 Figures for Chapter 15 THE FOREIGN EXCHANGE MARKET (Investments : Spot and Derivatives Markets) © K. Cuthbertson and D. Nitzsche
Figures for Chapter 15 THE FOREIGN EXCHANGE MARKET (Investments : Spot and Derivatives Markets) © K. Cuthbertson and D. Nitzsche
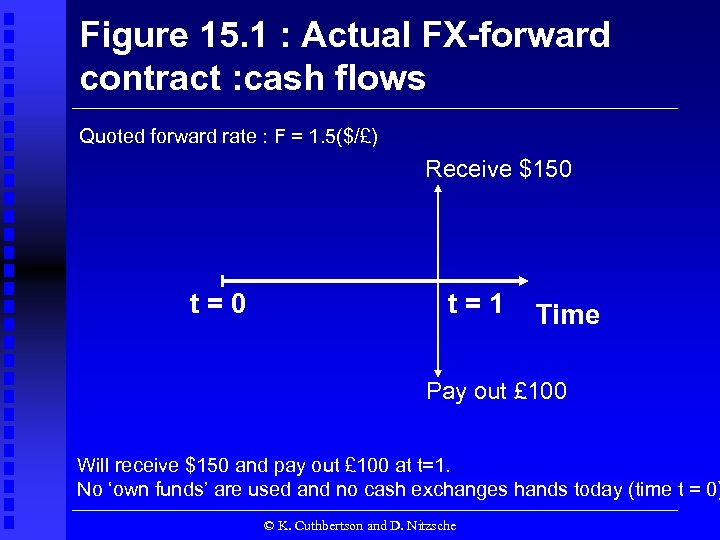 Figure 15. 1 : Actual FX-forward contract : cash flows Quoted forward rate : F = 1. 5($/£) Receive $150 t=1 Time Pay out £ 100 Will receive $150 and pay out £ 100 at t=1. No ‘own funds’ are used and no cash exchanges hands today (time t = 0) © K. Cuthbertson and D. Nitzsche
Figure 15. 1 : Actual FX-forward contract : cash flows Quoted forward rate : F = 1. 5($/£) Receive $150 t=1 Time Pay out £ 100 Will receive $150 and pay out £ 100 at t=1. No ‘own funds’ are used and no cash exchanges hands today (time t = 0) © K. Cuthbertson and D. Nitzsche
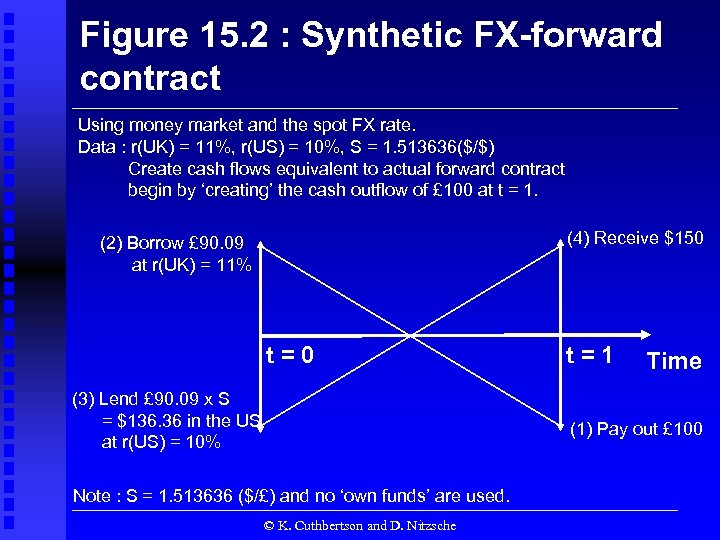 Figure 15. 2 : Synthetic FX-forward contract Using money market and the spot FX rate. Data : r(UK) = 11%, r(US) = 10%, S = 1. 513636($/$) Create cash flows equivalent to actual forward contract begin by ‘creating’ the cash outflow of £ 100 at t = 1. (4) Receive $150 (2) Borrow £ 90. 09 at r(UK) = 11% t=0 (3) Lend £ 90. 09 x S = $136. 36 in the US at r(US) = 10% t=1 Time (1) Pay out £ 100 Note : S = 1. 513636 ($/£) and no ‘own funds’ are used. © K. Cuthbertson and D. Nitzsche
