3884b0d31c3ed57ab5ac21dd37425566.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 5
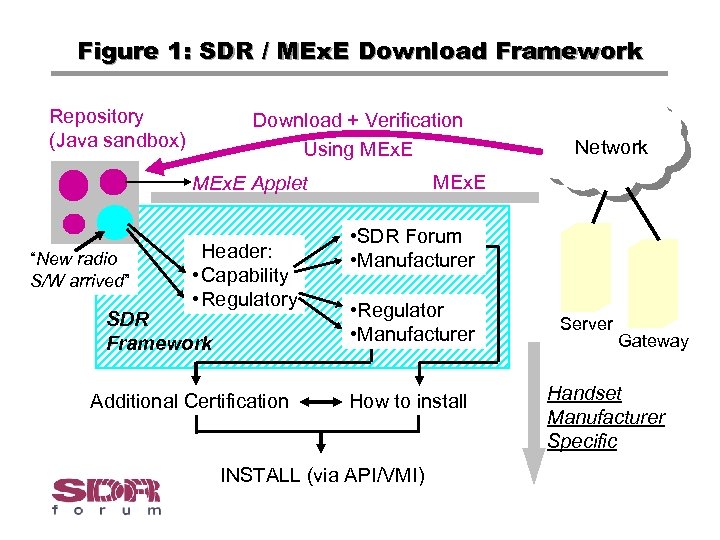 Figure 1: SDR / MEx. E Download Framework Repository (Java sandbox) Download + Verification Using MEx. E Applet “New radio S/W arrived” Header: • Capability • Regulatory SDR Framework Additional Certification Network • SDR Forum • Manufacturer • Regulator • Manufacturer How to install INSTALL (via API/VMI) Server Gateway Handset Manufacturer Specific
Figure 1: SDR / MEx. E Download Framework Repository (Java sandbox) Download + Verification Using MEx. E Applet “New radio S/W arrived” Header: • Capability • Regulatory SDR Framework Additional Certification Network • SDR Forum • Manufacturer • Regulator • Manufacturer How to install INSTALL (via API/VMI) Server Gateway Handset Manufacturer Specific
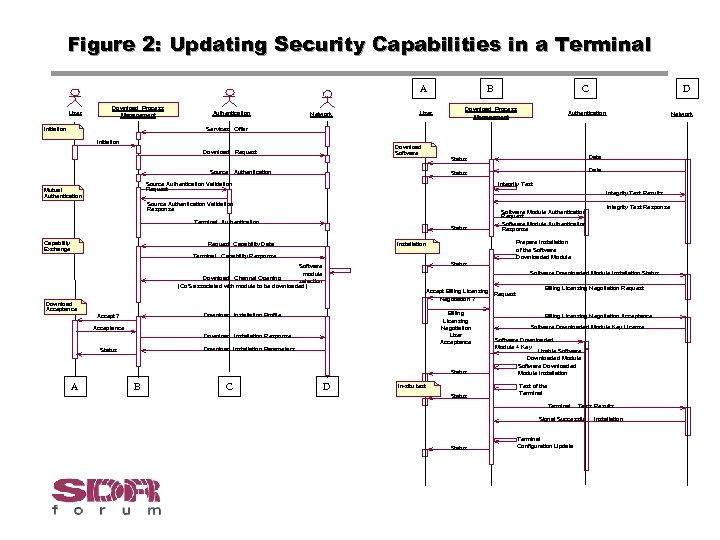 Figure 2: Updating Security Capabilities in a Terminal A User Download Process Management Initiation Authentication Network User B C D Download Process Management Authentication Network Services Offer Initiation Download Software Download Request Data Status Source Authentication Mutual Authentication Integrity Test Results Source Authentication Validation Response Terminal Authentication Capability Exchange Data Status Source Authentication Validation Request Status Software Module Authentication Request Software Module Authentication Response Prepare Installation of the Software Downloaded Module Installation Request Capability Data Terminal Capability Response Status Software module Download Channel Opening selection (Qo. S associated with module to be downloaded) Download Acceptance Software Downloaded Module Installation Status Accept Billing Licensing Request Negotiation ? Billing Licensing Negotiation User Acceptance Download Installation Profile Accept ? Acceptance Download Installation Response Download Installation Parameters Status A B C Integrity Test Response D In-situ test Status Billing Licensing Negotiation Request Billing Licensing Negotiation Acceptance Software Downloaded Module Key License Software Downloaded Module + Key Usable Software Downloaded Module Installation Test of the Terminal Tests Results Signal Successful Status Terminal Configuration Update Installation
Figure 2: Updating Security Capabilities in a Terminal A User Download Process Management Initiation Authentication Network User B C D Download Process Management Authentication Network Services Offer Initiation Download Software Download Request Data Status Source Authentication Mutual Authentication Integrity Test Results Source Authentication Validation Response Terminal Authentication Capability Exchange Data Status Source Authentication Validation Request Status Software Module Authentication Request Software Module Authentication Response Prepare Installation of the Software Downloaded Module Installation Request Capability Data Terminal Capability Response Status Software module Download Channel Opening selection (Qo. S associated with module to be downloaded) Download Acceptance Software Downloaded Module Installation Status Accept Billing Licensing Request Negotiation ? Billing Licensing Negotiation User Acceptance Download Installation Profile Accept ? Acceptance Download Installation Response Download Installation Parameters Status A B C Integrity Test Response D In-situ test Status Billing Licensing Negotiation Request Billing Licensing Negotiation Acceptance Software Downloaded Module Key License Software Downloaded Module + Key Usable Software Downloaded Module Installation Test of the Terminal Tests Results Signal Successful Status Terminal Configuration Update Installation
