e6d57cedc88b99193622482190975987.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Financial Condition Reporting GIRO / CAS Convention 2001 Nigel Gillott, Peter Hinton, John P Ryan Thursday 4 October 2001
Financial Condition Reporting GIRO / CAS Convention 2001 Nigel Gillott, Peter Hinton, John P Ryan Thursday 4 October 2001
 Financial Condition Reporting n The FSA’s & EU Supervisors view n The FCR Paper n Areas for further research n Methods of modeling risk n Modeling operational risk n Bringing it all together including tail dependency n Relevance of risk measures n Overlaying hard to quantify risks with a DFA model n Use of insurance to reduce capital requirements Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 2
Financial Condition Reporting n The FSA’s & EU Supervisors view n The FCR Paper n Areas for further research n Methods of modeling risk n Modeling operational risk n Bringing it all together including tail dependency n Relevance of risk measures n Overlaying hard to quantify risks with a DFA model n Use of insurance to reduce capital requirements Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 2
 FSA view n Adequate resources n What are adequate resources? n Test resources (as part of business plan) n Document process n How will FSA monitor? n Guidance Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 3
FSA view n Adequate resources n What are adequate resources? n Test resources (as part of business plan) n Document process n How will FSA monitor? n Guidance Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 3
 Adequate resources n Meet customer liabilities even if things go wrong n Resources include: capital, reinsurance, procedures, guarantees (if enforceable), contingent capital, qualified staff n Firm (insurers, banks, etc) must (as part of business plan) test ability to cope with reasonable adverse scenarios n Well-run firms doing this anyway n Process documented - so available to FSA (Prin 11) Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 4
Adequate resources n Meet customer liabilities even if things go wrong n Resources include: capital, reinsurance, procedures, guarantees (if enforceable), contingent capital, qualified staff n Firm (insurers, banks, etc) must (as part of business plan) test ability to cope with reasonable adverse scenarios n Well-run firms doing this anyway n Process documented - so available to FSA (Prin 11) Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 4
 FSA monitoring n Yet to be determined how FSA will monitor n Consultation (March 2002? ) n Directors’ certificate? n Brief description of tests? n Vulnerability? n Public / private? n Information useful to company itself Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 5
FSA monitoring n Yet to be determined how FSA will monitor n Consultation (March 2002? ) n Directors’ certificate? n Brief description of tests? n Vulnerability? n Public / private? n Information useful to company itself Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 5
 Guidance n Stress and scenario testing n Guidance on all things that can affect companies - reinsurance, disasters etc n Operational risk n Combination of events n Common causes Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 6
