5cb9fb27fb65aa6bebef14b976ab3077.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
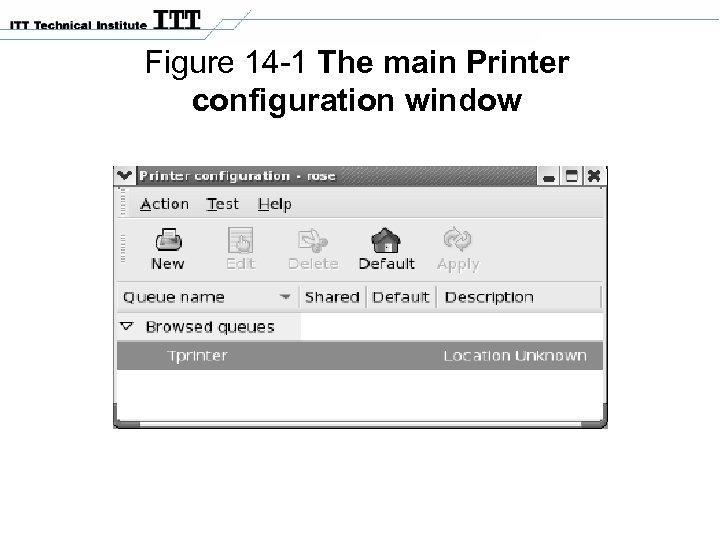 Figure 14 -1 The main Printer configuration window
Figure 14 -1 The main Printer configuration window
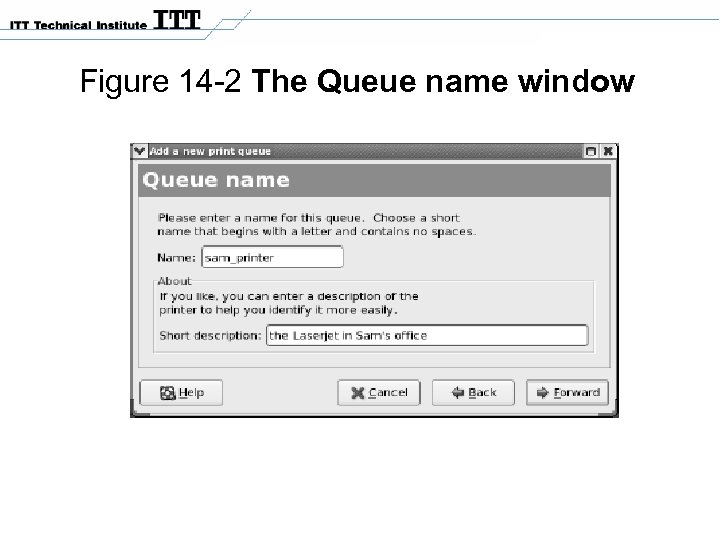 Figure 14 -2 The Queue name window
Figure 14 -2 The Queue name window
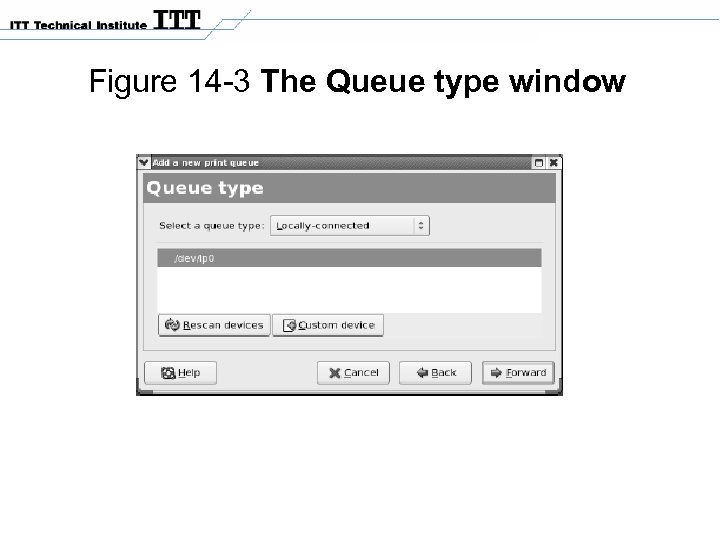 Figure 14 -3 The Queue type window
Figure 14 -3 The Queue type window
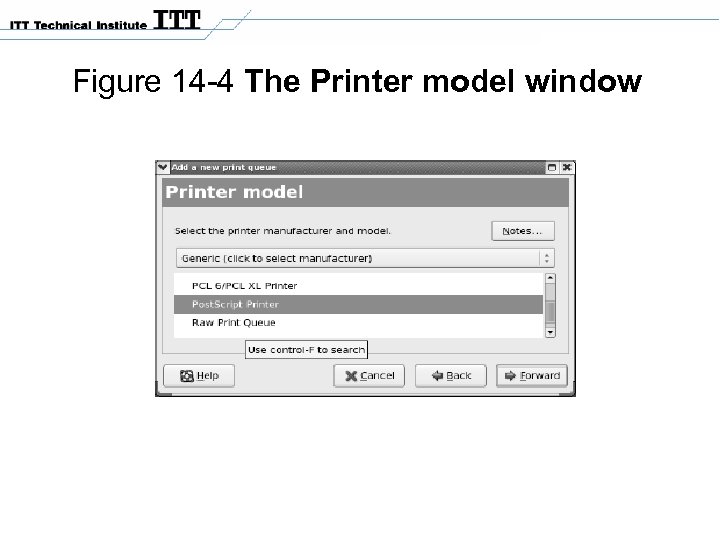 Figure 14 -4 The Printer model window
Figure 14 -4 The Printer model window
 Using CUPS • Common Unix Printer System (CUPS) , uses IPP/1. 1 to provide a complete printing system for Unix/Linux systems. It is free software provided under the terms of the GNU General Public License and GNU Library Public License. It’s also installed by default in a Fedora Linux installation, even if printing support is not selected. • Printers for CUPS are listed in the files /etc/printcap and /etc/cups/printers. conf. Before setting up a printer, check what printers are already available with lpstat –t so you don’t assign a new printer to a port that is already in use. • Printer Drivers Usually the generic Postscript driver will work for all Postscript printers.
Using CUPS • Common Unix Printer System (CUPS) , uses IPP/1. 1 to provide a complete printing system for Unix/Linux systems. It is free software provided under the terms of the GNU General Public License and GNU Library Public License. It’s also installed by default in a Fedora Linux installation, even if printing support is not selected. • Printers for CUPS are listed in the files /etc/printcap and /etc/cups/printers. conf. Before setting up a printer, check what printers are already available with lpstat –t so you don’t assign a new printer to a port that is already in use. • Printer Drivers Usually the generic Postscript driver will work for all Postscript printers.
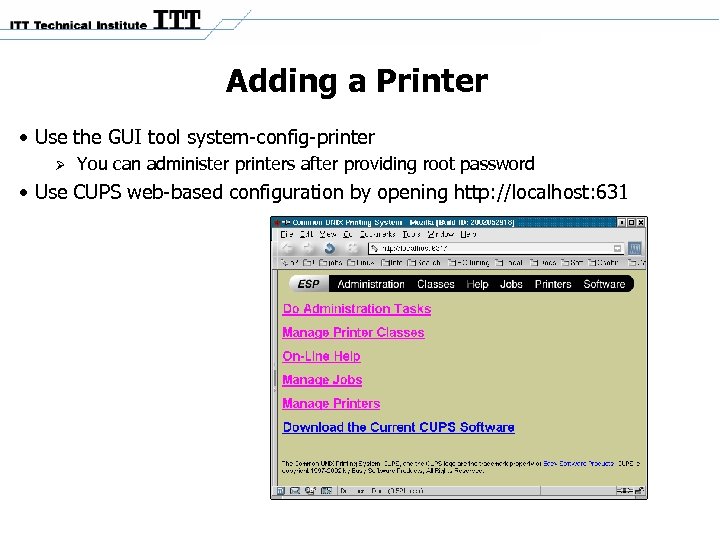 Adding a Printer • Use the GUI tool system-config-printer You can administer printers after providing root password • Use CUPS web-based configuration by opening http: //localhost: 631
