11284e0017959c8f617f802bd9d5180f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 FIN 413 Corporate Financial Policy Clifford W. Smith, Jr. Spring 2007 Handout 6 * Covers readings on course outline through Smith/Wakeman (1984)
FIN 413 Corporate Financial Policy Clifford W. Smith, Jr. Spring 2007 Handout 6 * Covers readings on course outline through Smith/Wakeman (1984)
 Leasing v Just about any asset that can be purchased can also be leased. v Two parties to the contract – the lessee is the user of the asset – the lessor is the owner of the asset v The largest group of lessors are the original equipment manufacturers (e. g. IBM, Xerox) but there also many third party-leasing companies.
Leasing v Just about any asset that can be purchased can also be leased. v Two parties to the contract – the lessee is the user of the asset – the lessor is the owner of the asset v The largest group of lessors are the original equipment manufacturers (e. g. IBM, Xerox) but there also many third party-leasing companies.
 Types of Leases v Operating Lease (maintenance or service lease) – – short-term (less than 5 years) not fully amortized lessor supplies maintenance or service often cancelable v Financial Lease (capital lease) – long-term and fully amortized – lessee supplies service and maintenance – usually not cancelable
Types of Leases v Operating Lease (maintenance or service lease) – – short-term (less than 5 years) not fully amortized lessor supplies maintenance or service often cancelable v Financial Lease (capital lease) – long-term and fully amortized – lessee supplies service and maintenance – usually not cancelable
 Leasing v Modigliani/Miller theorem implies that with no taxes, no contracting costs, and a fixed investment policy, leasing policy does not affect firm value.
Leasing v Modigliani/Miller theorem implies that with no taxes, no contracting costs, and a fixed investment policy, leasing policy does not affect firm value.
 Traditional Approaches to Leasing v Leases contain options – option to cancel or extend – option to purchase v We can price these options with Black/Scholes model, but B/S requires M/M assumptions. v This approach cannot tell you why a lease is cancelable because all important effects of leasing are assumed away.
Traditional Approaches to Leasing v Leases contain options – option to cancel or extend – option to purchase v We can price these options with Black/Scholes model, but B/S requires M/M assumptions. v This approach cannot tell you why a lease is cancelable because all important effects of leasing are assumed away.
 Traditional Approaches to Leasing v Leasing affects tax liability. – Differential tax rates – ITCs: Pan AM – Double-dip leasing v Taxes are very important to understand leasing behavior, but the analysis here is frequently a mechanical application of tax rules in the capital budgeting decision.
Traditional Approaches to Leasing v Leasing affects tax liability. – Differential tax rates – ITCs: Pan AM – Double-dip leasing v Taxes are very important to understand leasing behavior, but the analysis here is frequently a mechanical application of tax rules in the capital budgeting decision.
 Avoiding Constructive Sale Rules v Term must be less than 30 years. v Lessee should not have option to buy for less than fair market value. v No early balloon payments. v Lessor must make fair market return absent tax benefits. v Lessor should not limit lessee's ability to pay dividends or issue debt. v Renewal option must reflect fair market value.
Avoiding Constructive Sale Rules v Term must be less than 30 years. v Lessee should not have option to buy for less than fair market value. v No early balloon payments. v Lessor must make fair market return absent tax benefits. v Lessor should not limit lessee's ability to pay dividends or issue debt. v Renewal option must reflect fair market value.
 Questions to be Answered About Leasing v Asset characteristics v Lessee characteristics v Lessor characteristics v Typical contract provisions
Questions to be Answered About Leasing v Asset characteristics v Lessee characteristics v Lessor characteristics v Typical contract provisions
 What Type of Assets are Most Commonly Leased?
What Type of Assets are Most Commonly Leased?
