acf36a9626e35b19f85738f05a78ddab.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Financial Performance and Transfer Pricing ACCT 7320 Controllership December 1, 2010
Financial Performance and Transfer Pricing ACCT 7320 Controllership December 1, 2010
 Management Control Systems n n A management control system -- involves gathering and using information for planning and control decisions. A management control system guides the behavior of managers and employees Basis for evaluation and reward n Consistent with “agency theory” n 2
Management Control Systems n n A management control system -- involves gathering and using information for planning and control decisions. A management control system guides the behavior of managers and employees Basis for evaluation and reward n Consistent with “agency theory” n 2
 Management Control Systems A management control system collects: • Financial data such as cost, revenue, and net income • • Usually an important factor! Nonfinancial data • As seen on BSC 3
Management Control Systems A management control system collects: • Financial data such as cost, revenue, and net income • • Usually an important factor! Nonfinancial data • As seen on BSC 3
 Four Types of Financial Responsibility Centers 1 2 3 4 Cost center –manager accountable for costs only. Revenue center –manager accountable for revenues only. Profit center –manager accountable for revenues and costs. Investment center –manager accountable for investments, revenues, and costs. 4
Four Types of Financial Responsibility Centers 1 2 3 4 Cost center –manager accountable for costs only. Revenue center –manager accountable for revenues only. Profit center –manager accountable for revenues and costs. Investment center –manager accountable for investments, revenues, and costs. 4
 Evaluating Management Control Systems n n n Motivation – desire to attain a selected goal combined with the resulting drive or pursuit toward that goal. Goal congruence – subordinates’ individual goals are consistent with top management’s goals. Effort – exertion toward a goal. 5
Evaluating Management Control Systems n n n Motivation – desire to attain a selected goal combined with the resulting drive or pursuit toward that goal. Goal congruence – subordinates’ individual goals are consistent with top management’s goals. Effort – exertion toward a goal. 5
 Organization Structure n n Total decentralization means minimum constraints, maximum freedom for managers at the lowest levels to make decisions. Total centralization means maximum constraints, minimum freedom for managers at the lowest levels to make decisions. 6
Organization Structure n n Total decentralization means minimum constraints, maximum freedom for managers at the lowest levels to make decisions. Total centralization means maximum constraints, minimum freedom for managers at the lowest levels to make decisions. 6
 Benefits of Decentralization – – – Creates greater responsiveness to local needs Leads to gains from quicker decision making Increases motivation of subunit managers Aids management development and learning Sharpens the focus of subunit managers 7
Benefits of Decentralization – – – Creates greater responsiveness to local needs Leads to gains from quicker decision making Increases motivation of subunit managers Aids management development and learning Sharpens the focus of subunit managers 7
 Recall the Costs of Decentralization – – Leads to suboptimal decision making (incongruent or dysfunctional decision making due to loss of control) Focuses manager’s attention on the subunit rather than the organization as a whole Increases costs of gathering information Results in duplication of activities 8
Recall the Costs of Decentralization – – Leads to suboptimal decision making (incongruent or dysfunctional decision making due to loss of control) Focuses manager’s attention on the subunit rather than the organization as a whole Increases costs of gathering information Results in duplication of activities 8
 Decentralization in Multinational Companies n Multinational corporations are often decentralized n n centralized control of subunits in three or four different continents is hard Decentralization enables managers to apply their knowledge of local business and political conditions. 9
Decentralization in Multinational Companies n Multinational corporations are often decentralized n n centralized control of subunits in three or four different continents is hard Decentralization enables managers to apply their knowledge of local business and political conditions. 9
 Decentralization in Multinational Companies n n n Often rotate managers between foreign locations and corporate headquarters. Job rotation with decentralization helps develop managers’ abilities to operate in the global environment. A drawback to decentralizing multinational companies is the lack of control. 10