Adding a Printer • Use the GUI tool system-config-printer You can administer printers after providing root password • Use CUPS web-based configuration by opening http: //localhost: 631
 Figure 14 -5 CUPS Web interface: main page
Figure 14 -5 CUPS Web interface: main page
 Figure 14 -6 CUPS Web interface: Add New Printer page
Figure 14 -6 CUPS Web interface: Add New Printer page
 Figure 14 -7 CUPS Web interface: Model/Driver page
Figure 14 -7 CUPS Web interface: Model/Driver page
 Figure 14 -8 CUPS Web interface: Printer page
Figure 14 -8 CUPS Web interface: Printer page
 Figure 14 -9 CUPS Web interface: Jobs page
Figure 14 -9 CUPS Web interface: Jobs page
 • CUPS offers a host of options that will allow you to configure it to meet your needs as a network administrator. You can set permissions on each printer, start and stop queues for troubleshooting, and upgrade driver—Post. Script Printer Definition, or PPD—files. You can even configure remote administration using the Web page, which is especially handy for servers that do not have a GUI installed, because it will allow you to use a Web browser from any computer on the network. • To configure remote administration, return to the CUPS Web page and click the Administration tab. Select the box that says Allow remote administration and click Change Settings. Type the root user and password and click OK. You can now access CUPS on that system from anywhere else on the network. © 2006 ITT Educational Services Inc. Linux operating System : : Unit 1: : Slide 12
• CUPS offers a host of options that will allow you to configure it to meet your needs as a network administrator. You can set permissions on each printer, start and stop queues for troubleshooting, and upgrade driver—Post. Script Printer Definition, or PPD—files. You can even configure remote administration using the Web page, which is especially handy for servers that do not have a GUI installed, because it will allow you to use a Web browser from any computer on the network. • To configure remote administration, return to the CUPS Web page and click the Administration tab. Select the box that says Allow remote administration and click Change Settings. Type the root user and password and click OK. You can now access CUPS on that system from anywhere else on the network. © 2006 ITT Educational Services Inc. Linux operating System : : Unit 1: : Slide 12
