37091fb6f83e3b12b8f6c9aa5654c020.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42
 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING A USER PERSPECTIVE Hoskin • Fizzell • Davidson Second Canadian Edition
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING A USER PERSPECTIVE Hoskin • Fizzell • Davidson Second Canadian Edition
 Shareholders’ Equity Chapter Eleven
Shareholders’ Equity Chapter Eleven
 Forms of Organization • Sole Proprietorship • Partnership • Corporation
Forms of Organization • Sole Proprietorship • Partnership • Corporation
 Sole Proprietorship • • Single-owner business Unlimited liability No reporting to shareholders Owner’s capital and withdrawals accounts • Profits are not taxed separately
Sole Proprietorship • • Single-owner business Unlimited liability No reporting to shareholders Owner’s capital and withdrawals accounts • Profits are not taxed separately
 Partnership • • • Two or more owners Partnership agreement Unlimited liability Profits are not taxed separately Partner’s capital and withdrawals accounts
Partnership • • • Two or more owners Partnership agreement Unlimited liability Profits are not taxed separately Partner’s capital and withdrawals accounts
 Corporation • Legally separate from the shareholders • Limited liability • Subject to taxation • Requires more paperwork and regulation
Corporation • Legally separate from the shareholders • Limited liability • Subject to taxation • Requires more paperwork and regulation
 Corporations • Companies may be incorporated under federal or provincial law • Need articles of incorporation documentation – Includes information on type of business, organization, management, and kinds of shares
Corporations • Companies may be incorporated under federal or provincial law • Need articles of incorporation documentation – Includes information on type of business, organization, management, and kinds of shares
 Shares • Authorized shares – The maximum number of shares that a company can issue, as specified in the articles – Many companies establish an unlimited number
Shares • Authorized shares – The maximum number of shares that a company can issue, as specified in the articles – Many companies establish an unlimited number
 Shares • Par value – A specified dollar amount attached to each share – Used in the past, no longer permitted • No par value shares – Used today
Shares • Par value – A specified dollar amount attached to each share – Used in the past, no longer permitted • No par value shares – Used today
 Shares • Legal capital – Total amount received for shares when initially sold – Must be kept intact – Cannot be paid out as dividends
Shares • Legal capital – Total amount received for shares when initially sold – Must be kept intact – Cannot be paid out as dividends
 Shares • Different classes of shares – Common shares – Preferred shares • Differ in the rights that accrue to their holders
Shares • Different classes of shares – Common shares – Preferred shares • Differ in the rights that accrue to their holders
 Common Shares • Represents the basic voting ownership rights of the company • Generally issued through underwriters – Details and features are outlined in a prospectus
Common Shares • Represents the basic voting ownership rights of the company • Generally issued through underwriters – Details and features are outlined in a prospectus
 Common Shares • Basic set of rights that allow the owner to share proportionately in: – Profits and losses – Selection of the management – Assets upon liquidation – Subsequent issues of shares (preemptive right)
Common Shares • Basic set of rights that allow the owner to share proportionately in: – Profits and losses – Selection of the management – Assets upon liquidation – Subsequent issues of shares (preemptive right)
 Common Shares • Measure of performance for shareholders – Earnings per share Net income Average common shares outstanding
Common Shares • Measure of performance for shareholders – Earnings per share Net income Average common shares outstanding
 Common Shares • Different classes of shares are entitled to different portions of the earnings • Preferred shares are restricted in the amounts of dividends • Common shares dividends not restricted
Common Shares • Different classes of shares are entitled to different portions of the earnings • Preferred shares are restricted in the amounts of dividends • Common shares dividends not restricted
 Common Shares • If a corporation declares a dividend, shareholders share proportionately • Common share carry the right to vote • Standard rule is one share, one vote