Figure 15. 2 : Synthetic FX-forward contract Using money market and the spot FX rate. Data : r(UK) = 11%, r(US) = 10%, S = 1. 513636($/$) Create cash flows equivalent to actual forward contract begin by ‘creating’ the cash outflow of £ 100 at t = 1. (4) Receive $150 (2) Borrow £ 90. 09 at r(UK) = 11% t=0 (3) Lend £ 90. 09 x S = $136. 36 in the US at r(US) = 10% t=1 Time (1) Pay out £ 100 Note : S = 1. 513636 ($/£) and no ‘own funds’ are used. © K. Cuthbertson and D. Nitzsche
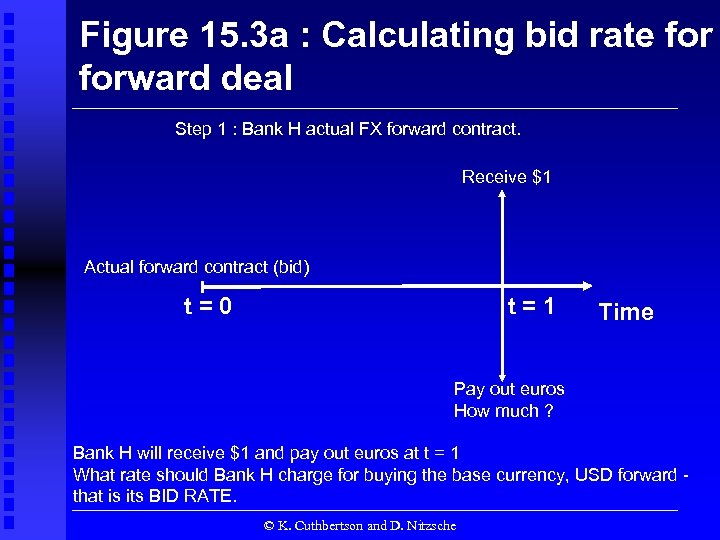 Figure 15. 3 a : Calculating bid rate forward deal Step 1 : Bank H actual FX forward contract. Receive $1 Actual forward contract (bid) t=0 t=1 Time Pay out euros How much ? Bank H will receive $1 and pay out euros at t = 1 What rate should Bank H charge for buying the base currency, USD forward that is its BID RATE. © K. Cuthbertson and D. Nitzsche
Figure 15. 3 a : Calculating bid rate forward deal Step 1 : Bank H actual FX forward contract. Receive $1 Actual forward contract (bid) t=0 t=1 Time Pay out euros How much ? Bank H will receive $1 and pay out euros at t = 1 What rate should Bank H charge for buying the base currency, USD forward that is its BID RATE. © K. Cuthbertson and D. Nitzsche
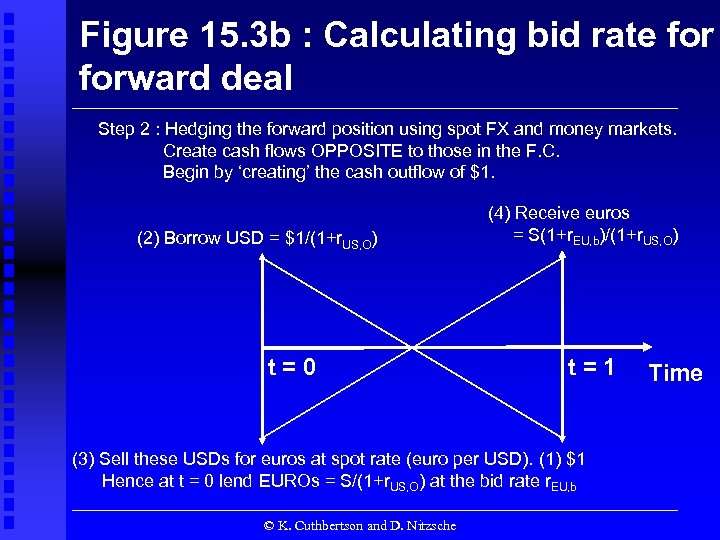 Figure 15. 3 b : Calculating bid rate forward deal Step 2 : Hedging the forward position using spot FX and money markets. Create cash flows OPPOSITE to those in the F. C. Begin by ‘creating’ the cash outflow of $1. (2) Borrow USD = $1/(1+r. US, O) t=0 (4) Receive euros = S(1+r. EU, b)/(1+r. US, O) t=1 (3) Sell these USDs for euros at spot rate (euro per USD). (1) $1 Hence at t = 0 lend EUROs = S/(1+r. US, O) at the bid rate r. EU, b © K. Cuthbertson and D. Nitzsche Time
