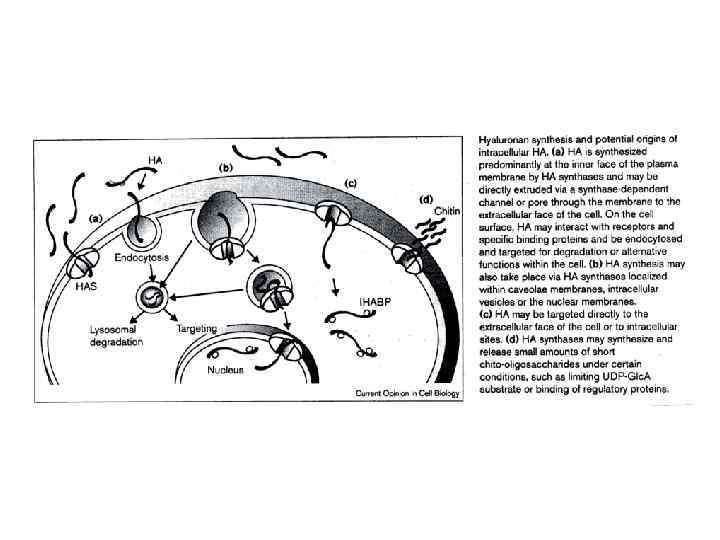
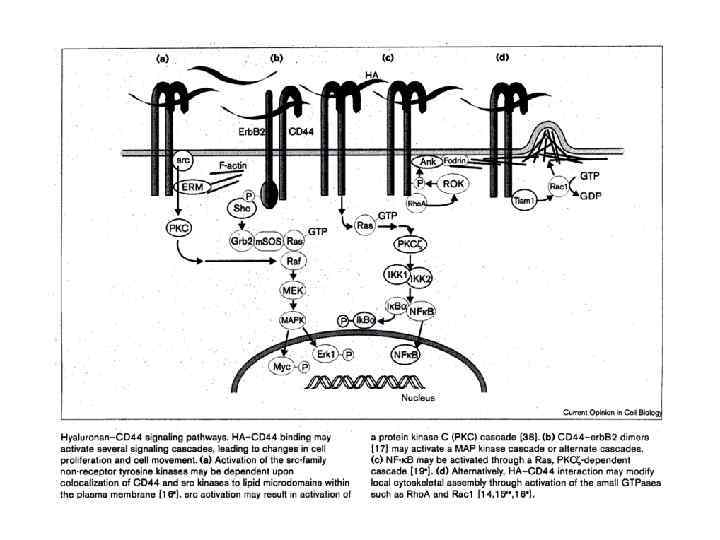
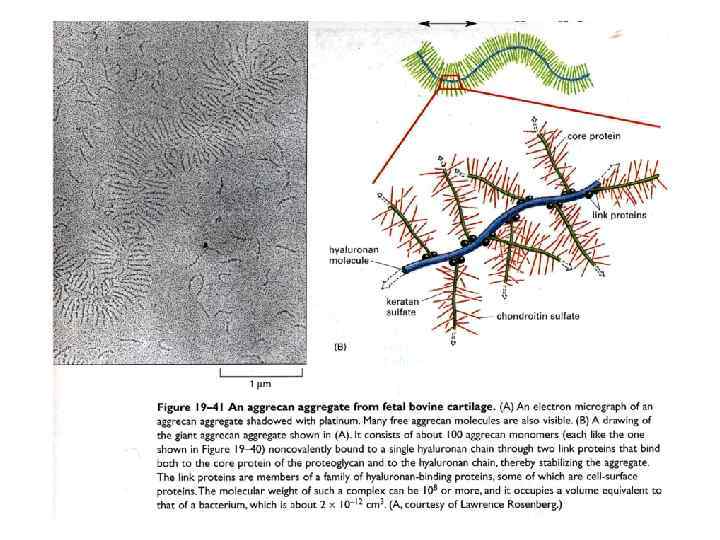
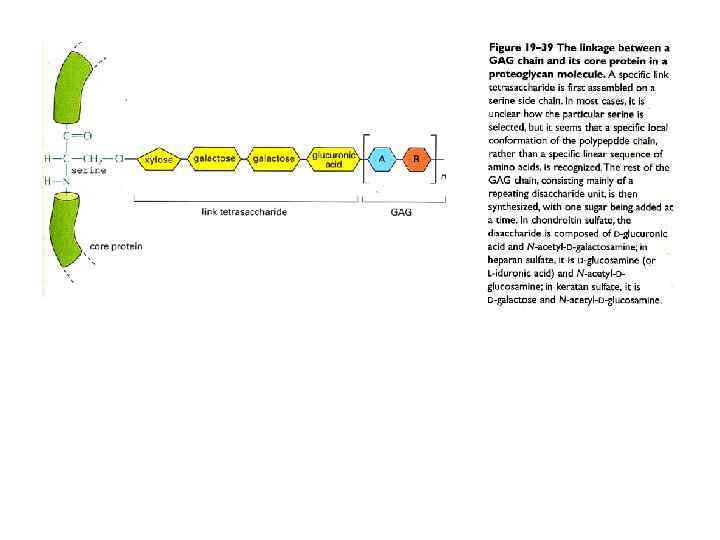
През МАТРИКС.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
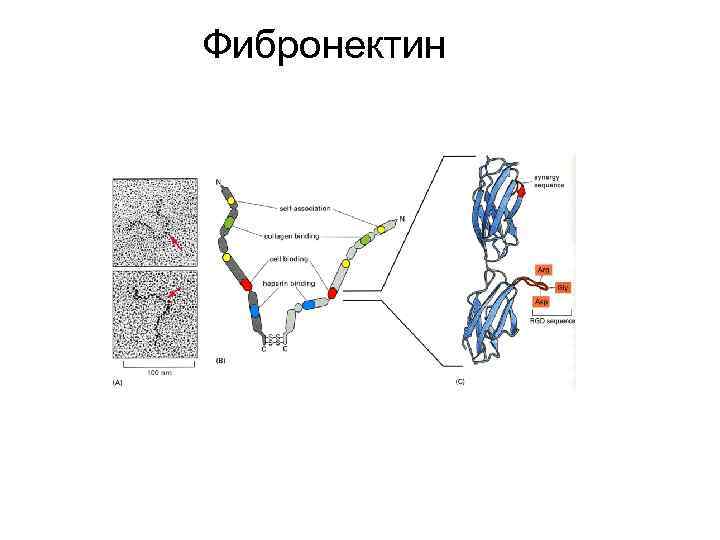
Фибронектин
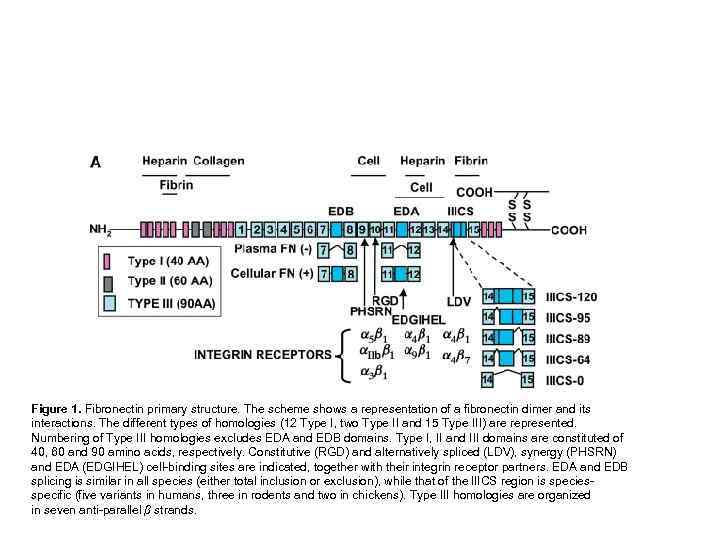
Figure 1. Fibronectin primary structure. The scheme shows a representation of a fibronectin dimer and its interactions. The different types of homologies (12 Type I, two Type II and 15 Type III) are represented. Numbering of Type III homologies excludes EDA and EDB domains. Type I, II and III domains are constituted of 40, 60 and 90 amino acids, respectively. Constitutive (RGD) and alternatively spliced (LDV), synergy (PHSRN) and EDA (EDGIHEL) cell-binding sites are indicated, together with their integrin receptor partners. EDA and EDB splicing is similar in all species (either total inclusion or exclusion), while that of the IIICS region is speciesspecific (five variants in humans, three in rodents and two in chickens). Type III homologies are organized in seven anti-parallel β strands.

