df0b0c8ded25a7d89f9f937916fe2d84.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42
 Financial Risk Management Zvi Wiener Following P. Jorion, Financial Risk Manager Handbook http: //pluto. huji. ac. il/~mswiener/zvi. html FRM 972 -2 -588 -3049
Financial Risk Management Zvi Wiener Following P. Jorion, Financial Risk Manager Handbook http: //pluto. huji. ac. il/~mswiener/zvi. html FRM 972 -2 -588 -3049
 Chapter 11 Introduction to Market Risk Management Following P. Jorion 2001 Financial Risk Manager Handbook http: //pluto. huji. ac. il/~mswiener/zvi. html FRM 972 -2 -588 -3049
Chapter 11 Introduction to Market Risk Management Following P. Jorion 2001 Financial Risk Manager Handbook http: //pluto. huji. ac. il/~mswiener/zvi. html FRM 972 -2 -588 -3049
 Old ways to measure risk • notional amounts • sensitivity measures (duration, Greeks( • scenarios • ALM, DFA assume linearity do not describe probability Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 3
Old ways to measure risk • notional amounts • sensitivity measures (duration, Greeks( • scenarios • ALM, DFA assume linearity do not describe probability Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 3
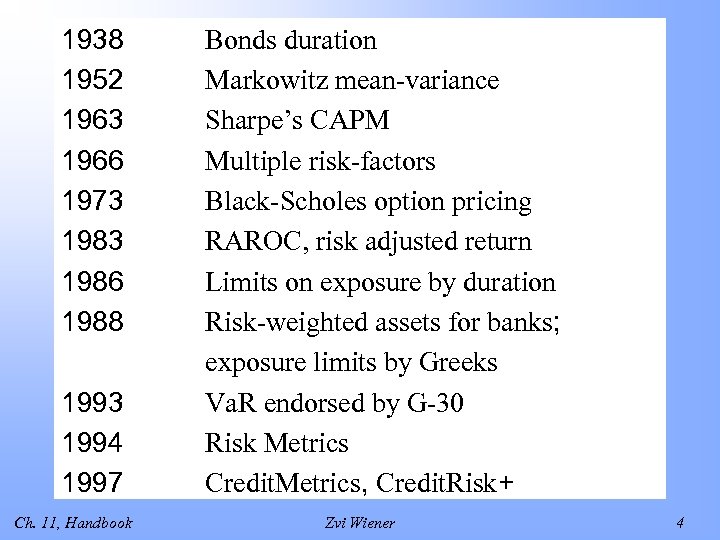 1938 1952 1963 1966 1973 1986 1988 1993 1994 1997 Ch. 11, Handbook Bonds duration Markowitz mean-variance Sharpe’s CAPM Multiple risk-factors Black-Scholes option pricing RAROC, risk adjusted return Limits on exposure by duration Risk-weighted assets for banks; exposure limits by Greeks Va. R endorsed by G-30 Risk Metrics Credit. Metrics, Credit. Risk+ Zvi Wiener 4
1938 1952 1963 1966 1973 1986 1988 1993 1994 1997 Ch. 11, Handbook Bonds duration Markowitz mean-variance Sharpe’s CAPM Multiple risk-factors Black-Scholes option pricing RAROC, risk adjusted return Limits on exposure by duration Risk-weighted assets for banks; exposure limits by Greeks Va. R endorsed by G-30 Risk Metrics Credit. Metrics, Credit. Risk+ Zvi Wiener 4
 How much can we lose? Everything correct, but useless answer. How much can we lose realistically? Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 5
How much can we lose? Everything correct, but useless answer. How much can we lose realistically? Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 5
 What is the current Risk? • Bonds • Stocks • Options • Credit • Forex • Total Ch. 11, Handbook duration, convexity volatility delta, gamma, vega rating target zone ? Zvi Wiener 6
What is the current Risk? • Bonds • Stocks • Options • Credit • Forex • Total Ch. 11, Handbook duration, convexity volatility delta, gamma, vega rating target zone ? Zvi Wiener 6
 Standard Approach Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 7
Standard Approach Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 7
 Modern Approach Financial Institution Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 8
Modern Approach Financial Institution Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 8
 Definition Va. R is defined as the predicted worst-case loss at a specific confidence level (e. g. 99%) over a certain period of time. Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 9
Definition Va. R is defined as the predicted worst-case loss at a specific confidence level (e. g. 99%) over a certain period of time. Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 9
