2354cd5a92fa70265fbed55b76fb5639.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Files Management Fe Angela M. Verzosa 1
Files Management Fe Angela M. Verzosa 1
 Files management ensures control at the file level • Files management ensures that records relating to a specific activity or subject are securely maintained together in one file. • This enables effective decision making and also ensures that the sequence of actions can be reconstructed, that is what happened, when, who did it, why. Fe Angela M. Verzosa 2
Files management ensures control at the file level • Files management ensures that records relating to a specific activity or subject are securely maintained together in one file. • This enables effective decision making and also ensures that the sequence of actions can be reconstructed, that is what happened, when, who did it, why. Fe Angela M. Verzosa 2
 Files management Filing involves *Arranging records according to a simple, logical system * Placing records in a storage container in correct sequence *Retrieving the records so that they can be used Fe Angela M. Verzosa 3
Files management Filing involves *Arranging records according to a simple, logical system * Placing records in a storage container in correct sequence *Retrieving the records so that they can be used Fe Angela M. Verzosa 3
 good filing systems… • contain complete and comprehensive files thereby enabling effective decision making • provide integrity and continuity regardless of changes in personnel • facilitate protection and preservation of records • provide low cost and efficient maintenance of records • reduce the possibility of misfiling and reduce duplication • mean less time spent searching for files and documents Fe Angela M. Verzosa 4
good filing systems… • contain complete and comprehensive files thereby enabling effective decision making • provide integrity and continuity regardless of changes in personnel • facilitate protection and preservation of records • provide low cost and efficient maintenance of records • reduce the possibility of misfiling and reduce duplication • mean less time spent searching for files and documents Fe Angela M. Verzosa 4
 Files management Filing systems Filing Rules Files Equipment Computer Applications Fe Angela M. Verzosa 5
Files management Filing systems Filing Rules Files Equipment Computer Applications Fe Angela M. Verzosa 5
 Filing systems • provide only the mechanical structure for arranging records. • inadequacies of filing stem from human failing, not system failure. • most suitable system should be applied to a particular type of record, uniformly. Fe Angela M. Verzosa 6
Filing systems • provide only the mechanical structure for arranging records. • inadequacies of filing stem from human failing, not system failure. • most suitable system should be applied to a particular type of record, uniformly. Fe Angela M. Verzosa 6
 CRITERIA of a good filing system… • Simplicity • Flexibility / Expansibility • Adaptability Fe Angela M. Verzosa 7
CRITERIA of a good filing system… • Simplicity • Flexibility / Expansibility • Adaptability Fe Angela M. Verzosa 7
 Filing methods • numerical • alphabetic • functional • geographic • form • chronologic Fe Angela M. Verzosa 8
Filing methods • numerical • alphabetic • functional • geographic • form • chronologic Fe Angela M. Verzosa 8
 Numerical System • File units are placed in numerical sequence • Originated from the registry system, used particularly in accessioning correspondences. • Unsuited to handling name files. • Ideally useful for case files (file units containing all documents pertaining to a particular transaction, usually developed in legal or business records. Fe Angela M. Verzosa 9
Numerical System • File units are placed in numerical sequence • Originated from the registry system, used particularly in accessioning correspondences. • Unsuited to handling name files. • Ideally useful for case files (file units containing all documents pertaining to a particular transaction, usually developed in legal or business records. Fe Angela M. Verzosa 9
