579a02b0e1a2064564fcf215c5cf04db.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 43
 Final Review Econ 240 A 1
Final Review Econ 240 A 1
 Outline n n n n The Big Picture Processes to remember ( and habits to form) for your quantitative career (FYQC) Concepts to remember FYQC Discrete Distributions Continuous distributions Central Limit Theorem Regression 2
Outline n n n n The Big Picture Processes to remember ( and habits to form) for your quantitative career (FYQC) Concepts to remember FYQC Discrete Distributions Continuous distributions Central Limit Theorem Regression 2
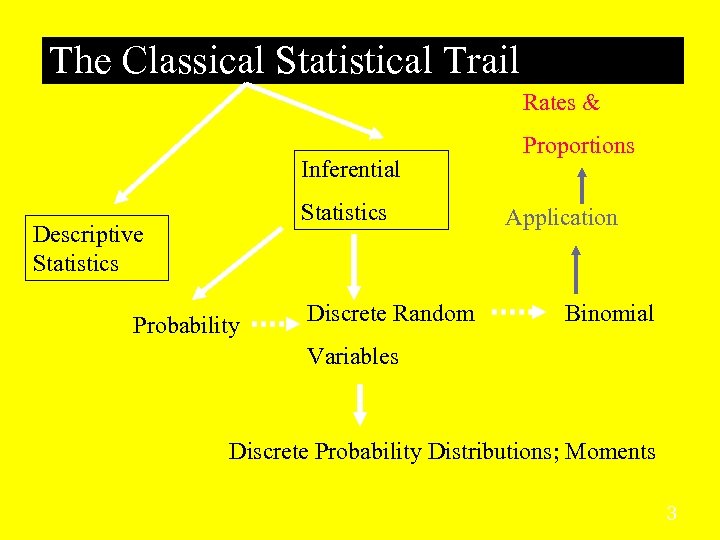 The Classical Statistical Trail Rates & Inferential Statistics Descriptive Statistics Probability Discrete Random Proportions Application Binomial Variables Discrete Probability Distributions; Moments 3
The Classical Statistical Trail Rates & Inferential Statistics Descriptive Statistics Probability Discrete Random Proportions Application Binomial Variables Discrete Probability Distributions; Moments 3
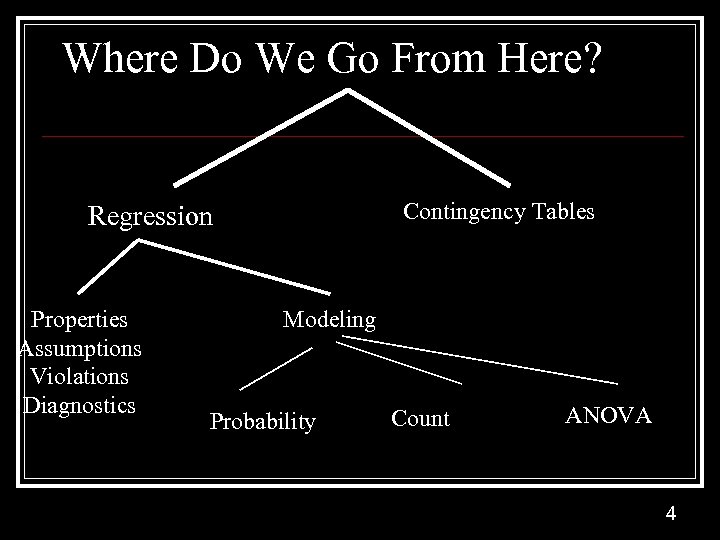 Where Do We Go From Here? Contingency Tables Regression Properties Assumptions Violations Diagnostics Modeling Probability Count ANOVA 4
Where Do We Go From Here? Contingency Tables Regression Properties Assumptions Violations Diagnostics Modeling Probability Count ANOVA 4
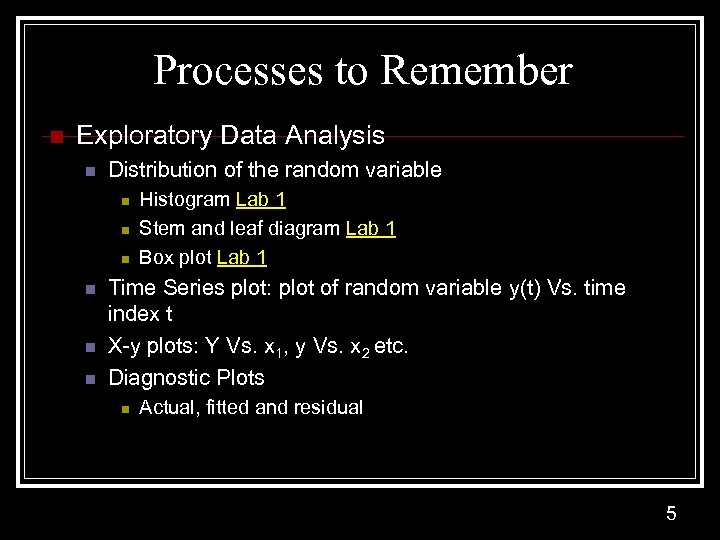 Processes to Remember n Exploratory Data Analysis n Distribution of the random variable n n n Histogram Lab 1 Stem and leaf diagram Lab 1 Box plot Lab 1 Time Series plot: plot of random variable y(t) Vs. time index t X-y plots: Y Vs. x 1, y Vs. x 2 etc. Diagnostic Plots n Actual, fitted and residual 5
