ccdbbda77e78b18b3f37985f046d111b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Financial Crisis- I
Financial Crisis- I
 Pre-Capitalist Finance “Money lenders” loaned their own money From ancient times Money was loaned to: Individuals for consumption The state, governments, for roads, wars, exploration Merchants for trade Rise of Banking Loans from deposited monies Renaissance Italy in 14 th Century See: Shakespeare’s Merchant of Venice
Pre-Capitalist Finance “Money lenders” loaned their own money From ancient times Money was loaned to: Individuals for consumption The state, governments, for roads, wars, exploration Merchants for trade Rise of Banking Loans from deposited monies Renaissance Italy in 14 th Century See: Shakespeare’s Merchant of Venice
 Capitalist Finance $ $ $ Commercial credit: finances trade ¢ Just as before, money borrowed to buy cheap and sell dear Industrial credit: finances real investment ¢ Money borrowed to build plants, buy machinery and raw materials and hire workers Consumer credit: finances personal consumption ¢ From pawnbrokers through installment plans to credit cards ¢ Mortgages to buy homes $ State credit: Governments borrow and lend ¢ Borrows to finance expendiures > tax revenues ¢ Lends at home and abroad, e. g. , foreign aid
Capitalist Finance $ $ $ Commercial credit: finances trade ¢ Just as before, money borrowed to buy cheap and sell dear Industrial credit: finances real investment ¢ Money borrowed to build plants, buy machinery and raw materials and hire workers Consumer credit: finances personal consumption ¢ From pawnbrokers through installment plans to credit cards ¢ Mortgages to buy homes $ State credit: Governments borrow and lend ¢ Borrows to finance expendiures > tax revenues ¢ Lends at home and abroad, e. g. , foreign aid
 Financial Institutions - 1 $ Banks ¢ Private banks u. Lend to consumers, business & governments u. Objective: profit ¢ National banks u. Central Banks: regulate money supply, oversee private banking sector u. Development Banks: fund investment, consumption, buy political support ¢ Supranational Banks u. International private banks u. World Bank
Financial Institutions - 1 $ Banks ¢ Private banks u. Lend to consumers, business & governments u. Objective: profit ¢ National banks u. Central Banks: regulate money supply, oversee private banking sector u. Development Banks: fund investment, consumption, buy political support ¢ Supranational Banks u. International private banks u. World Bank
 Financial Institutions - 2 $ Stock markets ¢ Buy & sell stocks ¢ Stocks are ownership shares, of various sorts u e. g. , some pay dividends, some don’t $ Commodity Markets ¢ Buy & sell commodies, e. g. , metals, soy beans, pork bellies, spot sales & futures contracts (that can be bought and sold $ Foreign exchange markets ¢ Buy & sell currencies $ Bond Markets ¢ Buy & sell bonds
Financial Institutions - 2 $ Stock markets ¢ Buy & sell stocks ¢ Stocks are ownership shares, of various sorts u e. g. , some pay dividends, some don’t $ Commodity Markets ¢ Buy & sell commodies, e. g. , metals, soy beans, pork bellies, spot sales & futures contracts (that can be bought and sold $ Foreign exchange markets ¢ Buy & sell currencies $ Bond Markets ¢ Buy & sell bonds
 Crises & Financial Crises $ Many kinds of crises: ¢ Commercial crises ¢ Industrial crises ¢ Financial crises $ All are Interrelated ¢ Remember discussion of growth & what has to happen: ¢ M-C(MP, L). . . P. . . C’-M’ ¢ Or, to be more complete:
Crises & Financial Crises $ Many kinds of crises: ¢ Commercial crises ¢ Industrial crises ¢ Financial crises $ All are Interrelated ¢ Remember discussion of growth & what has to happen: ¢ M-C(MP, L). . . P. . . C’-M’ ¢ Or, to be more complete:
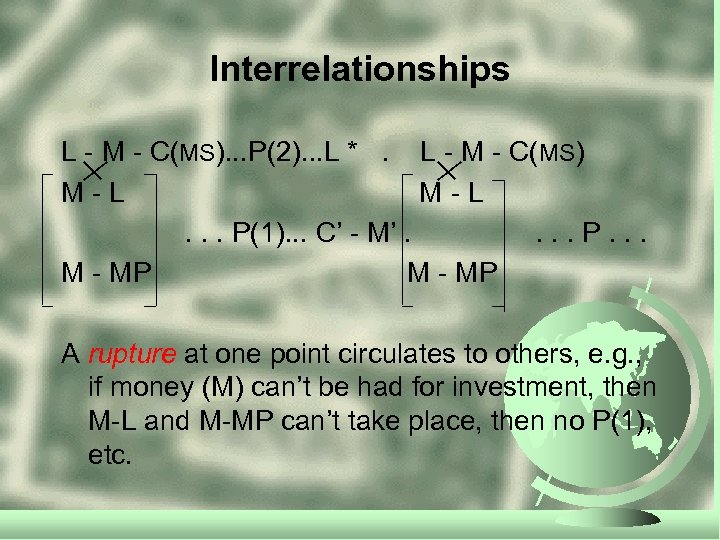 Interrelationships L - M - C(MS). . . P(2). . . L *. L - M - C(MS) M-L. . . P(1). . . C’ - M’. . P. . . M - MP A rupture at one point circulates to others, e. g. , if money (M) can’t be had for investment, then M-L and M-MP can’t take place, then no P(1), etc.