Common Shares • If a corporation declares a dividend, shareholders share proportionately • Common share carry the right to vote • Standard rule is one share, one vote
 Preferred Shares • Usually nonvoting • Have preference over common shares with regard to dividends • Preferred shareholders are not guaranteed a dividend
Preferred Shares • Usually nonvoting • Have preference over common shares with regard to dividends • Preferred shareholders are not guaranteed a dividend
 Preferred Shares • If a dividend is declared, preferred shareholders will receive dividends before common • Preferred dividend – Amount is usually stated as a dollar amount per share
Preferred Shares • If a dividend is declared, preferred shareholders will receive dividends before common • Preferred dividend – Amount is usually stated as a dollar amount per share
 Preferred Shares • Cumulative preferred shares – If a dividend is not declared in one year, the dividends carry over to the next year – Dividends in arrears • Dividends from prior years that have not been declared
Preferred Shares • Cumulative preferred shares – If a dividend is not declared in one year, the dividends carry over to the next year – Dividends in arrears • Dividends from prior years that have not been declared
 Preferred Shares • Convertible preferred shares – At the option of the shareholder – Can be converted into common shares based on a preset ratio
Preferred Shares • Convertible preferred shares – At the option of the shareholder – Can be converted into common shares based on a preset ratio
 Preferred Shares • Redeemable preferred shares – Can be bought back by the company (retired) – Price and time is specified • Retractable preferred shares – Can be sold back to the company (retired) at the option of the shareholder
Preferred Shares • Redeemable preferred shares – Can be bought back by the company (retired) – Price and time is specified • Retractable preferred shares – Can be sold back to the company (retired) at the option of the shareholder
 Preferred Shares • Participating preferred shares – Shareholders can share dividends in excess of those specified
Preferred Shares • Participating preferred shares – Shareholders can share dividends in excess of those specified
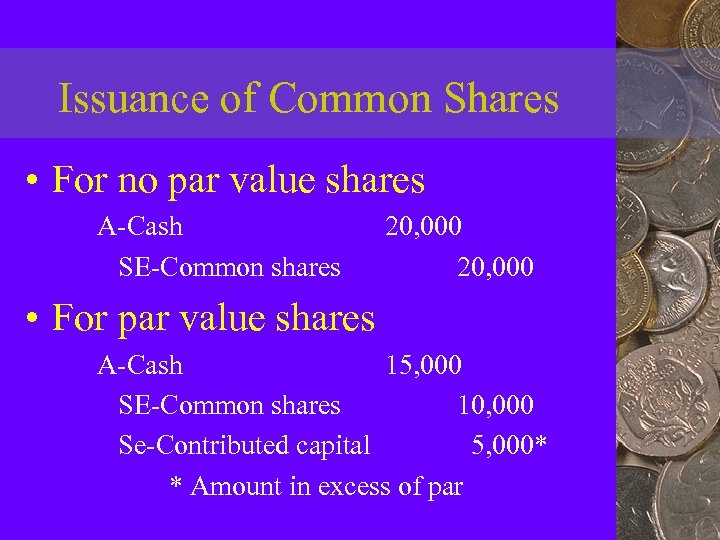 Issuance of Common Shares • For no par value shares A-Cash SE-Common shares 20, 000 • For par value shares A-Cash 15, 000 SE-Common shares 10, 000 Se-Contributed capital 5, 000* * Amount in excess of par
Issuance of Common Shares • For no par value shares A-Cash SE-Common shares 20, 000 • For par value shares A-Cash 15, 000 SE-Common shares 10, 000 Se-Contributed capital 5, 000* * Amount in excess of par
 Treasury Shares • Shares that have been repurchased by the issuing company • Usually cancelled immediately upon purchase
Treasury Shares • Shares that have been repurchased by the issuing company • Usually cancelled immediately upon purchase
 Shares • Authorized shares – Number approved for issue in the articles of incorporation • Issued shares – Number that have been sold (issued) by the company
Shares • Authorized shares – Number approved for issue in the articles of incorporation • Issued shares – Number that have been sold (issued) by the company
 Shares • Outstanding shares – Number that remain in the possession of shareholders outside the company
Shares • Outstanding shares – Number that remain in the possession of shareholders outside the company
 Repurchase of Shares • If the cost of repurchase differs from the original amount received SE-Common shares A-Cash SE-Contributed surplus 10, 000 9, 000 1, 000 OR: SE-Common shares SE-Retained earnings A-Cash 10, 000 2, 000 12, 000
Repurchase of Shares • If the cost of repurchase differs from the original amount received SE-Common shares A-Cash SE-Contributed surplus 10, 000 9, 000 1, 000 OR: SE-Common shares SE-Retained earnings A-Cash 10, 000 2, 000 12, 000
 Cash Dividends • Payments to shareholders from total net income retained in a company in the Retained Earnings account • Payment in return for the company’s use of the shareholders’ money
Cash Dividends • Payments to shareholders from total net income retained in a company in the Retained Earnings account • Payment in return for the company’s use of the shareholders’ money
 Cash Dividends • Paid only if Board of Directors has voted to declare a dividend • Declaration makes a legal liability • Not paid on treasury shares • Paid only on outstanding shares
Cash Dividends • Paid only if Board of Directors has voted to declare a dividend • Declaration makes a legal liability • Not paid on treasury shares • Paid only on outstanding shares
