bca7bd6242c59fbd7edd205950f1f500.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 59
 Figure 7. 1 The Nature of Waves 1
Figure 7. 1 The Nature of Waves 1
 A Beautiful Rainbow 2
A Beautiful Rainbow 2
 When a Strontium salt is dissolved in methanol (with a little water) and ignited, it gives a brillant red flame 3
When a Strontium salt is dissolved in methanol (with a little water) and ignited, it gives a brillant red flame 3
 Fireworks in Washington D. C. 4
Fireworks in Washington D. C. 4
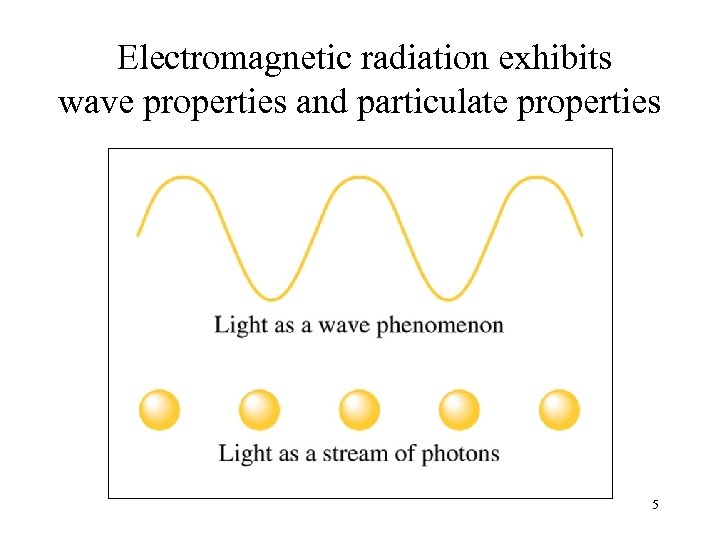 Electromagnetic radiation exhibits wave properties and particulate properties 5
Electromagnetic radiation exhibits wave properties and particulate properties 5
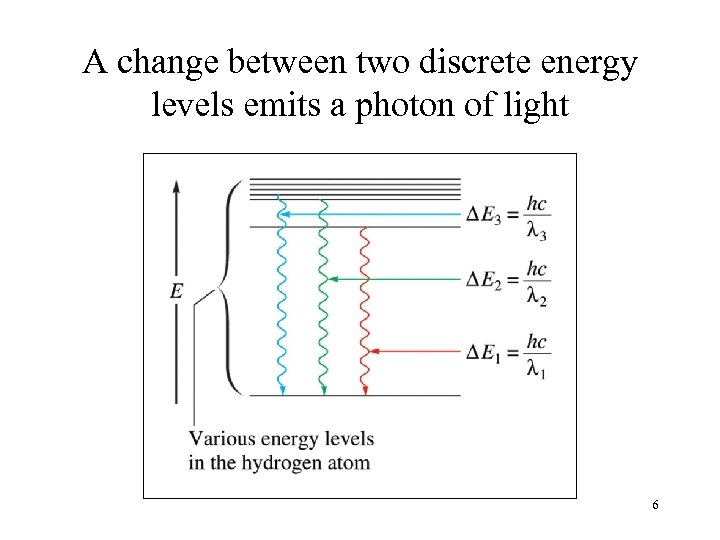 A change between two discrete energy levels emits a photon of light 6
A change between two discrete energy levels emits a photon of light 6
 Niels Bohr 7
Niels Bohr 7
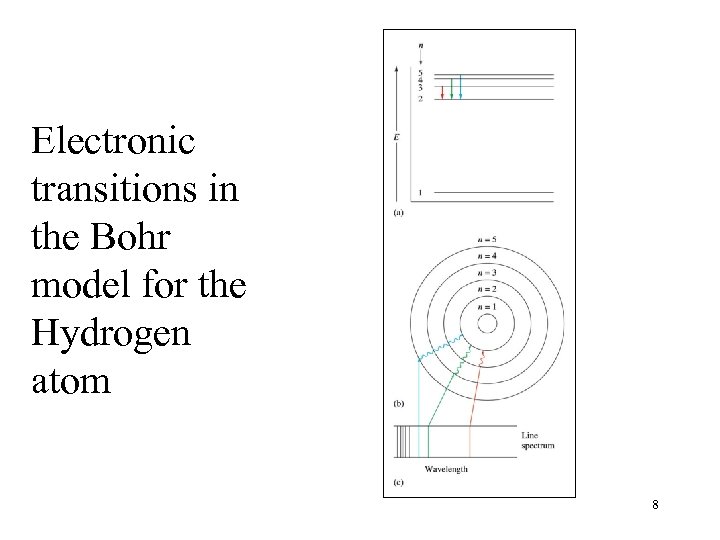 Electronic transitions in the Bohr model for the Hydrogen atom 8
Electronic transitions in the Bohr model for the Hydrogen atom 8
