b0bd1670df1a8eb49f452c11421ccc7c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 61
 Financial Reporting for Saccos Tax Planning & Management Julius Mwatu CFO – Indigo Telecom, Member – Taxation Workgroup
Financial Reporting for Saccos Tax Planning & Management Julius Mwatu CFO – Indigo Telecom, Member – Taxation Workgroup
 Our Menu Today TAX MANAGEMENT TAX COMPLIANCE Tax Planning Business tax Tax Crimes Withholding Tax Risks – Auditors Personal Tax Rights & Obligations VAT EAC & Saccos
Our Menu Today TAX MANAGEMENT TAX COMPLIANCE Tax Planning Business tax Tax Crimes Withholding Tax Risks – Auditors Personal Tax Rights & Obligations VAT EAC & Saccos
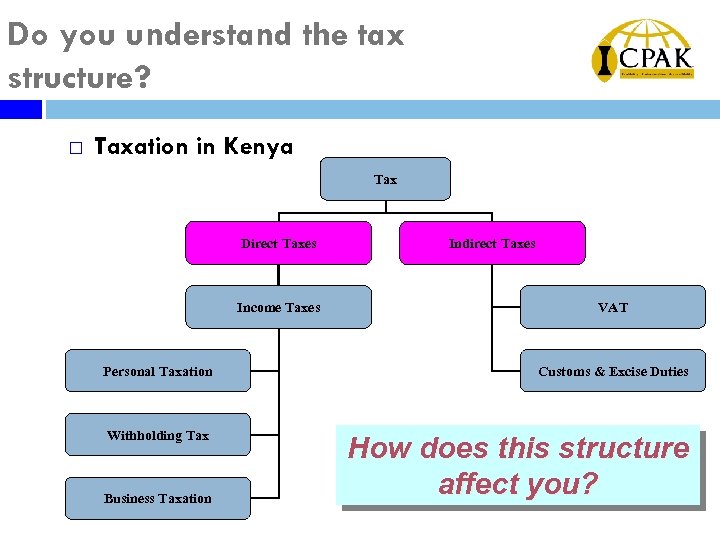 Do you understand the tax structure? ¨ Taxation in Kenya Tax Direct Taxes Income Taxes Indirect Taxes VAT Personal Taxation Customs & Excise Duties Withholding Tax How does this structure affect you? Business Taxation
Do you understand the tax structure? ¨ Taxation in Kenya Tax Direct Taxes Income Taxes Indirect Taxes VAT Personal Taxation Customs & Excise Duties Withholding Tax How does this structure affect you? Business Taxation
 Tax…
Tax…
 It’s a BIG risk!
It’s a BIG risk!
 Personal Taxation
Personal Taxation
 Are Management committee members employees or consultants?
Are Management committee members employees or consultants?
 What is taxable? ¨ All income of a person which accrued in or was derived from Kenya ¨ Applies to both resident or non-resident persons ¨ It could be cash or/and non-cash ¨ The tax year for individuals runs from 1 January to 31 December
What is taxable? ¨ All income of a person which accrued in or was derived from Kenya ¨ Applies to both resident or non-resident persons ¨ It could be cash or/and non-cash ¨ The tax year for individuals runs from 1 January to 31 December
 Withholding Tax
Withholding Tax
 Withholding tax ¨ Withholding tax is deductible upon payment of a taxable amount. ¨ Tax point … “Payment” is deemed to include the date of accrual/ crediting of the amount payable. ¨ Whose responsibility?
Withholding tax ¨ Withholding tax is deductible upon payment of a taxable amount. ¨ Tax point … “Payment” is deemed to include the date of accrual/ crediting of the amount payable. ¨ Whose responsibility?