 • The command-line tools that come with CUPS have the same name and often the same syntax as the old lpr and lpd tools, but they are not the same tools. They have been written to work with CUPS. © 2006 ITT Educational Services Inc. Linux operating System : : Unit 1: : Slide 13
• The command-line tools that come with CUPS have the same name and often the same syntax as the old lpr and lpd tools, but they are not the same tools. They have been written to work with CUPS. © 2006 ITT Educational Services Inc. Linux operating System : : Unit 1: : Slide 13
 Printing with lpr • One of the simplest ways to send a text file to the printer is to use the lpr command. To print the install. log file from /root type: lpr install. log lpr has several command-line arguments to control output. • View all arguments with man lpr. • A few of the most use arguments are: - – #number to specify the printer to use, – -h to suppress printing the burst page – -s to create a symbolic link instead of copying the file to the spool directory. • You can also pipe the results of other programs to lpr: cat install. log | lpr • Print to another print queue by naming the queue in the lpr line. For example, to print the install. log file to the laserjet print queue type: lpr –P laserjet install. log
Printing with lpr • One of the simplest ways to send a text file to the printer is to use the lpr command. To print the install. log file from /root type: lpr install. log lpr has several command-line arguments to control output. • View all arguments with man lpr. • A few of the most use arguments are: - – #number to specify the printer to use, – -h to suppress printing the burst page – -s to create a symbolic link instead of copying the file to the spool directory. • You can also pipe the results of other programs to lpr: cat install. log | lpr • Print to another print queue by naming the queue in the lpr line. For example, to print the install. log file to the laserjet print queue type: lpr –P laserjet install. log