 Definition (Jorion) Va. R is the maximum loss over a target horizon such that there is a low, prespecified probability that the actual loss will be larger. Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 10
Definition (Jorion) Va. R is the maximum loss over a target horizon such that there is a low, prespecified probability that the actual loss will be larger. Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 10
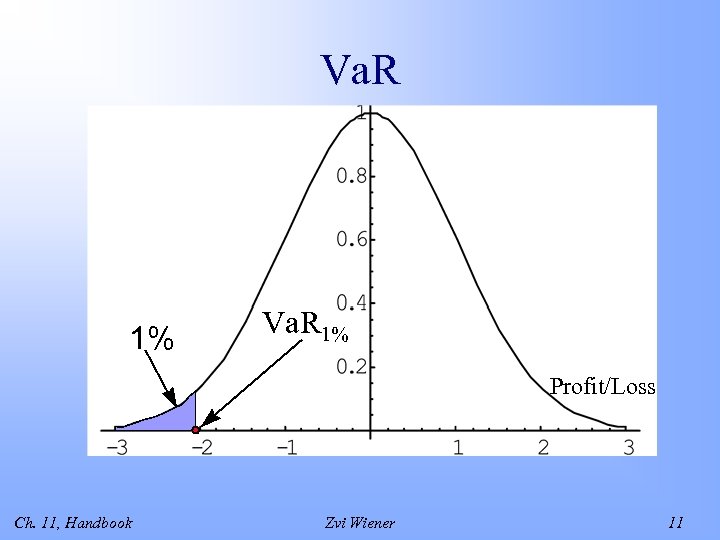 Va. R 1% Profit/Loss Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 11
Va. R 1% Profit/Loss Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 11
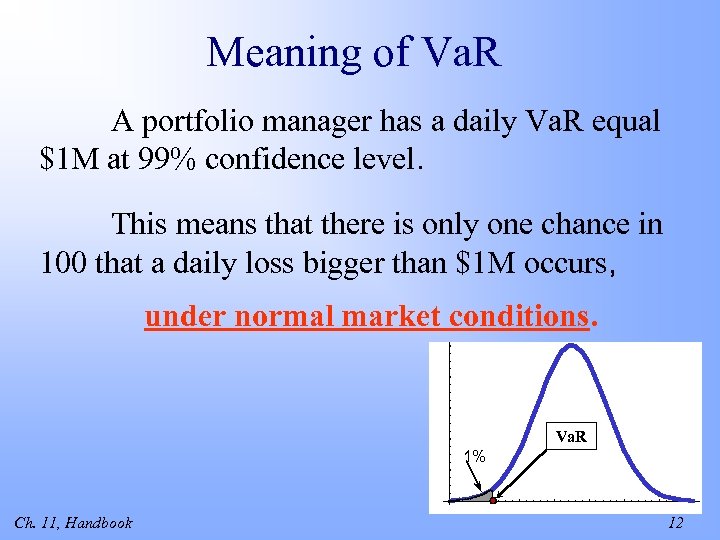 Meaning of Va. R A portfolio manager has a daily Va. R equal $1 M at 99% confidence level. This means that there is only one chance in 100 that a daily loss bigger than $1 M occurs, under normal market conditions. Va. R 1% Ch. 11, Handbook 12
Meaning of Va. R A portfolio manager has a daily Va. R equal $1 M at 99% confidence level. This means that there is only one chance in 100 that a daily loss bigger than $1 M occurs, under normal market conditions. Va. R 1% Ch. 11, Handbook 12
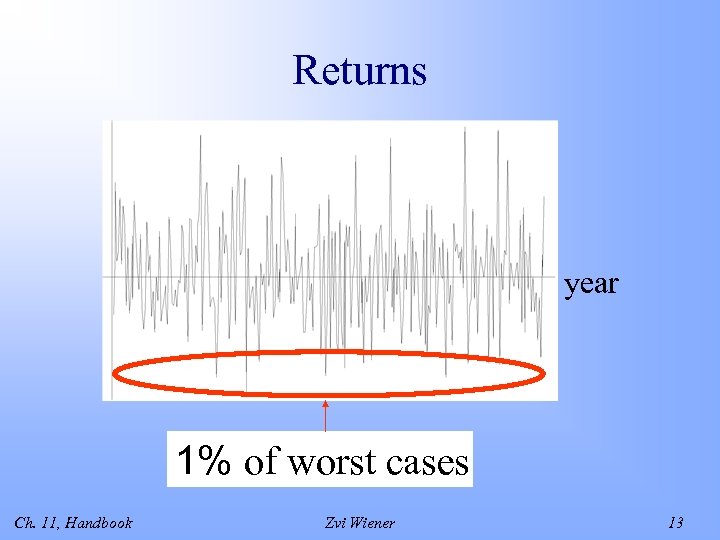 Returns year 1% of worst cases Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 13
Returns year 1% of worst cases Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 13
 Main Ideas • A few well known risk factors • Historical data + economic views • Diversification effects • Testability • Easy to communicate Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 14
Main Ideas • A few well known risk factors • Historical data + economic views • Diversification effects • Testability • Easy to communicate Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 14
 History of Va. R • ’ 80 s - major US banks - proprietary • 93 G-30 recommendations • - 94 Risk. Metrics by J. P. Morgan • - 98 Basel • SEC, FSA, ISDA, pension funds, dealers • Widely used and misused! Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 15
History of Va. R • ’ 80 s - major US banks - proprietary • 93 G-30 recommendations • - 94 Risk. Metrics by J. P. Morgan • - 98 Basel • SEC, FSA, ISDA, pension funds, dealers • Widely used and misused! Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 15
 FRM-99, Question 89 What is the correct interpretation of a $3 overnight Va. R figure with 99% confidence level? A. expect to lose at most $3 in 1 out of next 100 days B. expect to lose at least $3 in 95 out of next 100 days C. expect to lose at least $3 in 1 out of next 100 days D. expect to lose at most $6 in 2 out of next 100 days Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 16
FRM-99, Question 89 What is the correct interpretation of a $3 overnight Va. R figure with 99% confidence level? A. expect to lose at most $3 in 1 out of next 100 days B. expect to lose at least $3 in 95 out of next 100 days C. expect to lose at least $3 in 1 out of next 100 days D. expect to lose at most $6 in 2 out of next 100 days Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 16
 FRM-99, Question 89 What is the correct interpretation of a $3 overnight Va. R figure with 99% confidence level? A. expect to lose at most $3 in 1 out of next 100 days B. expect to lose at least $3 in 95 out of next 100 days C. expect to lose at least $3 in 1 out of next 100 days D. expect to lose at most $6 in 2 out of next 100 days Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 17