 Dividends ¨ Dividends could be cash, stock, redeemable preference shares, debentures, or payments during winding up ¨ Classified as exempt, qualifying or non-qualifying ¨ Qualifying – WHT is final, non-qualifying – WHT not final ¨ Rates – 5% (Residents); 10% (Non-residents) ¨ Exempt dividends – Paid to exempt persons listed on 1 st Schedule or those received by a resident co. controlling >12. 5% - S 7(2) ¨ Non-qualifying dividends – Paid by a designated co-op society (Taxed under section 19 A) - S 2 ¨ Qualifying dividends – All the others
Dividends ¨ Dividends could be cash, stock, redeemable preference shares, debentures, or payments during winding up ¨ Classified as exempt, qualifying or non-qualifying ¨ Qualifying – WHT is final, non-qualifying – WHT not final ¨ Rates – 5% (Residents); 10% (Non-residents) ¨ Exempt dividends – Paid to exempt persons listed on 1 st Schedule or those received by a resident co. controlling >12. 5% - S 7(2) ¨ Non-qualifying dividends – Paid by a designated co-op society (Taxed under section 19 A) - S 2 ¨ Qualifying dividends – All the others
 Exemptions ¨ Withholding tax is not deductible on payments to exempt persons who are in possession of a tax exemption certificate ¨ Examples of exempt persons - POSB – Interest on savings accounts - Local Authority - Registered pension/provident schemes - EA Dev Bank - NSSF
Exemptions ¨ Withholding tax is not deductible on payments to exempt persons who are in possession of a tax exemption certificate ¨ Examples of exempt persons - POSB – Interest on savings accounts - Local Authority - Registered pension/provident schemes - EA Dev Bank - NSSF
 Interest ¨ Classified as: - Exempt - 1 st Schedule - Qualifying – Interest received by individuals from bank or fin inst. , housing bonds [max: 300, 000/-, CBK) or - Non-qualifying - all the rest ¨ Qualifying – WHT is final, non-qualifying – WHT not final ¨ Rates – 15% (Bank interest and other sources); 25% (on bearer instruments)
Interest ¨ Classified as: - Exempt - 1 st Schedule - Qualifying – Interest received by individuals from bank or fin inst. , housing bonds [max: 300, 000/-, CBK) or - Non-qualifying - all the rest ¨ Qualifying – WHT is final, non-qualifying – WHT not final ¨ Rates – 15% (Bank interest and other sources); 25% (on bearer instruments)
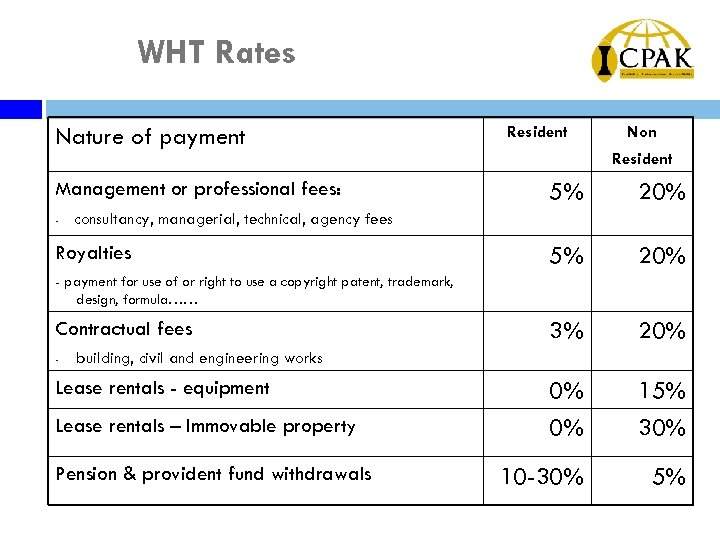 WHT Rates Nature of payment Management or professional fees: - Resident Non Resident 5% 20% 3% 20% 0% 0% 15% 30% 10 -30% 5% consultancy, managerial, technical, agency fees Royalties - payment for use of or right to use a copyright patent, trademark, design, formula…… Contractual fees - building, civil and engineering works Lease rentals - equipment Lease rentals – Immovable property Pension & provident fund withdrawals