Guidance n Stress and scenario testing n Guidance on all things that can affect companies - reinsurance, disasters etc n Operational risk n Combination of events n Common causes Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 6
 Institute of Actuaries paper on FCA n Provides a framework for evaluating a company’s financial position in relation to the risk it covers both from a solvency & a shareholder perspective n Concentrates on non-life insurance but covers the principles for all companies. n It covers both readily quantifiable risks and those not so readily quantifiable e. g. management succession n The Profession’s response to the FSA proposal. n Corley Report also calls for FCR reports for Life Co’s Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 7
Institute of Actuaries paper on FCA n Provides a framework for evaluating a company’s financial position in relation to the risk it covers both from a solvency & a shareholder perspective n Concentrates on non-life insurance but covers the principles for all companies. n It covers both readily quantifiable risks and those not so readily quantifiable e. g. management succession n The Profession’s response to the FSA proposal. n Corley Report also calls for FCR reports for Life Co’s Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 7
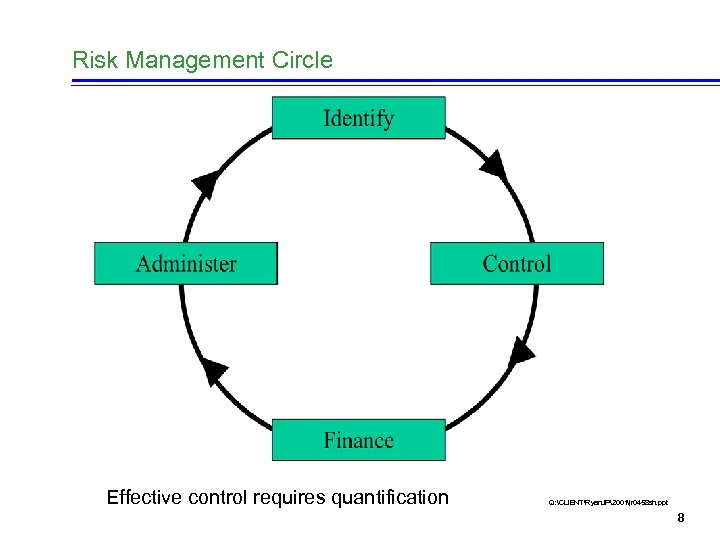 Risk Management Circle Effective control requires quantification Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 8
Risk Management Circle Effective control requires quantification Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 8
 Methods of Modelling Risk Financial Risk - investment models Financial Liabilities - actuarial models In many cases other disciplines will be required Some consultancy firms specialize in people risk Can the firm survive adverse scenarios? Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 9
Methods of Modelling Risk Financial Risk - investment models Financial Liabilities - actuarial models In many cases other disciplines will be required Some consultancy firms specialize in people risk Can the firm survive adverse scenarios? Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 9
 Operational Risk n ASSESSMENT OF OPERATIONAL RISK Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 10
Operational Risk n ASSESSMENT OF OPERATIONAL RISK Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 10
 Management and Business Risk n Some can be modelled using econometric or causal modelling techniques n Some are really risks for shareholders rather than capital issues n Stress testing can be a useful quantification technique n Insurance often cannot be used for this type of risk Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 11
Management and Business Risk n Some can be modelled using econometric or causal modelling techniques n Some are really risks for shareholders rather than capital issues n Stress testing can be a useful quantification technique n Insurance often cannot be used for this type of risk Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 11