Figure 15. 3 b : Calculating bid rate forward deal Step 2 : Hedging the forward position using spot FX and money markets. Create cash flows OPPOSITE to those in the F. C. Begin by ‘creating’ the cash outflow of $1. (2) Borrow USD = $1/(1+r. US, O) t=0 (4) Receive euros = S(1+r. EU, b)/(1+r. US, O) t=1 (3) Sell these USDs for euros at spot rate (euro per USD). (1) $1 Hence at t = 0 lend EUROs = S/(1+r. US, O) at the bid rate r. EU, b © K. Cuthbertson and D. Nitzsche Time
 Figure 15. 4 a : Calculating offer rate forward deal Step 1 : Bank H actual FX forward contract. Receive euros How much ? Actual forward contract (offer) t=0 t=1 Pay out $1 © K. Cuthbertson and D. Nitzsche Time
Figure 15. 4 a : Calculating offer rate forward deal Step 1 : Bank H actual FX forward contract. Receive euros How much ? Actual forward contract (offer) t=0 t=1 Pay out $1 © K. Cuthbertson and D. Nitzsche Time
 Figure 15. 4 b : Calculating offer rate forward deal Step 2 : Hedging the forward position using spot FX and money markets. Create cash flows OPPOSITE to those in the F. C. Begin by ‘creating’ the cash outflow of $1. (2) Borrow USD = $1/(1+r. US, O) t=0 (2) Lend $1/(1+r. US, b) (1) $1 t=1 Time (4) will pay out = S(1+r. EU, O)/(1+r. US, b) = F(offer) = 1. 00553 To lend USDs at t = 0 we have to first borrow euros and switch them into spot dollars © K. Cuthbertson and D. Nitzsche
Figure 15. 4 b : Calculating offer rate forward deal Step 2 : Hedging the forward position using spot FX and money markets. Create cash flows OPPOSITE to those in the F. C. Begin by ‘creating’ the cash outflow of $1. (2) Borrow USD = $1/(1+r. US, O) t=0 (2) Lend $1/(1+r. US, b) (1) $1 t=1 Time (4) will pay out = S(1+r. EU, O)/(1+r. US, b) = F(offer) = 1. 00553 To lend USDs at t = 0 we have to first borrow euros and switch them into spot dollars © K. Cuthbertson and D. Nitzsche