Processes to Remember n Exploratory Data Analysis n Distribution of the random variable n n n Histogram Lab 1 Stem and leaf diagram Lab 1 Box plot Lab 1 Time Series plot: plot of random variable y(t) Vs. time index t X-y plots: Y Vs. x 1, y Vs. x 2 etc. Diagnostic Plots n Actual, fitted and residual 5
 Concepts to Remember n Random Variable: takes on values with some probability n n Flipping a coin Repeated Independent Bernoulli Trials n Flipping a coin twice Random Sample n Likelihood of a random sample n n Prob(e 1^e 2 …^en) = Prob(e 1)*Prob(e 2)…*Prob(en) 6
Concepts to Remember n Random Variable: takes on values with some probability n n Flipping a coin Repeated Independent Bernoulli Trials n Flipping a coin twice Random Sample n Likelihood of a random sample n n Prob(e 1^e 2 …^en) = Prob(e 1)*Prob(e 2)…*Prob(en) 6
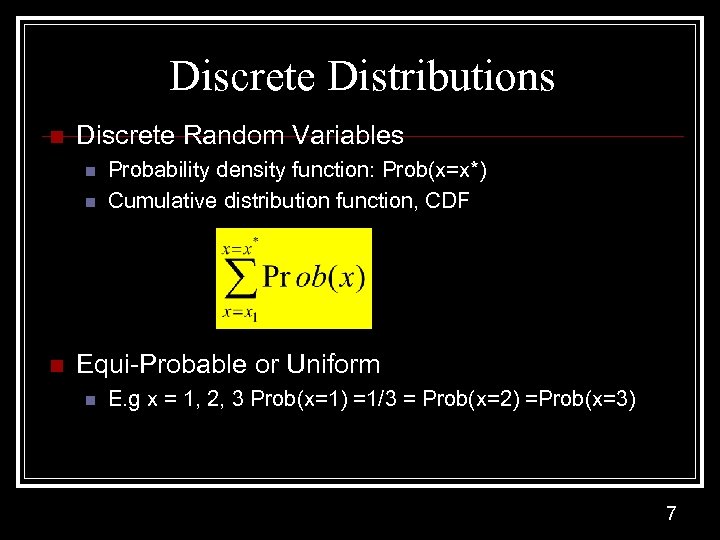 Discrete Distributions n Discrete Random Variables n n n Probability density function: Prob(x=x*) Cumulative distribution function, CDF Equi-Probable or Uniform n E. g x = 1, 2, 3 Prob(x=1) =1/3 = Prob(x=2) =Prob(x=3) 7
Discrete Distributions n Discrete Random Variables n n n Probability density function: Prob(x=x*) Cumulative distribution function, CDF Equi-Probable or Uniform n E. g x = 1, 2, 3 Prob(x=1) =1/3 = Prob(x=2) =Prob(x=3) 7