 Asset Characteristics v Period of use in relation to useful life. v Sensitivity to use and maintenance decisions – Owners internalize the costs of these decisions. Since a lessee does not have a claim on the residual value of the asset, he has incentives to abuse or under maintain the asset. – Adverse selection in leasing decisions
Asset Characteristics v Period of use in relation to useful life. v Sensitivity to use and maintenance decisions – Owners internalize the costs of these decisions. Since a lessee does not have a claim on the residual value of the asset, he has incentives to abuse or under maintain the asset. – Adverse selection in leasing decisions
 Controlling Asset Abuse v Penalty clause (security deposit) v Option to buy v Third party monitoring of maintenance v Service lease v Metering
Controlling Asset Abuse v Penalty clause (security deposit) v Option to buy v Third party monitoring of maintenance v Service lease v Metering
 Asset Characteristics v Firm specific assets – Production facilities vs. office space – Transportation and construction equipment vs. autobody stamping dies
Asset Characteristics v Firm specific assets – Production facilities vs. office space – Transportation and construction equipment vs. autobody stamping dies
 Leasing and Firm Specific Assets v Suppose GM wants to build an R&D facility. A group of doctors come to GM and say, "We have high tax rates, and you don't. Let us buy the building and lease it to you. " Time 0 10 years 20 years Value to GM 20 10 0 Opportunity Cost 18 9 0
Leasing and Firm Specific Assets v Suppose GM wants to build an R&D facility. A group of doctors come to GM and say, "We have high tax rates, and you don't. Let us buy the building and lease it to you. " Time 0 10 years 20 years Value to GM 20 10 0 Opportunity Cost 18 9 0
 Leasing and Firm Specific Assets v Klein, Crawford and Alchian ("Vertical integration, appropriable rents, and the competitive contracting process") discuss cases where ownership rights are important (i. e. leasing would be expensive). v The Fisher autobody case. v How can you solve the GM problem? – Don't lease – Include option to renew or option to extend lease in the lease contract
Leasing and Firm Specific Assets v Klein, Crawford and Alchian ("Vertical integration, appropriable rents, and the competitive contracting process") discuss cases where ownership rights are important (i. e. leasing would be expensive). v The Fisher autobody case. v How can you solve the GM problem? – Don't lease – Include option to renew or option to extend lease in the lease contract
 Lessee Characteristics v Tax incentives to lease v Capital structure issues – Leases are senior claims and can create claim dilution. Limited in bond contracts. Amortizing lease payments helps bondholders monitor outstanding senior claims. – Leases have characteristics similar to secured debt. Can reduce underinvestment problem. – Long-term noncancelable leases commit the firm to use the asset over the life of the lease. Can reduce asset substitution problem.
