a80c55879a014289bf8c5efe80581747.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13

FHI Biotechnology Approaches Marker-aided breeding Clonal Testing New varieties Transgenics Genome Sequencing GE trees

SUNY-ESF team summer 2011 Chuck Maynard, Co-PI Bill Powell, Co-PI Linda Mc. Guigan – TC lab manager (80% TACFNY) Kathleen Baier – technician (100% FHI) Andy Newhouse – technician (50% FHI/50% BRAG) Lilibeth Northern – technician (100% FHI) Amelia Bo Zhang – Ph. D grad (CPBR) Allison Oakes – MS grad (TACFNY) Kristen Russell Steward – MPS grad (FHI) Aaron Barrigar – Undergrad (BRAG) Mike Cook – Undergrad (BRAG) Jessica Miller – Undergrad (BRAG) Ashoor Howil – Undergrad (volunteer)

Objectives/deliverables • Held “Early Screening” workshop (1 st year) – Dana Nelson, Susan Mc. Cord, & Bill Powell – May 17 -19, 2010, Asheville, NC • Supplemental FHI grant – Develop an early screening assay (2 nd & 3 rd year) – Summary below Combined data from 5 experiments 48 -52 inoculations per leaf type Error bars = 1 SEM T-test: P< 0. 0001 (Andy Newhouse)
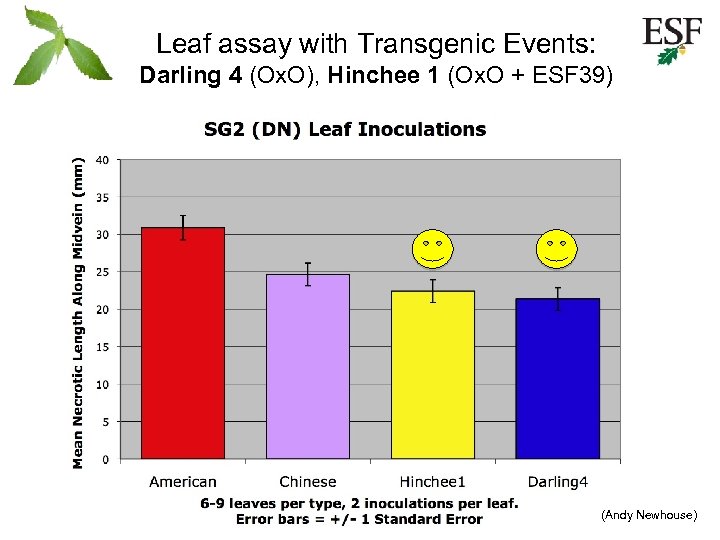
Leaf assay with Transgenic Events: Darling 4 (Ox. O), Hinchee 1 (Ox. O + ESF 39) (Andy Newhouse)

Darling 4 and Darling 5 inoculations this summer, small stem assays to determine levels of resistance & confirm leaf assays Confirmed gene expression (Andy Newhouse)

Objectives/deliverables • Establish field site in New York with eight older vector constructs (300 trees minimum) – Currently have five sites planted with two more planned • Lafayette Rd Experiment Station (Syracuse, NY) - 278 transgenic trees (23 events) • Heiberg Forest (Tully, NY) – 30 transgenic trees (six events) • Zoar Valley (near Buffalo, NY) – 61 transgenic trees (six events) • Lasdon Park (near NYC, NY) – 30 transgenic trees (six events) • Biofuel Center Demo Plot (near Raleigh, NC) – 20 transgenic trees ( four events) – Total of 419 transgenic American chestnut trees planted – Approximately 40 this spring and many more this fall • Estimated over 500 will be planted by end of year 2 – USDA APHIS BRS permit #10 -357 -118 r
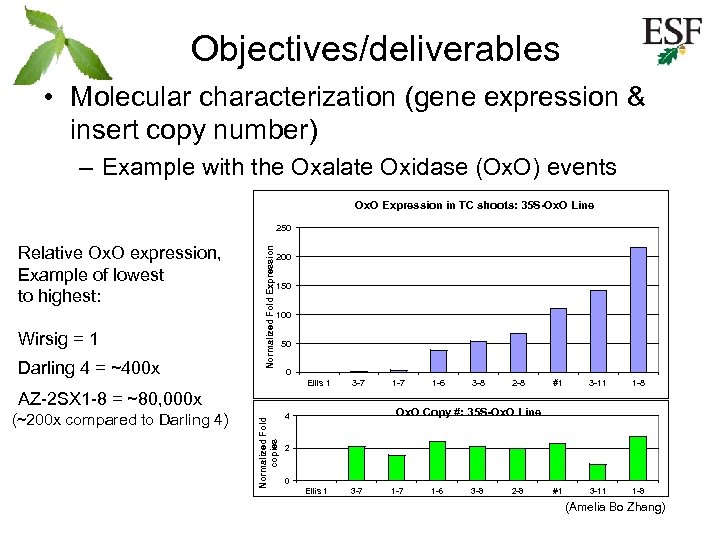
Objectives/deliverables • Molecular characterization (gene expression & insert copy number) – Example with the Oxalate Oxidase (Ox. O) events Ox. O Expression in TC shoots: 35 S-Ox. O Line Relative Ox. O expression, Example of lowest to highest: Wirsig = 1 Darling 4 = ~400 x Normalized Fold Expression 250 200 150 100 50 0 Ellis 1 3 -7 (~200 x compared to Darling 4) Normalized Fold copies AZ-2 SX 1 -8 = ~80, 000 x 1 -7 1 -6 3 -8 2 -8 #1 3 -11 1 -8 Ox. O Copy #: 35 S-Ox. O Line 4 2 0 Ellis 1 3 -7 1 -6 3 -8 2 -8 (Amelia Bo Zhang)