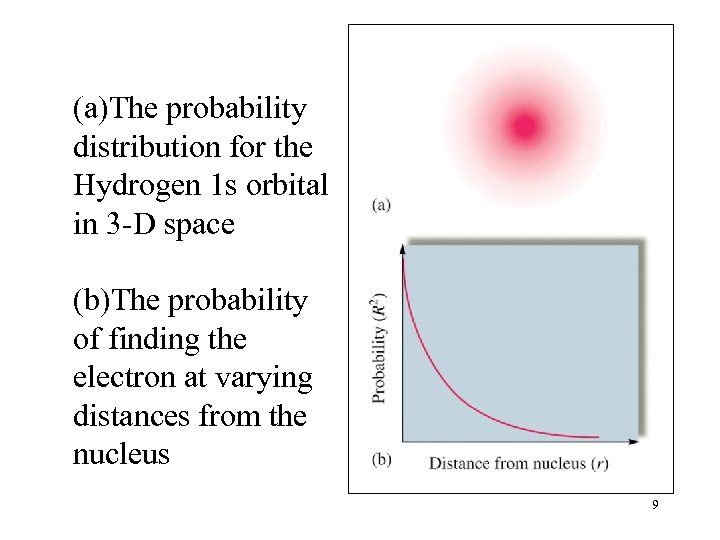 (a)The probability distribution for the Hydrogen 1 s orbital in 3 -D space (b)The probability of finding the electron at varying distances from the nucleus 9
(a)The probability distribution for the Hydrogen 1 s orbital in 3 -D space (b)The probability of finding the electron at varying distances from the nucleus 9
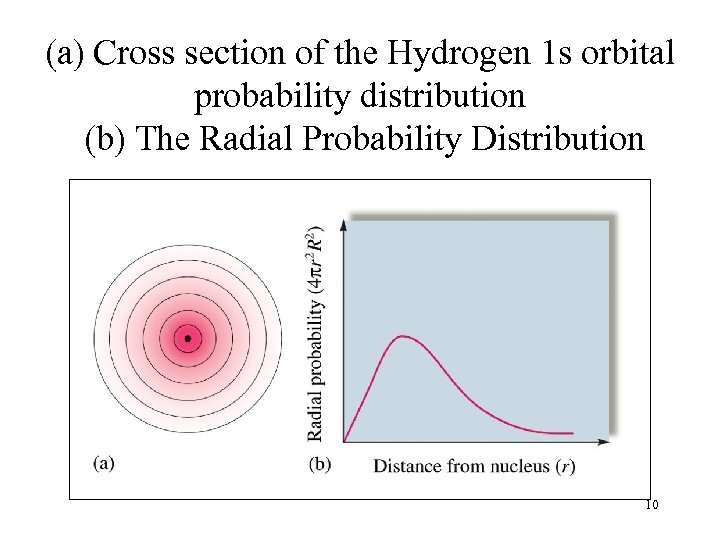 (a) Cross section of the Hydrogen 1 s orbital probability distribution (b) The Radial Probability Distribution 10
(a) Cross section of the Hydrogen 1 s orbital probability distribution (b) The Radial Probability Distribution 10
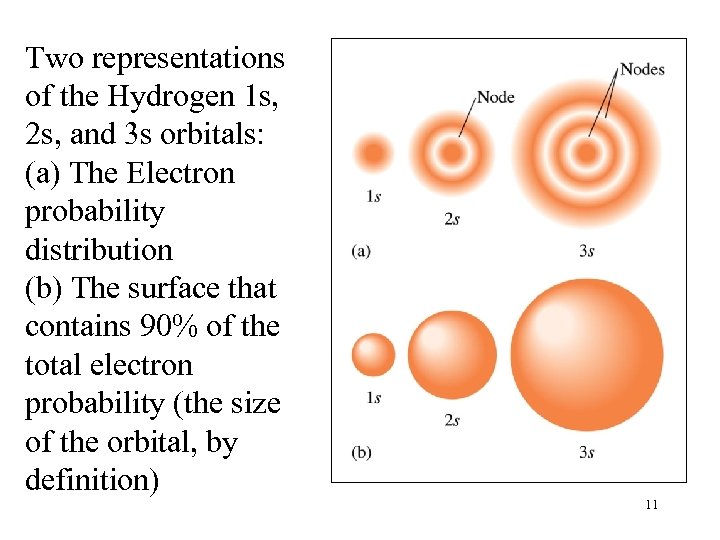 Two representations of the Hydrogen 1 s, 2 s, and 3 s orbitals: (a) The Electron probability distribution (b) The surface that contains 90% of the total electron probability (the size of the orbital, by definition) 11
Two representations of the Hydrogen 1 s, 2 s, and 3 s orbitals: (a) The Electron probability distribution (b) The surface that contains 90% of the total electron probability (the size of the orbital, by definition) 11
