9c2d243c17f4c7af5ea96c912fee0d30.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 File Management Chris A. Mattmann OODT Component Working Group
File Management Chris A. Mattmann OODT Component Working Group
 What is File Management? • Managing the locations and ancillary information about files, and collections of files – Ancillary information is metadata • What’s a product? – A collection of some set of files, and/or collections of files • So, you could have collections of other collections – Along with metadata about the product FILE-MGMT 2
What is File Management? • Managing the locations and ancillary information about files, and collections of files – Ancillary information is metadata • What’s a product? – A collection of some set of files, and/or collections of files • So, you could have collections of other collections – Along with metadata about the product FILE-MGMT 2
 The state of things • The existing CAS system does file management – For past missions and projects, it’s done the job well • CAS implementation – Needs an update, and overall refactoring to allow for modularity and separation of concerns, and general technology and architectural updates • In particular, a couple of new requirements and drivers for projects – Suggested some ways to extend and improve the CAS to satisfy the new requirements and drivers • What are these new requirements and drivers? FILE-MGMT 3
The state of things • The existing CAS system does file management – For past missions and projects, it’s done the job well • CAS implementation – Needs an update, and overall refactoring to allow for modularity and separation of concerns, and general technology and architectural updates • In particular, a couple of new requirements and drivers for projects – Suggested some ways to extend and improve the CAS to satisfy the new requirements and drivers • What are these new requirements and drivers? FILE-MGMT 3
 New Requirements and Drivers • Persisting archived files using dynamic metadata and flexible, adaptable policies based on product types – rather than the monolithic and inflexible existing method of Product. Type. Repository/Product. Name/Product. Version/ as the filesystem location to store products for all product types. • Clearly separating out the Workflow aspects of the File Manager, from Product ingestion, and flexibly supporting association of Workflows and their subsequent Tasks with any event, not only ingestion. FILE-MGMT 4
New Requirements and Drivers • Persisting archived files using dynamic metadata and flexible, adaptable policies based on product types – rather than the monolithic and inflexible existing method of Product. Type. Repository/Product. Name/Product. Version/ as the filesystem location to store products for all product types. • Clearly separating out the Workflow aspects of the File Manager, from Product ingestion, and flexibly supporting association of Workflows and their subsequent Tasks with any event, not only ingestion. FILE-MGMT 4
 New Requirements and Drivers • Leverage existing transactional models such as Java's Transaction API to support transactional management rather than building our own API. • If we do use any database communication, then making sure that all DB communication is dealt with using standard, available, existing db pooling APIs such as commonsdbcp , available from Apache. FILE-MGMT 5
