0e9ba4ca9d834f56fb57e983b280c432.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13
 FIN 437 Vicentiu Covrig The Market for Foreign Exchange (chapter 4 Eun and Resnick)) 1
FIN 437 Vicentiu Covrig The Market for Foreign Exchange (chapter 4 Eun and Resnick)) 1
 FIN 437 Vicentiu Covrig FOREX Market Participants l. FX market involves participants buying and selling currencies all over the world l. It includes trading currencies spot and forward; bank deposits of foreign currencies; foreign trade financing; trading in currency options, futures and swaps l FOREX market is a global over-the-counter market l. Market participants include international banks, their customers, nonbank dealers, FOREX brokers, and central banks 2
FIN 437 Vicentiu Covrig FOREX Market Participants l. FX market involves participants buying and selling currencies all over the world l. It includes trading currencies spot and forward; bank deposits of foreign currencies; foreign trade financing; trading in currency options, futures and swaps l FOREX market is a global over-the-counter market l. Market participants include international banks, their customers, nonbank dealers, FOREX brokers, and central banks 2
 FIN 437 Vicentiu Covrig Size of the FX market Largest in the world (1995): $1. 2 trillion daily Market Centers (1995): London = $464 billion daily New York= $244 billion daily Tokyo = $161 billion daily Trading systems: - Screen based dealing using a phone or an e-mail type system - EBS: Electronic Brokerage System 3
FIN 437 Vicentiu Covrig Size of the FX market Largest in the world (1995): $1. 2 trillion daily Market Centers (1995): London = $464 billion daily New York= $244 billion daily Tokyo = $161 billion daily Trading systems: - Screen based dealing using a phone or an e-mail type system - EBS: Electronic Brokerage System 3
 FIN 437 Vicentiu Covrig The Bid-Ask Spread n n In general, banks do not charge commissions on foreign currency transactions. They profit from bid-ask spread The bid-ask spread is the difference between the bid and ask prices The bid price is the price a dealer is willing to pay you for something (our case foreign currency); always listed first The ask price is the amount the dealer wants you to pay for the thing (our case foreign currency); listed second 4
FIN 437 Vicentiu Covrig The Bid-Ask Spread n n In general, banks do not charge commissions on foreign currency transactions. They profit from bid-ask spread The bid-ask spread is the difference between the bid and ask prices The bid price is the price a dealer is willing to pay you for something (our case foreign currency); always listed first The ask price is the amount the dealer wants you to pay for the thing (our case foreign currency); listed second 4
 FIN 437 Vicentiu Covrig The Bid-Ask Spread Interbank dealer quotes: - American terms: Euro, British Pound, Australian Dollar - European terms: all others Ex: You want to transact with a dealer that gives you the following quotations: $1. 6625(bid) - 1. 6635(ask)/£. The dealer buys (gets) one pound from you for $1. 6625 The dealer sells (gives) one pound to you for $1. 6635 The bid-ask spread is a function of liquidity of the market, the XR volatility as well as dealers’ inventory The retail bid-ask spread is wider than interbank spread 5
FIN 437 Vicentiu Covrig The Bid-Ask Spread Interbank dealer quotes: - American terms: Euro, British Pound, Australian Dollar - European terms: all others Ex: You want to transact with a dealer that gives you the following quotations: $1. 6625(bid) - 1. 6635(ask)/£. The dealer buys (gets) one pound from you for $1. 6625 The dealer sells (gives) one pound to you for $1. 6635 The bid-ask spread is a function of liquidity of the market, the XR volatility as well as dealers’ inventory The retail bid-ask spread is wider than interbank spread 5