![Discrete Distributions n Binomial: Prob(k) = [n!/k!*(n-k)!]* pk (1 -p)n-k n n E(k) = Discrete Distributions n Binomial: Prob(k) = [n!/k!*(n-k)!]* pk (1 -p)n-k n n E(k) =](https://present5.com/presentation/579a02b0e1a2064564fcf215c5cf04db/image-8.jpg) Discrete Distributions n Binomial: Prob(k) = [n!/k!*(n-k)!]* pk (1 -p)n-k n n E(k) = n*p, Var(k) = n*p*(1 -p) Simulated sample binomial random variable Lab 2 Rates and proportions Poisson 8
Discrete Distributions n Binomial: Prob(k) = [n!/k!*(n-k)!]* pk (1 -p)n-k n n E(k) = n*p, Var(k) = n*p*(1 -p) Simulated sample binomial random variable Lab 2 Rates and proportions Poisson 8
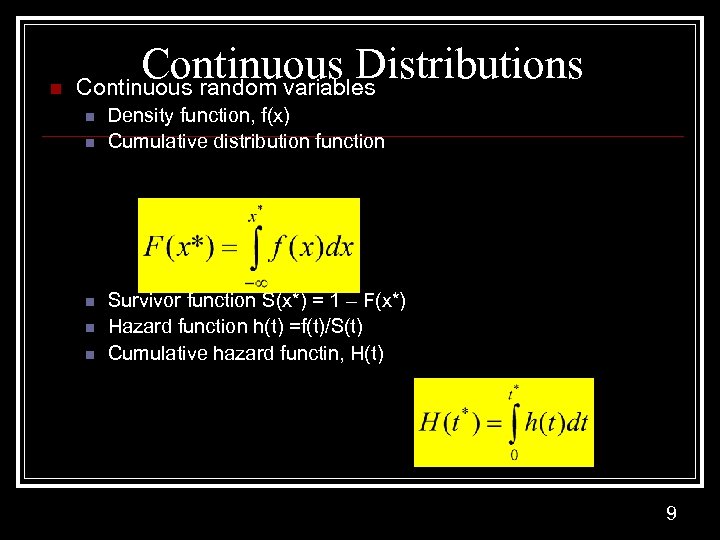 n Continuous Distributions Continuous random variables n n n Density function, f(x) Cumulative distribution function Survivor function S(x*) = 1 – F(x*) Hazard function h(t) =f(t)/S(t) Cumulative hazard functin, H(t) 9
n Continuous Distributions Continuous random variables n n n Density function, f(x) Cumulative distribution function Survivor function S(x*) = 1 – F(x*) Hazard function h(t) =f(t)/S(t) Cumulative hazard functin, H(t) 9
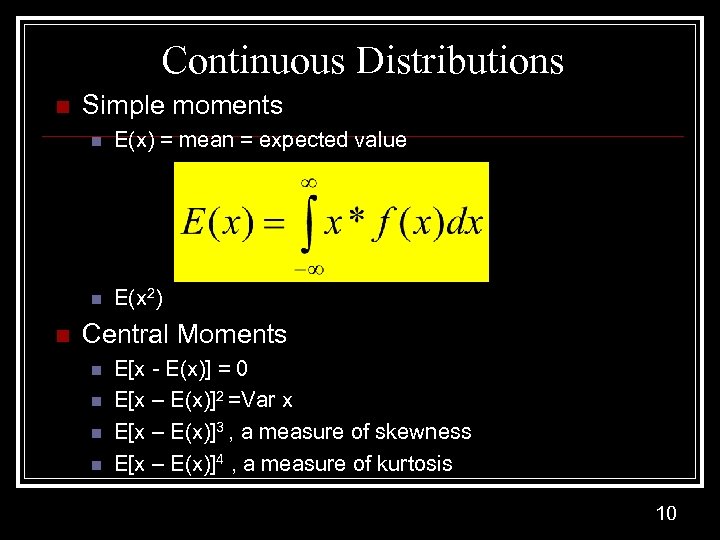 Continuous Distributions n Simple moments n n n E(x) = mean = expected value E(x 2) Central Moments n n E[x - E(x)] = 0 E[x – E(x)]2 =Var x E[x – E(x)]3 , a measure of skewness E[x – E(x)]4 , a measure of kurtosis 10
Continuous Distributions n Simple moments n n n E(x) = mean = expected value E(x 2) Central Moments n n E[x - E(x)] = 0 E[x – E(x)]2 =Var x E[x – E(x)]3 , a measure of skewness E[x – E(x)]4 , a measure of kurtosis 10
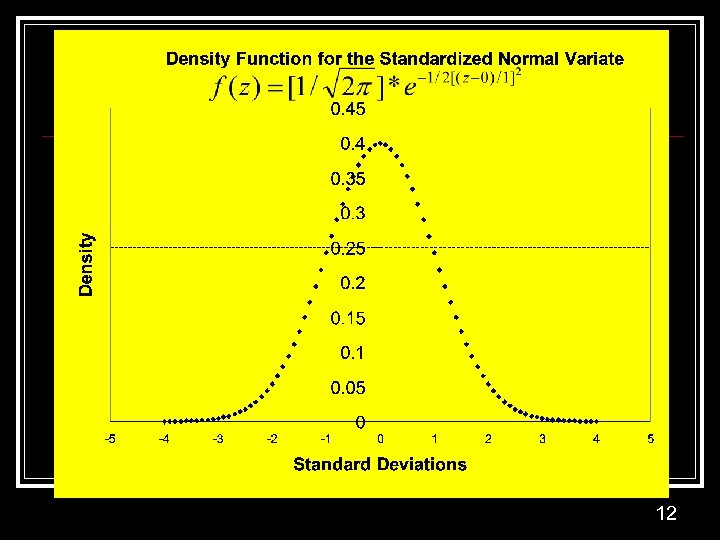
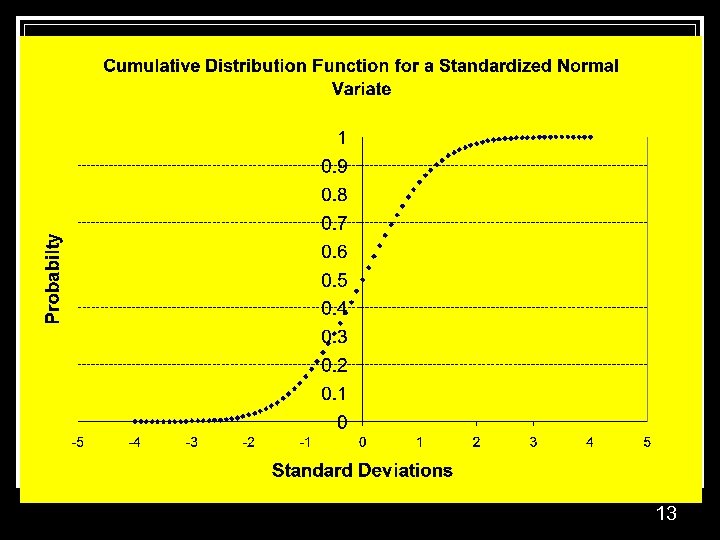