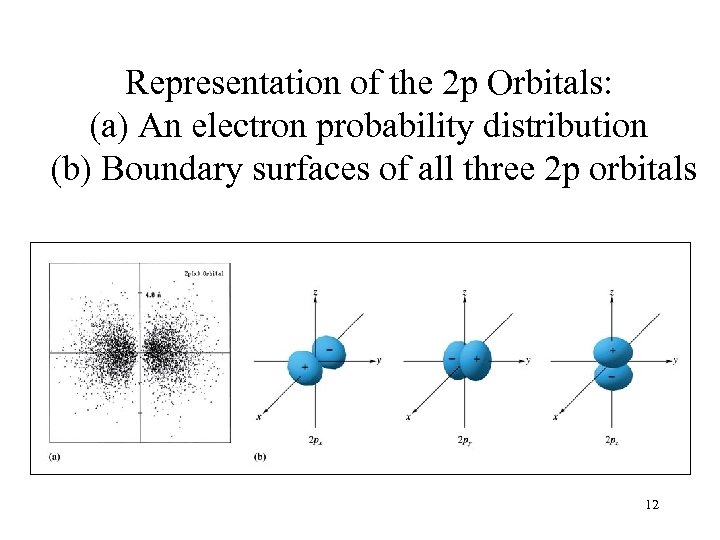 Representation of the 2 p Orbitals: (a) An electron probability distribution (b) Boundary surfaces of all three 2 p orbitals 12
Representation of the 2 p Orbitals: (a) An electron probability distribution (b) Boundary surfaces of all three 2 p orbitals 12
 Cross section of the electron probability distribution for a 3 p orbital 13
Cross section of the electron probability distribution for a 3 p orbital 13
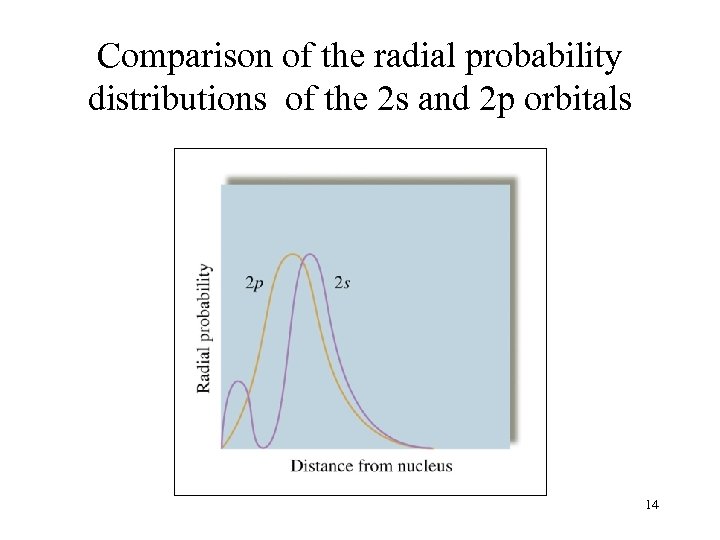 Comparison of the radial probability distributions of the 2 s and 2 p orbitals 14
Comparison of the radial probability distributions of the 2 s and 2 p orbitals 14
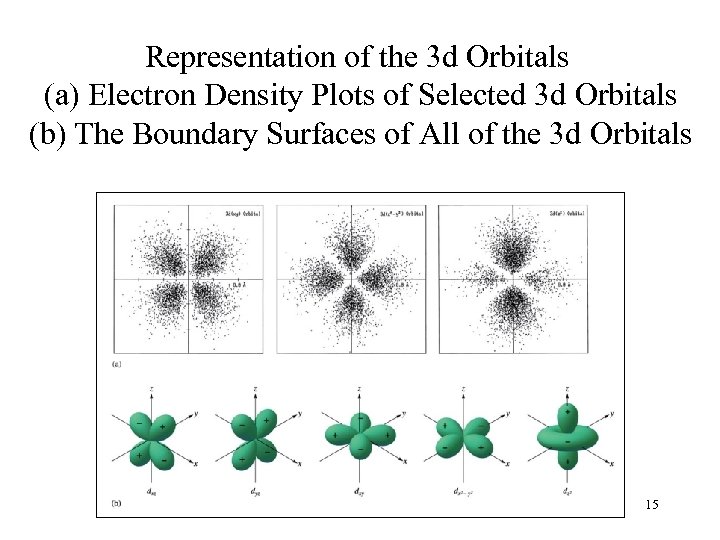 Representation of the 3 d Orbitals (a) Electron Density Plots of Selected 3 d Orbitals (b) The Boundary Surfaces of All of the 3 d Orbitals 15
Representation of the 3 d Orbitals (a) Electron Density Plots of Selected 3 d Orbitals (b) The Boundary Surfaces of All of the 3 d Orbitals 15
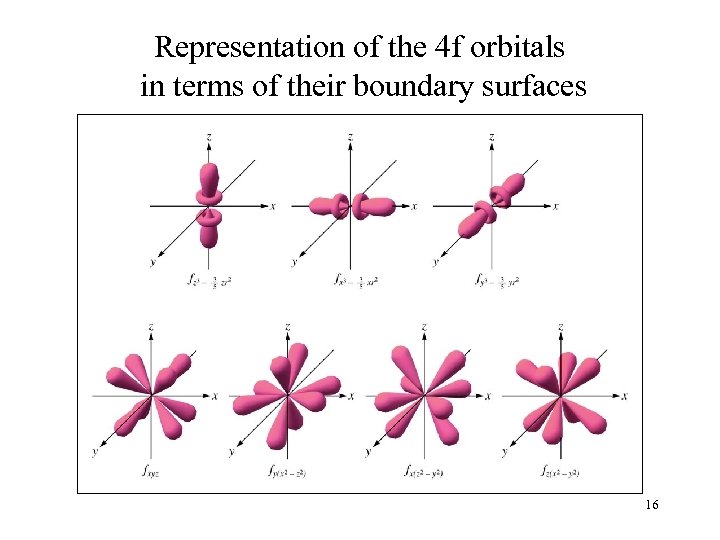 Representation of the 4 f orbitals in terms of their boundary surfaces 16