 FIN 437 Vicentiu Covrig FOREX Market Participants n The FOREX market is a two-tiered market: - Interbank Market (Wholesale) u. About 700 banks worldwide stand ready to make a market in Foreign exchange. u. Nonbank dealers account for about 20% of the market. u. There are FX brokers who match buy and sell orders but do not carry inventory and FX specialists. - Client Market (Retail) 6
FIN 437 Vicentiu Covrig FOREX Market Participants n The FOREX market is a two-tiered market: - Interbank Market (Wholesale) u. About 700 banks worldwide stand ready to make a market in Foreign exchange. u. Nonbank dealers account for about 20% of the market. u. There are FX brokers who match buy and sell orders but do not carry inventory and FX specialists. - Client Market (Retail) 6
 FIN 437 Vicentiu Covrig The Spot Market l. The spot market involves immediate purchase or sale of foreign exchange l. Direct quotation from US perspective nthe l U. S. dollar equivalent price of one unit of the foreign currency in US Dollars Indirect Quotation from US perspective nthe ne. g. l. The price of a U. S. dollar in the foreign currency “you get 100 yen to the dollar” direct quote is the reciprocal of the indirect quote 7
FIN 437 Vicentiu Covrig The Spot Market l. The spot market involves immediate purchase or sale of foreign exchange l. Direct quotation from US perspective nthe l U. S. dollar equivalent price of one unit of the foreign currency in US Dollars Indirect Quotation from US perspective nthe ne. g. l. The price of a U. S. dollar in the foreign currency “you get 100 yen to the dollar” direct quote is the reciprocal of the indirect quote 7
 FIN 437 Vicentiu Covrig Cross Rates The cross rate is the rate of exchange between two non-US currencies Suppose that S($/Euro) = 1. 25 and that S(Yen/$) = 110 Yen What must the Yen/Euro cross rate be? Yen/Euro= (Yen/$)x($/Euro) = 110 x 1. 25= 137. 5 n Suppose that S($/Euro) = 1. 25 and that S($/AUD) = 0. 5 What must the AUD/Euro cross rate be? 8
FIN 437 Vicentiu Covrig Cross Rates The cross rate is the rate of exchange between two non-US currencies Suppose that S($/Euro) = 1. 25 and that S(Yen/$) = 110 Yen What must the Yen/Euro cross rate be? Yen/Euro= (Yen/$)x($/Euro) = 110 x 1. 25= 137. 5 n Suppose that S($/Euro) = 1. 25 and that S($/AUD) = 0. 5 What must the AUD/Euro cross rate be? 8
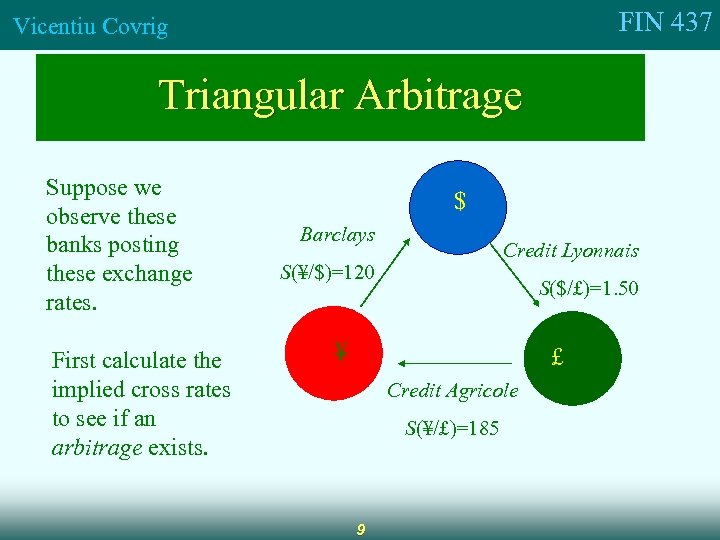 FIN 437 Vicentiu Covrig Triangular Arbitrage Suppose we observe these banks posting these exchange rates. First calculate the implied cross rates to see if an arbitrage exists. $ Barclays Credit Lyonnais S(¥/$)=120 S($/£)=1. 50 ¥ £ Credit Agricole S(¥/£)=185 9
FIN 437 Vicentiu Covrig Triangular Arbitrage Suppose we observe these banks posting these exchange rates. First calculate the implied cross rates to see if an arbitrage exists. $ Barclays Credit Lyonnais S(¥/$)=120 S($/£)=1. 50 ¥ £ Credit Agricole S(¥/£)=185 9
 FIN 437 Vicentiu Covrig Triangular Arbitrage When cross rates differ from one financial center to another, profit opportunities exist. Currency arbitrage involves buying a currency in one market while simultaneously selling it at a higher price in a second market The implied ¥/£ is 180. Credit Agricole has posted a quote of S(¥/£)=185 so there is an arbitrage opportunity. So, how can we make money here? Sell $150, 000 for £ at S($/£) = 1. 50 receive £ 100, 000 Sell our £ 100, 000 for ¥ at S(¥/£) = 185 receive ¥ 18, 500, 000 Sell ¥ 18, 500, 000 for $ at S(¥/$) = 120 receive $154, 167 profit per round trip = $ 154, 167 - $150, 000 = $4, 167 10