New Requirements and Drivers • Leverage existing transactional models such as Java's Transaction API to support transactional management rather than building our own API. • If we do use any database communication, then making sure that all DB communication is dealt with using standard, available, existing db pooling APIs such as commonsdbcp , available from Apache. FILE-MGMT 5
 New Requirements and Drivers • Clearly separating out the administrative portions of policy management from the existing webapp, and distinguishing what pieces of the webapp are usercentric, and what are administrative-centric. • Supporting heirarchical product structures, such as nested directories that contain many sub-directories, and sub-directories of those sub-directories, with files strewn about at all levels – rather than only supporting the existing method of flat product structures, where all files in a product are at the same tree level. FILE-MGMT 6
New Requirements and Drivers • Clearly separating out the administrative portions of policy management from the existing webapp, and distinguishing what pieces of the webapp are usercentric, and what are administrative-centric. • Supporting heirarchical product structures, such as nested directories that contain many sub-directories, and sub-directories of those sub-directories, with files strewn about at all levels – rather than only supporting the existing method of flat product structures, where all files in a product are at the same tree level. FILE-MGMT 6
 New Requirements and Drivers • Support metadata extraction based on product type or mime-type • Support dynamic product types. The file management component should not need to know about every product type a priori FILE-MGMT 7
New Requirements and Drivers • Support metadata extraction based on product type or mime-type • Support dynamic product types. The file management component should not need to know about every product type a priori FILE-MGMT 7
 New Requirements and Drivers • You can read/add to the list – Available at: http: //oodt. jpl. nasa. gov/wiki/display/oodt/Fil e+Management • Please, speak your mind! FILE-MGMT 8
New Requirements and Drivers • You can read/add to the list – Available at: http: //oodt. jpl. nasa. gov/wiki/display/oodt/Fil e+Management • Please, speak your mind! FILE-MGMT 8
 File Management: Architectural implications • Managing files – Data Store: follow the typical repository pattern – Manage information about Products, Product Types, and References to products • Managing metadata – Metadata Store: follow the typical registry pattern – Manage product Metadata • Key/Value pairs • Separate out the data store and metadata store – This allows data and metadata to be managed independently FILE-MGMT 9
File Management: Architectural implications • Managing files – Data Store: follow the typical repository pattern – Manage information about Products, Product Types, and References to products • Managing metadata – Metadata Store: follow the typical registry pattern – Manage product Metadata • Key/Value pairs • Separate out the data store and metadata store – This allows data and metadata to be managed independently FILE-MGMT 9
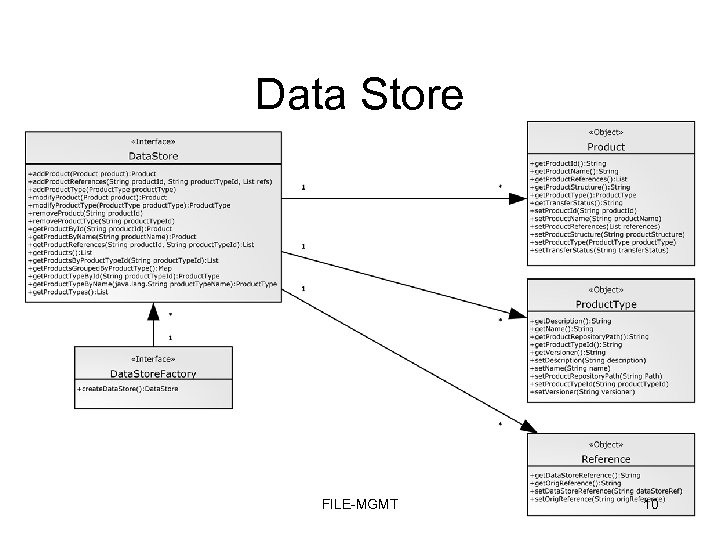 Data Store FILE-MGMT 10
Data Store FILE-MGMT 10
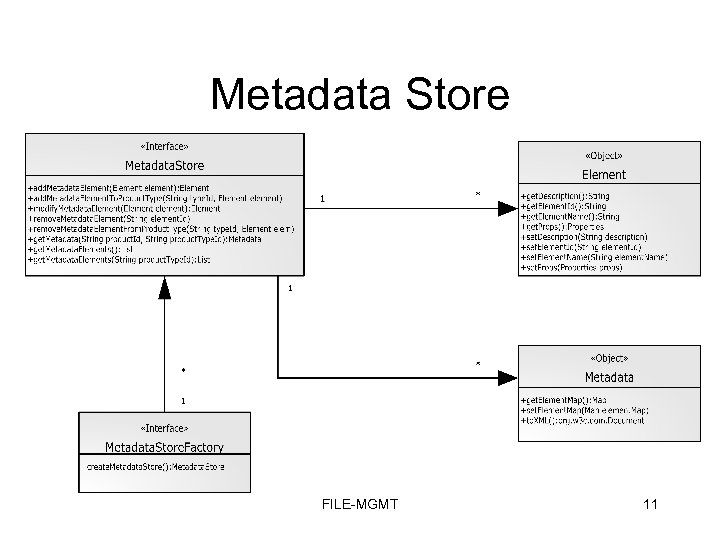 Metadata Store FILE-MGMT 11
Metadata Store FILE-MGMT 11