 Alphabetic System • File units are placed in alphabetical sequence. • First used to arrange records relating to persons, then gradually to records relating to subjects. • The system may be modified to group records related by a common subject by: *standardizing subject headings *subdividing the main subject headings • Other alphabetical filing systems are: *Alpha-numeric - uses letters to designate main subject headings and numerals for subordinate headings *Mnemonic - uses alphabetical symbols to denote subordinate headings. Fe Angela M. Verzosa 10
Alphabetic System • File units are placed in alphabetical sequence. • First used to arrange records relating to persons, then gradually to records relating to subjects. • The system may be modified to group records related by a common subject by: *standardizing subject headings *subdividing the main subject headings • Other alphabetical filing systems are: *Alpha-numeric - uses letters to designate main subject headings and numerals for subordinate headings *Mnemonic - uses alphabetical symbols to denote subordinate headings. Fe Angela M. Verzosa 10
 Functional Filing System • Records are the result of functions and are used in relation to them • Records should then be grouped and maintained according to the functions to which they relate. • The functional categories will reflect the organization’s purpose, mission, programs, projects and activities. • Every office or department within an organization has a function and these functions are generally carried out through a series of major programs. • These major programs are often divided into subprograms until one gets to the individual project level. Fe Angela M. Verzosa 11
Functional Filing System • Records are the result of functions and are used in relation to them • Records should then be grouped and maintained according to the functions to which they relate. • The functional categories will reflect the organization’s purpose, mission, programs, projects and activities. • Every office or department within an organization has a function and these functions are generally carried out through a series of major programs. • These major programs are often divided into subprograms until one gets to the individual project level. Fe Angela M. Verzosa 11
 Other Filing Systems • Geographic Filing: files records by location or place first, followed by the name or subject. • Forms : groups records according to their format or type (e. g. minutes, reports, invoices, receipts) • Subject Filing: places records under subject classification. • Chronologic Filing: files records by year, month, and date Angela M. Verzosa Fe 12
Other Filing Systems • Geographic Filing: files records by location or place first, followed by the name or subject. • Forms : groups records according to their format or type (e. g. minutes, reports, invoices, receipts) • Subject Filing: places records under subject classification. • Chronologic Filing: files records by year, month, and date Angela M. Verzosa Fe 12
 University/college classification system Filing *Institutional records *administrative records *academic dept records *faculty records *student/alumni records *school publications *theses and dissertations *memorabilia Fe Angela M. Verzosa 13
University/college classification system Filing *Institutional records *administrative records *academic dept records *faculty records *student/alumni records *school publications *theses and dissertations *memorabilia Fe Angela M. Verzosa 13
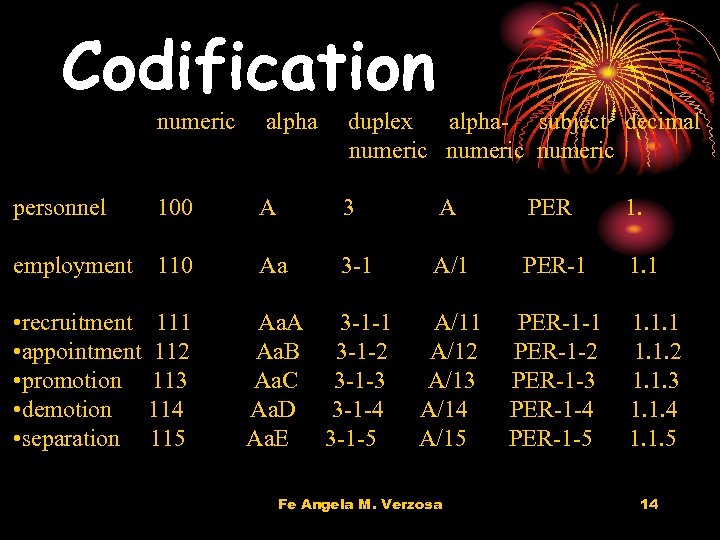 Codification numeric alpha duplex alpha- subject decimal numeric personnel 100 A 3 A PER 1. employment 110 Aa 3 -1 A/1 PER-1 1. 1 A/12 A/13 A/14 A/15 PER-1 -1 PER-1 -2 PER-1 -3 PER-1 -4 PER-1 -5 • recruitment 111 • appointment 112 • promotion 113 • demotion 114 • separation 115 Aa. A 3 -1 -1 Aa. B 3 -1 -2 Aa. C 3 -1 -3 Aa. D 3 -1 -4 Aa. E 3 -1 -5 Fe Angela M. Verzosa 1. 1. 1. 2 1. 1. 3 1. 1. 4 1. 1. 5 14
Codification numeric alpha duplex alpha- subject decimal numeric personnel 100 A 3 A PER 1. employment 110 Aa 3 -1 A/1 PER-1 1. 1 A/12 A/13 A/14 A/15 PER-1 -1 PER-1 -2 PER-1 -3 PER-1 -4 PER-1 -5 • recruitment 111 • appointment 112 • promotion 113 • demotion 114 • separation 115 Aa. A 3 -1 -1 Aa. B 3 -1 -2 Aa. C 3 -1 -3 Aa. D 3 -1 -4 Aa. E 3 -1 -5 Fe Angela M. Verzosa 1. 1. 1. 2 1. 1. 3 1. 1. 4 1. 1. 5 14
 Procedures in Filing • indexing by card or register • coding by writing symbols or captions, or highlighting indexed name or subject • sorting by tray, pigeon-hole, or multi-sorter • filing Fe Angela M. Verzosa 15