 Quantification of Operational Risk n It is more complex than pricing conventional insurance risk n The risks are more under control of the institution than many insured perils n Changes in practice can have a material impact n Organisations do not like to admit to Operational Risk losses n Some are not readily amenable to statistical analysis e. g. management succession risk Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 12
Quantification of Operational Risk n It is more complex than pricing conventional insurance risk n The risks are more under control of the institution than many insured perils n Changes in practice can have a material impact n Organisations do not like to admit to Operational Risk losses n Some are not readily amenable to statistical analysis e. g. management succession risk Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 12
 Scenarios n Distributions may not be the best approach to evaluating certain types of operational risk n Test the survival of the organisation to adverse scenarios n Especially suitable for “people risks” e. g. succession planning Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 13
Scenarios n Distributions may not be the best approach to evaluating certain types of operational risk n Test the survival of the organisation to adverse scenarios n Especially suitable for “people risks” e. g. succession planning Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 13
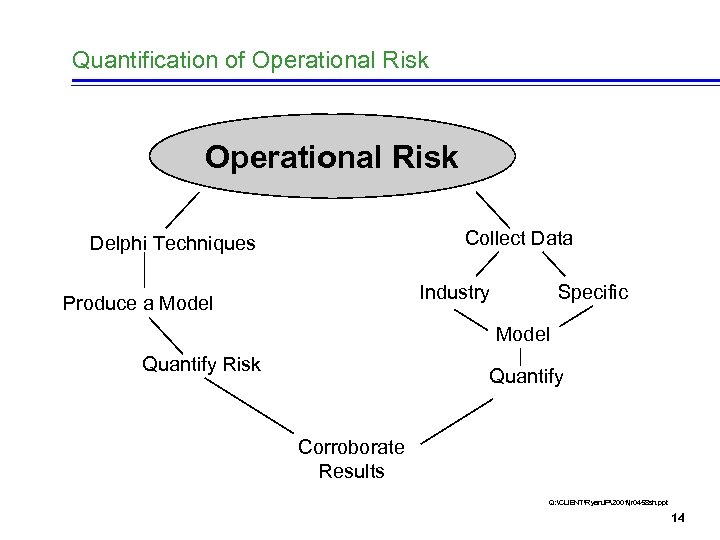 Quantification of Operational Risk Collect Data Delphi Techniques Industry Produce a Model Specific Model Quantify Risk Quantify Corroborate Results Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 14
Quantification of Operational Risk Collect Data Delphi Techniques Industry Produce a Model Specific Model Quantify Risk Quantify Corroborate Results Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 14
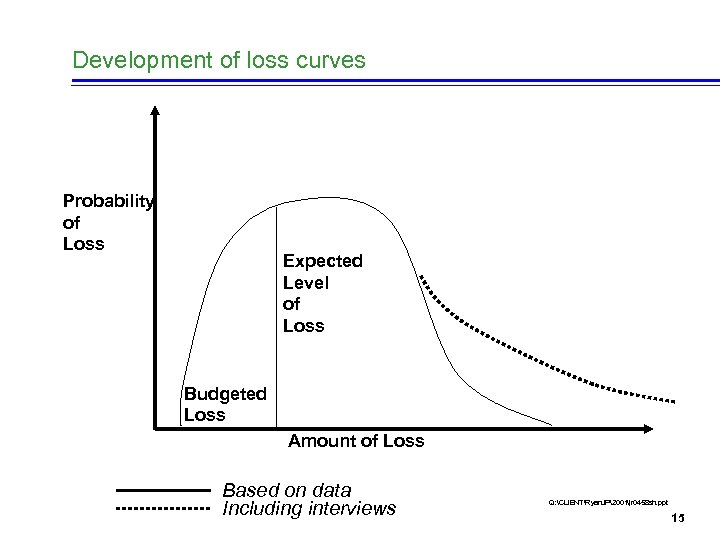 Development of loss curves Probability of Loss Expected Level of Loss Budgeted Loss Amount of Loss Based on data Including interviews Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 15
Development of loss curves Probability of Loss Expected Level of Loss Budgeted Loss Amount of Loss Based on data Including interviews Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 15
 Questions n The difficulty is the need to estimate the right tail in a skew distribution n How good is the left of the curve at predicting the right tail n Use of Bayesian statistics or credibility theory n What distributions fit the data n What techniques are best at supplementing the data for “missing large claims” Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 16
Questions n The difficulty is the need to estimate the right tail in a skew distribution n How good is the left of the curve at predicting the right tail n Use of Bayesian statistics or credibility theory n What distributions fit the data n What techniques are best at supplementing the data for “missing large claims” Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 16
 What are the other methods? n Delphi techniques n Decision trees and causal modelling ? Fuzzy Logic ? Others ? Use data bases for left side and other techniques for right side Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 17