 How is this different from the existing CAS? • Separation of concerns – Anything to do with data goes into the data store package – Anything to do with metadata goes into the metadata store package • Modularity – Can have different backend implementations of standard interfaces for data stores and metadata stores • Lucene as a backend for metadata, or if you prefer, traditional DB backend – Can have multiple data stores and metadata stores per CAS • The existing CAS lumped these two capabilities together – Was difficult to reason about how to pull them apart FILE-MGMT 12
How is this different from the existing CAS? • Separation of concerns – Anything to do with data goes into the data store package – Anything to do with metadata goes into the metadata store package • Modularity – Can have different backend implementations of standard interfaces for data stores and metadata stores • Lucene as a backend for metadata, or if you prefer, traditional DB backend – Can have multiple data stores and metadata stores per CAS • The existing CAS lumped these two capabilities together – Was difficult to reason about how to pull them apart FILE-MGMT 12
 What else do we need to do File Management? • Need a way to transfer a product from the client to the File Management service – Client gives URIs of files, or collections of files, which identify References belonging to a Product FILE-MGMT 13
What else do we need to do File Management? • Need a way to transfer a product from the client to the File Management service – Client gives URIs of files, or collections of files, which identify References belonging to a Product FILE-MGMT 13
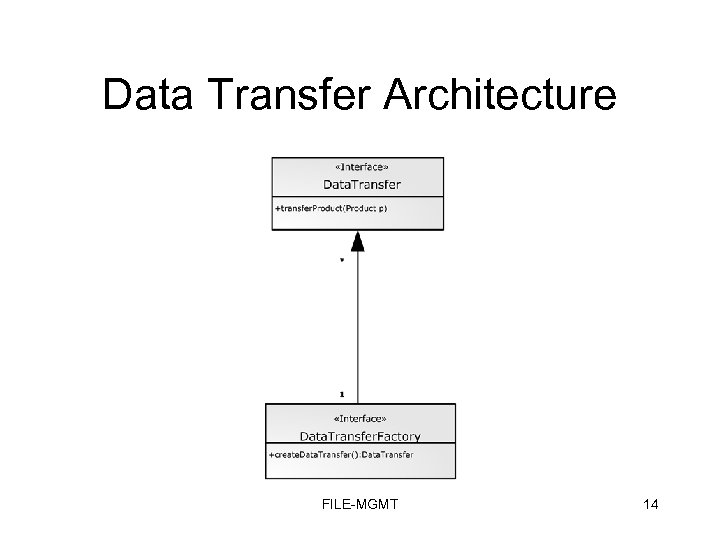 Data Transfer Architecture FILE-MGMT 14
Data Transfer Architecture FILE-MGMT 14
 Transferring files • How does the transfer actually occur? • You as a developer define how that happens – Implement the transfer. Product(Product p) method – Can have many different types of data transfer • Local – Use native system calls, or cp • Remote – Use whatever protocol you want, XML-RPC, SOAP, Web. DAV, etc. – Don’t use CORBA or RMI: they’re sooooo last year! FILE-MGMT 15
Transferring files • How does the transfer actually occur? • You as a developer define how that happens – Implement the transfer. Product(Product p) method – Can have many different types of data transfer • Local – Use native system calls, or cp • Remote – Use whatever protocol you want, XML-RPC, SOAP, Web. DAV, etc. – Don’t use CORBA or RMI: they’re sooooo last year! FILE-MGMT 15
 Translating the URIs • Translating the URIs from the client to the File Manager presents an interesting challenge – For example, where should file: ///home/chris/myfile be transferred to on the File Manager’s system? • Leverage and extend existing CAS method – Existing CAS would have answered the above questions with Product. Type. Repository. Path/Product. Name/Versio n. Id/ – Why should that be the only answer? FILE-MGMT 16
Translating the URIs • Translating the URIs from the client to the File Manager presents an interesting challenge – For example, where should file: ///home/chris/myfile be transferred to on the File Manager’s system? • Leverage and extend existing CAS method – Existing CAS would have answered the above questions with Product. Type. Repository. Path/Product. Name/Versio n. Id/ – Why should that be the only answer? FILE-MGMT 16