FIN 437 Vicentiu Covrig Triangular Arbitrage When cross rates differ from one financial center to another, profit opportunities exist. Currency arbitrage involves buying a currency in one market while simultaneously selling it at a higher price in a second market The implied ¥/£ is 180. Credit Agricole has posted a quote of S(¥/£)=185 so there is an arbitrage opportunity. So, how can we make money here? Sell $150, 000 for £ at S($/£) = 1. 50 receive £ 100, 000 Sell our £ 100, 000 for ¥ at S(¥/£) = 185 receive ¥ 18, 500, 000 Sell ¥ 18, 500, 000 for $ at S(¥/$) = 120 receive $154, 167 profit per round trip = $ 154, 167 - $150, 000 = $4, 167 10
 FIN 437 Vicentiu Covrig Triangular Arbitrage: exam type problem The Singapore dollar spot rate is 1. 7 SGD/$, the Swiss franc spot rate is 1. 35 SF/$ and the market cross-rate is 1. 15 SGD/SF. Calculate the implied cross-rate (SGD/SF). Calculate the triangular arbitrage profit that is possible if you start with $1 million. Show all your calculations. Cross rate: SGD/SF = (1. 7 SGD/$)/(1. 35 SF/$)= 1. 26 SGD/SF Arbitrage Direction: exchange (sell) SGD for SF Triangular arbitrage: Sell $1, 000 for SGD at S(SGD/$) = 1. 7 receive SGD 1, 700, 000 Sell our SGD 1, 700, 000 for SF at S(SGD/SF) = 1. 15 receive SF 1, 478, 261 Sell SF 1, 478, 261 for $ at S(SF/$) = 1. 35 receive $1, 095, 008 profit per round trip = $ 1, 095, 008 - $1, 000 = $95, 008 11
FIN 437 Vicentiu Covrig Triangular Arbitrage: exam type problem The Singapore dollar spot rate is 1. 7 SGD/$, the Swiss franc spot rate is 1. 35 SF/$ and the market cross-rate is 1. 15 SGD/SF. Calculate the implied cross-rate (SGD/SF). Calculate the triangular arbitrage profit that is possible if you start with $1 million. Show all your calculations. Cross rate: SGD/SF = (1. 7 SGD/$)/(1. 35 SF/$)= 1. 26 SGD/SF Arbitrage Direction: exchange (sell) SGD for SF Triangular arbitrage: Sell $1, 000 for SGD at S(SGD/$) = 1. 7 receive SGD 1, 700, 000 Sell our SGD 1, 700, 000 for SF at S(SGD/SF) = 1. 15 receive SF 1, 478, 261 Sell SF 1, 478, 261 for $ at S(SF/$) = 1. 35 receive $1, 095, 008 profit per round trip = $ 1, 095, 008 - $1, 000 = $95, 008 11
 FIN 437 Vicentiu Covrig The following sections in chapter 4 are not required for the exam: - Spot Foreign Exchange Microstructure - Swap transactions - Forward Market 12
FIN 437 Vicentiu Covrig The following sections in chapter 4 are not required for the exam: - Spot Foreign Exchange Microstructure - Swap transactions - Forward Market 12
 FIN 437 Vicentiu Covrig Learning outcomes • Know the structure of the FX market • Know the difference between wholesale (interbank) market and retail market • Who are the participants in the FX market? • Know how to read/use spot and forward quotes; direct and indirect method • Calculate currency cross-rates, without bid-ask quotes, when given two spot or forward FX quotations involving three currencies • Calculate the profit/loss on a triangular arbitrage opportunity given three currency quotations, without bid-ask spread • Recommended end-of-chapter questions: 2, 3, 4 • Recommended end-of-chapter problems: 1, 8 13
FIN 437 Vicentiu Covrig Learning outcomes • Know the structure of the FX market • Know the difference between wholesale (interbank) market and retail market • Who are the participants in the FX market? • Know how to read/use spot and forward quotes; direct and indirect method • Calculate currency cross-rates, without bid-ask quotes, when given two spot or forward FX quotations involving three currencies • Calculate the profit/loss on a triangular arbitrage opportunity given three currency quotations, without bid-ask spread • Recommended end-of-chapter questions: 2, 3, 4 • Recommended end-of-chapter problems: 1, 8 13


