d5bd4f8fad18b24924922b3a39df21c6.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 3
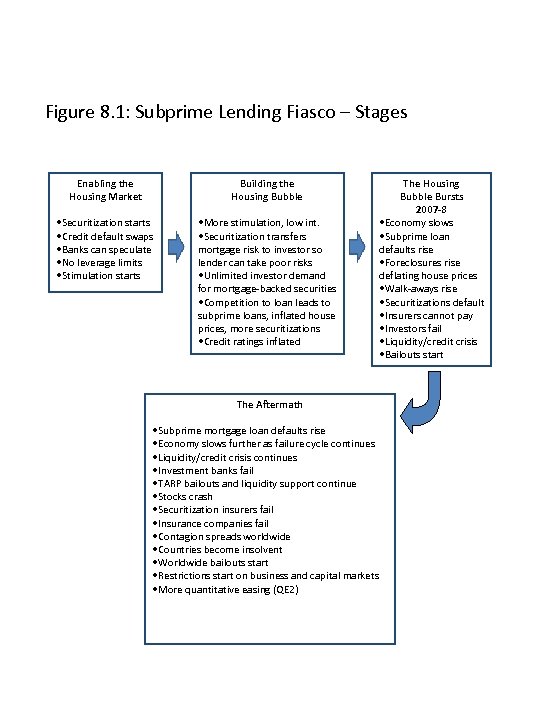
Figure 8. 1: Subprime Lending Fiasco – Stages Enabling the Housing Market Building the Housing Bubble • Securitization starts • Credit default swaps • Banks can speculate • No leverage limits • Stimulation starts • More stimulation, low int. • Securitization transfers mortgage risk to investor so lender can take poor risks • Unlimited investor demand for mortgage-backed securities • Competition to loan leads to subprime loans, inflated house prices, more securitizations • Credit ratings inflated The Aftermath • Subprime mortgage loan defaults rise • Economy slows further as failure cycle continues • Liquidity/credit crisis continues • Investment banks fail • TARP bailouts and liquidity support continue • Stocks crash • Securitization insurers fail • Insurance companies fail • Contagion spreads worldwide • Countries become insolvent • Worldwide bailouts start • Restrictions start on business and capital markets • More quantitative easing (QE 2) The Housing Bubble Bursts 2007 -8 • Economy slows • Subprime loan defaults rise • Foreclosures rise deflating house prices • Walk-aways rise • Securitizations default • Insurers cannot pay • Investors fail • Liquidity/credit crisis • Bailouts start
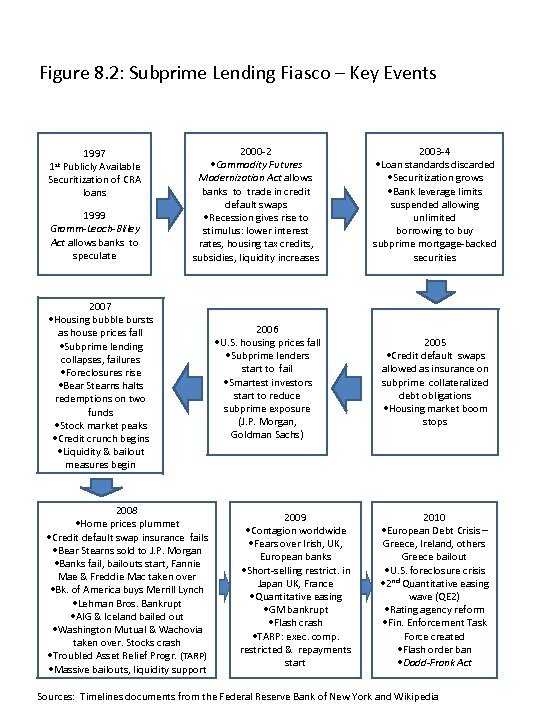
Figure 8. 2: Subprime Lending Fiasco – Key Events 1997 Publicly Available Securitization of CRA loans 1 st 1999 Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act allows banks to speculate 2000 -2 • Commodity Futures Modernization Act allows banks to trade in credit default swaps • Recession gives rise to stimulus: lower interest rates, housing tax credits, subsidies, liquidity increases 2007 • Housing bubble bursts as house prices fall • Subprime lending collapses, failures • Foreclosures rise • Bear Stearns halts redemptions on two funds • Stock market peaks • Credit crunch begins • Liquidity & bailout measures begin 2008 • Home prices plummet • Credit default swap insurance fails • Bear Stearns sold to J. P. Morgan • Banks fail, bailouts start, Fannie Mae & Freddie Mac taken over • Bk. of America buys Merrill Lynch • Lehman Bros. Bankrupt • AIG & Iceland bailed out • Washington Mutual & Wachovia taken over. Stocks crash • Troubled Asset Relief Progr. (TARP) • Massive bailouts, liquidity support 2006 • U. S. housing prices fall • Subprime lenders start to fail • Smartest investors start to reduce subprime exposure (J. P. Morgan, Goldman Sachs) 2009 • Contagion worldwide • Fears over Irish, UK, European banks • Short-selling restrict. in Japan UK, France • Quantitative easing • GM bankrupt • Flash crash • TARP: exec. comp. restricted & repayments start 2003 -4 • Loan standards discarded • Securitization grows • Bank leverage limits suspended allowing unlimited borrowing to buy subprime mortgage-backed securities 2005 • Credit default swaps allowed as insurance on subprime collateralized debt obligations • Housing market boom stops 2010 • European Debt Crisis – Greece, Ireland, others Greece bailout • U. S. foreclosure crisis • 2 nd Quantitative easing wave (QE 2) • Rating agency reform • Fin. Enforcement Task Force created • Flash order ban • Dodd-Frank Act Sources: Timelines documents from the Federal Reserve Bank of New York and Wikipedia
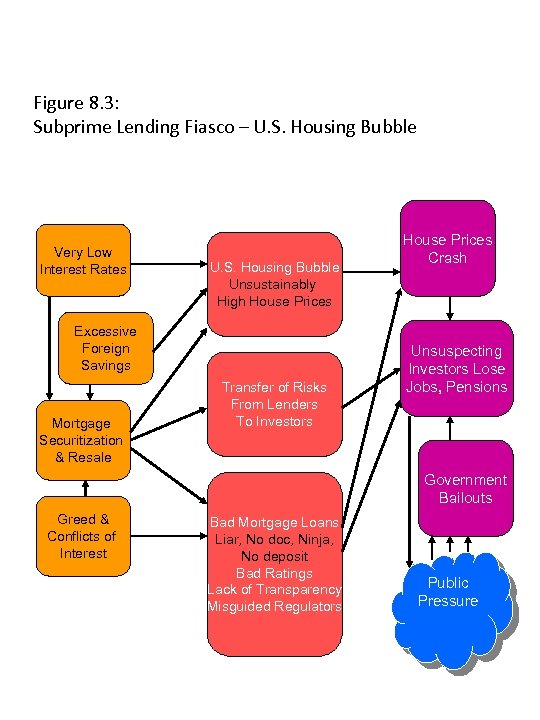
Figure 8. 3: Subprime Lending Fiasco – U. S. Housing Bubble Very Low Interest Rates U. S. Housing Bubble Unsustainably High House Prices Excessive Foreign Savings Mortgage Securitization & Resale Transfer of Risks From Lenders To Investors House Prices Crash Unsuspecting Investors Lose Jobs, Pensions Government Bailouts Greed & Conflicts of Interest Bad Mortgage Loans Liar, No doc, Ninja, No deposit Bad Ratings Lack of Transparency Misguided Regulators Public Pressure
d5bd4f8fad18b24924922b3a39df21c6.ppt