Lessee Characteristics v Tax incentives to lease v Capital structure issues – Leases are senior claims and can create claim dilution. Limited in bond contracts. Amortizing lease payments helps bondholders monitor outstanding senior claims. – Leases have characteristics similar to secured debt. Can reduce underinvestment problem. – Long-term noncancelable leases commit the firm to use the asset over the life of the lease. Can reduce asset substitution problem.
 Lessee Characteristics v Compensation-related issues – Leasing can affect return on invested capital and payments to bonus pool – If lease is fully amortized, this problem is reduced – Specialization in risk bearing
Lessee Characteristics v Compensation-related issues – Leasing can affect return on invested capital and payments to bonus pool – If lease is fully amortized, this problem is reduced – Specialization in risk bearing
 Lessor Characteristics v Tax incentives to lease v Leasing and market power
Lessor Characteristics v Tax incentives to lease v Leasing and market power
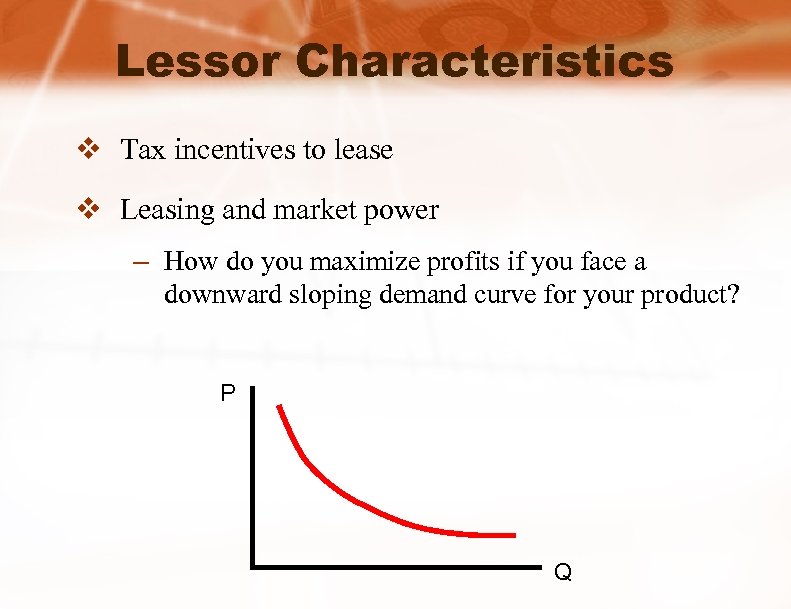 Lessor Characteristics v Tax incentives to lease v Leasing and market power – How do you maximize profits if you face a downward sloping demand curve for your product? P Q
Lessor Characteristics v Tax incentives to lease v Leasing and market power – How do you maximize profits if you face a downward sloping demand curve for your product? P Q
 Leasing and Market Power v First-degree price discrimination is not legal under US antitrust laws (Robinson/Patman Act) v Often the more inelastic demanders use asset more intensively than the elastic demanders. – One solution: Tie-in sales - IBM sold early computers and required that all purchasers use only IBM punch cards. – Tie-in sales are now also in violation of antitrust laws.
Leasing and Market Power v First-degree price discrimination is not legal under US antitrust laws (Robinson/Patman Act) v Often the more inelastic demanders use asset more intensively than the elastic demanders. – One solution: Tie-in sales - IBM sold early computers and required that all purchasers use only IBM punch cards. – Tie-in sales are now also in violation of antitrust laws.
 Leasing and Market Power v An alternative solution: Lease and charge metering fee. – Metering fees have passed the antitrust test because there is an economic justification for them in addition to price discrimination (i. e. curbing the asset abuse problem). v For some time, Xerox and IBM only leased their products, they did not sell them. Why? v Does this mean that a producer would never want to both lease and sell its product?