 Viewing the Queue • The lpq command is the main method used to monitor queues. To view the active jobs type: lpq All jobs in the default queue are displayed. • To display jobs in another queue use the –P destination option. lpq –P laserjet
Viewing the Queue • The lpq command is the main method used to monitor queues. To view the active jobs type: lpq All jobs in the default queue are displayed. • To display jobs in another queue use the –P destination option. lpq –P laserjet
 Removing a Print Job • Linux provides a command to remove jobs from the queue, lprm. To remove job 17 type: lprm 17 You can also remove all jobs with the command: lprm –
Removing a Print Job • Linux provides a command to remove jobs from the queue, lprm. To remove job 17 type: lprm 17 You can also remove all jobs with the command: lprm –
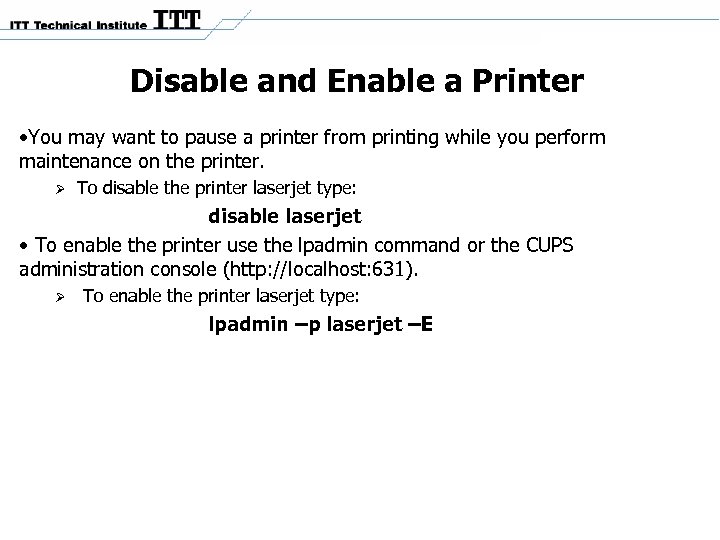 Disable and Enable a Printer • You may want to pause a printer from printing while you perform maintenance on the printer. To disable the printer laserjet type: disable laserjet • To enable the printer use the lpadmin command or the CUPS administration console (http: //localhost: 631). To enable the printer laserjet type: lpadmin –p laserjet –E
Disable and Enable a Printer • You may want to pause a printer from printing while you perform maintenance on the printer. To disable the printer laserjet type: disable laserjet • To enable the printer use the lpadmin command or the CUPS administration console (http: //localhost: 631). To enable the printer laserjet type: lpadmin –p laserjet –E
 Remove a Printer • If a printer is replaced or removed the old printer definition may need to be removed. To remove the printer laserjet type: lpadmin –x laserjet • You can use either GUI tool to remove configured printers Configured printers are available to all users by default. Removing a printer removes it for every user.
Remove a Printer • If a printer is replaced or removed the old printer definition may need to be removed. To remove the printer laserjet type: lpadmin –x laserjet • You can use either GUI tool to remove configured printers Configured printers are available to all users by default. Removing a printer removes it for every user.