WHT Rates Nature of payment Management or professional fees: - Resident Non Resident 5% 20% 3% 20% 0% 0% 15% 30% 10 -30% 5% consultancy, managerial, technical, agency fees Royalties - payment for use of or right to use a copyright patent, trademark, design, formula…… Contractual fees - building, civil and engineering works Lease rentals - equipment Lease rentals – Immovable property Pension & provident fund withdrawals
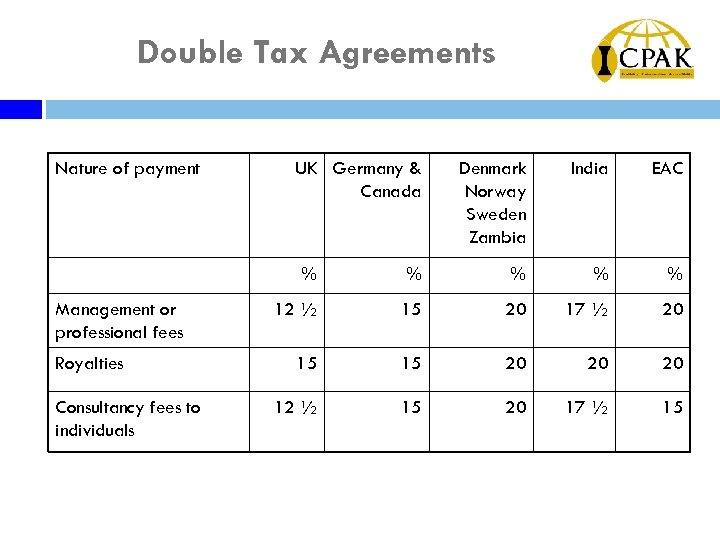 Double Tax Agreements Nature of payment UK Germany & Canada Denmark Norway Sweden Zambia India EAC % Management or professional fees Royalties Consultancy fees to individuals % % 12 ½ 15 20 17 ½ 20 15 15 20 20 20 12 ½ 15 20 17 ½ 15
Double Tax Agreements Nature of payment UK Germany & Canada Denmark Norway Sweden Zambia India EAC % Management or professional fees Royalties Consultancy fees to individuals % % 12 ½ 15 20 17 ½ 20 15 15 20 20 20 12 ½ 15 20 17 ½ 15
 Penalties ¨ ¨ 10% penalty (subject to a maximum of KShs 1 million) for failure to withhold or remit tax to KRA Interest charged at 2% per month or part thereof, on the principal WHT
Penalties ¨ ¨ 10% penalty (subject to a maximum of KShs 1 million) for failure to withhold or remit tax to KRA Interest charged at 2% per month or part thereof, on the principal WHT
 Employees or consultants?
Employees or consultants?
 Business Tax
Business Tax
 Gains or profits from business ¨ “Business” is defined to include any - trade, - profession or vocation - manufacture, - adventure and - concern in the nature of trade but does not include employment.
Gains or profits from business ¨ “Business” is defined to include any - trade, - profession or vocation - manufacture, - adventure and - concern in the nature of trade but does not include employment.
 Pertinent issues q Turnover tax regime q Taxation of partnerships q Taxation of Individuals
Pertinent issues q Turnover tax regime q Taxation of partnerships q Taxation of Individuals
 Specified sources of income ¨ ¨ ¨ Business income Employment income Investment income Farming income Rental income Any other
Specified sources of income ¨ ¨ ¨ Business income Employment income Investment income Farming income Rental income Any other
 Taxation of Saccos ¨ ¨ Interest income from members – Exempt Other non-mutual incomes – 30% of 50% of income