Figure 1. Fibronectin primary structure. The scheme shows a representation of a fibronectin dimer and its interactions (A). The different types of homologies (12 Type I, two Type II and 15 Type III) are represented. Numbering of Type III homologies excludes EDA and EDB domains. Type I, II and III domains are constituted of 40, 60 and 90 amino acids, respectively. Constitutive (RGD) and alternatively spliced (LDV), synergy (PHSRN) and EDA (EDGIHEL) cell-binding sites are indicated, together with their integrin receptor partners. EDA and EDB splicing is similar in all species (either total inclusion or exclusion), while that of the IIICS region is species-specific (five variants in humans, three in rodents and two in chickens). Type III homologies are organized in seven anti-parallel β strands
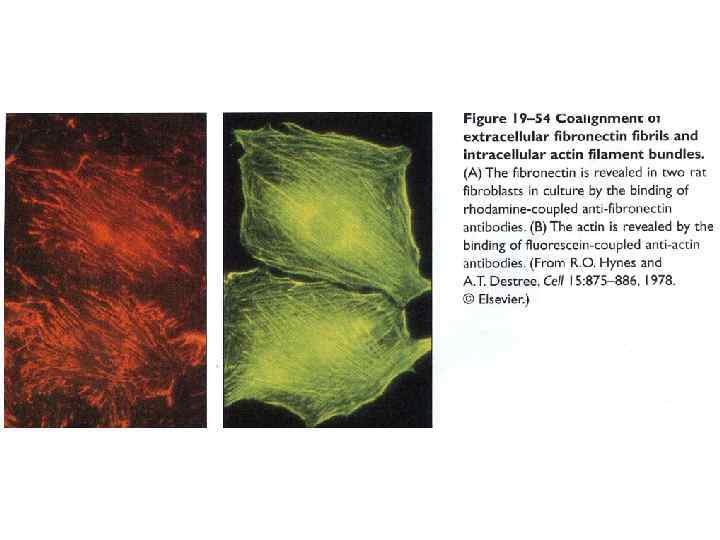
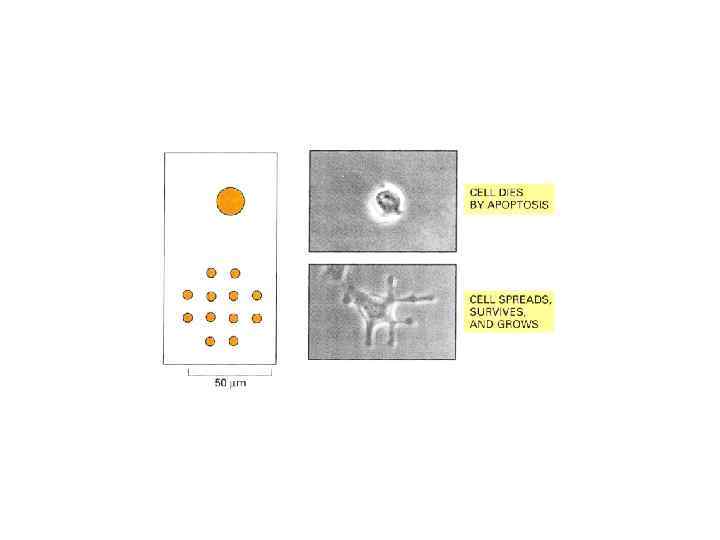
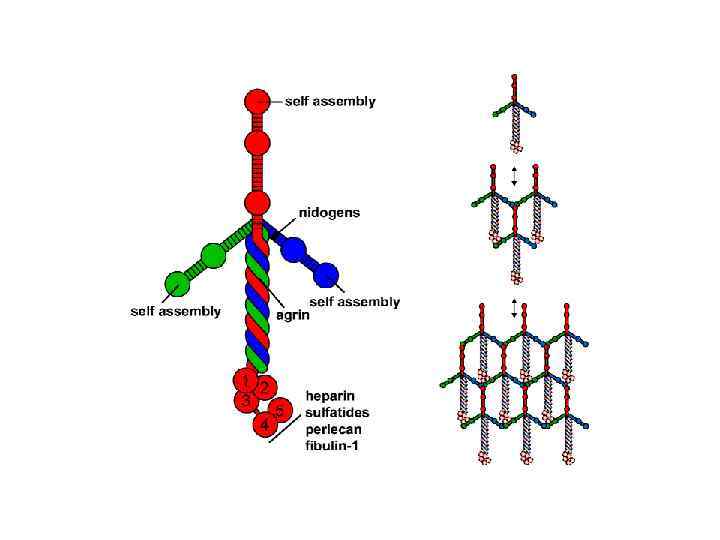
