Lecture 4_FC.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Financial institutions and intermediaries Introduction to Finance Lecture 4
Financial institutions and intermediaries Introduction to Finance Lecture 4
 Contents: Financial System. Financial Institutions. Key customers of financial Institutions. Depository/ Contractual/Investment Financial Institutions. How Financial Institutions Provide Financing for Firms.
Contents: Financial System. Financial Institutions. Key customers of financial Institutions. Depository/ Contractual/Investment Financial Institutions. How Financial Institutions Provide Financing for Firms.
 Financial System Encompasses the markets, intermediaries, service firms, and other institutions used to carry out the financial decisions of households, business firms and governments.
Financial System Encompasses the markets, intermediaries, service firms, and other institutions used to carry out the financial decisions of households, business firms and governments.
 Financial institutions Intermediaries that channel the savings of individuals, businesses and governments into loans or investments. They often serve as the main source of funds for businesses and individuals.
Financial institutions Intermediaries that channel the savings of individuals, businesses and governments into loans or investments. They often serve as the main source of funds for businesses and individuals.
 Key customers of Financial Institutions Net suppliers (for funds): individuals They save more money than they borrow. Net demanders (for funds): firms, governments. They borrow more money than they save.
Key customers of Financial Institutions Net suppliers (for funds): individuals They save more money than they borrow. Net demanders (for funds): firms, governments. They borrow more money than they save.
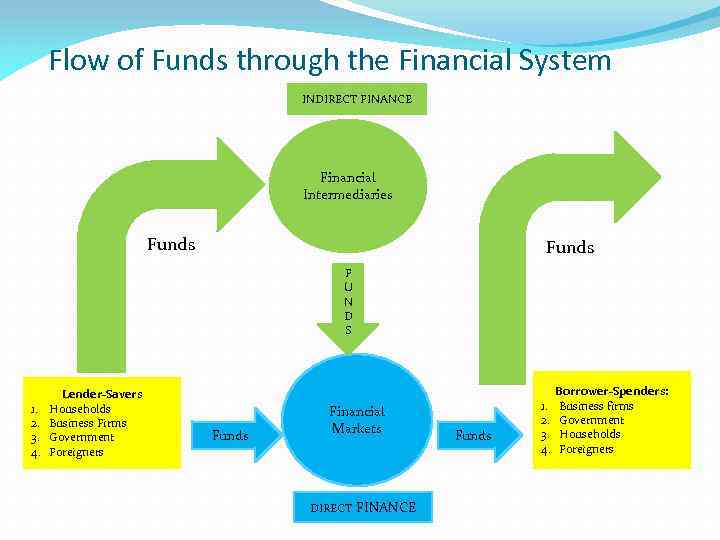 Flow of Funds through the Financial System INDIRECT FINANCE Financial Intermediaries Funds F U N D S 1. 2. 3. 4. Lender-Savers Households Business Firms Government Foreigners Funds Financial Markets DIRECT FINANCE Funds 1. 2. 3. 4. Borrower-Spenders: Business firms Government Households Foreigners
Flow of Funds through the Financial System INDIRECT FINANCE Financial Intermediaries Funds F U N D S 1. 2. 3. 4. Lender-Savers Households Business Firms Government Foreigners Funds Financial Markets DIRECT FINANCE Funds 1. 2. 3. 4. Borrower-Spenders: Business firms Government Households Foreigners
 3 Major Types of Financial Institutions: 1. Depository institutions 2. Contractual institutions 3. Investment institutions
3 Major Types of Financial Institutions: 1. Depository institutions 2. Contractual institutions 3. Investment institutions
 Depository Institutions Commercial Banks Savings and Loan Associations Saving Banks Credit Unions
Depository Institutions Commercial Banks Savings and Loan Associations Saving Banks Credit Unions
 Commercial Bank Financial institution that accumulate deposits from savers and provide credit to firms, individuals, and government agencies. Serves as a key source of credit to support expansions by firms.