 Versioners • Have the concept of a Versioner interface • Versioner is called by the File Manager before the product is transferred from the client to the File Manager system – Versioner uses the Product metadata, and the original product references to generate data store URIs that tell the Data. Transfer implementation where to physically transfer the files for a particular Product FILE-MGMT 17
Versioners • Have the concept of a Versioner interface • Versioner is called by the File Manager before the product is transferred from the client to the File Manager system – Versioner uses the Product metadata, and the original product references to generate data store URIs that tell the Data. Transfer implementation where to physically transfer the files for a particular Product FILE-MGMT 17
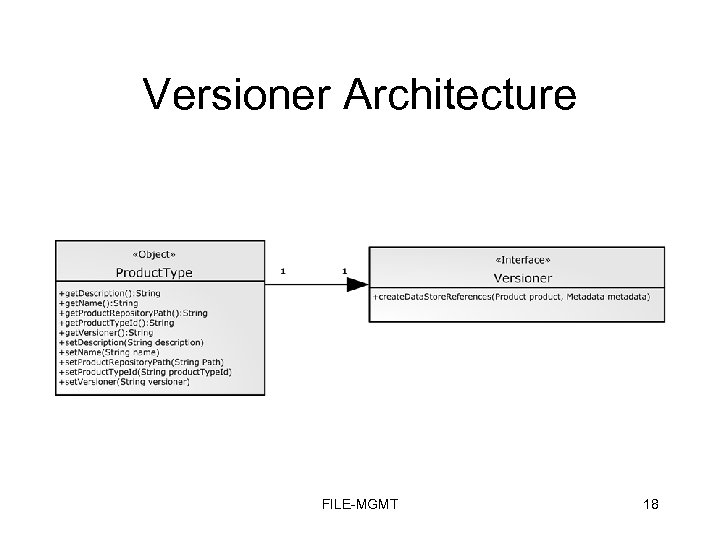 Versioner Architecture FILE-MGMT 18
Versioner Architecture FILE-MGMT 18
 Versioner Example • Given an mp 3 Product, with Metadata: – Mp 3 Artist: 50 cent – Mp 3 Genre: rap • And with references: – file: ///home/chris/mp 3 s/gangsta-rap. mp 3 FILE-MGMT 19
Versioner Example • Given an mp 3 Product, with Metadata: – Mp 3 Artist: 50 cent – Mp 3 Genre: rap • And with references: – file: ///home/chris/mp 3 s/gangsta-rap. mp 3 FILE-MGMT 19
 Versioner Example • Use a Music. Versioner public class Music. Versioner implements Versioner{ public void create. Data. Store. References(Product p, Metadata m) throws Versioning. Exception{ String orig. Uri = ((Reference)p. get. References(). get(0)). get. Orig. Reference(); String mp 3 Repo. Path = get. Repo. Path(“Mp 3 Product. Type. Name”); String data. Store. Uri = mp 3 Repo. Path + m. get. Element. Map(). get(“Mp 3 Genre”) + “/” + m. get. Element. Map(). get(“Mp 3 Artist”) + “/” + get. File. Name(orig. Uri); ((Reference)p. get. References(). get(0). set. Data. Store. Ref(data. Store. Uri); } } FILE-MGMT 20
Versioner Example • Use a Music. Versioner public class Music. Versioner implements Versioner{ public void create. Data. Store. References(Product p, Metadata m) throws Versioning. Exception{ String orig. Uri = ((Reference)p. get. References(). get(0)). get. Orig. Reference(); String mp 3 Repo. Path = get. Repo. Path(“Mp 3 Product. Type. Name”); String data. Store. Uri = mp 3 Repo. Path + m. get. Element. Map(). get(“Mp 3 Genre”) + “/” + m. get. Element. Map(). get(“Mp 3 Artist”) + “/” + get. File. Name(orig. Uri); ((Reference)p. get. References(). get(0). set. Data. Store. Ref(data. Store. Uri); } } FILE-MGMT 20
 Versioner Example • So – file: ///home/chris/mp 3 s/gangsta-rap. mp 3 • …Yields – file: ///path/to/mp 3/repo/rap/50 cent/gangstarap. mp 3 FILE-MGMT 21
Versioner Example • So – file: ///home/chris/mp 3 s/gangsta-rap. mp 3 • …Yields – file: ///path/to/mp 3/repo/rap/50 cent/gangstarap. mp 3 FILE-MGMT 21
 The File Manager • So, how do we put all these different generic interfaces together? • Well, something like the following – A File Manager has… • One or more data stores, to store data to • One or more metadata stores, to store metadata to • A set of Versioners that are associated with Product Types in order to figure out how to generate the reference data store URIs for a particular product • A Data Transferer that moves a Product’s file from the client to the File Manager using the source URIs and the data store URIs • An external interface to it (e. g. , XML-RPC, Web. DAV, etc. ) FILE-MGMT 22