 SAMBA • "Samba is an Open Source/Free Software suite that provides seamless file and print services to SMB/CIFS clients. " Samba is freely available, unlike other SMB/CIFS implementations, and allows for interoperability between Linux/Unix servers and Windows-based clients. • Samba allows Windows users to use printers connected to Linux systems just as they would use any other shared printers. © 2006 ITT Educational Services Inc. Linux operating System : : Unit 1: : Slide 19
SAMBA • "Samba is an Open Source/Free Software suite that provides seamless file and print services to SMB/CIFS clients. " Samba is freely available, unlike other SMB/CIFS implementations, and allows for interoperability between Linux/Unix servers and Windows-based clients. • Samba allows Windows users to use printers connected to Linux systems just as they would use any other shared printers. © 2006 ITT Educational Services Inc. Linux operating System : : Unit 1: : Slide 19
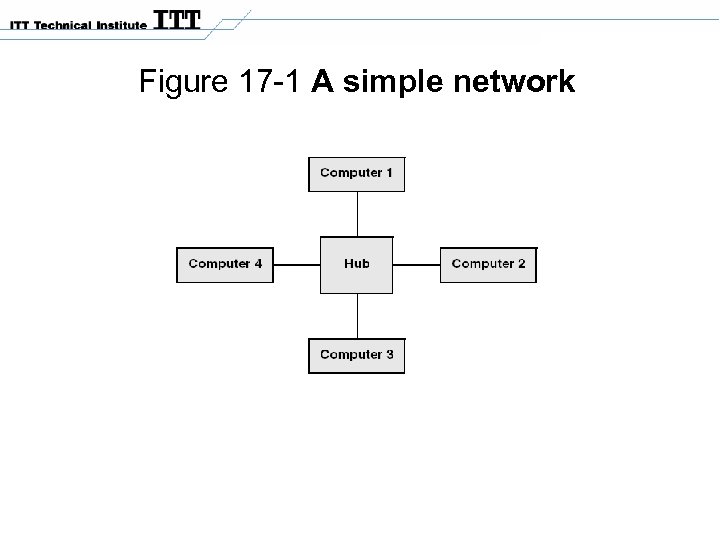 Figure 17 -1 A simple network
Figure 17 -1 A simple network
 IP addressing • An Internet Protocol (IP) address is a numerical identification (logical address) that is assigned to devices participating in a computer network utilizing the Internet Protocol for communication between its nodes. • Although IP addresses are stored as binary numbers, they are usually displayed in human-readable notations, such as 208. 77. 188. 166 (for IPv 4), and 2001: db 8: 0: 1234: 0: 567: 1: 1 (for IPv 6 - eight groups of four hexadecimal digits) • The role of the IP address has been characterized as follows: "A name indicates what we seek. An address indicates where it is. A route indicates how to get there. " © 2006 ITT Educational Services Inc. Linux operating System : : Unit 1: : Slide 21
IP addressing • An Internet Protocol (IP) address is a numerical identification (logical address) that is assigned to devices participating in a computer network utilizing the Internet Protocol for communication between its nodes. • Although IP addresses are stored as binary numbers, they are usually displayed in human-readable notations, such as 208. 77. 188. 166 (for IPv 4), and 2001: db 8: 0: 1234: 0: 567: 1: 1 (for IPv 6 - eight groups of four hexadecimal digits) • The role of the IP address has been characterized as follows: "A name indicates what we seek. An address indicates where it is. A route indicates how to get there. " © 2006 ITT Educational Services Inc. Linux operating System : : Unit 1: : Slide 21
 subnet masking • (SUBNETwork) A logical division of a local area network, which is created to improve performance and provide security. To enhance performance, subnets limit the number of nodes that compete for available bandwidth. Instead of one network handling all the traffic, the network is divided into groups of clients and servers that interact with each other most of the time. For security, the subnet divisions can be based on servers that have restricted applications. Routers are bridges are used to traverse network segments. In an IP network, the subnet is identified by a subnet mask • (SUBNETwork mask) The technique used by the IP protocol to create a subnet address. The subnet mask is a binary pattern that is stored in the client machine, server or router. It is matched with the IP address of a packet to determine which network segment the packet is destined for © 2006 ITT Educational Services Inc. Linux operating System : : Unit 1: : Slide 22