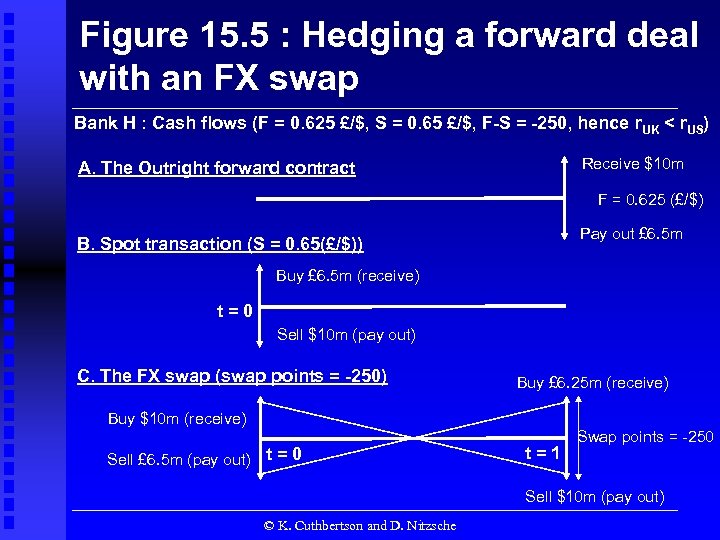 Figure 15. 5 : Hedging a forward deal with an FX swap Bank H : Cash flows (F = 0. 625 £/$, S = 0. 65 £/$, F-S = -250, hence r. UK < r. US) Receive $10 m A. The Outright forward contract F = 0. 625 (£/$) Pay out £ 6. 5 m B. Spot transaction (S = 0. 65(£/$)) Buy £ 6. 5 m (receive) t=0 Sell $10 m (pay out) C. The FX swap (swap points = -250) Buy £ 6. 25 m (receive) Buy $10 m (receive) Sell £ 6. 5 m (pay out) t = 0 t=1 Swap points = -250 Sell $10 m (pay out) © K. Cuthbertson and D. Nitzsche
Figure 15. 5 : Hedging a forward deal with an FX swap Bank H : Cash flows (F = 0. 625 £/$, S = 0. 65 £/$, F-S = -250, hence r. UK < r. US) Receive $10 m A. The Outright forward contract F = 0. 625 (£/$) Pay out £ 6. 5 m B. Spot transaction (S = 0. 65(£/$)) Buy £ 6. 5 m (receive) t=0 Sell $10 m (pay out) C. The FX swap (swap points = -250) Buy £ 6. 25 m (receive) Buy $10 m (receive) Sell £ 6. 5 m (pay out) t = 0 t=1 Swap points = -250 Sell $10 m (pay out) © K. Cuthbertson and D. Nitzsche
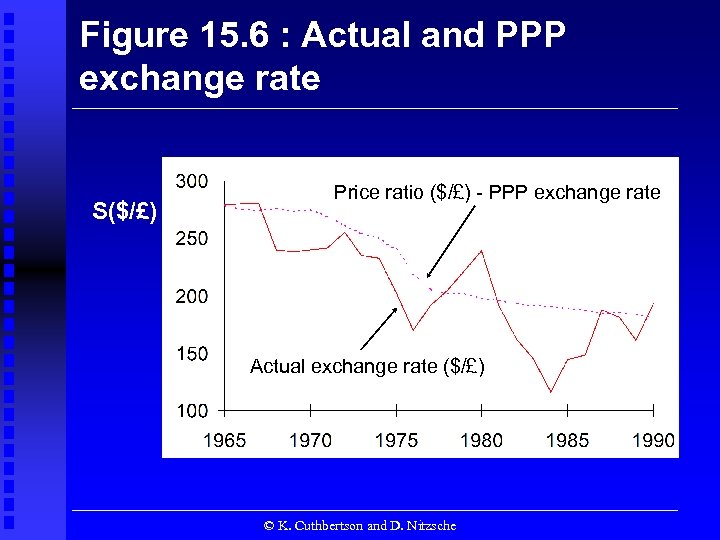 Figure 15. 6 : Actual and PPP exchange rate S($/£) Price ratio ($/£) - PPP exchange rate Actual exchange rate ($/£) © K. Cuthbertson and D. Nitzsche
Figure 15. 6 : Actual and PPP exchange rate S($/£) Price ratio ($/£) - PPP exchange rate Actual exchange rate ($/£) © K. Cuthbertson and D. Nitzsche