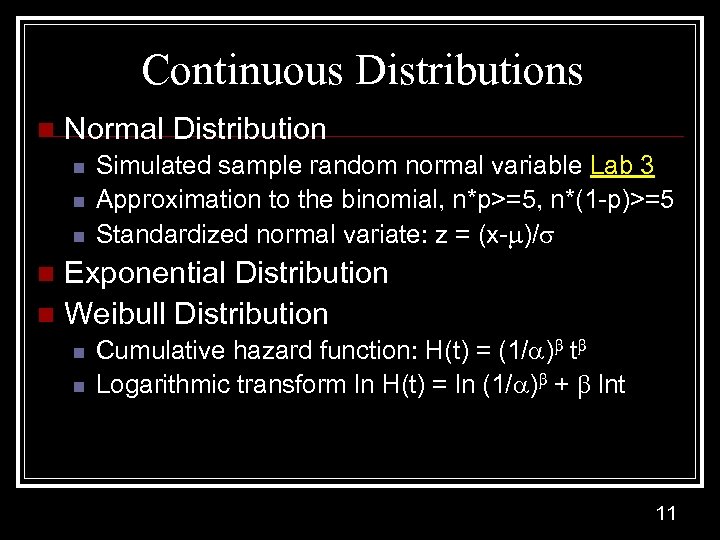 Continuous Distributions n Normal Distribution n Simulated sample random normal variable Lab 3 Approximation to the binomial, n*p>=5, n*(1 -p)>=5 Standardized normal variate: z = (x- )/ Exponential Distribution n Weibull Distribution n Cumulative hazard function: H(t) = (1/ ) t Logarithmic transform ln H(t) = ln (1/ ) + lnt 11
Continuous Distributions n Normal Distribution n Simulated sample random normal variable Lab 3 Approximation to the binomial, n*p>=5, n*(1 -p)>=5 Standardized normal variate: z = (x- )/ Exponential Distribution n Weibull Distribution n Cumulative hazard function: H(t) = (1/ ) t Logarithmic transform ln H(t) = ln (1/ ) + lnt 11
 12
12
 13
13
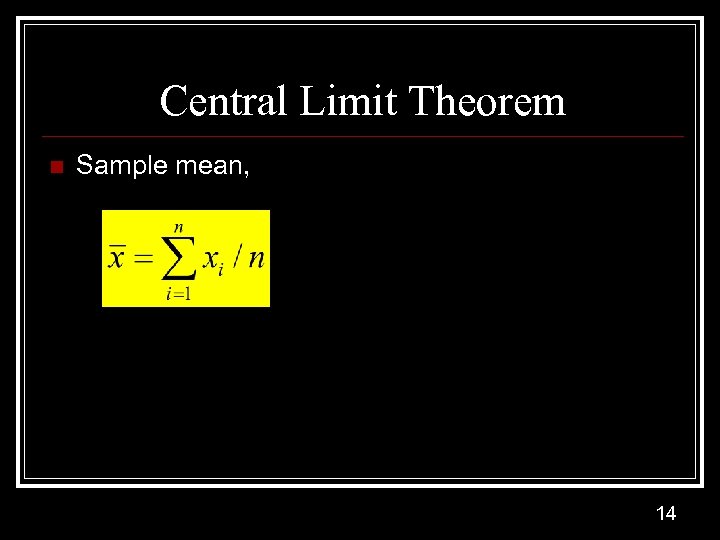 Central Limit Theorem n Sample mean, 14
Central Limit Theorem n Sample mean, 14
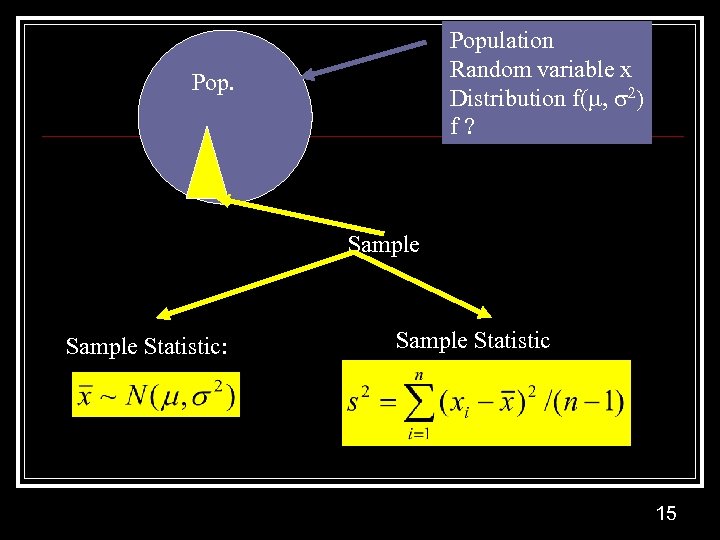 Population Random variable x Distribution f( , 2) f? Pop. Sample Statistic: Sample Statistic 15
Population Random variable x Distribution f( , 2) f? Pop. Sample Statistic: Sample Statistic 15
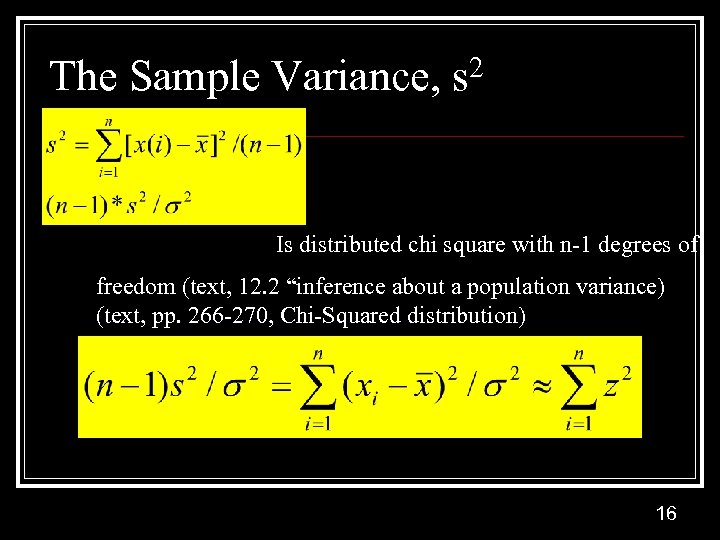 The Sample Variance, s 2 Is distributed chi square with n-1 degrees of freedom (text, 12. 2 “inference about a population variance) (text, pp. 266 -270, Chi-Squared distribution) 16
The Sample Variance, s 2 Is distributed chi square with n-1 degrees of freedom (text, 12. 2 “inference about a population variance) (text, pp. 266 -270, Chi-Squared distribution) 16
 Regression Models n Statistical distributions and tests n n Student’s t F Chi Square Assumptions n Pathologies n 17
Regression Models n Statistical distributions and tests n n Student’s t F Chi Square Assumptions n Pathologies n 17