Representation of the 4 f orbitals in terms of their boundary surfaces 16
 The angular momentum quantum number (l) and the s, p, d, f notation 17
The angular momentum quantum number (l) and the s, p, d, f notation 17
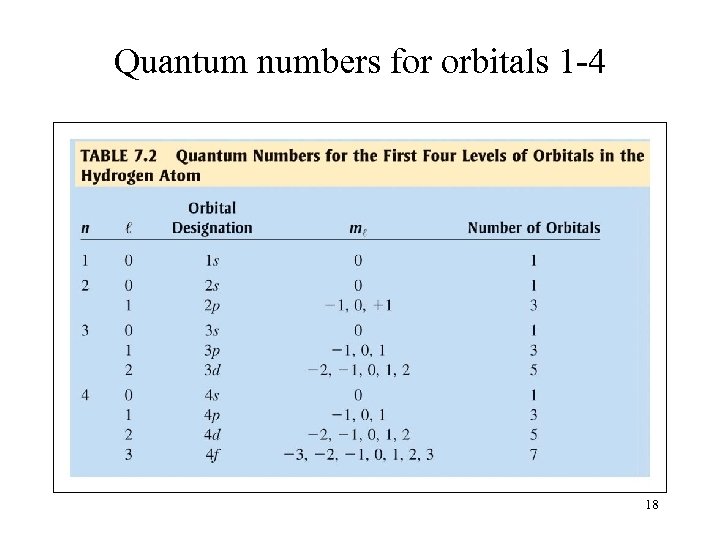 Quantum numbers for orbitals 1 -4 18
Quantum numbers for orbitals 1 -4 18
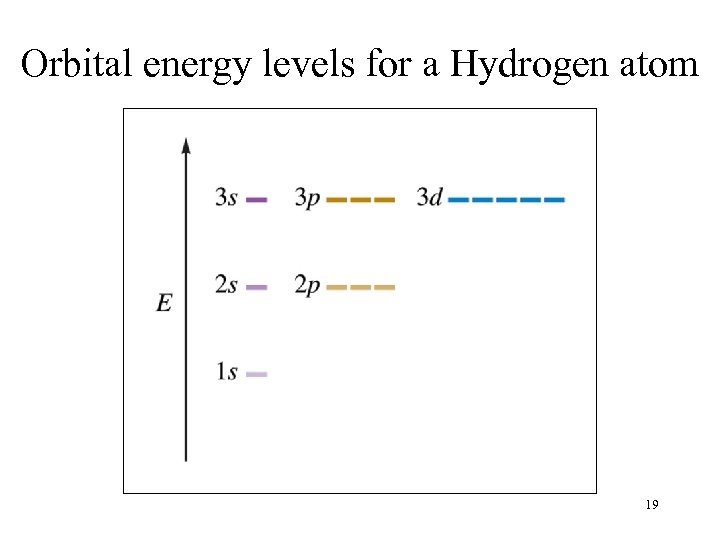 Orbital energy levels for a Hydrogen atom 19
Orbital energy levels for a Hydrogen atom 19
 A picture of the spinning electron 20
A picture of the spinning electron 20
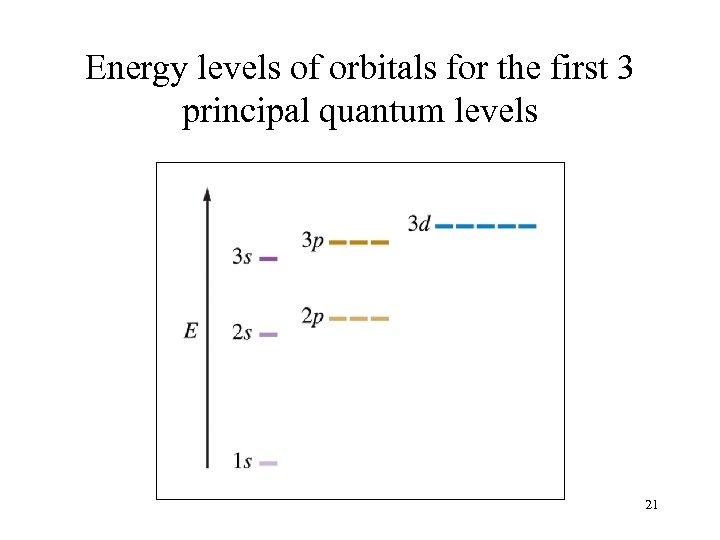 Energy levels of orbitals for the first 3 principal quantum levels 21
Energy levels of orbitals for the first 3 principal quantum levels 21
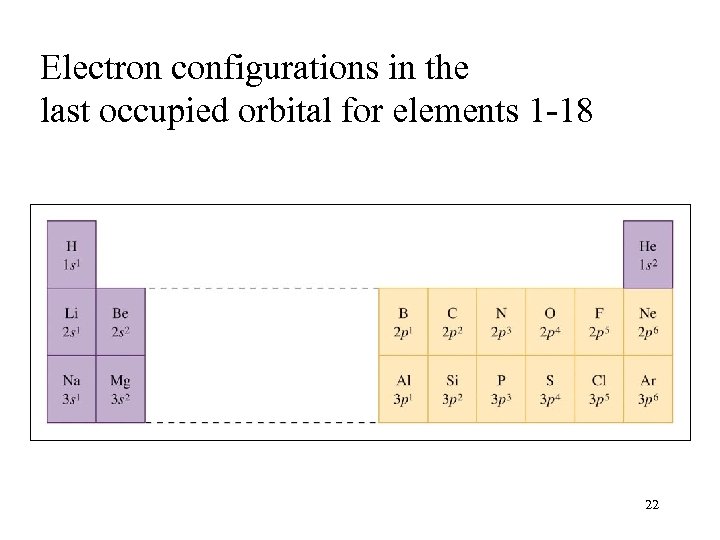 Electron configurations in the last occupied orbital for elements 1 -18 22
Electron configurations in the last occupied orbital for elements 1 -18 22
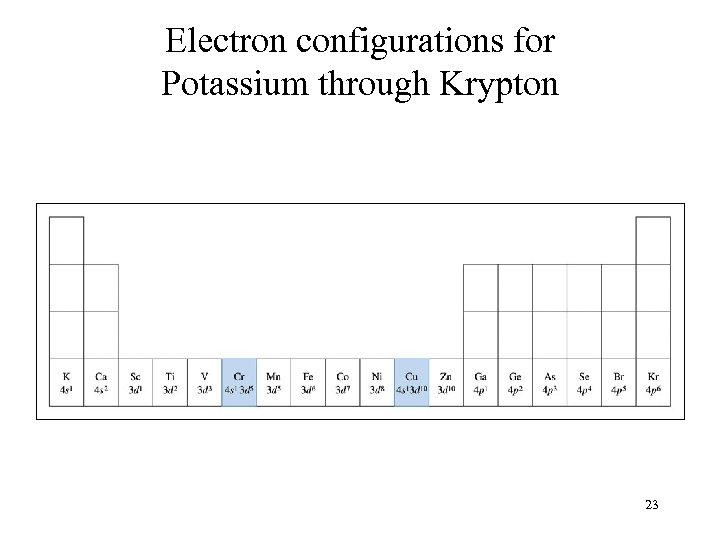 Electron configurations for Potassium through Krypton 23
Electron configurations for Potassium through Krypton 23
