c6b3b261223be21f034887f0c463dde3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Financial management Management and control systems Training for Programme Operators March 2012
Financial management Management and control systems Training for Programme Operators March 2012
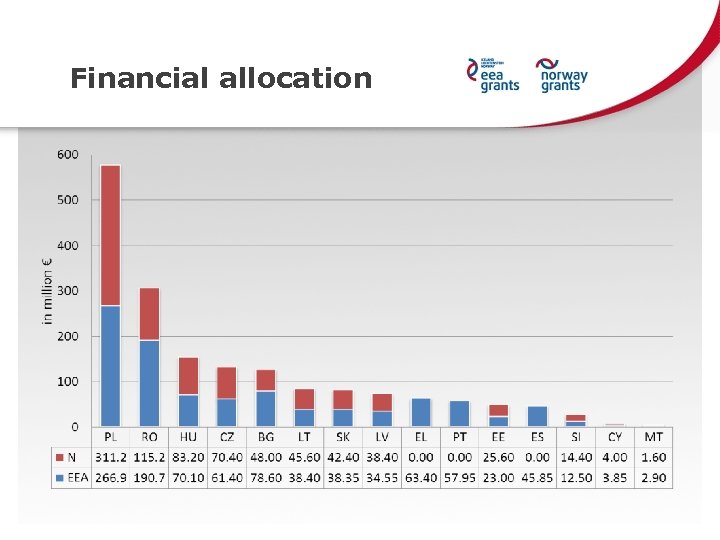 Financial allocation
Financial allocation
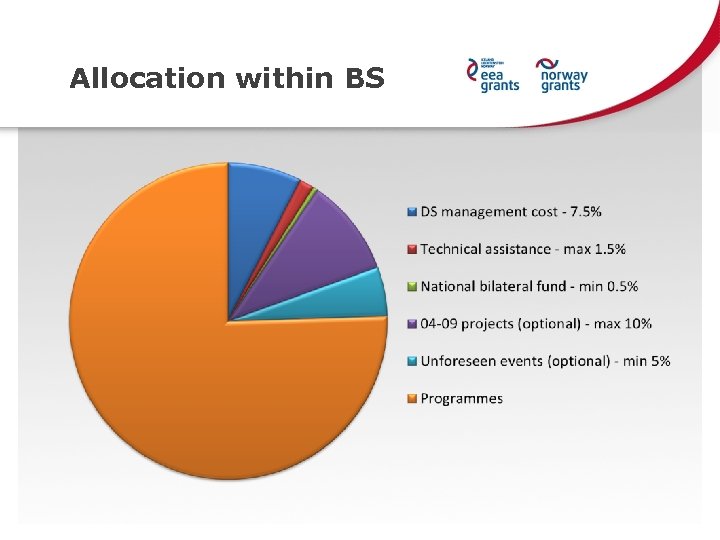 Allocation within BS
Allocation within BS
 Allocation in programme
Allocation in programme
 Financial model Pre-financing model § Advance instalments to POs based on future cash needs § Reporting on use of funds received previously § Pre-financing requests reviewed by FMO and cross-checked against previous requests and reported incurred expenditure § Small amount retained from each claim, released at programme completion
Financial model Pre-financing model § Advance instalments to POs based on future cash needs § Reporting on use of funds received previously § Pre-financing requests reviewed by FMO and cross-checked against previous requests and reported incurred expenditure § Small amount retained from each claim, released at programme completion
 Financial reporting § Interim financial reports and final financial report certified by CA § Fixed reporting periods covering four calendar month every year § Fixed deadline for reporting and fixed payment dates § FMO can withhold payments in case of delayed or incomplete reporting
Financial reporting § Interim financial reports and final financial report certified by CA § Fixed reporting periods covering four calendar month every year § Fixed deadline for reporting and fixed payment dates § FMO can withhold payments in case of delayed or incomplete reporting
 Financial reporting chart
Financial reporting chart
 Financial flow
Financial flow
 Advantages of financial setup § Pre-financing more suitable to the programming approach than reimbursement model § Easier access to liquidity for Programme Operators § De-centralised financial controls can be adapted to the size of grant and type of projects § More predictable workload and more reliable disbursement forecast
Advantages of financial setup § Pre-financing more suitable to the programming approach than reimbursement model § Easier access to liquidity for Programme Operators § De-centralised financial controls can be adapted to the size of grant and type of projects § More predictable workload and more reliable disbursement forecast
 Management and control systems – national level (1) Financial control at national level § Responsibility of the Certifying Authority § Certification of expenditure declared by POs § Exception: programmes operated by the FMO or a DS entity Certification of financial reports § Part of interim financial report and final programme report § Certification procedure and method to be designed by CA Eligible expenditure of a programme § Expenditure incurred directly by the PO (programme management, bilateral funds at programme level, etc. ) § Re-granting: payments to projects from the PO, and not expenditure incurred by project promoters
Management and control systems – national level (1) Financial control at national level § Responsibility of the Certifying Authority § Certification of expenditure declared by POs § Exception: programmes operated by the FMO or a DS entity Certification of financial reports § Part of interim financial report and final programme report § Certification procedure and method to be designed by CA Eligible expenditure of a programme § Expenditure incurred directly by the PO (programme management, bilateral funds at programme level, etc. ) § Re-granting: payments to projects from the PO, and not expenditure incurred by project promoters
 Management and control systems – national level (2) Management and control functions of the NFP § Overall responsibility for reaching the objectives of the FMs § Monitor progress and quality of implementation of programmes § Progress towards programme outcomes and objectives § Fulfilment of publicity requirements § Signing programme implementation agreements with POs Management and control functions of the AA § Audits on effective functioning of management and control systems both at national and PO level § Project audits based on an appropriate sample § Annual audit report and opinion § Closure declaration
Management and control systems – national level (2) Management and control functions of the NFP § Overall responsibility for reaching the objectives of the FMs § Monitor progress and quality of implementation of programmes § Progress towards programme outcomes and objectives § Fulfilment of publicity requirements § Signing programme implementation agreements with POs Management and control functions of the AA § Audits on effective functioning of management and control systems both at national and PO level § Project audits based on an appropriate sample § Annual audit report and opinion § Closure declaration
 Management and control systems – programme level Setting up management and control systems § Responsibility of the Programme Operator § Collecting applications, selecting projects, signing project contracts § Verification of project outputs and project expenditure § Ensuring payments to projects § Verification of compliance with the Regulation, the programme agreement, applicable national law and EU law § Reporting to the FMO / NFP / CA / Irregularities authority § Information and publicity System design § NFP / CA / AA encouraged to give guidance to POs § Verification function can be delegated by the POs § Consider economies of scale, capacity, past experience