 Regression Models n Time Series n n Linear trend model: y(t) =a + b*t +e(t) Lab 4 Exponential trend model: y(t) =exp[a+b*t+e(t)] n n n Natural logarithmic transformation ln Ln y(t) = a + b*t + e(t) Lab 4 Linear rates of change: yi = a + b*xi + ei n n dy/dx = b Returns generating process: n [ri(t) – rf 0] = + *[r. M(t) – rf 0] + ei(t) Lab 6 18
Regression Models n Time Series n n Linear trend model: y(t) =a + b*t +e(t) Lab 4 Exponential trend model: y(t) =exp[a+b*t+e(t)] n n n Natural logarithmic transformation ln Ln y(t) = a + b*t + e(t) Lab 4 Linear rates of change: yi = a + b*xi + ei n n dy/dx = b Returns generating process: n [ri(t) – rf 0] = + *[r. M(t) – rf 0] + ei(t) Lab 6 18
 Regression Models n Percentage rates of change, elasticities n Cross-section n Ln assetsi =a + b*ln revenuei + ei Lab 5 § dln assets/dlnrevenue = b = [dassets/drevenue]/[assets/revenue] = marginal/average 19
Regression Models n Percentage rates of change, elasticities n Cross-section n Ln assetsi =a + b*ln revenuei + ei Lab 5 § dln assets/dlnrevenue = b = [dassets/drevenue]/[assets/revenue] = marginal/average 19
 Linear Trend Model n Linear trend model: y(t) =a + b*t +e(t) Lab 4 20
Linear Trend Model n Linear trend model: y(t) =a + b*t +e(t) Lab 4 20
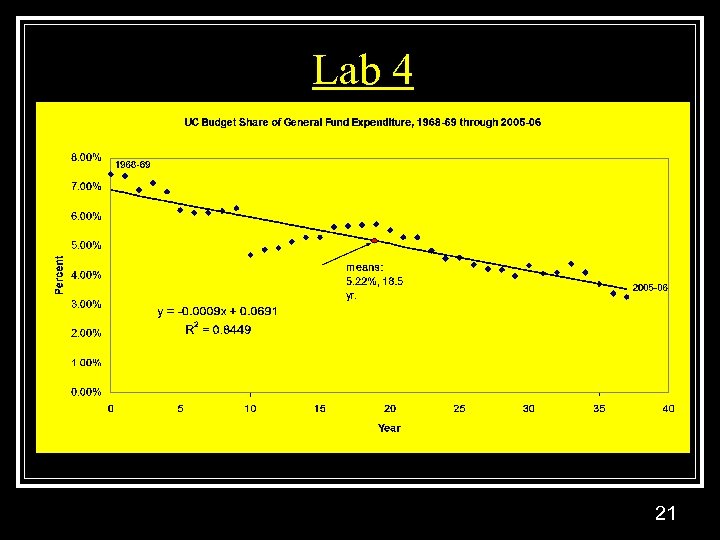 Lab 4 21
Lab 4 21
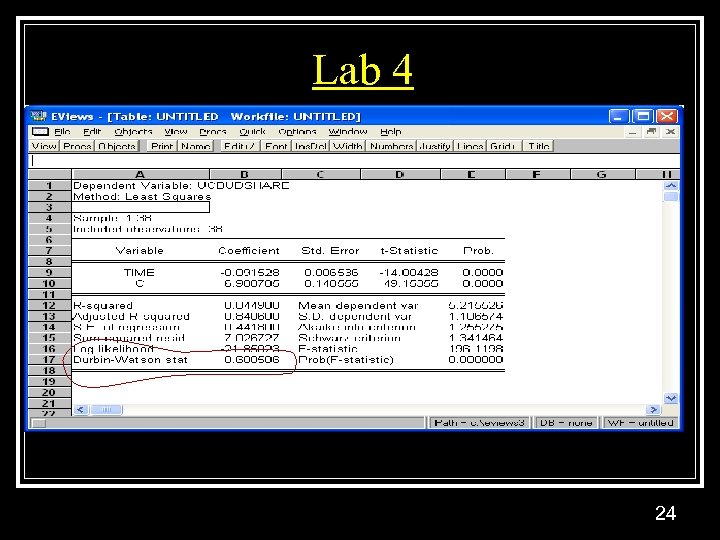
![Lab Four F-test: F 1, 36 = [R 2/1]/{[1 -R 2]/36} = 196 = Lab Four F-test: F 1, 36 = [R 2/1]/{[1 -R 2]/36} = 196 =](https://present5.com/presentation/579a02b0e1a2064564fcf215c5cf04db/image-22.jpg) Lab Four F-test: F 1, 36 = [R 2/1]/{[1 -R 2]/36} = 196 = Explained Mean Square/Unexplained mean square t-test: H 0: b=0 HA: b≠ 0 t =[ -0. 000915 – 0]/0. 0000653 = -14 22