subnet masking • (SUBNETwork) A logical division of a local area network, which is created to improve performance and provide security. To enhance performance, subnets limit the number of nodes that compete for available bandwidth. Instead of one network handling all the traffic, the network is divided into groups of clients and servers that interact with each other most of the time. For security, the subnet divisions can be based on servers that have restricted applications. Routers are bridges are used to traverse network segments. In an IP network, the subnet is identified by a subnet mask • (SUBNETwork mask) The technique used by the IP protocol to create a subnet address. The subnet mask is a binary pattern that is stored in the client machine, server or router. It is matched with the IP address of a packet to determine which network segment the packet is destined for © 2006 ITT Educational Services Inc. Linux operating System : : Unit 1: : Slide 22
 default gateway • the device that passes traffic from the local subnet to devices on other subnets. The default gateway often connects a local network to the Internet, although internal gateways for local networks also exist. © 2006 ITT Educational Services Inc. Linux operating System : : Unit 1: : Slide 23
default gateway • the device that passes traffic from the local subnet to devices on other subnets. The default gateway often connects a local network to the Internet, although internal gateways for local networks also exist. © 2006 ITT Educational Services Inc. Linux operating System : : Unit 1: : Slide 23
 Domain Name System (DNS) • The DNS translates Internet domain and host names to IP addresses. DNS automatically converts the names we type in our Web browser address bar to the IP addresses of Web servers hosting those sites. © 2006 ITT Educational Services Inc. Linux operating System : : Unit 1: : Slide 24
Domain Name System (DNS) • The DNS translates Internet domain and host names to IP addresses. DNS automatically converts the names we type in our Web browser address bar to the IP addresses of Web servers hosting those sites. © 2006 ITT Educational Services Inc. Linux operating System : : Unit 1: : Slide 24
 Private IP addresses • An IP address is considered private if the IP number falls within one of the IP address ranges reserved for private uses by Internet standards groups. These private IP address ranges exist: • 10. 0 through 10. 255 169. 254. 0. 0 through 169. 254. 255 (APIPA only) 172. 16. 0. 0 through 172. 31. 255 192. 168. 0. 0 through 192. 168. 255 © 2006 ITT Educational Services Inc. Linux operating System : : Unit 1: : Slide 25
Private IP addresses • An IP address is considered private if the IP number falls within one of the IP address ranges reserved for private uses by Internet standards groups. These private IP address ranges exist: • 10. 0 through 10. 255 169. 254. 0. 0 through 169. 254. 255 (APIPA only) 172. 16. 0. 0 through 172. 31. 255 192. 168. 0. 0 through 192. 168. 255 © 2006 ITT Educational Services Inc. Linux operating System : : Unit 1: : Slide 25
 Network Address Translation (NAT) • In computer networking, network address translation (NAT) is the process of modifying network address information in datagram packet headers while in transit across a traffic routing device for the purpose of remapping a given address space into another. • Most often today, NAT is used in conjunction with network masquerading (or IP masquerading) which is a technique that hides an entire address space, usually consisting of private network addresses behind a single IP address in another, often public address space. This mechanism is implemented in a routing device that uses stateful translation tables to map the "hidden" addresses into a single address and then rewrites the outgoing Internet Protocol (IP) packets on exit so that they appear to originate from the router. • In the reverse communications path, responses are mapped back to the originating IP address using the rules ("state") stored in the translation tables. © 2006 ITT Educational Services Inc. Linux operating System : : Unit 1: : Slide 26