Taxation of Saccos ¨ ¨ Interest income from members – Exempt Other non-mutual incomes – 30% of 50% of income
 Value Added Tax
Value Added Tax
 Value Added Tax (VAT)? ¨ VAT is a general consumption tax assessed on the value added to goods and services. The Kenya VAT Act was enacted in 1989, and commenced on 1 January 1990 Replaced Sales Tax It is a general tax that applies, in principle, to all commercial activities involving the production and distribution of goods and the provision of services. It is a consumption tax - Its borne ultimately by the final consumer
Value Added Tax (VAT)? ¨ VAT is a general consumption tax assessed on the value added to goods and services. The Kenya VAT Act was enacted in 1989, and commenced on 1 January 1990 Replaced Sales Tax It is a general tax that applies, in principle, to all commercial activities involving the production and distribution of goods and the provision of services. It is a consumption tax - Its borne ultimately by the final consumer
 VAT Registration ¨ ¨ Registration is now online – KRA online A taxpayer should register for VAT if His business has supplied taxable goods or taxable services or expects to supply taxable goods or taxable services or both, the value of which is KShs. 5 Million or more in a period of 12 months (taxable person) To register within 30 days Deregistration – if turnover falls below KShs. 5 Million
VAT Registration ¨ ¨ Registration is now online – KRA online A taxpayer should register for VAT if His business has supplied taxable goods or taxable services or expects to supply taxable goods or taxable services or both, the value of which is KShs. 5 Million or more in a period of 12 months (taxable person) To register within 30 days Deregistration – if turnover falls below KShs. 5 Million
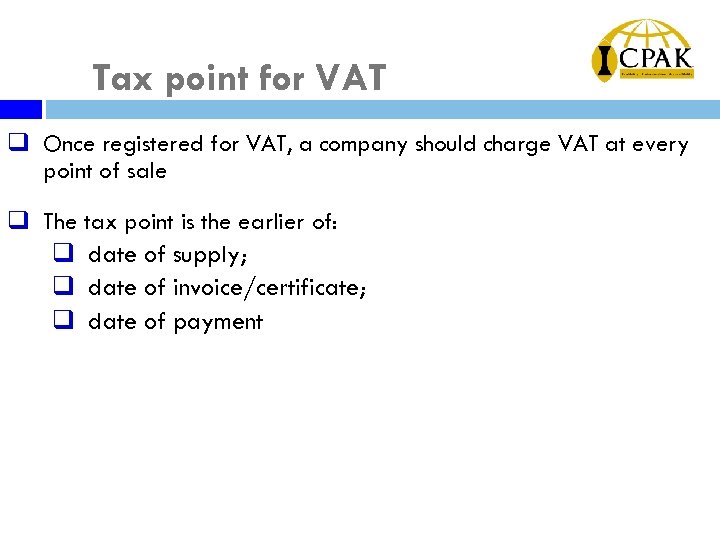 Tax point for VAT q Once registered for VAT, a company should charge VAT at every point of sale q The tax point is the earlier of: q date of supply; q date of invoice/certificate; q date of payment
Tax point for VAT q Once registered for VAT, a company should charge VAT at every point of sale q The tax point is the earlier of: q date of supply; q date of invoice/certificate; q date of payment
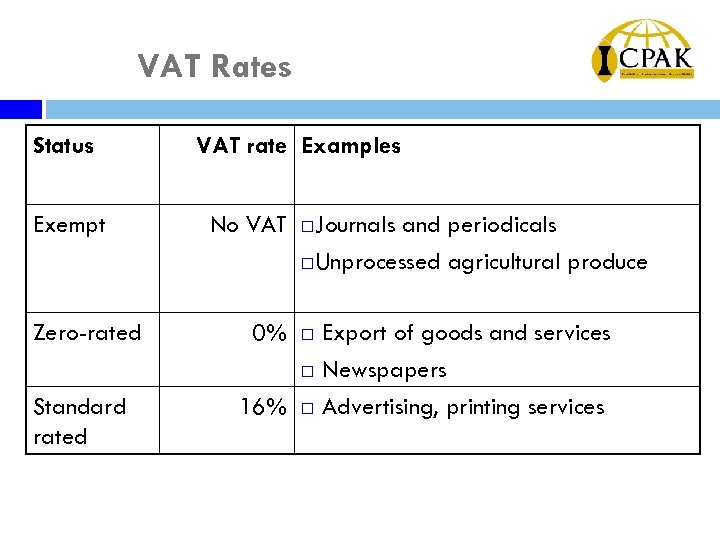 VAT Rates Status Exempt Zero-rated Standard rated VAT rate Examples No VAT ¨ Journals and periodicals ¨Unprocessed agricultural produce 0% ¨ Export of goods and services ¨ Newspapers 16% ¨ Advertising, printing services
