlation at the tail? – Extreme events show that correlation between risks tend to move towards 1 § Integration of risk quantification: – Emerging methodologies to quantify non-financial risks – Integration of risk measures allow linkage between measures of risk silos and overall risk appetite and tolerance 7

Primary Benefits of ERM Programs § Optimize capital utilization. Links decision making to risk/capital to ensure returns are adequate for risks taken § Enhance accountability about risks by ensuring there is a process to identify, understand manage significant risks to protect enterprise value § Potential to reduce the number and impact of surprises § Increase transparency about risks, thereby improving credibility with investors and other stakeholders § Address regulatory focus on enterprise-wide risk perspective 8

Key Considerations for FBOs § Status vs. Structure—what must an FHC build in the US? – No prescriptive regulatory requirements – Receptive to what can be shown to “work” in practice – Practical need to invest in local ERM increases with scale/complexity of US operations – Analogous to home-host challenge for regulators § How to avoid redundancy and conflict with HO risk management, legal entity structures and global BU management? – Ensure comprehensive and timely risk information available locally, since a problem will have to managed here first – Support global risk governance by providing information upstream § HO oversight a key consideration for US regulators – Local ERM can help ensure effective oversight – Local ERM provides a “window” on entire US risk profile for Fed § Focus on risk information and reporting – Local needs and HO needs will differ 9

ERM Challenges and Critical Success Factors § Visible executive support § Solution that is tailored to company § Focus on better management of risk, not just risk reduction § Need to leverage existing risk processes and minimize complexity 10 § Create and reward transparency § Change Management approach is critical § Recognize and compensate for risk capability, competency and culture § Recognize what gets measured gets managed and vise-versa (don’t remove focus on core risks)

E&Y Contacts § Hank Prybylski Partner and Practice Leader, Global Financial Services Risk Management (212) 773 -2823 lawrence. prybylsky@ey. com § Christopher Maher Partner (212) 773 -6524 chris. maher@ey. com § Don Vangel Advisor, Regulatory Affairs (212) 773 -2129 donald. vangel@ey. com 11

ERNST & YOUNG LLP © 2007 Ernst & Young LLP. All Rights Reserved. Ernst & Young is a registered trademark. 12 www. ey. com
fb3a6f82a2fd415b6ccefff663620b89.ppt