Interrelationships L - M - C(MS). . . P(2). . . L *. L - M - C(MS) M-L. . . P(1). . . C’ - M’. . P. . . M - MP A rupture at one point circulates to others, e. g. , if money (M) can’t be had for investment, then M-L and M-MP can’t take place, then no P(1), etc.
 Circulation of Crisis in Industrial Circuit - 1 $ $ $ Crisis of Industrial credit means no M No M (no bank credit, no stock sales, etc. ), then no M-L, M-MP, …P…, C’, M’ No L (refusal of labor market), or no MP (trade disruption), then no …P…C’, M’ No …P…, then no C’, M’ No C’-M’, then no revenue, no profit, no beginning again in new period
Circulation of Crisis in Industrial Circuit - 1 $ $ $ Crisis of Industrial credit means no M No M (no bank credit, no stock sales, etc. ), then no M-L, M-MP, …P…, C’, M’ No L (refusal of labor market), or no MP (trade disruption), then no …P…C’, M’ No …P…, then no C’, M’ No C’-M’, then no revenue, no profit, no beginning again in new period
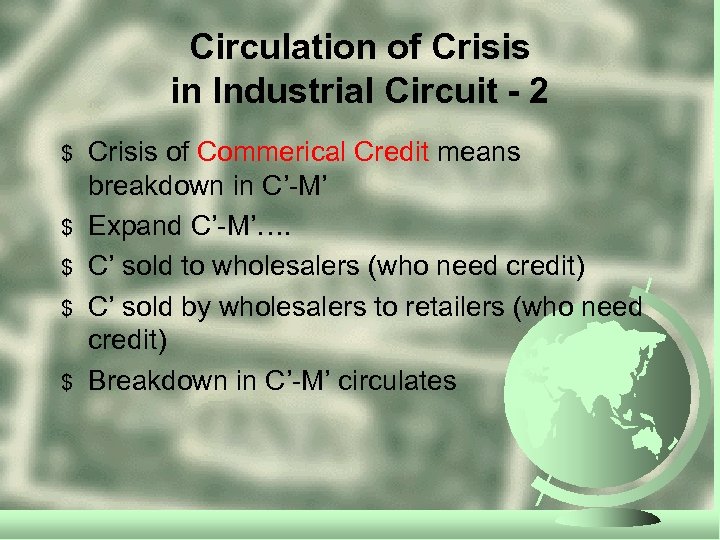 Circulation of Crisis in Industrial Circuit - 2 $ $ $ Crisis of Commerical Credit means breakdown in C’-M’ Expand C’-M’…. C’ sold to wholesalers (who need credit) C’ sold by wholesalers to retailers (who need credit) Breakdown in C’-M’ circulates
Circulation of Crisis in Industrial Circuit - 2 $ $ $ Crisis of Commerical Credit means breakdown in C’-M’ Expand C’-M’…. C’ sold to wholesalers (who need credit) C’ sold by wholesalers to retailers (who need credit) Breakdown in C’-M’ circulates
 Circulation of Crisis in Reproduction of Labor - 1 $ No L-M (refusal to enter labor market), then no wage), more …P(2) …, Life but no L. (assuming ability to produce consumer goods) ¢ E. g. , frontier, unsubordinated colonials $ No L-M (no jobs), then no wage, less C(MS), more …P(2) …, less L. (assuming some MS purchased with savings) ¢ E. g. , downturn, rising unemployment $ In other words: a breakdown in the subordination of life to labor, or in the reproduction of labor.
Circulation of Crisis in Reproduction of Labor - 1 $ No L-M (refusal to enter labor market), then no wage), more …P(2) …, Life but no L. (assuming ability to produce consumer goods) ¢ E. g. , frontier, unsubordinated colonials $ No L-M (no jobs), then no wage, less C(MS), more …P(2) …, less L. (assuming some MS purchased with savings) ¢ E. g. , downturn, rising unemployment $ In other words: a breakdown in the subordination of life to labor, or in the reproduction of labor.