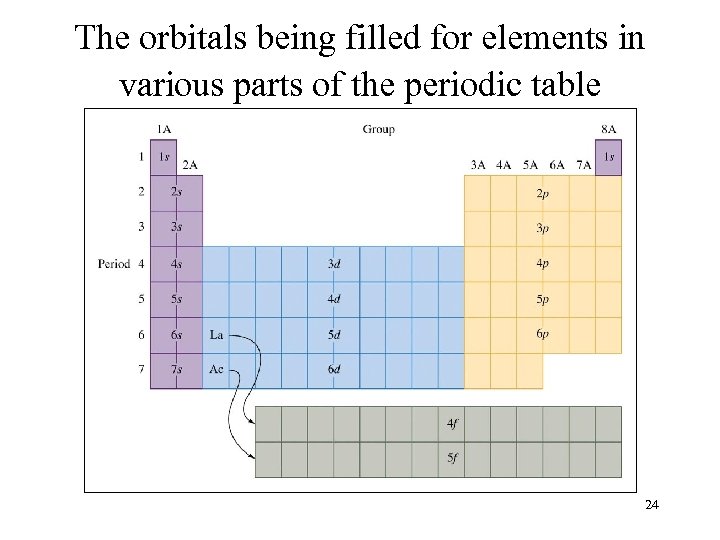 The orbitals being filled for elements in various parts of the periodic table 24
The orbitals being filled for elements in various parts of the periodic table 24
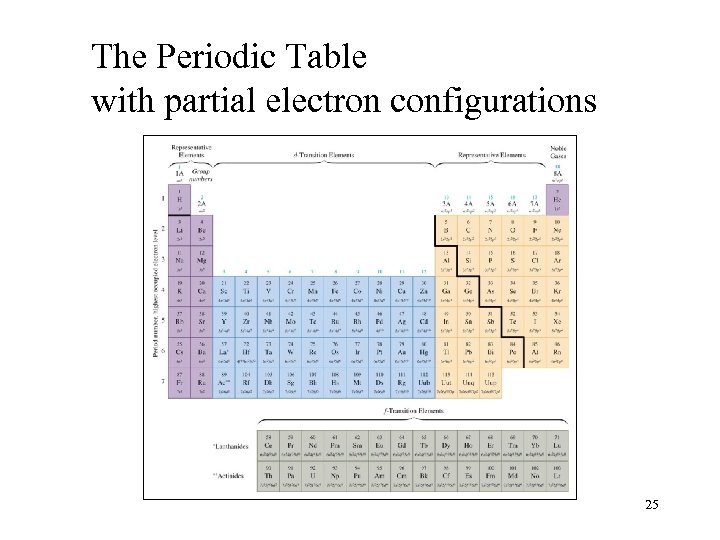 The Periodic Table with partial electron configurations 25
The Periodic Table with partial electron configurations 25
 The End 26
The End 26
 27
27
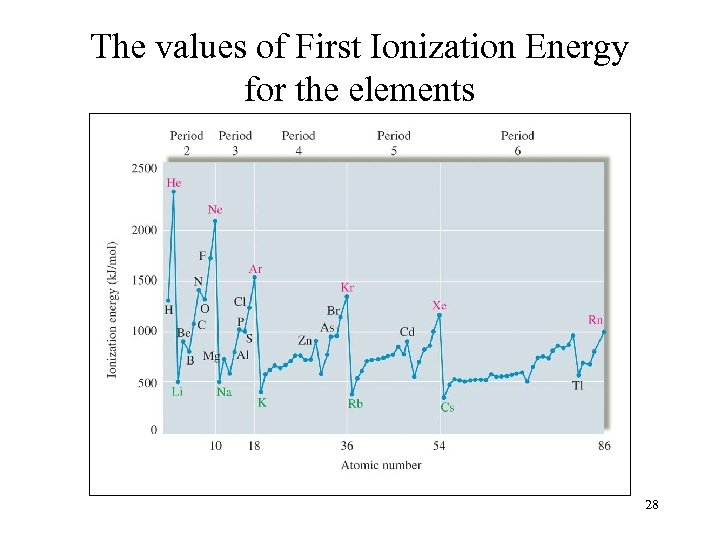 The values of First Ionization Energy for the elements 28
The values of First Ionization Energy for the elements 28
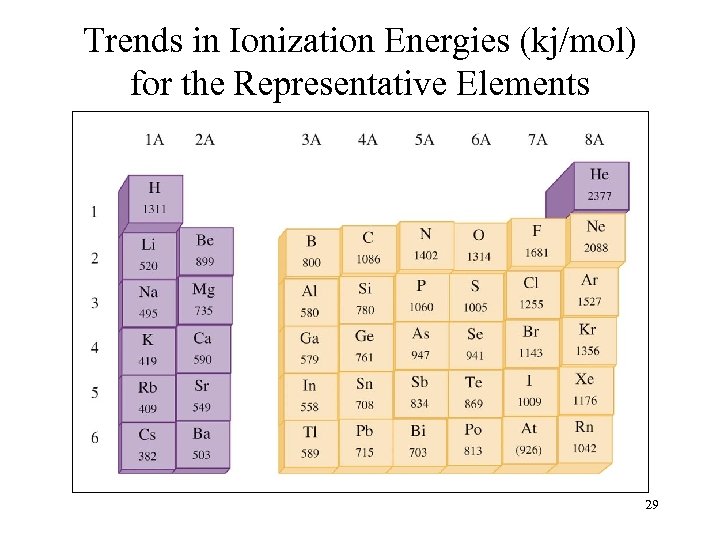 Trends in Ionization Energies (kj/mol) for the Representative Elements 29
Trends in Ionization Energies (kj/mol) for the Representative Elements 29
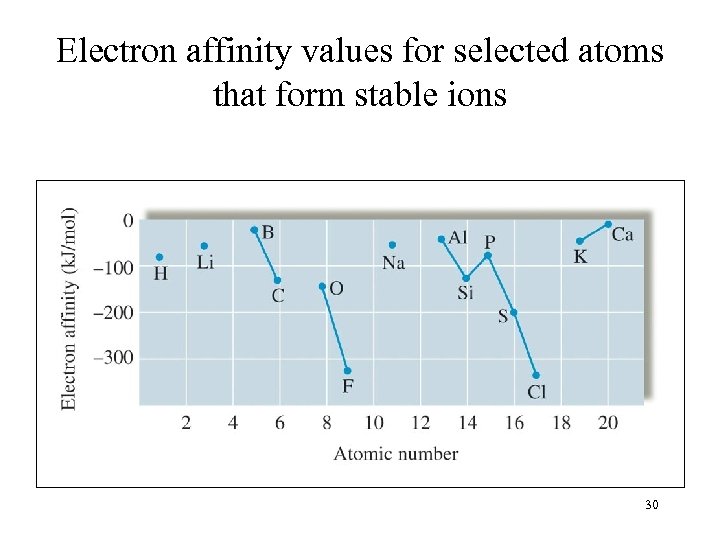 Electron affinity values for selected atoms that form stable ions 30
Electron affinity values for selected atoms that form stable ions 30
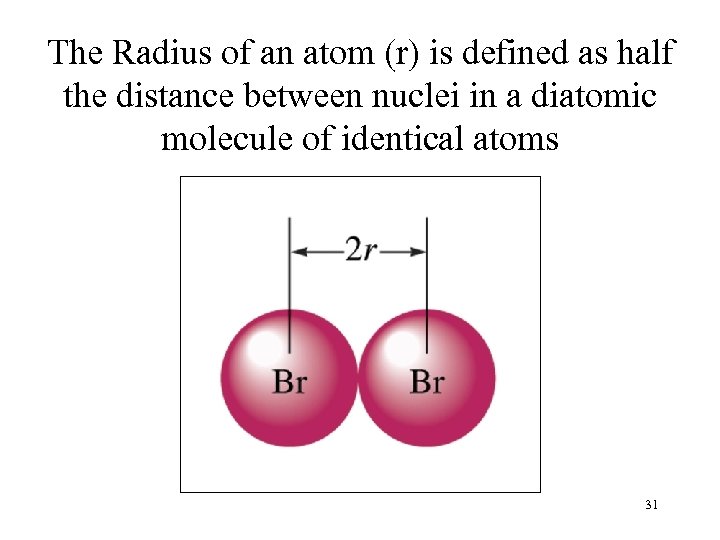 The Radius of an atom (r) is defined as half the distance between nuclei in a diatomic molecule of identical atoms 31