What are the other methods? n Delphi techniques n Decision trees and causal modelling ? Fuzzy Logic ? Others ? Use data bases for left side and other techniques for right side Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 17
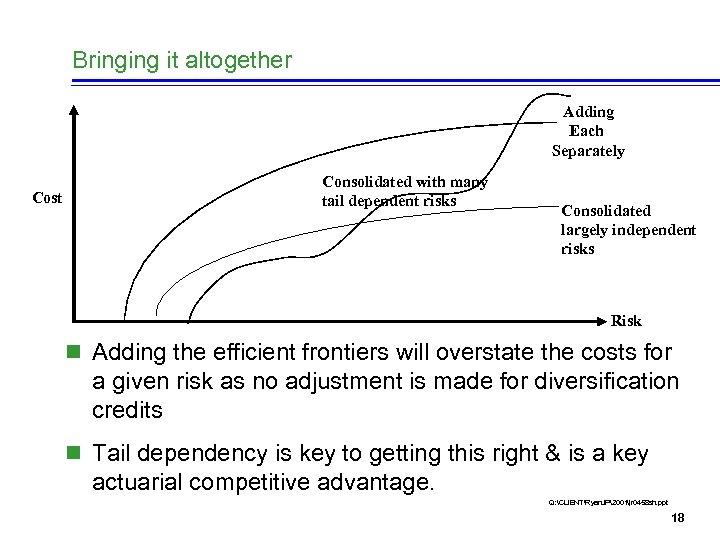 Bringing it altogether Adding Each Separately Cost Consolidated with many tail dependent risks Consolidated largely independent risks Risk n Adding the efficient frontiers will overstate the costs for a given risk as no adjustment is made for diversification credits n Tail dependency is key to getting this right & is a key actuarial competitive advantage. Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 18
Bringing it altogether Adding Each Separately Cost Consolidated with many tail dependent risks Consolidated largely independent risks Risk n Adding the efficient frontiers will overstate the costs for a given risk as no adjustment is made for diversification credits n Tail dependency is key to getting this right & is a key actuarial competitive advantage. Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 18
 Tail Dependency Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 19
Tail Dependency Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 19
 Risk Measures n Var works well for symmetrical risks n ECOR is better for skew risks such as most insurance risks n A coherent measure needs to be used across the group as a whole n Beware of tail dependency n Other constraints are also needed such as a requirement to maintain a credit rating Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 20
Risk Measures n Var works well for symmetrical risks n ECOR is better for skew risks such as most insurance risks n A coherent measure needs to be used across the group as a whole n Beware of tail dependency n Other constraints are also needed such as a requirement to maintain a credit rating Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 20
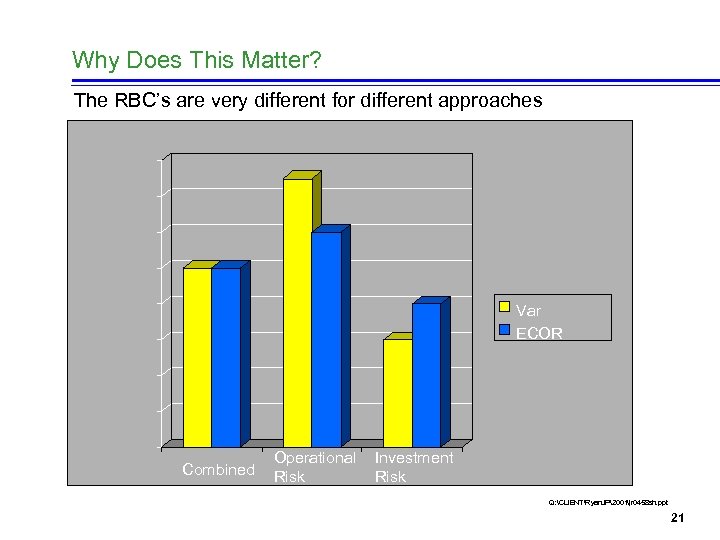 Why Does This Matter? The RBC’s are very different for different approaches Var ECOR Combined Operational Risk Investment Risk Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 21
Why Does This Matter? The RBC’s are very different for different approaches Var ECOR Combined Operational Risk Investment Risk Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 21
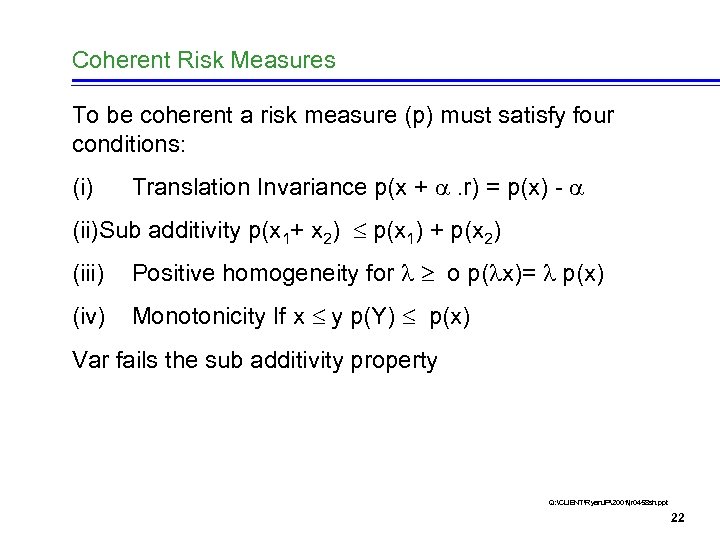 Coherent Risk Measures To be coherent a risk measure (p) must satisfy four conditions: (i) Translation Invariance p(x + . r) = p(x) - (ii)Sub additivity p(x 1+ x 2) p(x 1) + p(x 2) (iii) Positive homogeneity for o p( x)= p(x) (iv) Monotonicity If x y p(Y) p(x) Var fails the sub additivity property Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 22
Coherent Risk Measures To be coherent a risk measure (p) must satisfy four conditions: (i) Translation Invariance p(x + . r) = p(x) - (ii)Sub additivity p(x 1+ x 2) p(x 1) + p(x 2) (iii) Positive homogeneity for o p( x)= p(x) (iv) Monotonicity If x y p(Y) p(x) Var fails the sub additivity property Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 22