Procedures in Filing • indexing by card or register • coding by writing symbols or captions, or highlighting indexed name or subject • sorting by tray, pigeon-hole, or multi-sorter • filing Fe Angela M. Verzosa 15
 Common filing problems • too many filing places • everybody a file clerk • files disorderly; show no particular plan or arrangement • system does not fit the way material is called for • some records seem to belong under more than one category • filing decisions erratic or inconsistent • bulging folders • accumulation of unnecessary or personal records Fe Angela M. Verzosa 16
Common filing problems • too many filing places • everybody a file clerk • files disorderly; show no particular plan or arrangement • system does not fit the way material is called for • some records seem to belong under more than one category • filing decisions erratic or inconsistent • bulging folders • accumulation of unnecessary or personal records Fe Angela M. Verzosa 16
 Common filing problems • related records are filed under different categories • the retrieval rate is poor (inability to locate the required document quickly) • missing and misplaced documents mean too much time spent looking for files • a high level of duplication exists • users are setting up personal records systems • incomplete files and backlogs of unfiled records exist • filing cabinets are jammed with files bulging with documents Fe Angela M. Verzosa 17
Common filing problems • related records are filed under different categories • the retrieval rate is poor (inability to locate the required document quickly) • missing and misplaced documents mean too much time spent looking for files • a high level of duplication exists • users are setting up personal records systems • incomplete files and backlogs of unfiled records exist • filing cabinets are jammed with files bulging with documents Fe Angela M. Verzosa 17
 Improve your filing… • Begin each calendar year with a new set of files • Files should not exceed ½ thickness • Dedicate time each week for filing to prevent backlog • Avoid filing extraneous unnecessary duplicate copies • Avoid tightly jammed files • Safeguard access and confidentiality of records Fe Angela M. Verzosa 18
Improve your filing… • Begin each calendar year with a new set of files • Files should not exceed ½ thickness • Dedicate time each week for filing to prevent backlog • Avoid filing extraneous unnecessary duplicate copies • Avoid tightly jammed files • Safeguard access and confidentiality of records Fe Angela M. Verzosa 18
 When to create new files… • a new function, subject, activity or project is commenced or • an existing subject, activity or project is further developed and needs to be split across several files • an existing file becomes too large and a new part is required • no existing file is appropriate for the document(s) Fe Angela M. Verzosa 19
When to create new files… • a new function, subject, activity or project is commenced or • an existing subject, activity or project is further developed and needs to be split across several files • an existing file becomes too large and a new part is required • no existing file is appropriate for the document(s) Fe Angela M. Verzosa 19
 Files Equipment • made of steel • compact and space-efficient • allowance for easy extraction & replacement of files • mobile • proximity to authorized personnel Fe Angela M. Verzosa 20
Files Equipment • made of steel • compact and space-efficient • allowance for easy extraction & replacement of files • mobile • proximity to authorized personnel Fe Angela M. Verzosa 20
 Training Personnel • receiving and opening mails • placing mail/other papers in correct files • extracting and replacing files • opening/creating new files • indexing & cross-referencing • keeping a record of file movements • retrieving lost/missing files • destroying/disposing files • retiring non-current files Fe Angela M. Verzosa 21
Training Personnel • receiving and opening mails • placing mail/other papers in correct files • extracting and replacing files • opening/creating new files • indexing & cross-referencing • keeping a record of file movements • retrieving lost/missing files • destroying/disposing files • retiring non-current files Fe Angela M. Verzosa 21
 Questions? Contact verzosaf@dlsu. edu. ph Fe Angela M. Verzosa 22
Questions? Contact verzosaf@dlsu. edu. ph Fe Angela M. Verzosa 22