VAT Rates Status Exempt Zero-rated Standard rated VAT rate Examples No VAT ¨ Journals and periodicals ¨Unprocessed agricultural produce 0% ¨ Export of goods and services ¨ Newspapers 16% ¨ Advertising, printing services
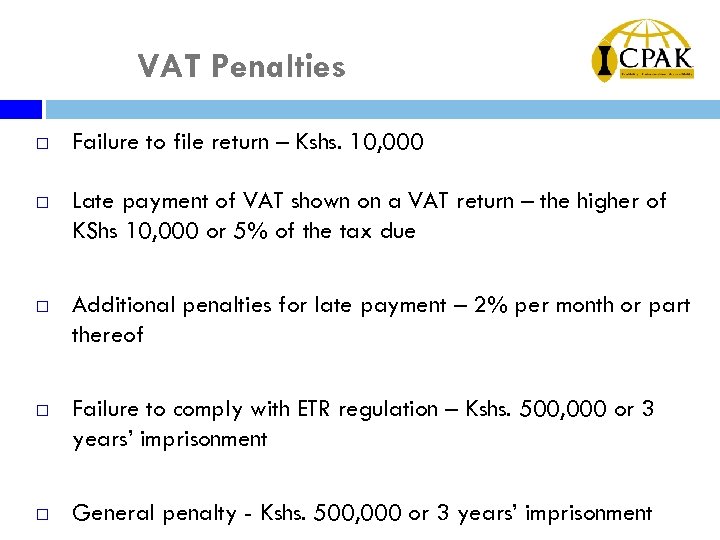 VAT Penalties ¨ Failure to file return – Kshs. 10, 000 ¨ Late payment of VAT shown on a VAT return – the higher of KShs 10, 000 or 5% of the tax due ¨ Additional penalties for late payment – 2% per month or part thereof ¨ Failure to comply with ETR regulation – Kshs. 500, 000 or 3 years’ imprisonment ¨ General penalty - Kshs. 500, 000 or 3 years’ imprisonment
VAT Penalties ¨ Failure to file return – Kshs. 10, 000 ¨ Late payment of VAT shown on a VAT return – the higher of KShs 10, 000 or 5% of the tax due ¨ Additional penalties for late payment – 2% per month or part thereof ¨ Failure to comply with ETR regulation – Kshs. 500, 000 or 3 years’ imprisonment ¨ General penalty - Kshs. 500, 000 or 3 years’ imprisonment
 Tax Planning & Strategy
Tax Planning & Strategy
 Do you have a tax strategy…?
Do you have a tax strategy…?
 Tax Strategy… Strategy Planning Staffing Tax Management Processes Communication Coverage Accounting
Tax Strategy… Strategy Planning Staffing Tax Management Processes Communication Coverage Accounting
 Tax Planning versus tax crimes How thin is the thin line…? Tax Planning • Tax Crimes ¨ Paying the right amount of tax at the right time in the right way. • Tax evasion (tax crime) is the general term for efforts to reduce taxes or pay no taxes by illegal means. ¨ Tax avoidance (planning) is the legal utilisation of the tax regime to one's own advantage, by means that are within the law. ¨ Why? To reduce the tax burden; To defer tax payment; To avoid penalties; To manage tax risks; • Tax crimes are therefore acts or omissions that are in violation of tax laws and regulations. • Its dependent upon the amount of admissible evidence against the taxpayer, not the amount involved.
Tax Planning versus tax crimes How thin is the thin line…? Tax Planning • Tax Crimes ¨ Paying the right amount of tax at the right time in the right way. • Tax evasion (tax crime) is the general term for efforts to reduce taxes or pay no taxes by illegal means. ¨ Tax avoidance (planning) is the legal utilisation of the tax regime to one's own advantage, by means that are within the law. ¨ Why? To reduce the tax burden; To defer tax payment; To avoid penalties; To manage tax risks; • Tax crimes are therefore acts or omissions that are in violation of tax laws and regulations. • Its dependent upon the amount of admissible evidence against the taxpayer, not the amount involved.