 Developing adverse scenarios for soft risks n Not readily quantifiable n Develop control processes & assess impact on whole organization under different DFA scenarios n It is the Board’s responsibility to assess risk. The report provides a regular & systematic framework n It adds value to the company in reducing & controlling risk n In many cases holding capital is not necessarily the best approach n Can we develop some case studies? Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 23
Developing adverse scenarios for soft risks n Not readily quantifiable n Develop control processes & assess impact on whole organization under different DFA scenarios n It is the Board’s responsibility to assess risk. The report provides a regular & systematic framework n It adds value to the company in reducing & controlling risk n In many cases holding capital is not necessarily the best approach n Can we develop some case studies? Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 23
 Insurance to cover Operational Risk n This is a non-trivial subject. n Basel has many doubts. Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 24
Insurance to cover Operational Risk n This is a non-trivial subject. n Basel has many doubts. Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 24
 Coverage Gaps n If complete cover is not available then capital will need to be held against remaining risk n Insurance should mitigate operational risk cost and so should be allowable n Operational Risk models would need to be run with and without insurance n Contracts with material exclusions may not mitigate overall capital requirements much n All Risks Cover is preferable n Much operational risk violates an underwriting rule that the insured should not be able to manipulate his loss experience n Some risks may not be insurable e. g. management succession risk Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 25
Coverage Gaps n If complete cover is not available then capital will need to be held against remaining risk n Insurance should mitigate operational risk cost and so should be allowable n Operational Risk models would need to be run with and without insurance n Contracts with material exclusions may not mitigate overall capital requirements much n All Risks Cover is preferable n Much operational risk violates an underwriting rule that the insured should not be able to manipulate his loss experience n Some risks may not be insurable e. g. management succession risk Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 25
 Claims Disputes n Some financial impact as a dispute creates coverage gap n Change insurance practice of conducting investigations at point of claim to investigating at point of sale n Financial Enhancement Ratings (FER) n Different in conditions (DIC) coverage Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 26
Claims Disputes n Some financial impact as a dispute creates coverage gap n Change insurance practice of conducting investigations at point of claim to investigating at point of sale n Financial Enhancement Ratings (FER) n Different in conditions (DIC) coverage Q: CLIENTRyan. JP2001jr 0458 sh. ppt 26