Decentralization in Multinational Companies n n n Often rotate managers between foreign locations and corporate headquarters. Job rotation with decentralization helps develop managers’ abilities to operate in the global environment. A drawback to decentralizing multinational companies is the lack of control. 10
 Transactions between Divisions n What happens when transactions occur between divisions (subunits)? Effects on individual divisional performance n Effects on the overall organization n n The control design of the control system affects the outcome 11
Transactions between Divisions n What happens when transactions occur between divisions (subunits)? Effects on individual divisional performance n Effects on the overall organization n n The control design of the control system affects the outcome 11
 Transfer Pricing n n A transfer price is the price one subunit charges for a product/service supplied to another subunit of the same organization. Creates revenues for the selling subunit and purchase costs for the buying subunit, affecting each subunit’s operating income. 12
Transfer Pricing n n A transfer price is the price one subunit charges for a product/service supplied to another subunit of the same organization. Creates revenues for the selling subunit and purchase costs for the buying subunit, affecting each subunit’s operating income. 12
 Transfer Pricing n What is the behavioral objective for transfer prices? Subunit managers need only consider how their actions will affect subunit performance without evaluating their impact on companywide performance. n A well designed TP policy will lead to goal congruence n 13
Transfer Pricing n What is the behavioral objective for transfer prices? Subunit managers need only consider how their actions will affect subunit performance without evaluating their impact on companywide performance. n A well designed TP policy will lead to goal congruence n 13
 Major Decisions about TPs n Two major decisions in transfer pricing policy: • • n Sourcing -- should segments be free to decide whether to sell/buy from other segments Pricing method-- what transfer price should be set for any transfer Criteria for “good” policy? n n n goal congruence managerial effort subunit autonomy [where desired] 14
Major Decisions about TPs n Two major decisions in transfer pricing policy: • • n Sourcing -- should segments be free to decide whether to sell/buy from other segments Pricing method-- what transfer price should be set for any transfer Criteria for “good” policy? n n n goal congruence managerial effort subunit autonomy [where desired] 14
 Transfer-Pricing Methods n 1 Three general methods for transfer pricing: Market-based • 2 Cost-based • 3 Price of a similar product/ service publicly listed Some basis of “cost” (plus a margin? ) Negotiated • Whatever the subunit managers agree [Also Dual Method: • Revenue to seller, cost to buyer not equal] 15
Transfer-Pricing Methods n 1 Three general methods for transfer pricing: Market-based • 2 Cost-based • 3 Price of a similar product/ service publicly listed Some basis of “cost” (plus a margin? ) Negotiated • Whatever the subunit managers agree [Also Dual Method: • Revenue to seller, cost to buyer not equal] 15
 Effects on Income n n Except for tax impacts, no impact on overall consolidated income Affects distribution of income among segments 16
Effects on Income n n Except for tax impacts, no impact on overall consolidated income Affects distribution of income among segments 16
 The Importance of Transfer Pricing n Evaluation of a division for sale n n Minority interest in a subsidiary n n (Is subsidiary being "plundered"? ) Tax minimization n n (What earnings are relevant? ) (Can shift income to some degree. ) Governmental contracting n (Endorses full-cost TPs. ) 17
The Importance of Transfer Pricing n Evaluation of a division for sale n n Minority interest in a subsidiary n n (Is subsidiary being "plundered"? ) Tax minimization n n (What earnings are relevant? ) (Can shift income to some degree. ) Governmental contracting n (Endorses full-cost TPs. ) 17
 What Can Happen Regarding Goal Congruity? Internal Outsourcing is production is best for company better for company overall Deal is completed internally Purchaser goes outside Good outcome Bad outcome Good outcome 18
What Can Happen Regarding Goal Congruity? Internal Outsourcing is production is best for company better for company overall Deal is completed internally Purchaser goes outside Good outcome Bad outcome Good outcome 18