 Personal Taxation ¨ ¨ ¨ ¨ School fees Medical benefits Loans to employees Pensions/Provident Funds Mortgage Home Ownership Savings Scheme Benefits in kind Insurance relief 1
Personal Taxation ¨ ¨ ¨ ¨ School fees Medical benefits Loans to employees Pensions/Provident Funds Mortgage Home Ownership Savings Scheme Benefits in kind Insurance relief 1
 Personal Taxation ¨ ¨ ¨ Staff training and development Staff party expenses Study leave Home leave passages Telephone benefit 1
Personal Taxation ¨ ¨ ¨ Staff training and development Staff party expenses Study leave Home leave passages Telephone benefit 1
 Tax Crimes
Tax Crimes
 Why do we commit tax crimes
Why do we commit tax crimes
 Why do we commit tax crimes? ¨ Lack of effective tax planning measures ¨ Inadequate knowledge of taxation ¨ Unrealistic tax regimes (perceived? ) ¨ Inefficient tax authorities ¨ Self – discipline ¨ Payback (perceived? )
Why do we commit tax crimes? ¨ Lack of effective tax planning measures ¨ Inadequate knowledge of taxation ¨ Unrealistic tax regimes (perceived? ) ¨ Inefficient tax authorities ¨ Self – discipline ¨ Payback (perceived? )
 When do you become a tax criminal? ¨ ¨ Failure to file tax returns Filing false tax returns Conspiracy to impede/defeat the collection of tax (Tax planning? ? ) Keeping two sets of books
When do you become a tax criminal? ¨ ¨ Failure to file tax returns Filing false tax returns Conspiracy to impede/defeat the collection of tax (Tax planning? ? ) Keeping two sets of books
 Rights & Obligations
Rights & Obligations
 The Balancing Act. . . Your rights & Obligations ¨ Taxpayers Charter Balanced? ? Yes/No The right (s) has nothing right Perceptions ce n ‘Su sta b ov rf e m’ or Obligations Rights
The Balancing Act. . . Your rights & Obligations ¨ Taxpayers Charter Balanced? ? Yes/No The right (s) has nothing right Perceptions ce n ‘Su sta b ov rf e m’ or Obligations Rights
 Tax Risks…
Tax Risks…
 Tax Risk Management… Strategy Planning Staffing Tax Management Processes Communication Coverage Accounting
Tax Risk Management… Strategy Planning Staffing Tax Management Processes Communication Coverage Accounting
 …where the buck stops… Introduction
…where the buck stops… Introduction
 The Auditors Risk… ¨ Auditors’ exposure on “other taxes” The numerous forms? VAT, PAYE, WHT, Customs, Business tax Auditors/ tax advisor seem to concentrate on business tax only Are we doing tax health – checks, and, can we use the findings to adjust accounts under audit? The dual role of business? Saccos are both tax payers & tax collectors Tax penalties accrue in both Is tax compliance a contingency or is it a risk