FRM-99, Question 89 What is the correct interpretation of a $3 overnight Va. R figure with 99% confidence level? A. expect to lose at most $3 in 1 out of next 100 days B. expect to lose at least $3 in 95 out of next 100 days C. expect to lose at least $3 in 1 out of next 100 days D. expect to lose at most $6 in 2 out of next 100 days Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 17
 Va. R caveats • Va. R does not describe the worst loss • Va. R does not describe losses in the left tail • Va. R is measured with some error Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 18
Va. R caveats • Va. R does not describe the worst loss • Va. R does not describe losses in the left tail • Va. R is measured with some error Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 18
 Other Measures of Risk • The entire distribution • The expected left tail loss • The standard deviation • The semi-standard deviation Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 19
Other Measures of Risk • The entire distribution • The expected left tail loss • The standard deviation • The semi-standard deviation Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 19
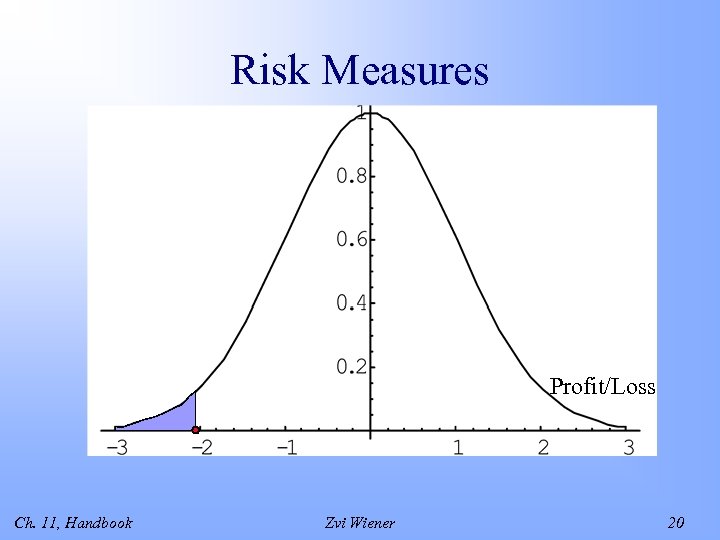 Risk Measures Profit/Loss Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 20
Risk Measures Profit/Loss Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 20
 Properties of Risk Measure • Monotonicity (X
Properties of Risk Measure • Monotonicity (X
 No subadditivity of Va. R Bond has a face value of $100, 000, during the target period there is a probability of 0. 75% that there will be a default (loss of $100, 000). Note that Va. R 99% = 0 in this case. What is Va. R 99% of a position consisting of 2 independent bonds? Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 22
No subadditivity of Va. R Bond has a face value of $100, 000, during the target period there is a probability of 0. 75% that there will be a default (loss of $100, 000). Note that Va. R 99% = 0 in this case. What is Va. R 99% of a position consisting of 2 independent bonds? Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 22
 FRM-98, Question 22 Consider arbitrary portfolios A and B and their combined portfolio C. Which of the following relationships always holds for Va. Rs of A, B, and C? A. Va. RA+ Va. RB = Va. RC B. Va. RA+ Va. RB Va. RC C. Va. RA+ Va. RB Va. RC D. None of the above Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 23
FRM-98, Question 22 Consider arbitrary portfolios A and B and their combined portfolio C. Which of the following relationships always holds for Va. Rs of A, B, and C? A. Va. RA+ Va. RB = Va. RC B. Va. RA+ Va. RB Va. RC C. Va. RA+ Va. RB Va. RC D. None of the above Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 23
 FRM-98, Question 22 Consider arbitrary portfolios A and B and their combined portfolio C. Which of the following relationships always holds for Va. Rs of A, B, and C? A. Va. RA+ Va. RB = Va. RC B. Va. RA+ Va. RB Va. RC C. Va. RA+ Va. RB Va. RC D. None of the above Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 24
FRM-98, Question 22 Consider arbitrary portfolios A and B and their combined portfolio C. Which of the following relationships always holds for Va. Rs of A, B, and C? A. Va. RA+ Va. RB = Va. RC B. Va. RA+ Va. RB Va. RC C. Va. RA+ Va. RB Va. RC D. None of the above Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 24