 Figure 3: The Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) • PKI is generally viewed as an essential technology for E-business. It should be amenable to wireless as well as wired transactions • PKI “signs and seals” an electronic transaction: identifies, authenticates the parties involved, and protects their information from compromise • Each PKI user has a registered identity stored in a digital certificate • PKI provides i) confidentiality through encryption; ii) authentication, data integrity & nonrepudiation through digital certificate signatures • PKI acts in a consistent manner across a wide variety of applications
Figure 3: The Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) • PKI is generally viewed as an essential technology for E-business. It should be amenable to wireless as well as wired transactions • PKI “signs and seals” an electronic transaction: identifies, authenticates the parties involved, and protects their information from compromise • Each PKI user has a registered identity stored in a digital certificate • PKI provides i) confidentiality through encryption; ii) authentication, data integrity & nonrepudiation through digital certificate signatures • PKI acts in a consistent manner across a wide variety of applications
 Figure 4: Elements of a PKI • Manages key and certificate lifecycle on behalf of users and applications • Partial list of PKI functions: – Certification Authority (CA, issues digital certificates) – Certificate repository and revocation system – Key management (issuance, update, backup, recovery, etc. ) – Cross-certification (extend 3 rd-party trust between CA domains) – Support for legacy applications • All users have registered identity thru a PK certificate (via CA) • User’s corresponding secret key must be protected in the terminal (e. g. , tamper-proof Smart. Card or encrypted storage) • Standard protocol for application interface is PKI X. 509
Figure 4: Elements of a PKI • Manages key and certificate lifecycle on behalf of users and applications • Partial list of PKI functions: – Certification Authority (CA, issues digital certificates) – Certificate repository and revocation system – Key management (issuance, update, backup, recovery, etc. ) – Cross-certification (extend 3 rd-party trust between CA domains) – Support for legacy applications • All users have registered identity thru a PK certificate (via CA) • User’s corresponding secret key must be protected in the terminal (e. g. , tamper-proof Smart. Card or encrypted storage) • Standard protocol for application interface is PKI X. 509
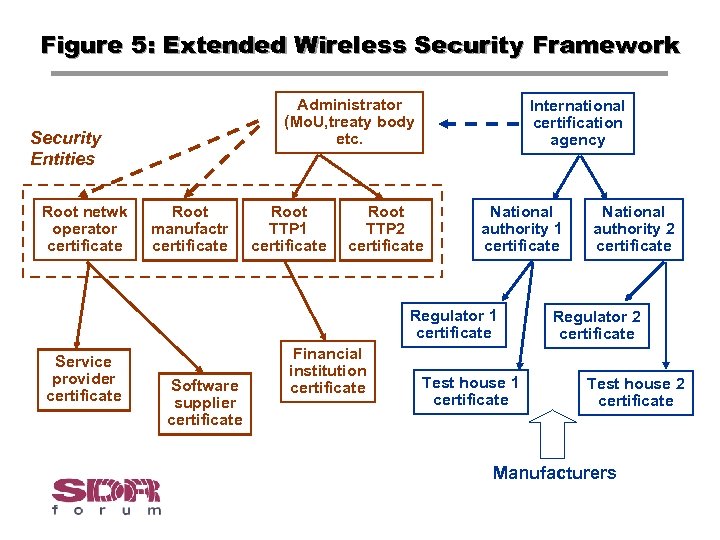 Figure 5: Extended Wireless Security Framework Administrator (Mo. U, treaty body etc. Security Entities Root netwk operator certificate Root manufactr certificate Root TTP 1 certificate International certification agency Root TTP 2 certificate National authority 1 certificate Regulator 1 certificate Service provider certificate Software supplier certificate Financial institution certificate Test house 1 certificate National authority 2 certificate Regulator 2 certificate Test house 2 certificate Manufacturers
Figure 5: Extended Wireless Security Framework Administrator (Mo. U, treaty body etc. Security Entities Root netwk operator certificate Root manufactr certificate Root TTP 1 certificate International certification agency Root TTP 2 certificate National authority 1 certificate Regulator 1 certificate Service provider certificate Software supplier certificate Financial institution certificate Test house 1 certificate National authority 2 certificate Regulator 2 certificate Test house 2 certificate Manufacturers