 Circulation of Crisis in Reproduction of Labor - 2 $ Crisis of Consumer Credit ¢ E. g. , default on consumer debt repo’s ¢ E. g. , defaults on mortgages foreclosures $ Surge in Consumer defaults ¢ collapse in consumer demand for durables and housing $ Collapse in consumer demand ¢ drop in aggregate demand, drop in both C’-M’ and in M – C(MS) which provokes fall in investment, employment etc. $ Collapse in market for consumer debt ¢ E. g. , mortgages and mortgage-based securities
Circulation of Crisis in Reproduction of Labor - 2 $ Crisis of Consumer Credit ¢ E. g. , default on consumer debt repo’s ¢ E. g. , defaults on mortgages foreclosures $ Surge in Consumer defaults ¢ collapse in consumer demand for durables and housing $ Collapse in consumer demand ¢ drop in aggregate demand, drop in both C’-M’ and in M – C(MS) which provokes fall in investment, employment etc. $ Collapse in market for consumer debt ¢ E. g. , mortgages and mortgage-based securities
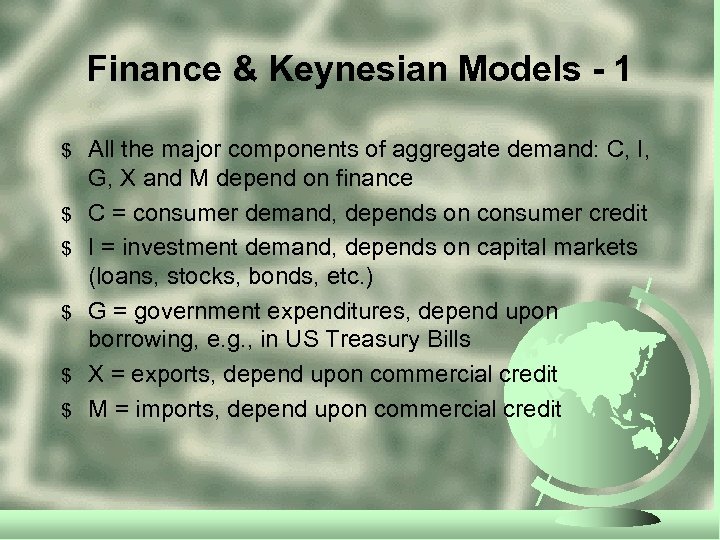 Finance & Keynesian Models - 1 $ $ $ All the major components of aggregate demand: C, I, G, X and M depend on finance C = consumer demand, depends on consumer credit I = investment demand, depends on capital markets (loans, stocks, bonds, etc. ) G = government expenditures, depend upon borrowing, e. g. , in US Treasury Bills X = exports, depend upon commercial credit M = imports, depend upon commercial credit
Finance & Keynesian Models - 1 $ $ $ All the major components of aggregate demand: C, I, G, X and M depend on finance C = consumer demand, depends on consumer credit I = investment demand, depends on capital markets (loans, stocks, bonds, etc. ) G = government expenditures, depend upon borrowing, e. g. , in US Treasury Bills X = exports, depend upon commercial credit M = imports, depend upon commercial credit
 Finance & Keynesian Models - 2 $ Two-way relationship: ¢ ¢ $ Healthy credit growth in C, I, G, X, M. Healthy growth confident credit markets, but…. Breakdown in credit breakdown in C, I, G, X, M Breakdown in C, I, G, X, M breakdown in credit markets. Monetary Policy ¢ Central bank affects finance through interest rates and handling of government debt u. Via reserve requirements, discount rate, open market operations ¢ Regulation of finance part of monetary policy
Finance & Keynesian Models - 2 $ Two-way relationship: ¢ ¢ $ Healthy credit growth in C, I, G, X, M. Healthy growth confident credit markets, but…. Breakdown in credit breakdown in C, I, G, X, M Breakdown in C, I, G, X, M breakdown in credit markets. Monetary Policy ¢ Central bank affects finance through interest rates and handling of government debt u. Via reserve requirements, discount rate, open market operations ¢ Regulation of finance part of monetary policy
 Financial Crises & Regulation - 1 $ Regulations were created because: ¢ the “free market” was subject to manipulation and abuse and regularly produced crises that undermined part or all of the economy. $ Examples: ¢ Tulip Mania (1634 -1637) ¢ Bank Panics and Crises of: 1792, 17961797, 1819, 1825, 1837, 1847, 1857, 1866, 1873, 1884, 1893, 1896, 1907 ¢ Wall Street Crash of 1929.