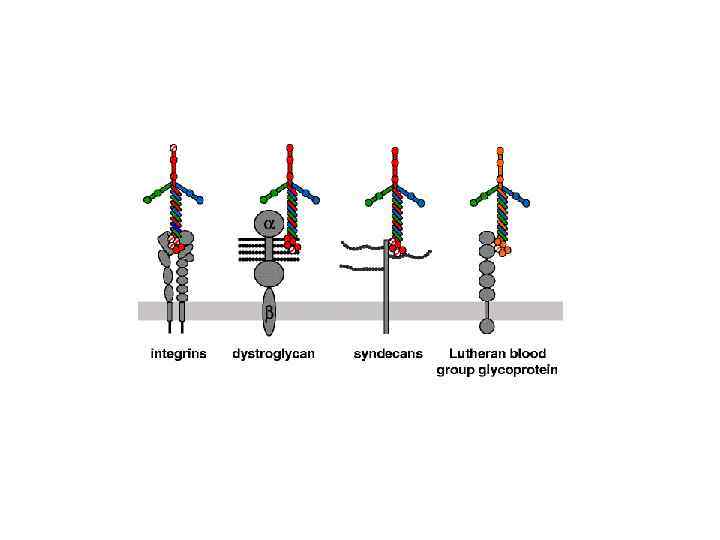
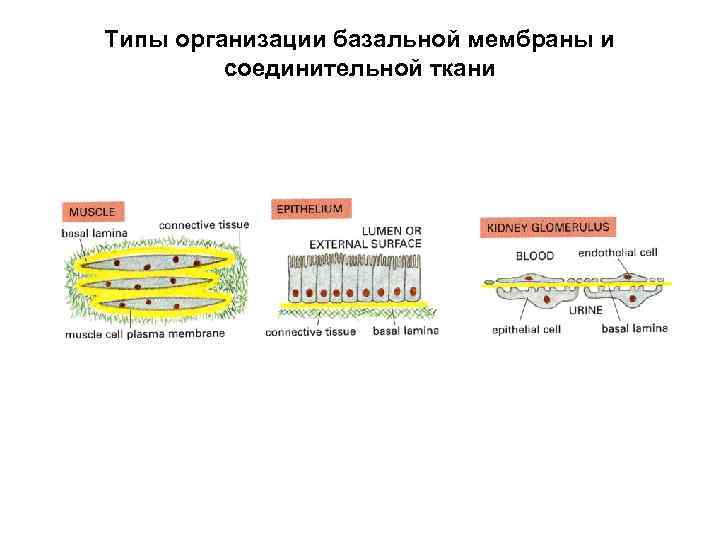
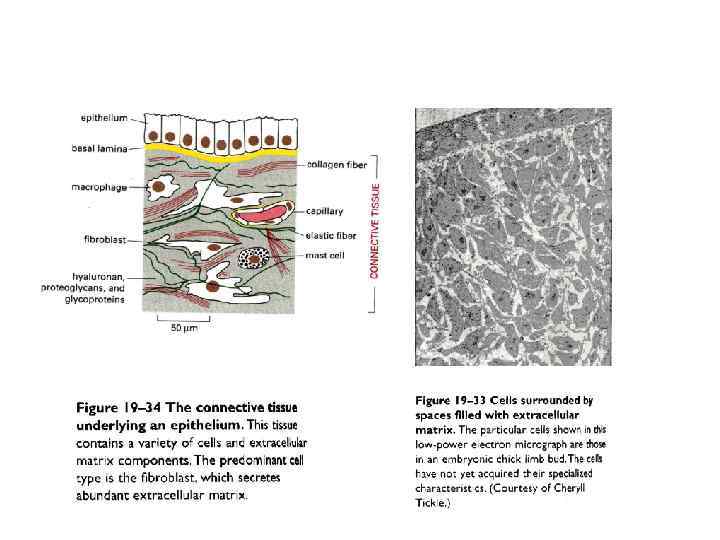
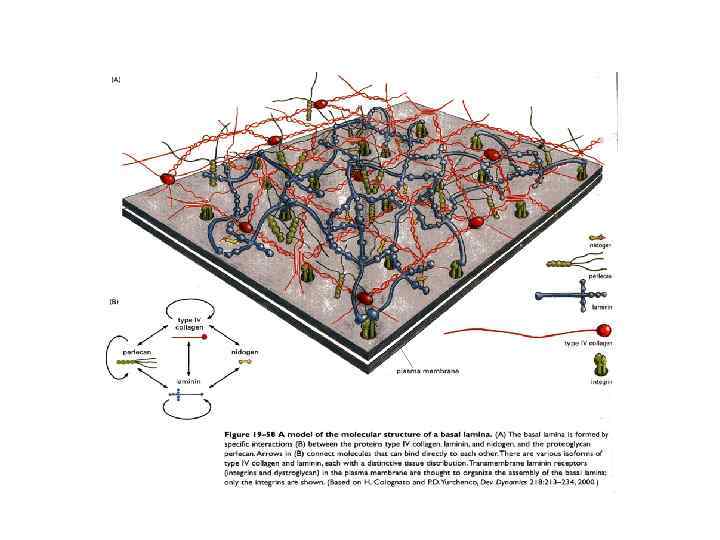
Типы организации базальной мембраны и соединительной ткани
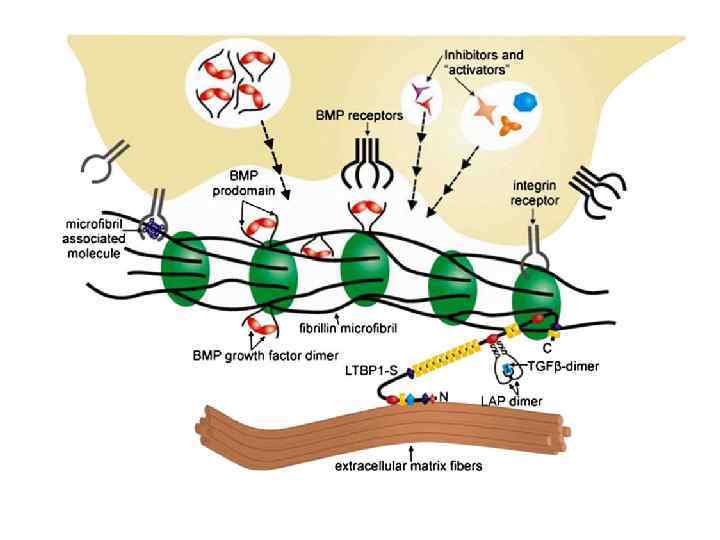

Representation of cellular and molecular interactions with fibrillin microfibrils that work in concert to control growth factor signaling. The large latent TGFβ complex is