Commercial Bank Financial institution that accumulate deposits from savers and provide credit to firms, individuals, and government agencies. Serves as a key source of credit to support expansions by firms.
 Commercial Bank Sources of funds: Deposits Uses of funds: Loans Purchase debt securities
Commercial Bank Sources of funds: Deposits Uses of funds: Loans Purchase debt securities
 Role of Commercial Banks as Financial intermediaries: Repackage of deposits Credit worthiness Diversify loans Serve as financial intermediaries
Role of Commercial Banks as Financial intermediaries: Repackage of deposits Credit worthiness Diversify loans Serve as financial intermediaries
 Regulation of commercial banks The banking System is regulated by the National bank (Central Bank) of a country.
Regulation of commercial banks The banking System is regulated by the National bank (Central Bank) of a country.
 Savings & Loan Associations (Thrift) S&L is a financial institution that specializes in accepting savings deposits and making mortgages and other loans.
Savings & Loan Associations (Thrift) S&L is a financial institution that specializes in accepting savings deposits and making mortgages and other loans.
 Savings & Loan Associations (Thrift) It is generally a locally owned and privately managed home financing institution; It receives individuals` savings and uses these funds to make long-term amortized loans to home purchasers; It makes loans for the construction, purchase, repair, or refinancing of houses; It is state or federally chartered.
Savings & Loan Associations (Thrift) It is generally a locally owned and privately managed home financing institution; It receives individuals` savings and uses these funds to make long-term amortized loans to home purchasers; It makes loans for the construction, purchase, repair, or refinancing of houses; It is state or federally chartered.
 Saving Banks Financial institutions whose primary purpose is accepting saving deposits Specialize in real estate financing.
Saving Banks Financial institutions whose primary purpose is accepting saving deposits Specialize in real estate financing.
 Credit Unions Are non-profit financial cooperatives owned by their members and governed by a board of directors elected by, and from among, those members. Accept deposits from their members and use them to make short-term loans.
Credit Unions Are non-profit financial cooperatives owned by their members and governed by a board of directors elected by, and from among, those members. Accept deposits from their members and use them to make short-term loans.
 Credit Unions The countries with the most credit union activity are highly diverse. According to the World Council, the countries with the greatest number of credit union members were: the United States (92 million), India (20 million), Canada (11 million), South Korea(5. 6 million), Kenya and Brazil(3. 9 million each), Thailand (3. 6 million), Australia 3. 4 million, Ireland (3. 0 million), and Mexico (2. 6 million).
Credit Unions The countries with the most credit union activity are highly diverse. According to the World Council, the countries with the greatest number of credit union members were: the United States (92 million), India (20 million), Canada (11 million), South Korea(5. 6 million), Kenya and Brazil(3. 9 million each), Thailand (3. 6 million), Australia 3. 4 million, Ireland (3. 0 million), and Mexico (2. 6 million).
 Credit Unions The countries with the highest percentage of credit union members in the economically active population were : Ireland(75%), Barbados(72%), St. Lucia(67%), Belize (65%), Grenada (59%), Trinidad & Tobago and Jamaica (54% each), Canada (46%), Antigua & Barbuda (45%), and the United States (44%). Several African and Latin American countries also have high credit union membership rates, as does Australia. The average percentage for all countries considered in the report is 7. 5% Credit unions were launched in 1992 in Poland, and as of 2012 there were 2, 000 credit union branches there with 2. 2 million members
Credit Unions The countries with the highest percentage of credit union members in the economically active population were : Ireland(75%), Barbados(72%), St. Lucia(67%), Belize (65%), Grenada (59%), Trinidad & Tobago and Jamaica (54% each), Canada (46%), Antigua & Barbuda (45%), and the United States (44%). Several African and Latin American countries also have high credit union membership rates, as does Australia. The average percentage for all countries considered in the report is 7. 5% Credit unions were launched in 1992 in Poland, and as of 2012 there were 2, 000 credit union branches there with 2. 2 million members
 2. Contractual Institutions Insurance Companies Pension Funds
2. Contractual Institutions Insurance Companies Pension Funds
 Insurance Companies Financial institutions that provide various types of insurance (life, property, health) for their customers.