 Confidence level low confidence leads to an imprecise result. For example 99. 99% and 10 business days will require history of 100*10 = 100, 000 days in order to have only 1 point. Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 25
Confidence level low confidence leads to an imprecise result. For example 99. 99% and 10 business days will require history of 100*10 = 100, 000 days in order to have only 1 point. Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 25
 Time horizon long time horizon can lead to an imprecise result. 1% - 10 days means that we will see such a loss approximately once in 100*10 = 3 years. 5% and 1 day horizon means once in a month. Various subportfolios may require various horizons. Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 26
Time horizon long time horizon can lead to an imprecise result. 1% - 10 days means that we will see such a loss approximately once in 100*10 = 3 years. 5% and 1 day horizon means once in a month. Various subportfolios may require various horizons. Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 26
 Time horizon When the distribution is stable one can translate Va. R over different time periods. This formula is valid (in particular) for iid normally distributed returns. Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 27
Time horizon When the distribution is stable one can translate Va. R over different time periods. This formula is valid (in particular) for iid normally distributed returns. Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 27
 FRM-97, Question 7 To convert Va. R from a one day holding period to a ten day holding period the Va. R number is generally multiplied by: A. 2. 33 B. 3. 16 C. 7. 25 D. 10 Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 28
FRM-97, Question 7 To convert Va. R from a one day holding period to a ten day holding period the Va. R number is generally multiplied by: A. 2. 33 B. 3. 16 C. 7. 25 D. 10 Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 28
 FRM-97, Question 7 To convert Va. R from a one day holding period to a ten day holding period the Va. R number is generally multiplied by: A. 2. 33 B. 3. 16 C. 7. 25 D. 10 Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 29
FRM-97, Question 7 To convert Va. R from a one day holding period to a ten day holding period the Va. R number is generally multiplied by: A. 2. 33 B. 3. 16 C. 7. 25 D. 10 Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 29
 Basel Rules • horizon of 10 business days • 99% confidence interval • an observation period of at least a year of historical data, updated once a quarter Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 30
Basel Rules • horizon of 10 business days • 99% confidence interval • an observation period of at least a year of historical data, updated once a quarter Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 30
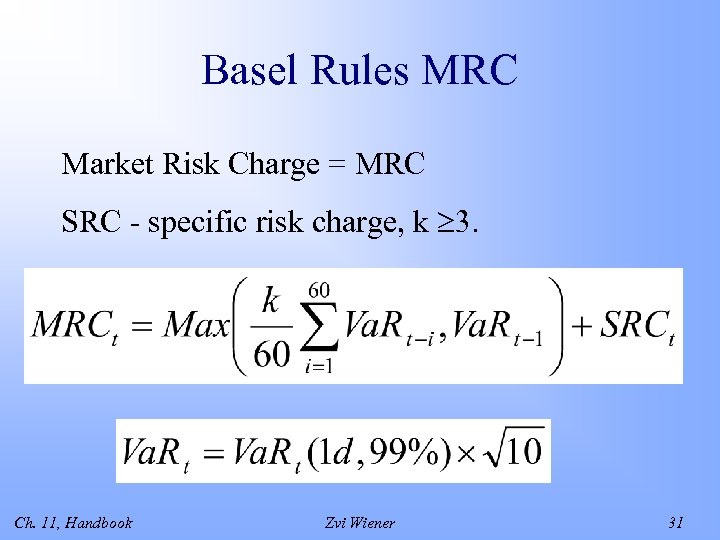 Basel Rules MRC Market Risk Charge = MRC SRC - specific risk charge, k 3. Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 31
Basel Rules MRC Market Risk Charge = MRC SRC - specific risk charge, k 3. Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 31
 FRM-97, Question 16 Which of the following quantitative standards is NOT required by the Amendment to the Capital Accord to Incorporate Market Risk? A. Minimum holding period of 10 days B. 99% one-tailed confidence interval C. Minimum historical observations of two years D. Update the data sets at least quarterly Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 32