Lab Four F-test: F 1, 36 = [R 2/1]/{[1 -R 2]/36} = 196 = Explained Mean Square/Unexplained mean square t-test: H 0: b=0 HA: b≠ 0 t =[ -0. 000915 – 0]/0. 0000653 = -14 22
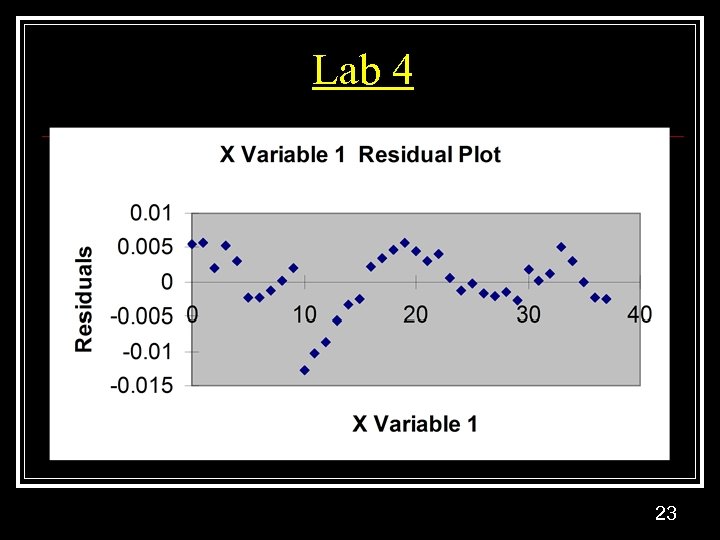 Lab 4 23
Lab 4 23
 Lab 4 24
Lab 4 24
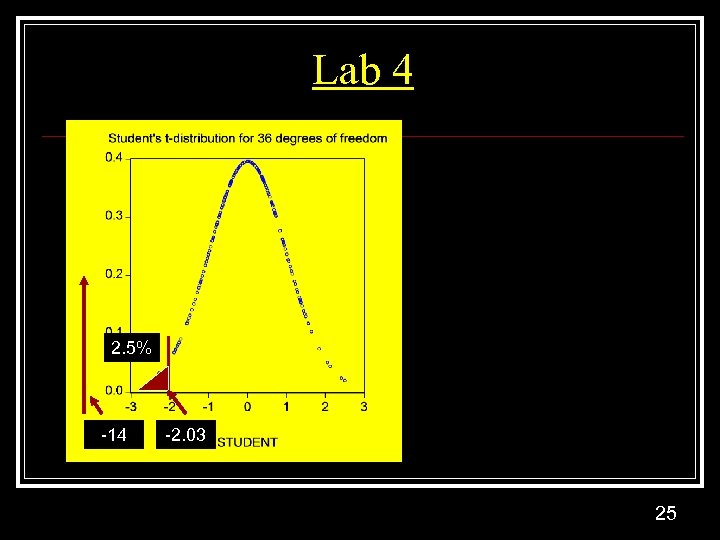 Lab 4 2. 5% -14 -2. 03 25
Lab 4 2. 5% -14 -2. 03 25
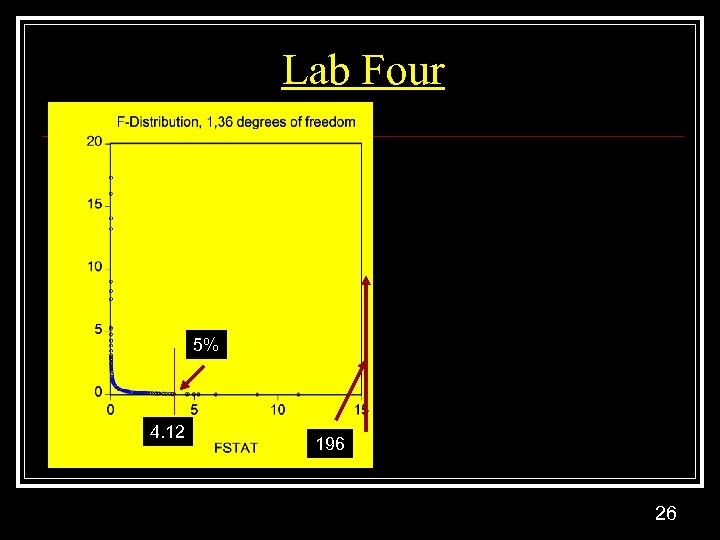 Lab Four 5% 4. 12 196 26
Lab Four 5% 4. 12 196 26
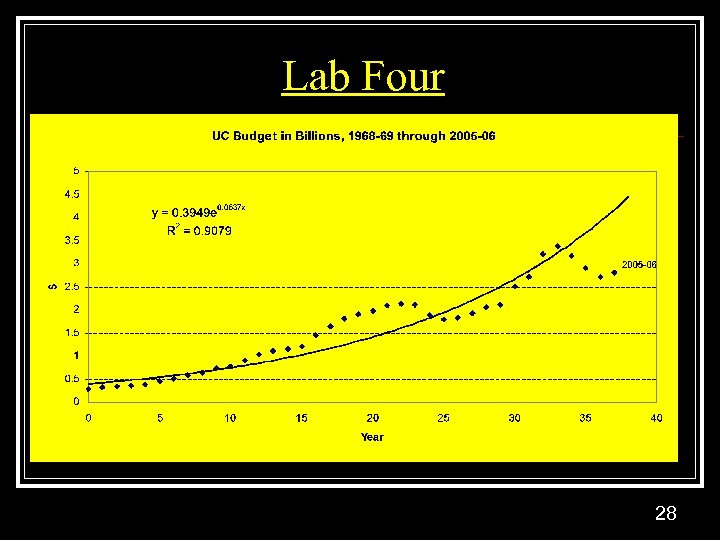
![Exponential Trend Model n Exponential trend model: y(t) =exp[a+b*t+e(t)] n n Natural logarithmic transformation Exponential Trend Model n Exponential trend model: y(t) =exp[a+b*t+e(t)] n n Natural logarithmic transformation](https://present5.com/presentation/579a02b0e1a2064564fcf215c5cf04db/image-27.jpg) Exponential Trend Model n Exponential trend model: y(t) =exp[a+b*t+e(t)] n n Natural logarithmic transformation ln Ln y(t) = a + b*t + e(t) Lab 4 27
Exponential Trend Model n Exponential trend model: y(t) =exp[a+b*t+e(t)] n n Natural logarithmic transformation ln Ln y(t) = a + b*t + e(t) Lab 4 27
 Lab Four 28
Lab Four 28
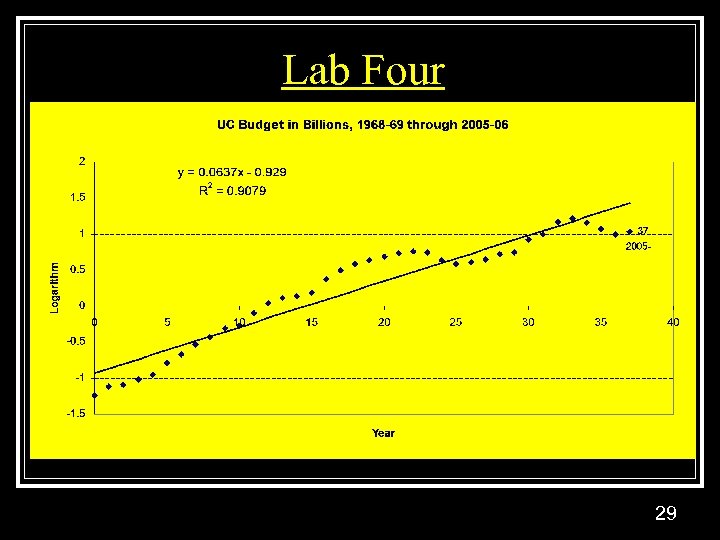 Lab Four 29
Lab Four 29
 Percentage Rates of Change, Elasticities n Percentage rates of change, elasticities n Cross-section n Ln assetsi =a + b*ln revenuei + ei Lab 5 § dln assets/dlnrevenue = b = [dassets/drevenue]/[assets/revenue] = marginal/average 30
Percentage Rates of Change, Elasticities n Percentage rates of change, elasticities n Cross-section n Ln assetsi =a + b*ln revenuei + ei Lab 5 § dln assets/dlnrevenue = b = [dassets/drevenue]/[assets/revenue] = marginal/average 30