 Dividend Dates • Date of declaration – Date of the Board of Directors vote SE-Dividends declared L-Dividends payable xx xx
Dividend Dates • Date of declaration – Date of the Board of Directors vote SE-Dividends declared L-Dividends payable xx xx
 Dividend Dates • Date of record – Date on which a shareholder must own the shares in order to receive the dividend – No journal entry is made
Dividend Dates • Date of record – Date on which a shareholder must own the shares in order to receive the dividend – No journal entry is made
 Dividend Dates • Date of payment – Date on which the payment is made L-Dividends payable A-Cash xx xx
Dividend Dates • Date of payment – Date on which the payment is made L-Dividends payable A-Cash xx xx
 Property Dividends • Dividend declared that will be settled with some resource other than cash • Also known as dividends in kind • Valued at fair market value
Property Dividends • Dividend declared that will be settled with some resource other than cash • Also known as dividends in kind • Valued at fair market value
 Stock Dividends • Additional shares of the company are issued instead of cash or property • Issuance does not alter the overall value of the company
Stock Dividends • Additional shares of the company are issued instead of cash or property • Issuance does not alter the overall value of the company
 Stock Dividends • Example – Company has 100 shares outstanding, owned equally by 10 people – A 10% stock dividend is issued – Each shareholder receives 1 new share, resulting in 110 shares outstanding
Stock Dividends • Example – Company has 100 shares outstanding, owned equally by 10 people – A 10% stock dividend is issued – Each shareholder receives 1 new share, resulting in 110 shares outstanding
 Stock Dividends • Why issue stock dividends? – Shareholder may be better off • Market adjusts the value of the shares – Company is able to capitalize its retained earnings
Stock Dividends • Why issue stock dividends? – Shareholder may be better off • Market adjusts the value of the shares – Company is able to capitalize its retained earnings
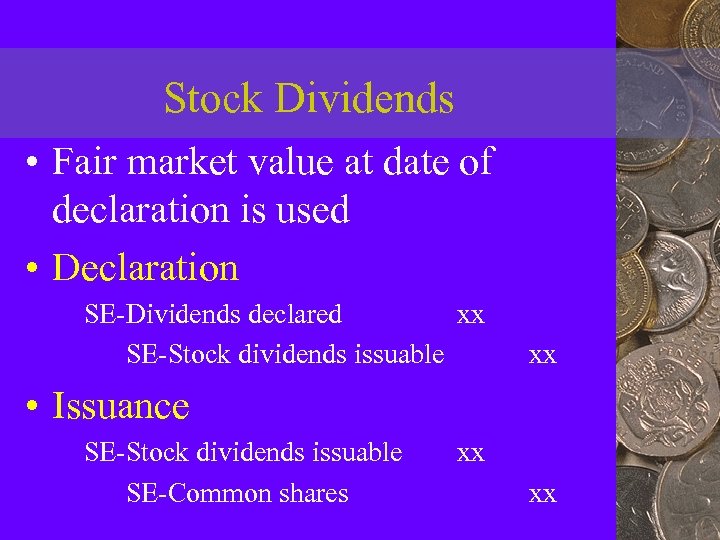 Stock Dividends • Fair market value at date of declaration is used • Declaration SE-Dividends declared xx SE-Stock dividends issuable xx • Issuance SE-Stock dividends issuable SE-Common shares xx xx
Stock Dividends • Fair market value at date of declaration is used • Declaration SE-Dividends declared xx SE-Stock dividends issuable xx • Issuance SE-Stock dividends issuable SE-Common shares xx xx
 Stock Splits • Usually stated as a ratio – Example: A two-for-one stock split • Each share currently held is exchanged for two new shares • Number of shares outstanding is doubled • No change in dollar amounts of any shareholders’ equity account
Stock Splits • Usually stated as a ratio – Example: A two-for-one stock split • Each share currently held is exchanged for two new shares • Number of shares outstanding is doubled • No change in dollar amounts of any shareholders’ equity account
 Stock Options • An agreement between two parties to either buy or sell a share at a fixed price at some future date – Exercise price: the fixed price – Call option: agreement to buy – Put option: agreement to sell
Stock Options • An agreement between two parties to either buy or sell a share at a fixed price at some future date – Exercise price: the fixed price – Call option: agreement to buy – Put option: agreement to sell
 Statement of Retained Earnings • Changes in retained earnings can be summarized in a separate statement – Beginning of year balance – Net income or loss for the year – Dividends declared – End of year balance
Statement of Retained Earnings • Changes in retained earnings can be summarized in a separate statement – Beginning of year balance – Net income or loss for the year – Dividends declared – End of year balance
 Price/Earnings Ratio = Market price per share Earnings per share A higher valuation usually indicates higher earnings potential, lower risk, or an assessment of future market share
Price/Earnings Ratio = Market price per share Earnings per share A higher valuation usually indicates higher earnings potential, lower risk, or an assessment of future market share
 Return on Shareholders’ Equity ROE = Net income - Preferred dividends Average common shareholders’ equity Measures the return to common shareholders only
Return on Shareholders’ Equity ROE = Net income - Preferred dividends Average common shareholders’ equity Measures the return to common shareholders only