FRM-97, Question 16 Which of the following quantitative standards is NOT required by the Amendment to the Capital Accord to Incorporate Market Risk? A. Minimum holding period of 10 days B. 99% one-tailed confidence interval C. Minimum historical observations of two years D. Update the data sets at least quarterly Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 32
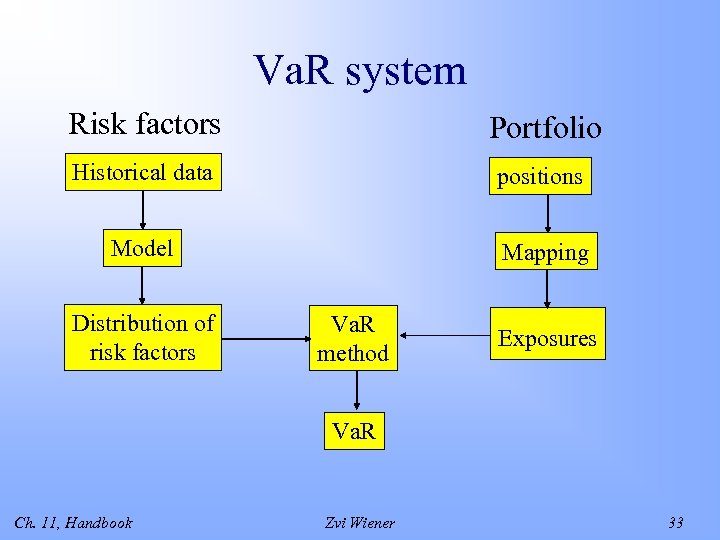 Va. R system Risk factors Portfolio Historical data positions Model Mapping Distribution of risk factors Va. R method Exposures Va. R Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 33
Va. R system Risk factors Portfolio Historical data positions Model Mapping Distribution of risk factors Va. R method Exposures Va. R Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 33
 FRM-97, Question 23 The standard Va. R calculation for extension to multiple periods also assumes that positions are fixed. If risk management enforces loss limits, the true Va. R will be: A. the same B. greater than calculated C. less then calculated D. unable to determine Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 34
FRM-97, Question 23 The standard Va. R calculation for extension to multiple periods also assumes that positions are fixed. If risk management enforces loss limits, the true Va. R will be: A. the same B. greater than calculated C. less then calculated D. unable to determine Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 34
 FRM-97, Question 23 The standard Va. R calculation for extension to multiple periods also assumes that positions are fixed. If risk management enforces loss limits, the true Va. R will be: A. the same B. greater than calculated C. less then calculated D. unable to determine Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 35
FRM-97, Question 23 The standard Va. R calculation for extension to multiple periods also assumes that positions are fixed. If risk management enforces loss limits, the true Va. R will be: A. the same B. greater than calculated C. less then calculated D. unable to determine Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 35
 FRM-97, Question 9 A trading desk has limits only in outright foreign exchange and outright interest rate risk. Which of the following products can not be traded within the current structure? A. Vanilla IR swaps, bonds and IR futures B. IR futures, vanilla and callable IR swaps C. Repos and bonds D. FX swaps, back-to-back exotic FX options Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 36
FRM-97, Question 9 A trading desk has limits only in outright foreign exchange and outright interest rate risk. Which of the following products can not be traded within the current structure? A. Vanilla IR swaps, bonds and IR futures B. IR futures, vanilla and callable IR swaps C. Repos and bonds D. FX swaps, back-to-back exotic FX options Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 36
 FRM-97, Question 9 A trading desk has limits only in outright foreign exchange and outright interest rate risk. Which of the following products can not be traded within the current structure? A. Vanilla IR swaps, bonds and IR futures B. IR futures, vanilla and callable IR swaps C. Repos and bonds No limits! D. FX swaps, back-to-back exotic FX options Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 37