The Radius of an atom (r) is defined as half the distance between nuclei in a diatomic molecule of identical atoms 31
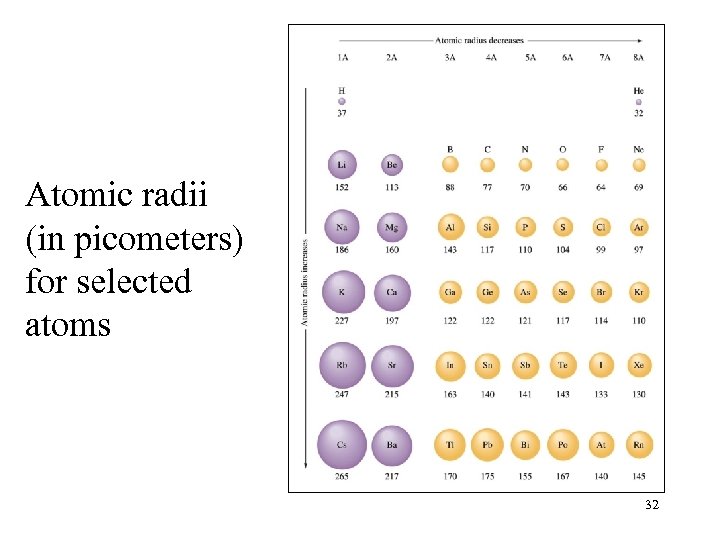 Atomic radii (in picometers) for selected atoms 32
Atomic radii (in picometers) for selected atoms 32
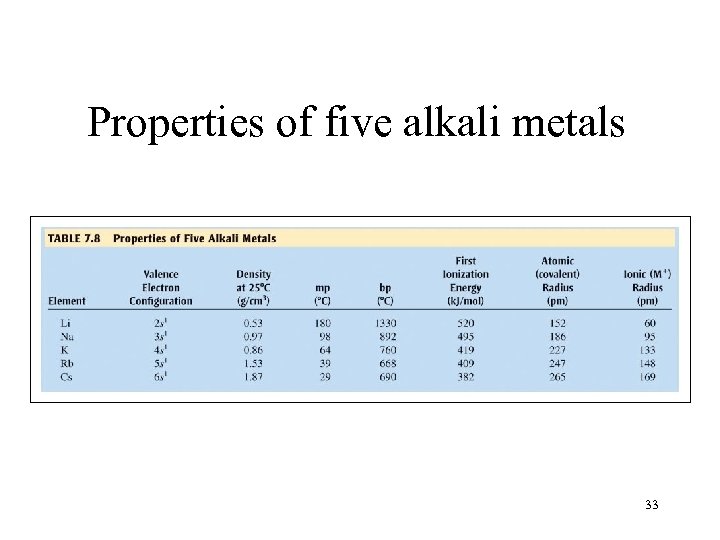 Properties of five alkali metals 33
Properties of five alkali metals 33
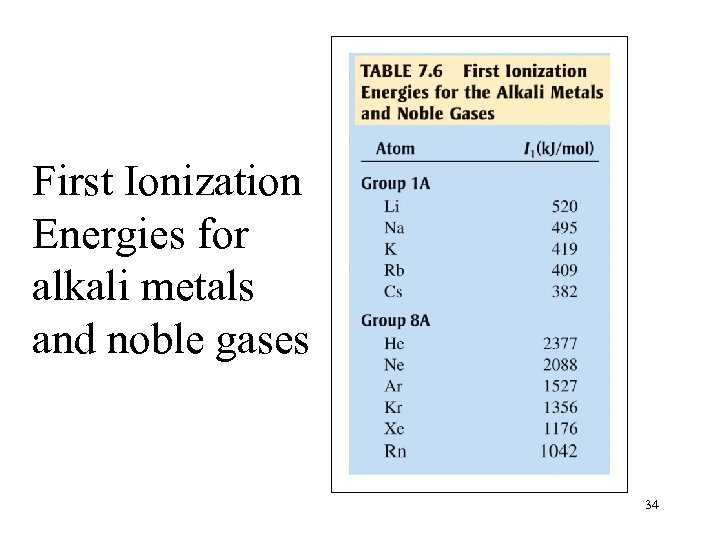 First Ionization Energies for alkali metals and noble gases 34
First Ionization Energies for alkali metals and noble gases 34
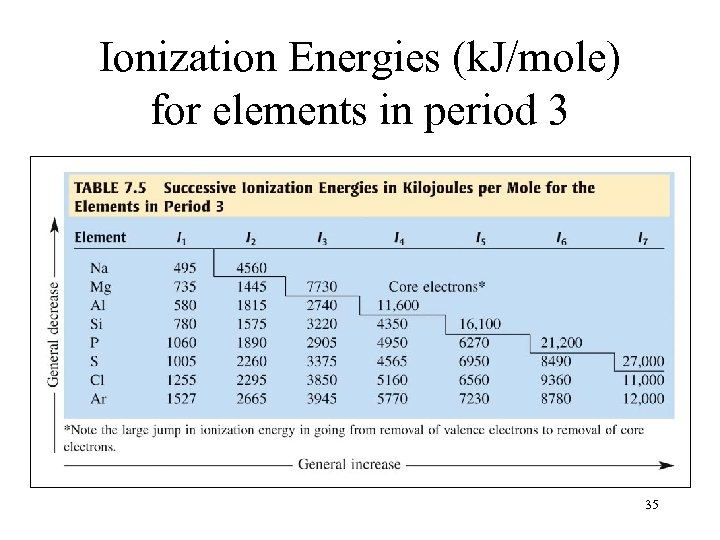 Ionization Energies (k. J/mole) for elements in period 3 35
Ionization Energies (k. J/mole) for elements in period 3 35
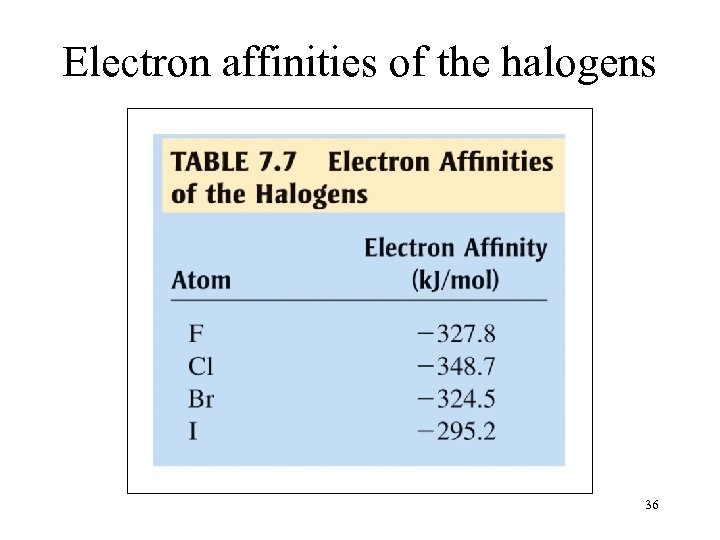 Electron affinities of the halogens 36
Electron affinities of the halogens 36
 Dmitri I. Mendeleev 37
Dmitri I. Mendeleev 37
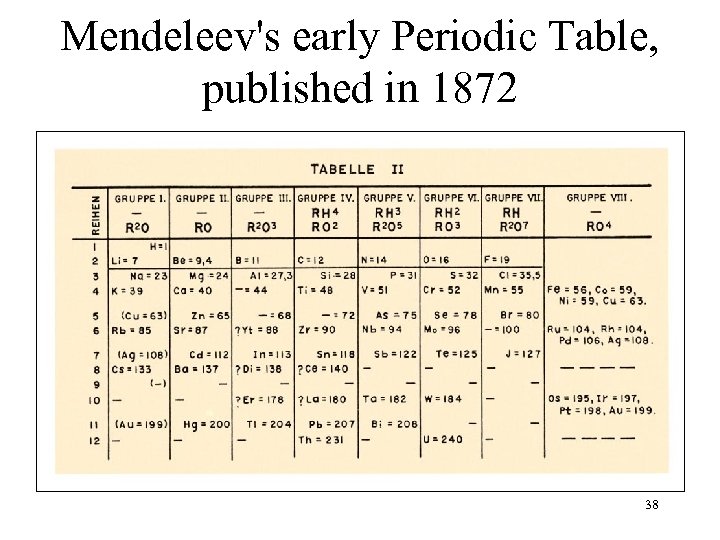 Mendeleev's early Periodic Table, published in 1872 38
Mendeleev's early Periodic Table, published in 1872 38
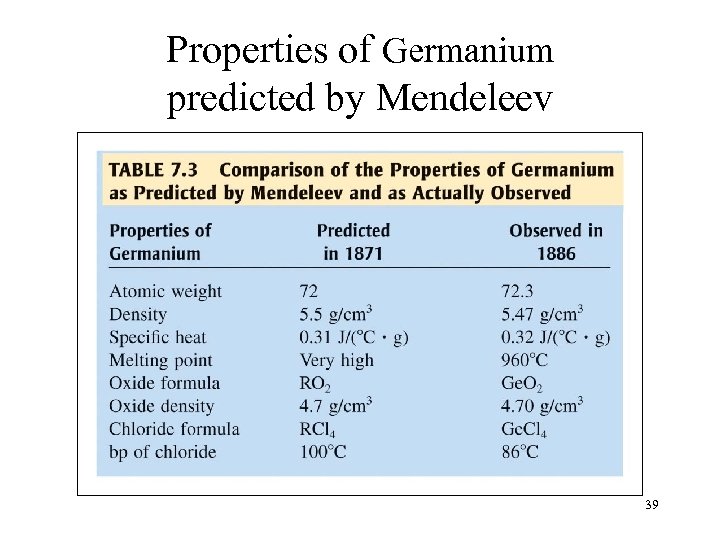 Properties of Germanium predicted by Mendeleev 39