 Setting Transfer Prices Range of Acceptable Prices: Ceiling: The outside market price that buyer would pay [Room to share benefit. ] Floor: The outlay costs of supplier + opportunity cost. n n If idle capacity, it’s just outlay cost If no idle capacity, then it’s sales price to current outside customer. 19
Setting Transfer Prices Range of Acceptable Prices: Ceiling: The outside market price that buyer would pay [Room to share benefit. ] Floor: The outlay costs of supplier + opportunity cost. n n If idle capacity, it’s just outlay cost If no idle capacity, then it’s sales price to current outside customer. 19
 Comparison of Methods Achievement of Goal Congruence n n n Market Price: Yes, if markets competitive Cost-Based: Often, but not always Negotiated: Yes 20
Comparison of Methods Achievement of Goal Congruence n n n Market Price: Yes, if markets competitive Cost-Based: Often, but not always Negotiated: Yes 20
 Comparison of Methods Usefulness for Evaluating Subunit Performance n n n Market Price: Yes, if markets competitive Cost-Based: Difficult, unless transfer price exceeds full cost Negotiated: Yes 21
Comparison of Methods Usefulness for Evaluating Subunit Performance n n n Market Price: Yes, if markets competitive Cost-Based: Difficult, unless transfer price exceeds full cost Negotiated: Yes 21
 Comparison of Methods Motivating Management Effort n n n Market Price: Yes Cost-Based: Yes, if based on budgeted costs; less incentive if based on actual cost Negotiated: Yes 22
Comparison of Methods Motivating Management Effort n n n Market Price: Yes Cost-Based: Yes, if based on budgeted costs; less incentive if based on actual cost Negotiated: Yes 22
 Comparison of Methods Preserving Subunit Autonomy n n n Market Price: Yes, if markets competitive Cost-Based: No, it is rule based Negotiated: Yes 23
Comparison of Methods Preserving Subunit Autonomy n n n Market Price: Yes, if markets competitive Cost-Based: No, it is rule based Negotiated: Yes 23
 Comparison of Methods Other Factors to Consider n n n Market Price: No market may exist Cost-Based: Useful for determining full. Negotiated: cost; easy to implement Bargaining takes time and may need to be reviewed 24
Comparison of Methods Other Factors to Consider n n n Market Price: No market may exist Cost-Based: Useful for determining full. Negotiated: cost; easy to implement Bargaining takes time and may need to be reviewed 24
 Tax & Multinational Transfer Pricing 25
Tax & Multinational Transfer Pricing 25
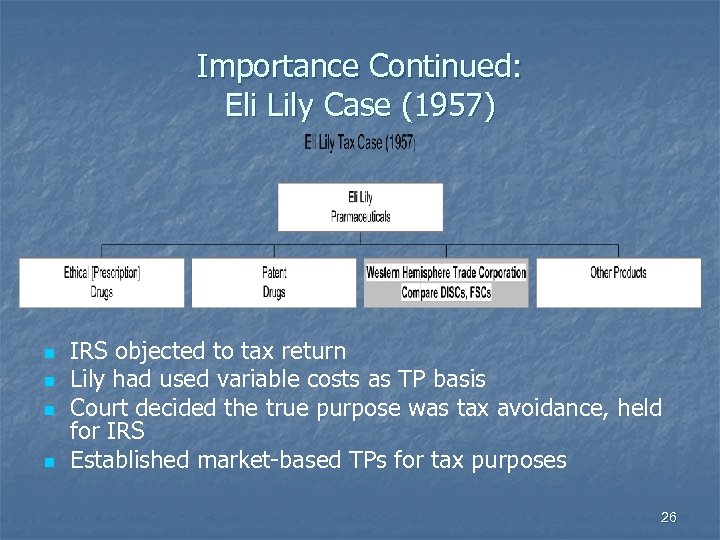 Importance Continued: Eli Lily Case (1957) n n IRS objected to tax return Lily had used variable costs as TP basis Court decided the true purpose was tax avoidance, held for IRS Established market-based TPs for tax purposes 26
Importance Continued: Eli Lily Case (1957) n n IRS objected to tax return Lily had used variable costs as TP basis Court decided the true purpose was tax avoidance, held for IRS Established market-based TPs for tax purposes 26
 Tax & Multinational Transfer Pricing n n n Transfer prices often have tax implications. Tax factors include not only income taxes, but also payroll taxes, customs duties, tariffs, sales taxes, and other levies on organizations. Section 482 of the U. S. Internal Revenue Service Code governs taxation of multinational transfer pricing. 27
Tax & Multinational Transfer Pricing n n n Transfer prices often have tax implications. Tax factors include not only income taxes, but also payroll taxes, customs duties, tariffs, sales taxes, and other levies on organizations. Section 482 of the U. S. Internal Revenue Service Code governs taxation of multinational transfer pricing. 27
 Multinational Transfer Pricing n Section 482 requires that transfer prices for both tangible and intangible property between a company and its foreign division be set to equal the price that would be charged by an unrelated third party in a comparable transaction. 28
Multinational Transfer Pricing n Section 482 requires that transfer prices for both tangible and intangible property between a company and its foreign division be set to equal the price that would be charged by an unrelated third party in a comparable transaction. 28
 Multinational Transfer Pricing n n Transfer prices can reduce income tax payments by recognizing more income in low tax rate countries and less income in high tax rate countries. Tax regulations of different countries restrict the transfer prices that companies can choose. 29
Multinational Transfer Pricing n n Transfer prices can reduce income tax payments by recognizing more income in low tax rate countries and less income in high tax rate countries. Tax regulations of different countries restrict the transfer prices that companies can choose. 29
 The End 30
The End 30