The Auditors Risk… ¨ Auditors’ exposure on “other taxes” The numerous forms? VAT, PAYE, WHT, Customs, Business tax Auditors/ tax advisor seem to concentrate on business tax only Are we doing tax health – checks, and, can we use the findings to adjust accounts under audit? The dual role of business? Saccos are both tax payers & tax collectors Tax penalties accrue in both Is tax compliance a contingency or is it a risk
 Tax on Investments…
Tax on Investments…
 Invest wisely… ¨ Land stamp Rates ¨ duty - Collected by KRA - Leasehold Buildings Transfer ¨ - commercial or non-commercial Shares & Unit trusts
Invest wisely… ¨ Land stamp Rates ¨ duty - Collected by KRA - Leasehold Buildings Transfer ¨ - commercial or non-commercial Shares & Unit trusts
 Buildings cont. . . Tax Incentives Use of Pension as collateral You can assign up to 60% of the accrued benefits as security for mortgages
Buildings cont. . . Tax Incentives Use of Pension as collateral You can assign up to 60% of the accrued benefits as security for mortgages
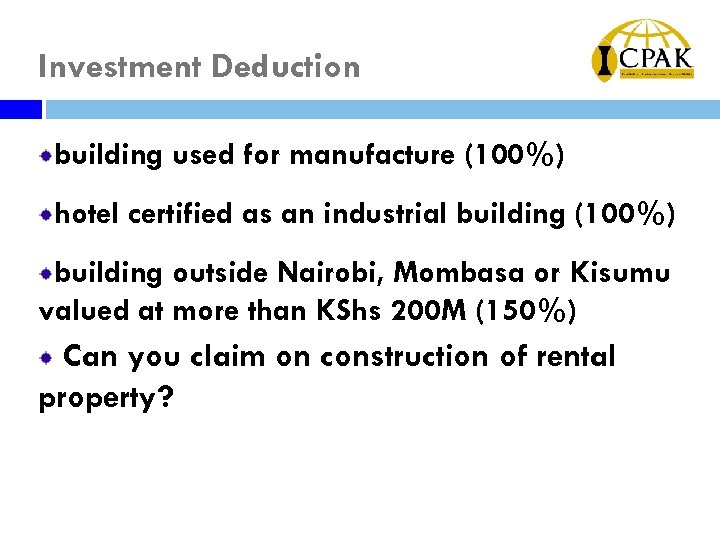 Investment Deduction building used for manufacture (100%) hotel certified as an industrial building (100%) building outside Nairobi, Mombasa or Kisumu valued at more than KShs 200 M (150%) Can you claim on construction of rental property?
Investment Deduction building used for manufacture (100%) hotel certified as an industrial building (100%) building outside Nairobi, Mombasa or Kisumu valued at more than KShs 200 M (150%) Can you claim on construction of rental property?
 Tax on Buildings Investment deduction VAT 5 claim
Tax on Buildings Investment deduction VAT 5 claim
 East Africa & the EAC…
East Africa & the EAC…
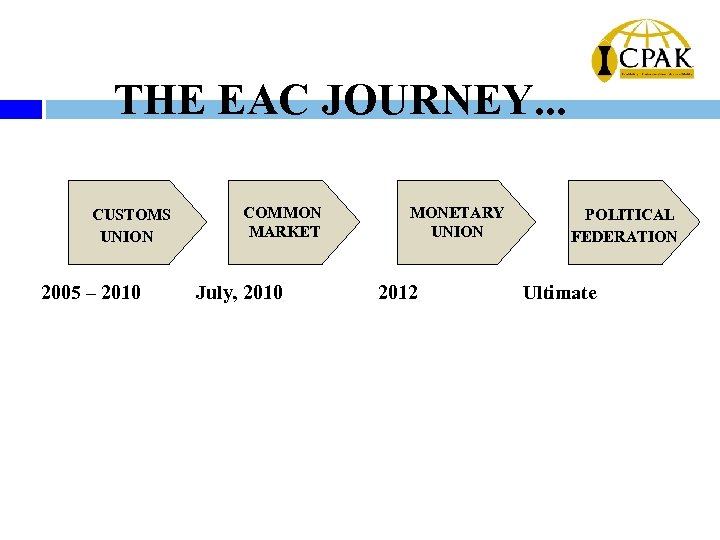 THE EAC JOURNEY. . . CUSTOMS UNION 2005 – 2010 COMMON MARKET July, 2010 MONETARY UNION 2012 POLITICAL FEDERATION Ultimate
THE EAC JOURNEY. . . CUSTOMS UNION 2005 – 2010 COMMON MARKET July, 2010 MONETARY UNION 2012 POLITICAL FEDERATION Ultimate
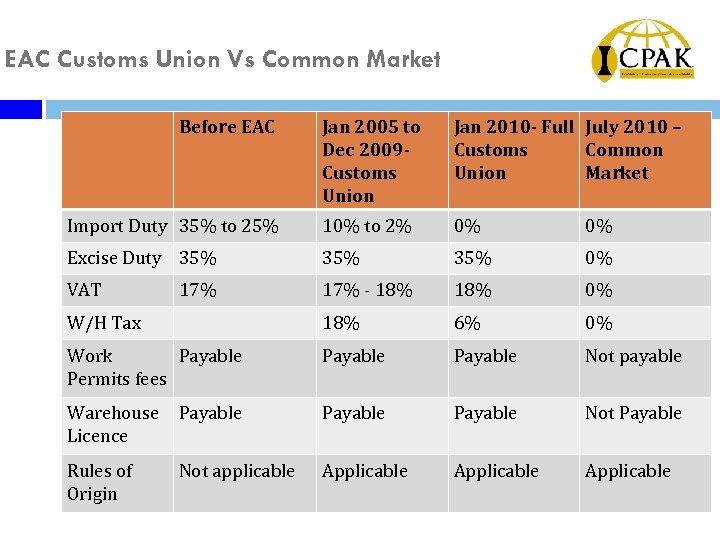 EAC Customs Union Vs Common Market Before EAC Jan 2005 to Dec 2009 Customs Union Jan 2010 - Full July 2010 – Customs Common Union Market Import Duty 35% to 25% 10% to 2% 0% 0% Excise Duty 35% 35% 0% VAT 17% - 18% 0% W/H Tax 18% 6% 0% Work Payable Permits fees Payable Not payable Warehouse Licence Payable Not Payable Rules of Origin Not applicable Applicable 17%