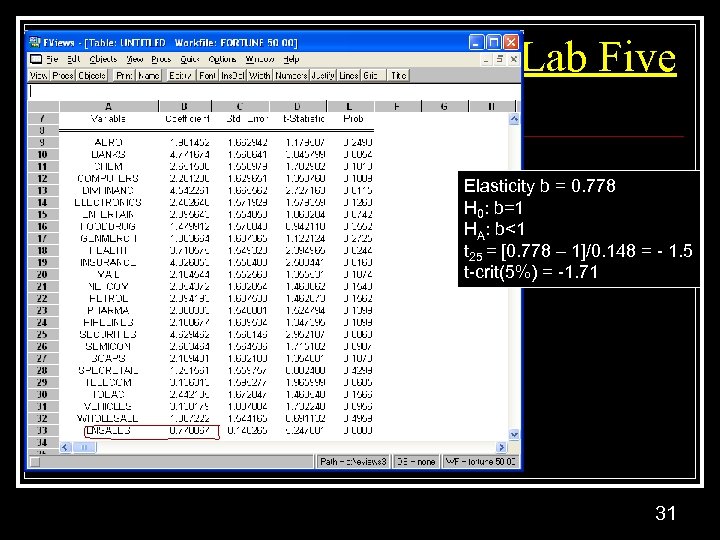 Lab Five Elasticity b = 0. 778 H 0: b=1 HA: b<1 t 25 = [0. 778 – 1]/0. 148 = - 1. 5 t-crit(5%) = -1. 71 31
Lab Five Elasticity b = 0. 778 H 0: b=1 HA: b<1 t 25 = [0. 778 – 1]/0. 148 = - 1. 5 t-crit(5%) = -1. 71 31
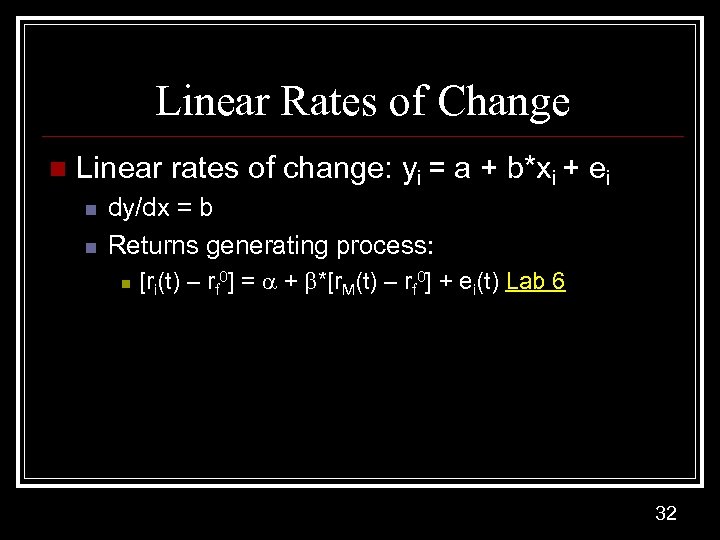 Linear Rates of Change n Linear rates of change: yi = a + b*xi + ei n n dy/dx = b Returns generating process: n [ri(t) – rf 0] = + *[r. M(t) – rf 0] + ei(t) Lab 6 32
Linear Rates of Change n Linear rates of change: yi = a + b*xi + ei n n dy/dx = b Returns generating process: n [ri(t) – rf 0] = + *[r. M(t) – rf 0] + ei(t) Lab 6 32
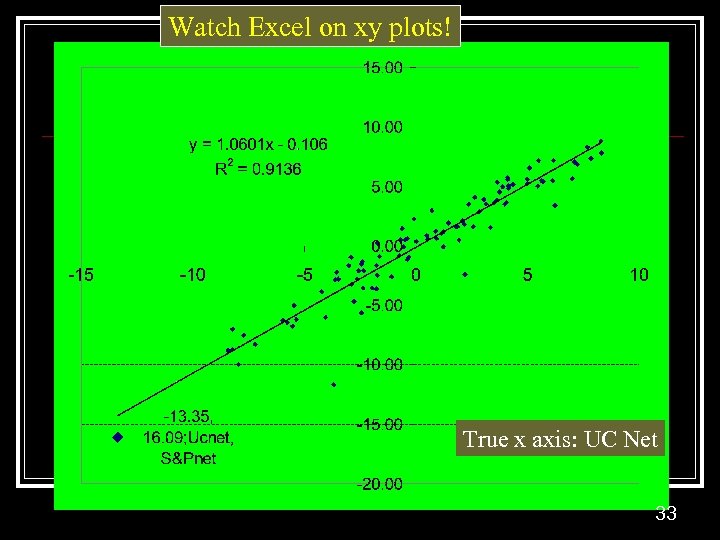 Watch Excel on xy plots! True x axis: UC Net 33
Watch Excel on xy plots! True x axis: UC Net 33
 Lab Six r. GE = a + b*r. SP 500 + e 34
Lab Six r. GE = a + b*r. SP 500 + e 34
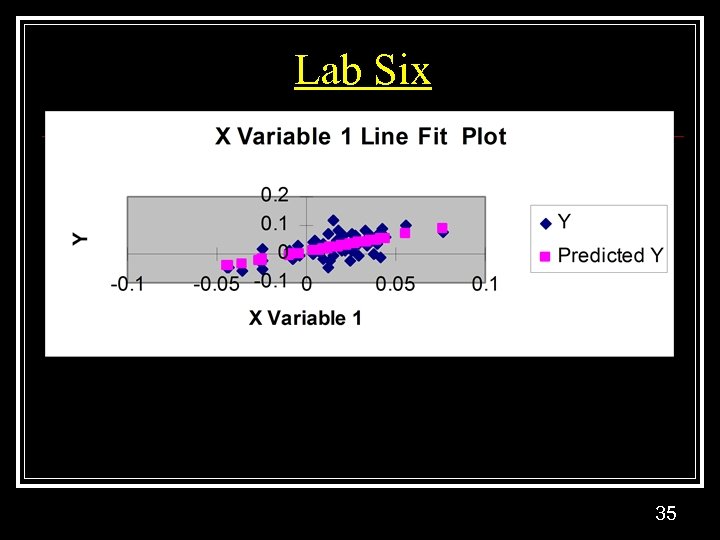 Lab Six 35
Lab Six 35
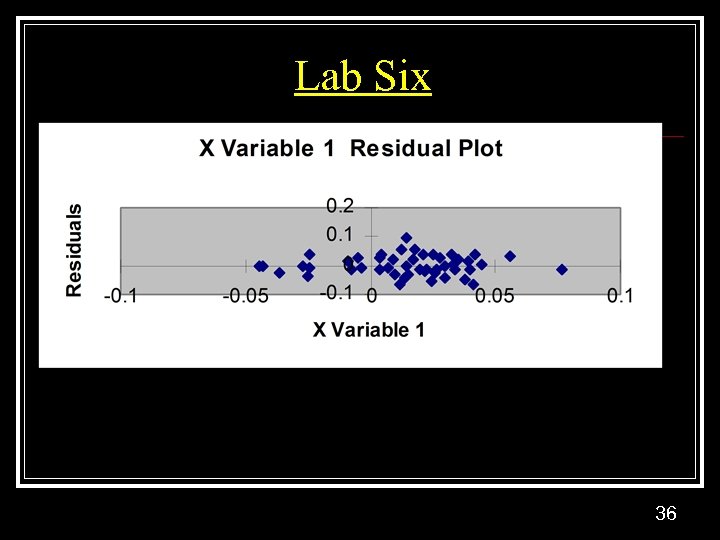 Lab Six 36
Lab Six 36
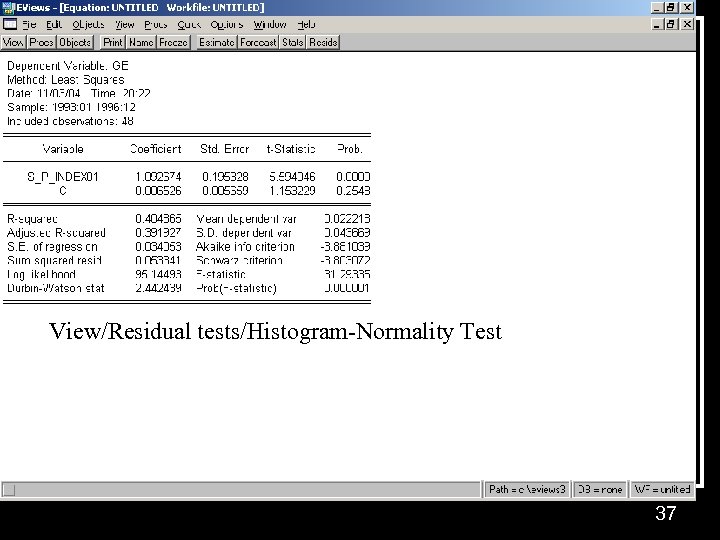 View/Residual tests/Histogram-Normality Test 37
View/Residual tests/Histogram-Normality Test 37
 Linear Multivariate Regression n House Price, # of bedrooms, house size, lot size n Pi = a + b*bedroomsi + c*house_sizei + d*lot_sizei + ei 38
Linear Multivariate Regression n House Price, # of bedrooms, house size, lot size n Pi = a + b*bedroomsi + c*house_sizei + d*lot_sizei + ei 38
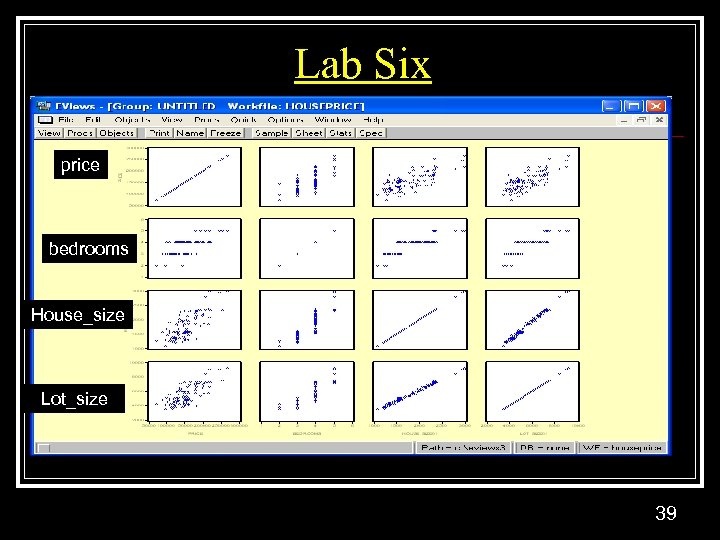 Lab Six price bedrooms House_size Lot_size 39