The File Manager • So, how do we put all these different generic interfaces together? • Well, something like the following – A File Manager has… • One or more data stores, to store data to • One or more metadata stores, to store metadata to • A set of Versioners that are associated with Product Types in order to figure out how to generate the reference data store URIs for a particular product • A Data Transferer that moves a Product’s file from the client to the File Manager using the source URIs and the data store URIs • An external interface to it (e. g. , XML-RPC, Web. DAV, etc. ) FILE-MGMT 22
 What’s implemented so far? • The basic components of the architecture • Several default implementations of the interfaces – javax. sql. Data. Source based implementations of Data. Store and Metadata. Store • Uses Apache’s DBCP for connection pooling – Local Data Transfer using Apache’s commons-io component that can handle heirarchical product structures, as well as flat product structures – Several versioners, including one that versions Products using the existing CAS approach of Product. Type. Repository. Path/Product. Name/Version, along with one that versions a product’s references based on production date time – An external interface based on Apache’s XML-RPC FILE-MGMT 23
What’s implemented so far? • The basic components of the architecture • Several default implementations of the interfaces – javax. sql. Data. Source based implementations of Data. Store and Metadata. Store • Uses Apache’s DBCP for connection pooling – Local Data Transfer using Apache’s commons-io component that can handle heirarchical product structures, as well as flat product structures – Several versioners, including one that versions Products using the existing CAS approach of Product. Type. Repository. Path/Product. Name/Version, along with one that versions a product’s references based on production date time – An external interface based on Apache’s XML-RPC FILE-MGMT 23
 What needs to be done? • A lot! – Check out http: //oodt. jpl. nasa. gov/vc/, and log in with your JPL Username and Password. Navigate to “SVN”, and check out the cas-filemgr component. – Modify the code – Look for bugs – Contribute! • I find new bugs everyday – Feel free to talk to me about it – Create issues in JIRA (http: //oodt. jpl. nasa. gov/jira/) • Bug Fixes, RFIs, new features, you name it! • Be sure to check out the apidocs – You can build these yourself by checking out cas-filemgr from our SVN repository, and then typing: maven site – Or you can visit: http: //terra. jpl. nasa. gov/~mattmann/oco/javadoc/casfilemgr/ FILE-MGMT 24
What needs to be done? • A lot! – Check out http: //oodt. jpl. nasa. gov/vc/, and log in with your JPL Username and Password. Navigate to “SVN”, and check out the cas-filemgr component. – Modify the code – Look for bugs – Contribute! • I find new bugs everyday – Feel free to talk to me about it – Create issues in JIRA (http: //oodt. jpl. nasa. gov/jira/) • Bug Fixes, RFIs, new features, you name it! • Be sure to check out the apidocs – You can build these yourself by checking out cas-filemgr from our SVN repository, and then typing: maven site – Or you can visit: http: //terra. jpl. nasa. gov/~mattmann/oco/javadoc/casfilemgr/ FILE-MGMT 24
 Questions? FILE-MGMT 25
Questions? FILE-MGMT 25