Properties of Germanium predicted by Mendeleev 39
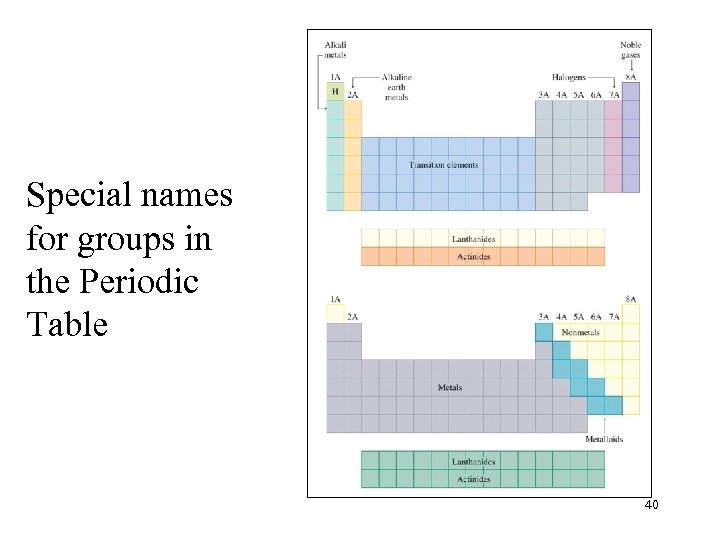 Special names for groups in the Periodic Table 40
Special names for groups in the Periodic Table 40
 Sodium metal 41
Sodium metal 41
 Potassium metal in a vial 42
Potassium metal in a vial 42
 Potassium reacts violently with water 43
Potassium reacts violently with water 43
 Calcium metal 44
Calcium metal 44
 Chromium may be used for plating 45
Chromium may be used for plating 45
 Dr. Glenn Seaborg 46
Dr. Glenn Seaborg 46
 The End 47
The End 47
 48
48
 Wave-Generating Apparatus 49
Wave-Generating Apparatus 49
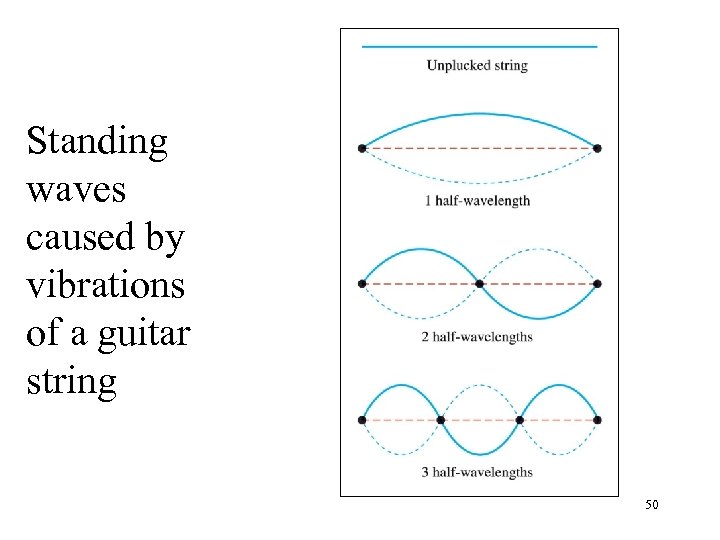 Standing waves caused by vibrations of a guitar string 50
Standing waves caused by vibrations of a guitar string 50
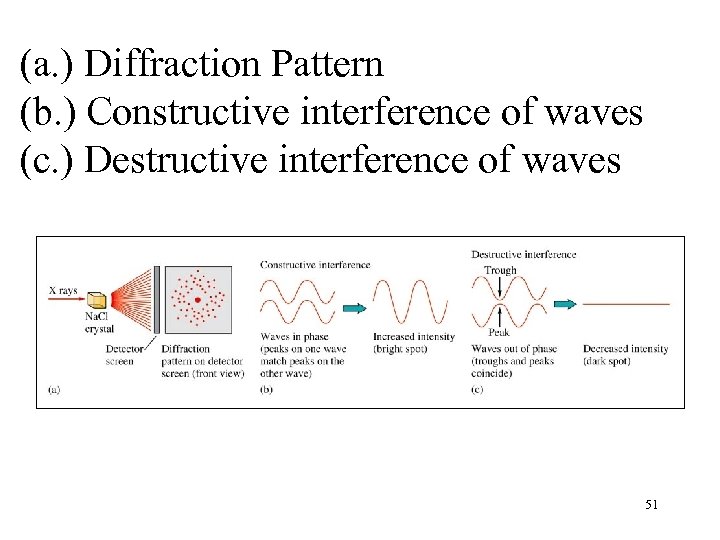 (a. ) Diffraction Pattern (b. ) Constructive interference of waves (c. ) Destructive interference of waves 51
(a. ) Diffraction Pattern (b. ) Constructive interference of waves (c. ) Destructive interference of waves 51