Objectives/deliverables – Test selected events for Phytophthora resistance • Steve Jeffers, Clemson • USDA APHIS BRS transportation notice # 11 -125 -101 n • First two events sent with clonal controls (10 trees each) Gene expression of ESF 39 antimicrobial peptide in root tissues of Hinchee 1 & 2 events No significant difference in relative expression between the two events (p = 0. 8117, α =. 05, t = 0. 2463, df = 8)

Objectives/deliverables • Supplemental FHI grant, add two early flowering gene constructs from Steve Strauss’ lab to the transformation pipeline to determine if they can induce early flowering in the greenhouse. (2 nd & 3 rd year) 7 events with heat shock promoter, 1 event with constitutive promoter Trees with desirable traits Early flowering transgenic tree cross Segregate out ~50% of plants with transgene Early flowering F 1, BC 2, etc. Non-transgenic

Objectives/deliverables (additional deliverables not specified in original FHI grant) • Clone candidate genes (CGs) from full-length c. DNA library from Chinese chestnut stems (up to 30 total). – Collaborations with Penn State, Clemson, USFS, UGA, & SUNY-ESF • Adding the new 2 nd Generation CG vectors to the transformation pipeline – UGA & SUNY-ESF Chinese chestnut CG, putative ID 1 β-1, 3 glucanase 9 Ethylene-response transcription factor 2 CBS domain protein 10 Cysteine proteinase inhibitor 3 UDP glucosyltransferase 11 Lipid transfer protein SSH 4 Thaumatin-like protein 12 SKDH (Shikimate dehydrogenase) 5 DAHP synthase (DHS 1) 13 Myo-inositol-1 phosphate synthase 6 Acid phosphatase 14 Triacylglycerol lipase 7 Laccase / diphenol oxidase 15 ACC oxidase 8 Proline-rich protein 16 Germin-like protein (working)

Objectives/deliverables (non-supplemental, additional deliverables not specified in original FHI grant) • Clone putative Phytophthora (Ink disease) resistance enhancing genes from same c. DNA library. Chinese chestnut CG, putative ID 1 RPH 1 (Phytophthora resistance) 2 NPR 3/4 (Phytophthora resistance) (working)

Suggestion Darling 4 event is an excellent choice for deregulation & freedom to operate test case. Good results from leaf assays, conformation of enhanced resistance this summer. Even if only partial enhancement, it would be useful to the breeding program if deregulated It breaks down oxalic acid produced by the fungus, taking away one of the pathogen’s main weapons. No antifungal activity, so likely less regulation. A similar enzyme gene is up for deregulation in transgenic peanut (Virginia Tech. petition APHIS petition #10 -070 -01 p) for Sclerotinia Blight Resistance. Chinese chestnut has a uniquely expressed germin-like protein from the same gene family as Ox. O. Driven by a vascular promoter (Vsp. B from soybean) for more controlled expression. So far, no differences in mycorrhizal associations, insect feeding, and plant colonization in BRAG environmental impact studies.

Highlights • Leaf assays are being developed as an early, non-destructive assay for blight resistance – First transgenic events are looking promising • Currently have over 400 transgenic trees planted representing 23 events. Will have over 500 trees & more events by end of year. – Most planted with the help of the general public – The number of events/year is greatly expanding – Next spring planting at the Bronx Botanical Garden • Near where the blight was first described – Testing insert copy number, gene expression, & leaf assays • Have cloned 18 “cisgenic” candidate genes from Chinese chestnut – 16 for Chestnut Blight and 2 for Ink disease (Phytophthora root rot) – Most are in the transformation pipelines at SUNY-ESF or UGA • Are testing early (continuous) flowering genes to enhance breeding Thank you for your support
a80c55879a014289bf8c5efe80581747.ppt