Insurance Companies Financial institutions that provide various types of insurance (life, property, health) for their customers.
 Pension Fund Financial institution that receive payments from employees and invest the proceeds on their behalf.
Pension Fund Financial institution that receive payments from employees and invest the proceeds on their behalf.
 3. Investment Institutions Finance Companies Mutual Funds Securities Firms
3. Investment Institutions Finance Companies Mutual Funds Securities Firms
 Mutual Funds Financial institution that sells shares to individuals, pool these funds and use the proceeds to invest in securities.
Mutual Funds Financial institution that sells shares to individuals, pool these funds and use the proceeds to invest in securities.
 Types of Mutual Funds: Money market mutual fund Bond mutual fund Stock mutual fund
Types of Mutual Funds: Money market mutual fund Bond mutual fund Stock mutual fund
 Role of Mutual Funds as Financial Intermediaries Finance new investment by firms Let to hold diversified portfolio of securities Make investment decisions Determine, which debt security to purchase Invest in stocks that satisfy their specific investment objective (such as growth in value or high dividend income).
Role of Mutual Funds as Financial Intermediaries Finance new investment by firms Let to hold diversified portfolio of securities Make investment decisions Determine, which debt security to purchase Invest in stocks that satisfy their specific investment objective (such as growth in value or high dividend income).
 Securities Firms Financial institutions such as investment banks, investment companies and brokerage firms that help firms place securities and help investors.
Securities Firms Financial institutions such as investment banks, investment companies and brokerage firms that help firms place securities and help investors.
 Role of Securities Firms as Financial Intermediaries Placing Securities Serve as investment companies Play a brokerage role
Role of Securities Firms as Financial Intermediaries Placing Securities Serve as investment companies Play a brokerage role
 Finance companies Financial institutions which issue debt securities and lend the proceeds to individuals or firms in need of funds.
Finance companies Financial institutions which issue debt securities and lend the proceeds to individuals or firms in need of funds.
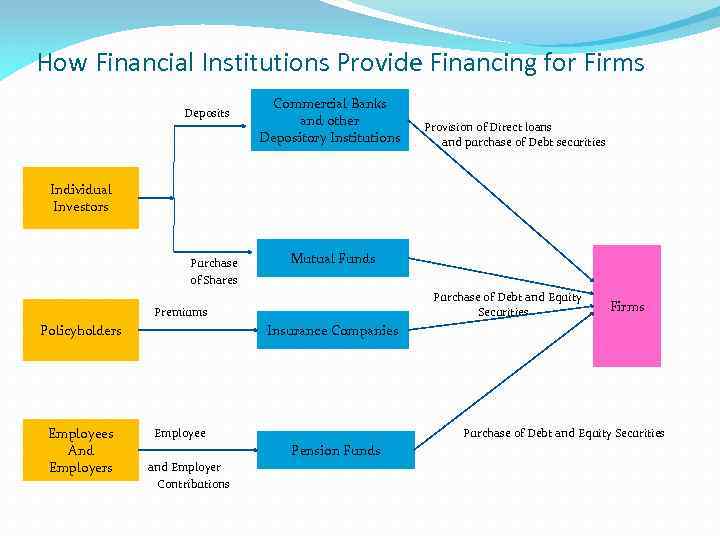 How Financial Institutions Provide Financing for Firms Commercial Banks Deposits and other Provision of Direct loans Depository Institutions and purchase of Debt securities Individual Investors Mutual Funds Purchase of Shares Purchase of Debt and Equity Premiums Securities Policyholders Insurance Companies Firms Employees Employee Purchase of Debt and Equity Securities Pension Funds And and Employers Contributions