Lab Six price bedrooms House_size Lot_size 39
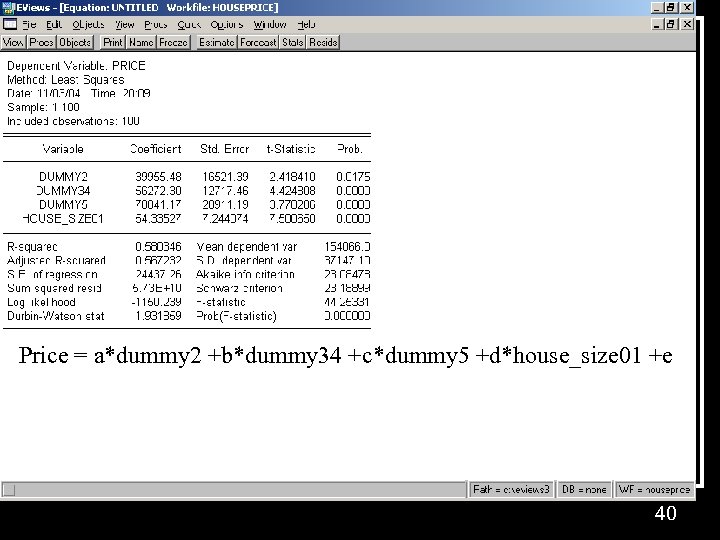 Price = a*dummy 2 +b*dummy 34 +c*dummy 5 +d*house_size 01 +e 40
Price = a*dummy 2 +b*dummy 34 +c*dummy 5 +d*house_size 01 +e 40
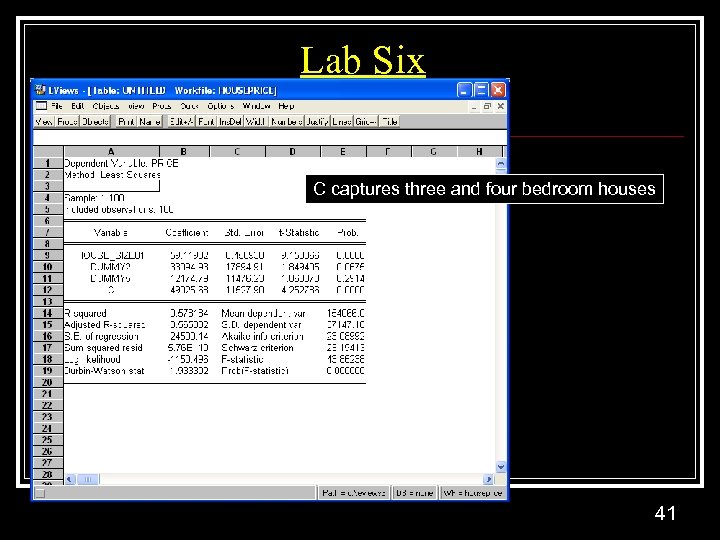 Lab Six C captures three and four bedroom houses 41
Lab Six C captures three and four bedroom houses 41
 Regression Models n How to handle zeros? n Labs Six and Seven: Lottery data-file n n Linear probability model: dependent variable: zero -one Logit: dependent variable: zero-one Probit: dependent variable: zero-one Tobit: dependent variable: lottery See Project I Power. Point application to vehicle type data 42
Regression Models n How to handle zeros? n Labs Six and Seven: Lottery data-file n n Linear probability model: dependent variable: zero -one Logit: dependent variable: zero-one Probit: dependent variable: zero-one Tobit: dependent variable: lottery See Project I Power. Point application to vehicle type data 42
 Regression Models n Failure time models n Exponential n n Survivor: S(t) = exp[- *t], ln S(t) = - *t Hazard rate, h(t) = Cumulative hazard function, H(t) = *t Weibull n n n Hazard rate, h(t) = f(t)/S(t) = ( / )(t/ ) -1 Cumulative hazard function: H(t) = (1/ ) t Logarithmic transform ln H(t) = ln (1/ ) + lnt 43
Regression Models n Failure time models n Exponential n n Survivor: S(t) = exp[- *t], ln S(t) = - *t Hazard rate, h(t) = Cumulative hazard function, H(t) = *t Weibull n n n Hazard rate, h(t) = f(t)/S(t) = ( / )(t/ ) -1 Cumulative hazard function: H(t) = (1/ ) t Logarithmic transform ln H(t) = ln (1/ ) + lnt 43