associated with fibrillin microfibrils through interactions between LTBPs and fibrillin. BMP complexes are targeted to fibrillin microfibrils through direct interactions with fibrillin. Cells receive positional information through integrin interactions with fibrillin or with microfibril-associated proteins and can activate ECM-sequestered growth factors or inhibit activated growth factors as required by the tissue or developmental context. Defects in fibrillin microfibril structure, perceived by the cell, can result in the secretion of activators of growth factor signaling, leading to MFS and related disorders of the connective tissue

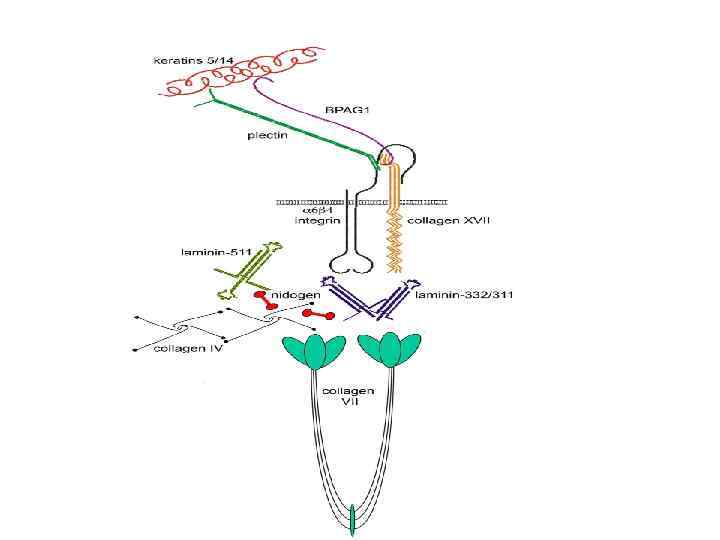


Базальная мембрана в зачатке конечности цыпленка
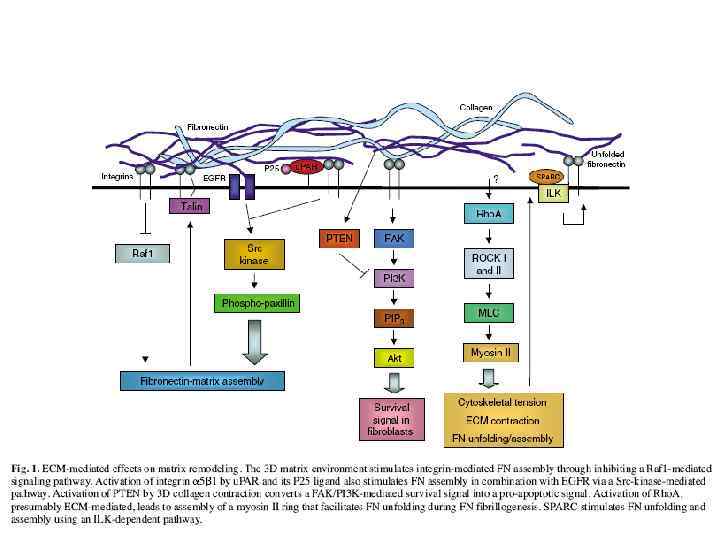
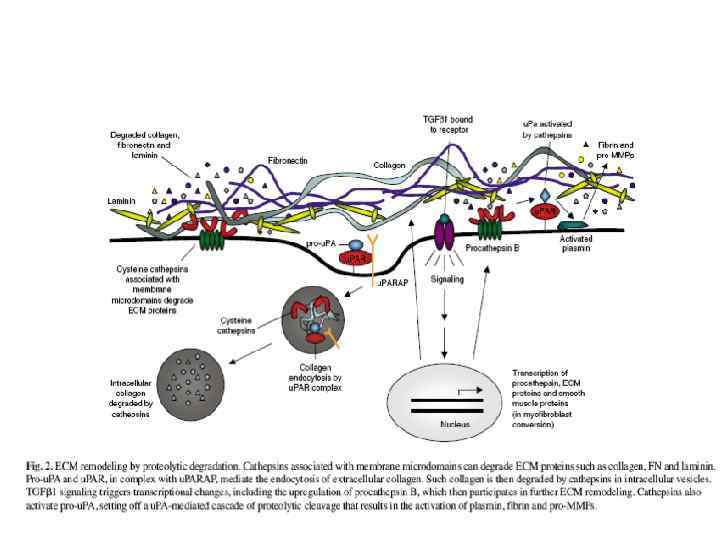
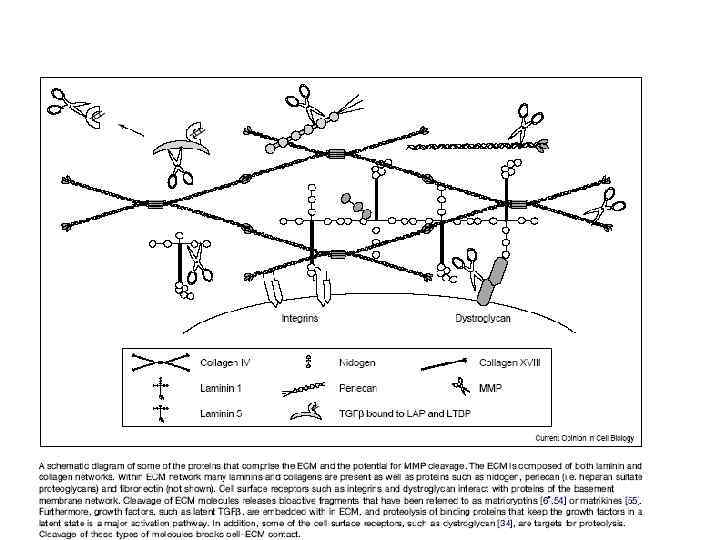
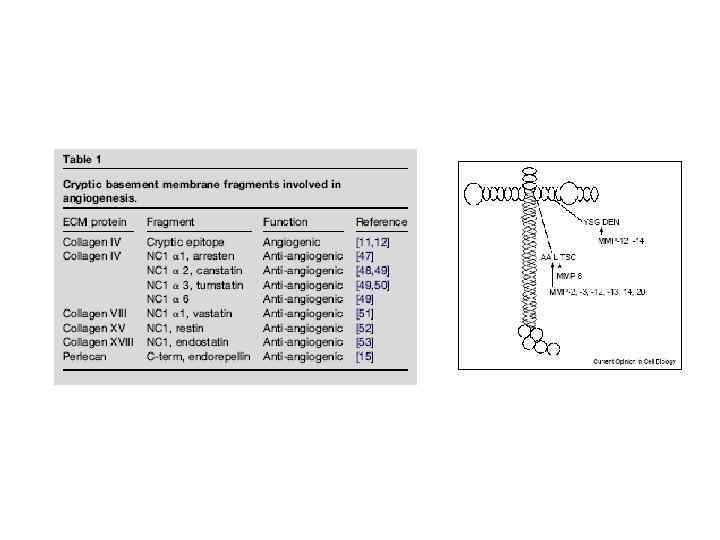
През МАТРИКС.ppt