Leasing and Market Power v An alternative solution: Lease and charge metering fee. – Metering fees have passed the antitrust test because there is an economic justification for them in addition to price discrimination (i. e. curbing the asset abuse problem). v For some time, Xerox and IBM only leased their products, they did not sell them. Why? v Does this mean that a producer would never want to both lease and sell its product?
 Lessor Characteristics v Comparative advantage in disposing of asset – At one time, Kodak handled all short-term cancelable leases (rentals) in house but Citibank handled most long-term noncancelable leases. v Bonding quality by manufacturer – Lease with option to cancel
Lessor Characteristics v Comparative advantage in disposing of asset – At one time, Kodak handled all short-term cancelable leases (rentals) in house but Citibank handled most long-term noncancelable leases. v Bonding quality by manufacturer – Lease with option to cancel
 Contract Provisions v Deposits and penalty clauses v Option to buy asset or extend lease v Restrictions on subleasing v Service vs. net lease v Capital vs. operating lease v Metering v Bonding of maintenance by third parties
Contract Provisions v Deposits and penalty clauses v Option to buy asset or extend lease v Restrictions on subleasing v Service vs. net lease v Capital vs. operating lease v Metering v Bonding of maintenance by third parties
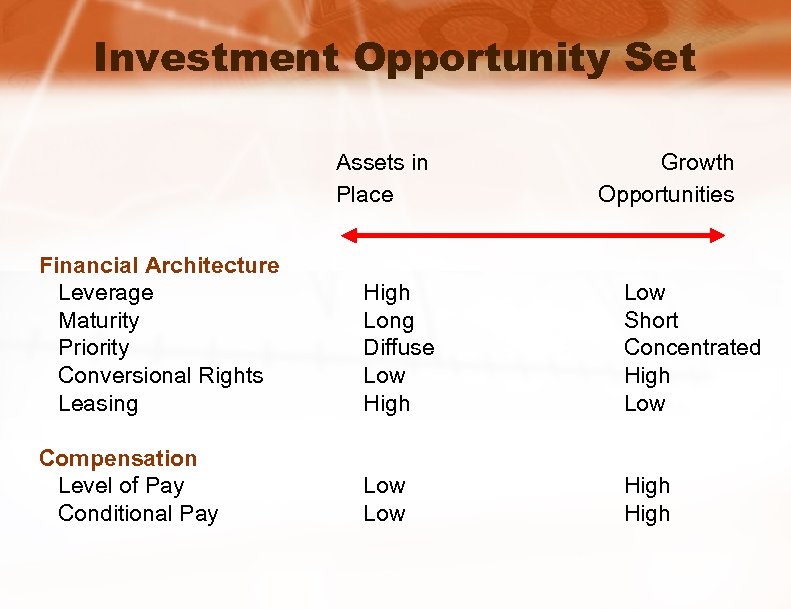 Investment Opportunity Set Assets in Place Growth Opportunities Financial Architecture Leverage Maturity Priority Conversional Rights Leasing High Long Diffuse Low High Low Short Concentrated High Low Compensation Level of Pay Conditional Pay Low High
Investment Opportunity Set Assets in Place Growth Opportunities Financial Architecture Leverage Maturity Priority Conversional Rights Leasing High Long Diffuse Low High Low Short Concentrated High Low Compensation Level of Pay Conditional Pay Low High
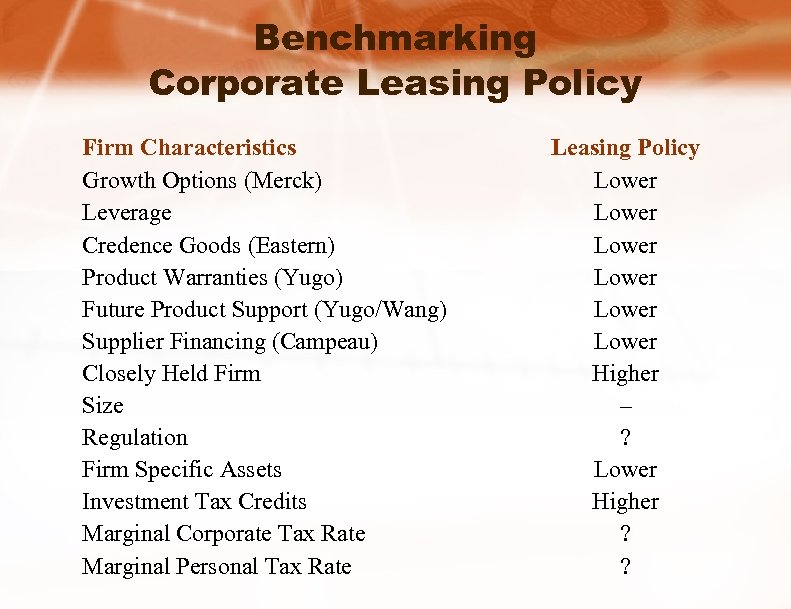 Benchmarking Corporate Leasing Policy Firm Characteristics Growth Options (Merck) Leverage Credence Goods (Eastern) Product Warranties (Yugo) Future Product Support (Yugo/Wang) Supplier Financing (Campeau) Closely Held Firm Size Regulation Firm Specific Assets Investment Tax Credits Marginal Corporate Tax Rate Marginal Personal Tax Rate Leasing Policy Lower Lower Higher – ? Lower Higher ? ?
Benchmarking Corporate Leasing Policy Firm Characteristics Growth Options (Merck) Leverage Credence Goods (Eastern) Product Warranties (Yugo) Future Product Support (Yugo/Wang) Supplier Financing (Campeau) Closely Held Firm Size Regulation Firm Specific Assets Investment Tax Credits Marginal Corporate Tax Rate Marginal Personal Tax Rate Leasing Policy Lower Lower Higher – ? Lower Higher ? ?