Financial Crises & Regulation - 1 $ Regulations were created because: ¢ the “free market” was subject to manipulation and abuse and regularly produced crises that undermined part or all of the economy. $ Examples: ¢ Tulip Mania (1634 -1637) ¢ Bank Panics and Crises of: 1792, 17961797, 1819, 1825, 1837, 1847, 1857, 1866, 1873, 1884, 1893, 1896, 1907 ¢ Wall Street Crash of 1929.
 Financial Crises & Regulation - 2 $ Primary purposes of regulation: ¢ To create and maintain confidence in various financial institutions and their operations ¢ In order to create and maintain useful flows of money to finance consumption, investment, trade and government expenditures ¢ To protect those who depend upon credit from misconduct and exploitation
Financial Crises & Regulation - 2 $ Primary purposes of regulation: ¢ To create and maintain confidence in various financial institutions and their operations ¢ In order to create and maintain useful flows of money to finance consumption, investment, trade and government expenditures ¢ To protect those who depend upon credit from misconduct and exploitation
 Financial Crises & Regulation - 3 $ Financial regulation includes: ¢ Specification of what actions are legal and which ones are illegal and… ¢ Specification of what institutions can do what u. Broadly this involves laws passed by congress ¢ Supervision to enforce laws, prosecute violations of laws ¢ Institutions to supervise, to check to see if regulations are being adhered to, investigate violations and prosecute them.
Financial Crises & Regulation - 3 $ Financial regulation includes: ¢ Specification of what actions are legal and which ones are illegal and… ¢ Specification of what institutions can do what u. Broadly this involves laws passed by congress ¢ Supervision to enforce laws, prosecute violations of laws ¢ Institutions to supervise, to check to see if regulations are being adhered to, investigate violations and prosecute them.
 Financial Crises & Regulation - 4 $ Regulatory institutions in the US include: ¢ Federal Reserve System (Fed) u Regulates member banks reserves, etc. ¢ Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) u Insures deposits, regulates bank deposit behavior ¢ US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) u Regulates securities markets (stock, bonds, etc. ) ¢ National Credit Union Administration (NCUA) u Licences, supervises and regulates credit federal credit unions ¢ Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) u Oversee and regulate commodities markets, futures & options
Financial Crises & Regulation - 4 $ Regulatory institutions in the US include: ¢ Federal Reserve System (Fed) u Regulates member banks reserves, etc. ¢ Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) u Insures deposits, regulates bank deposit behavior ¢ US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) u Regulates securities markets (stock, bonds, etc. ) ¢ National Credit Union Administration (NCUA) u Licences, supervises and regulates credit federal credit unions ¢ Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) u Oversee and regulate commodities markets, futures & options
 Great Depression & Financial Regulation $ Stock Market Crash of 1929 ¢ October 29, 1929 “Black Tuesday” ¢ Financial collapse contributed to collapse of economy more generally ¢ Despite Federal Reserve Act of 1913 $ New financial regulations in 1930 s: ¢ Farm Credit Administration, ¢ Federal Securities Act, Glass-Steagall Act (creates FDIC, lets Fed set max interest rates on S&L, splits commercial and investment banking), ¢ Export-Import Bank created, ¢ Exchange Stabilization Fund created, Federal Farm Mortgage Corporation, SEC created, etc.
Great Depression & Financial Regulation $ Stock Market Crash of 1929 ¢ October 29, 1929 “Black Tuesday” ¢ Financial collapse contributed to collapse of economy more generally ¢ Despite Federal Reserve Act of 1913 $ New financial regulations in 1930 s: ¢ Farm Credit Administration, ¢ Federal Securities Act, Glass-Steagall Act (creates FDIC, lets Fed set max interest rates on S&L, splits commercial and investment banking), ¢ Export-Import Bank created, ¢ Exchange Stabilization Fund created, Federal Farm Mortgage Corporation, SEC created, etc.
 Keynesian Era & financial Crises $ $ $ Comprehensive financial regulation at home meant virtually no domestic financial crises Bretton Woods agreement on fixed exchange rates with IMF as overseer and lender of last resort UNTIL: accelerating inflation and growing gov. debt, trade deficits and speculative attacks on the dollar lead to abandonment of Bretton Woods, volitile flexible exchange rates and negative interest rates.
Keynesian Era & financial Crises $ $ $ Comprehensive financial regulation at home meant virtually no domestic financial crises Bretton Woods agreement on fixed exchange rates with IMF as overseer and lender of last resort UNTIL: accelerating inflation and growing gov. debt, trade deficits and speculative attacks on the dollar lead to abandonment of Bretton Woods, volitile flexible exchange rates and negative interest rates.
 --END--
--END--