EAC Customs Union Vs Common Market Before EAC Jan 2005 to Dec 2009 Customs Union Jan 2010 - Full July 2010 – Customs Common Union Market Import Duty 35% to 25% 10% to 2% 0% 0% Excise Duty 35% 35% 0% VAT 17% - 18% 0% W/H Tax 18% 6% 0% Work Payable Permits fees Payable Not payable Warehouse Licence Payable Not Payable Rules of Origin Not applicable Applicable 17%
 Pertinent Issues
Pertinent Issues
 Is it a Change we can believe in? ¨ Need to position ourselves! SWOT Analysis! Lets embrace the Common Market ¨ Other barriers ¨ Our culture
Is it a Change we can believe in? ¨ Need to position ourselves! SWOT Analysis! Lets embrace the Common Market ¨ Other barriers ¨ Our culture
 Are we seeing the same “Animal”? ¨ ¨ Do we understand the benefits the same way? We need to anticipate challenges & be proactive? ¨ Implementation ¨ National sovereignty ¨ Non-tariff barriers
Are we seeing the same “Animal”? ¨ ¨ Do we understand the benefits the same way? We need to anticipate challenges & be proactive? ¨ Implementation ¨ National sovereignty ¨ Non-tariff barriers
 How does EAC affect our tax policy? ¨ ¨ Tax is a bitter pill Subtle shift towards indirect taxes ¨ Harmonisation likely to tilt the compass ¨ Are we looking at more direct tax measures in future?
How does EAC affect our tax policy? ¨ ¨ Tax is a bitter pill Subtle shift towards indirect taxes ¨ Harmonisation likely to tilt the compass ¨ Are we looking at more direct tax measures in future?
 Lets not overload the system ¨ ¨ Free movement of “Everything”? Any anticipated reciprocation?
Lets not overload the system ¨ ¨ Free movement of “Everything”? Any anticipated reciprocation?
 We know where we are!…
We know where we are!…
 Let us exercise our rights for change! Vote wisely for your Chairman Vote wisely for your ICPAK Representation Accounting Profession is broad… TAXATION is BIG & Deep!
Let us exercise our rights for change! Vote wisely for your Chairman Vote wisely for your ICPAK Representation Accounting Profession is broad… TAXATION is BIG & Deep!
 Let us exercise our rights for change! Presenter’s contact details: Julius Mwatu – MBA, BSc. , CPA(K), CPS(K), CFA(EA) Chief Finance Officer – Indigo Telecom Email: julius@indigo. co. ke Telephone: 3876805 -8 / 0728 -888 555
Let us exercise our rights for change! Presenter’s contact details: Julius Mwatu – MBA, BSc. , CPA(K), CPS(K), CFA(EA) Chief Finance Officer – Indigo Telecom Email: julius@indigo. co. ke Telephone: 3876805 -8 / 0728 -888 555
 Kwaheri
Kwaheri