Management and control systems – programme level Setting up management and control systems § Responsibility of the Programme Operator § Collecting applications, selecting projects, signing project contracts § Verification of project outputs and project expenditure § Ensuring payments to projects § Verification of compliance with the Regulation, the programme agreement, applicable national law and EU law § Reporting to the FMO / NFP / CA / Irregularities authority § Information and publicity System design § NFP / CA / AA encouraged to give guidance to POs § Verification function can be delegated by the POs § Consider economies of scale, capacity, past experience
 Audit report and opinion (1) System description by NFP, CA, AA, POs; report and opinion by AA § Compliance with the Regulation and generally accepted accounting principles § Proportionality in relation to the effectiveness of achieving the objectives of the programmes § Assess adequacy of design, not the practical effectiveness Timing, conditions § NFP/CA/AA: before Donor approval of the first programme or within 12 months of the Mo. U signature, any payments to programmes are conditional upon Donor review § POs: within 6 months of the submission of the first interim financial report
Audit report and opinion (1) System description by NFP, CA, AA, POs; report and opinion by AA § Compliance with the Regulation and generally accepted accounting principles § Proportionality in relation to the effectiveness of achieving the objectives of the programmes § Assess adequacy of design, not the practical effectiveness Timing, conditions § NFP/CA/AA: before Donor approval of the first programme or within 12 months of the Mo. U signature, any payments to programmes are conditional upon Donor review § POs: within 6 months of the submission of the first interim financial report
 Audit report and opinion(2) Approach § Formal appointment of relevant entities § Approved written procedures covering all areas of responsibilities foreseen in the Regulation § Agreements / acts of delegation of functions, if relevant § Detailed verification of procedures can be done at a later stage during audits on effective functioning of systems Previous audits § AA can rely on previous findings if the entities involved and the systems are the same § Results of SF/CF 2007 -13 compliance assessment
Audit report and opinion(2) Approach § Formal appointment of relevant entities § Approved written procedures covering all areas of responsibilities foreseen in the Regulation § Agreements / acts of delegation of functions, if relevant § Detailed verification of procedures can be done at a later stage during audits on effective functioning of systems Previous audits § AA can rely on previous findings if the entities involved and the systems are the same § Results of SF/CF 2007 -13 compliance assessment
 Proportionality Ø Main criticism of FM 2004 -09 Ø Trade-off between cost of control and tolerable error rate Ø Issues to consider when setting up control systems Desk check vs. on-the-spot check 100% verification vs. sample based verification Ex-ante vs. ex-post verification Adequate tools (e. g. IT systems, templates, checklists, etc. ) § Strict reporting deadlines towards the FMO § Adequate payment flow to projects to be ensured § §
Proportionality Ø Main criticism of FM 2004 -09 Ø Trade-off between cost of control and tolerable error rate Ø Issues to consider when setting up control systems Desk check vs. on-the-spot check 100% verification vs. sample based verification Ex-ante vs. ex-post verification Adequate tools (e. g. IT systems, templates, checklists, etc. ) § Strict reporting deadlines towards the FMO § Adequate payment flow to projects to be ensured § §
 New modalities Ø Proof of expenditure § Option A: invoices or accounting documents of equivalent probative value § Option B: report by an independent and certified auditor § Differentiation can be made between project promoters and donor project partners Ø Indirect costs (overheads) § Project promoters and partners may opt for a flat rate up to certain limits § Methodology to ensure fair apportionment of overall overheads
New modalities Ø Proof of expenditure § Option A: invoices or accounting documents of equivalent probative value § Option B: report by an independent and certified auditor § Differentiation can be made between project promoters and donor project partners Ø Indirect costs (overheads) § Project promoters and partners may opt for a flat rate up to certain limits § Methodology to ensure fair apportionment of overall overheads
 Exceptional situations Ø Specific cases § NFP acting as PO § PO acting as project promoter § DPP acting as donor project partner Ø Potential risks and issues § Financing from different budgets § Conflict of interest in project selection § Conflict of interest in control functions Ø Mitigation measures § Segregation of functions within the entity concerned § Clear responsibilities and reporting lines § Transparency, accountability and good governance
Exceptional situations Ø Specific cases § NFP acting as PO § PO acting as project promoter § DPP acting as donor project partner Ø Potential risks and issues § Financing from different budgets § Conflict of interest in project selection § Conflict of interest in control functions Ø Mitigation measures § Segregation of functions within the entity concerned § Clear responsibilities and reporting lines § Transparency, accountability and good governance