Network Address Translation (NAT) • In computer networking, network address translation (NAT) is the process of modifying network address information in datagram packet headers while in transit across a traffic routing device for the purpose of remapping a given address space into another. • Most often today, NAT is used in conjunction with network masquerading (or IP masquerading) which is a technique that hides an entire address space, usually consisting of private network addresses behind a single IP address in another, often public address space. This mechanism is implemented in a routing device that uses stateful translation tables to map the "hidden" addresses into a single address and then rewrites the outgoing Internet Protocol (IP) packets on exit so that they appear to originate from the router. • In the reverse communications path, responses are mapped back to the originating IP address using the rules ("state") stored in the translation tables. © 2006 ITT Educational Services Inc. Linux operating System : : Unit 1: : Slide 26
 Configuring the System • Kudzu detects and configures new hardware • System-config-network or iwconfig can be used to augment the information kudzu collects. © 2006 ITT Educational Services Inc. Linux operating System : : Unit 1: : Slide 27
Configuring the System • Kudzu detects and configures new hardware • System-config-network or iwconfig can be used to augment the information kudzu collects. © 2006 ITT Educational Services Inc. Linux operating System : : Unit 1: : Slide 27
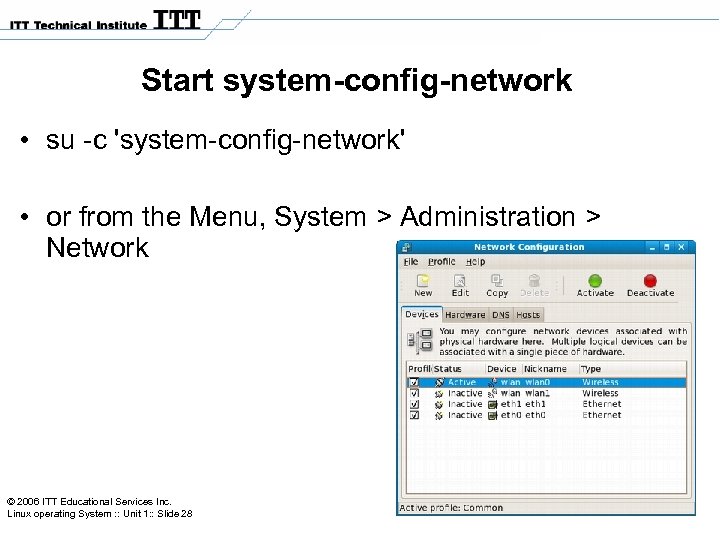 Start system-config-network • su -c 'system-config-network' • or from the Menu, System > Administration > Network © 2006 ITT Educational Services Inc. Linux operating System : : Unit 1: : Slide 28
Start system-config-network • su -c 'system-config-network' • or from the Menu, System > Administration > Network © 2006 ITT Educational Services Inc. Linux operating System : : Unit 1: : Slide 28
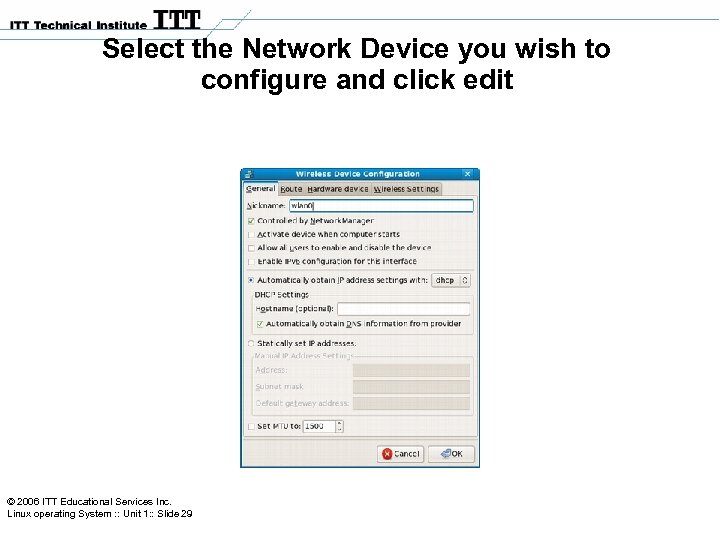 Select the Network Device you wish to configure and click edit © 2006 ITT Educational Services Inc. Linux operating System : : Unit 1: : Slide 29
Select the Network Device you wish to configure and click edit © 2006 ITT Educational Services Inc. Linux operating System : : Unit 1: : Slide 29
 To allow Network. Manager to control both your wired and wireless devices you need to make the following changes. • Tick "Controlled by Network. Manager" Untick "Activate device when computer starts" Click OK to save the changes © 2006 ITT Educational Services Inc. Linux operating System : : Unit 1: : Slide 30
To allow Network. Manager to control both your wired and wireless devices you need to make the following changes. • Tick "Controlled by Network. Manager" Untick "Activate device when computer starts" Click OK to save the changes © 2006 ITT Educational Services Inc. Linux operating System : : Unit 1: : Slide 30
 Reboot the machine for the changes to take effect. © 2006 ITT Educational Services Inc. Linux operating System : : Unit 1: : Slide 31
Reboot the machine for the changes to take effect. © 2006 ITT Educational Services Inc. Linux operating System : : Unit 1: : Slide 31
 • Network. Manager • Ensure this is started in your services © 2006 ITT Educational Services Inc. Linux operating System : : Unit 1: : Slide 32
• Network. Manager • Ensure this is started in your services © 2006 ITT Educational Services Inc. Linux operating System : : Unit 1: : Slide 32