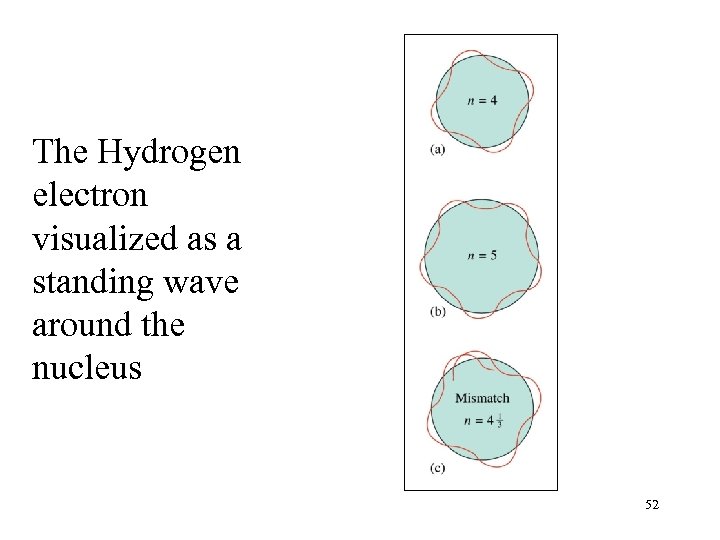 The Hydrogen electron visualized as a standing wave around the nucleus 52
The Hydrogen electron visualized as a standing wave around the nucleus 52
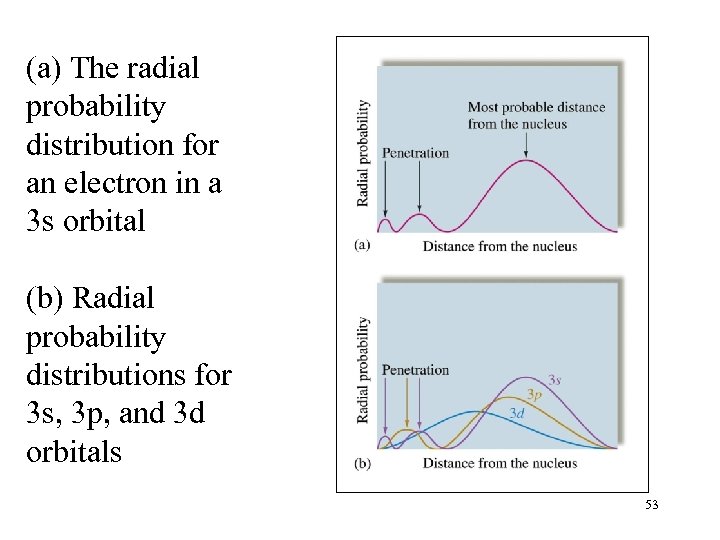 (a) The radial probability distribution for an electron in a 3 s orbital (b) Radial probability distributions for 3 s, 3 p, and 3 d orbitals 53
(a) The radial probability distribution for an electron in a 3 s orbital (b) Radial probability distributions for 3 s, 3 p, and 3 d orbitals 53
 Electrified Pickle 54
Electrified Pickle 54
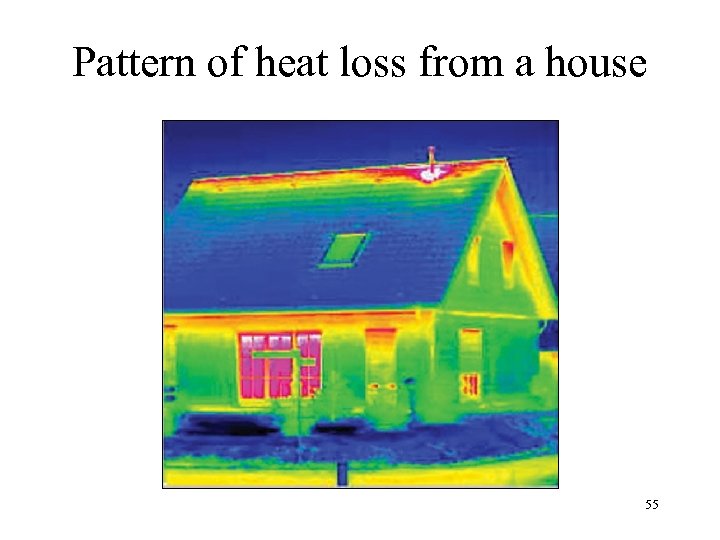 Pattern of heat loss from a house 55
Pattern of heat loss from a house 55
 The black mamba snake's venom kills by blocking potassium channels in nerve cells 56
The black mamba snake's venom kills by blocking potassium channels in nerve cells 56
 Albert Einstein 57
Albert Einstein 57
 Hydration Energies for Li+, Na+, and K+ Ions 58
Hydration Energies for Li+, Na+, and K+ Ions 58
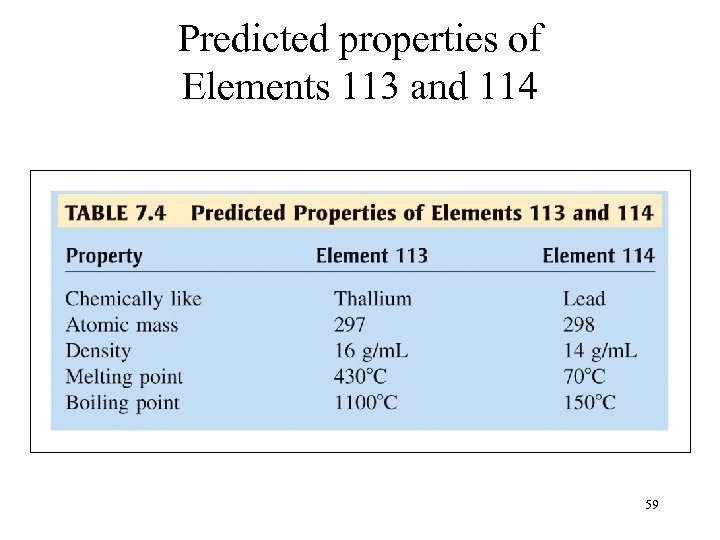 Predicted properties of Elements 113 and 114 59
Predicted properties of Elements 113 and 114 59