FRM-97, Question 9 A trading desk has limits only in outright foreign exchange and outright interest rate risk. Which of the following products can not be traded within the current structure? A. Vanilla IR swaps, bonds and IR futures B. IR futures, vanilla and callable IR swaps C. Repos and bonds No limits! D. FX swaps, back-to-back exotic FX options Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 37
 Stress-testing • scenario analysis • stressing models, volatilities and correlations • developing policy responses Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 38
Stress-testing • scenario analysis • stressing models, volatilities and correlations • developing policy responses Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 38
 Scenario Analysis • Moving key variables one at a time • Using historical scenarios • Creating prospective scenarios The goal is to identify areas of potential vulnerability. Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 39
Scenario Analysis • Moving key variables one at a time • Using historical scenarios • Creating prospective scenarios The goal is to identify areas of potential vulnerability. Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 39
 FRM-97, Question 4 The use of scenario analysis allows one to: A. assess the behavior of portfolios under large moves B. research market shocks which occurred in the past C. analyze the distribution of historical P&L D. perform effective back-testing Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 40
FRM-97, Question 4 The use of scenario analysis allows one to: A. assess the behavior of portfolios under large moves B. research market shocks which occurred in the past C. analyze the distribution of historical P&L D. perform effective back-testing Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 40
 FRM-98, Question 20 Va. R measure should be supplemented by portfolio stress-testing because: A. Va. R measures indicate that the minimum is Va. R, they do not indicate the actual loss B. stress testing provides a precise maximum loss level C. Va. R measures are correct only 95% of time D. stress testing scenarios incorporate reasonably probable events. Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 41
FRM-98, Question 20 Va. R measure should be supplemented by portfolio stress-testing because: A. Va. R measures indicate that the minimum is Va. R, they do not indicate the actual loss B. stress testing provides a precise maximum loss level C. Va. R measures are correct only 95% of time D. stress testing scenarios incorporate reasonably probable events. Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 41
 FRM-00, Question 105 Va. R analysis should be complemented by stress -testing because stress-testing: A. Provides a maximum loss in dollars. B. Summarizes the expected loss over a target horizon within a minimum confidence interval. C. Assesses the behavior of portfolio at a 99% confidence level. D. Identifies losses that go beyond the normal losses measured by Va. R. Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 42
FRM-00, Question 105 Va. R analysis should be complemented by stress -testing because stress-testing: A. Provides a maximum loss in dollars. B. Summarizes the expected loss over a target horizon within a minimum confidence interval. C. Assesses the behavior of portfolio at a 99% confidence level. D. Identifies losses that go beyond the normal losses measured by Va. R. Ch. 11, Handbook Zvi Wiener 42