How Financial Institutions Provide Financing for Firms Commercial Banks Deposits and other Provision of Direct loans Depository Institutions and purchase of Debt securities Individual Investors Mutual Funds Purchase of Shares Purchase of Debt and Equity Premiums Securities Policyholders Insurance Companies Firms Employees Employee Purchase of Debt and Equity Securities Pension Funds And and Employers Contributions
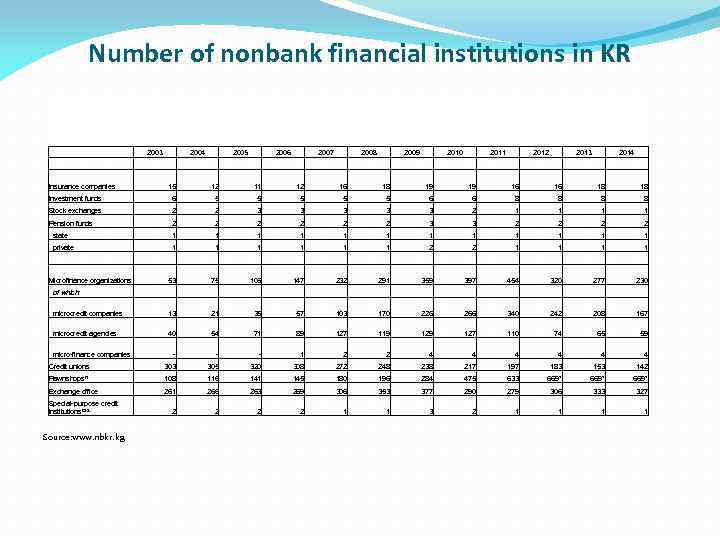 Number of nonbank financial institutions in KR 2003 2004 Insurance companies 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 15 12 11 12 16 18 19 19 16 16 18 18 Investment funds 6 5 5 5 6 6 8 8 Stock exchanges 2 2 3 3 3 2 1 1 Pension funds 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 state 1 1 1 private 1 1 1 2 2 1 1 1 359 397 454 Microfinance organizations of which: 53 75 106 147 232 291 320 1 277 230 microcredit companies 13 21 35 57 103 170 226 266 340 242 208 167 microcredit agencies 40 54 71 89 127 119 127 110 74 65 59 - - - 1 2 2 4 4 4 Credit unions micro-finance companies 303 305 320 308 272 248 238 217 197 183 153 142 Pawnshops/1 108 116 141 145 180 196 284 475 633 669* Exchange office 261 266 263 269 306 353 377 290 279 306 333 327 2 2 1 1 3 2 1 1 Special-purpose credit institutions/2/3 Source: www. nbkr. kg
Number of nonbank financial institutions in KR 2003 2004 Insurance companies 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 15 12 11 12 16 18 19 19 16 16 18 18 Investment funds 6 5 5 5 6 6 8 8 Stock exchanges 2 2 3 3 3 2 1 1 Pension funds 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 state 1 1 1 private 1 1 1 2 2 1 1 1 359 397 454 Microfinance organizations of which: 53 75 106 147 232 291 320 1 277 230 microcredit companies 13 21 35 57 103 170 226 266 340 242 208 167 microcredit agencies 40 54 71 89 127 119 127 110 74 65 59 - - - 1 2 2 4 4 4 Credit unions micro-finance companies 303 305 320 308 272 248 238 217 197 183 153 142 Pawnshops/1 108 116 141 145 180 196 284 475 633 669* Exchange office 261 266 263 269 306 353 377 290 279 306 333 327 2 2 1 1 3 2 1 1 Special-purpose credit institutions/2/3 Source: www. nbkr. kg
 “Başarılı bir insan olmaya çalışmayın; değerli bir insan olmaya çalışın. Başarılı insan, hayattan verdiğinden fazlasını alır. Değerli insan ise, hayattan aldığndan fazlasını verir. ”
“Başarılı bir insan olmaya çalışmayın; değerli bir insan olmaya çalışın. Başarılı insan, hayattan verdiğinden fazlasını alır. Değerli insan ise, hayattan aldığndan fazlasını verir. ”


