c972ccdc6ee2c4e2df6c1476ae6d7ddf.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 103
 Fertile Crescent • Rich fertile soil (Tigris and Euphrates Rivers) • Mesopotamia
Fertile Crescent • Rich fertile soil (Tigris and Euphrates Rivers) • Mesopotamia
 Paleolithic Era Neolithic Revolution • Paleolithic – hunters followed their food- nomads • Neolithic – settle down, farming and domesticating animals = first civilization
Paleolithic Era Neolithic Revolution • Paleolithic – hunters followed their food- nomads • Neolithic – settle down, farming and domesticating animals = first civilization
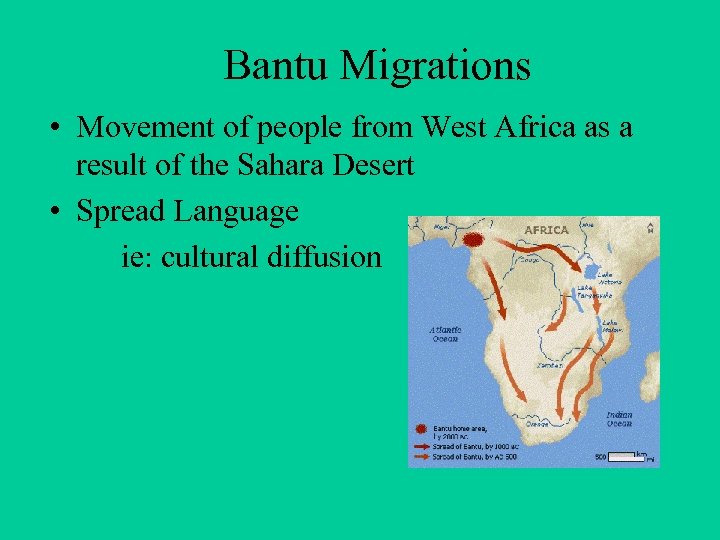 Bantu Migrations • Movement of people from West Africa as a result of the Sahara Desert • Spread Language ie: cultural diffusion
Bantu Migrations • Movement of people from West Africa as a result of the Sahara Desert • Spread Language ie: cultural diffusion
 Mandate of Heaven • Order from god which selects leadership in China = Dynastic Cycle • Dynasties: Zhou-feudalism Qin-central gov’t and Great Wall Han-Golden Age: Confucianism, paper, arts and wheelbarrow
Mandate of Heaven • Order from god which selects leadership in China = Dynastic Cycle • Dynasties: Zhou-feudalism Qin-central gov’t and Great Wall Han-Golden Age: Confucianism, paper, arts and wheelbarrow
 Chinese Inventions • • • Paper Wheelbarrow Ship rudder Acupuncture gunpowder
Chinese Inventions • • • Paper Wheelbarrow Ship rudder Acupuncture gunpowder
 Feudalism • Military service exchanged for land protection (Japan, China, Europe) • “decentralized gov’t”- no single all powerful ruler
Feudalism • Military service exchanged for land protection (Japan, China, Europe) • “decentralized gov’t”- no single all powerful ruler
 Bushido and Chivalry • Code of conduct for a samurai • Code of conduct for a Knight
Bushido and Chivalry • Code of conduct for a samurai • Code of conduct for a Knight
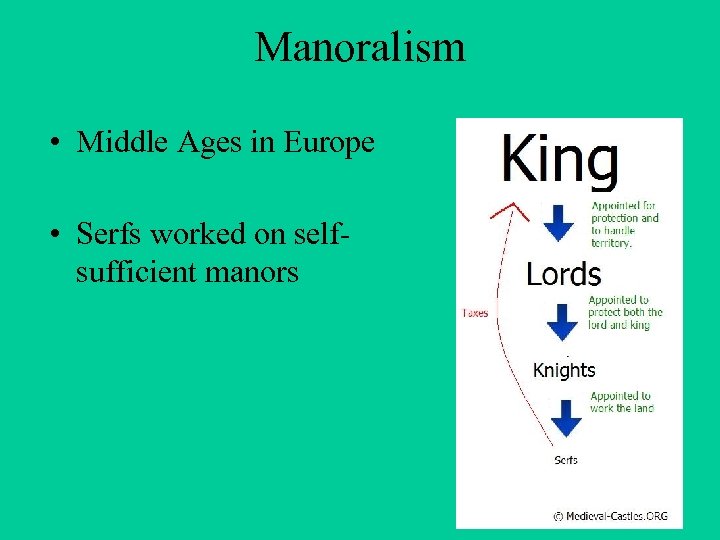 Manoralism • Middle Ages in Europe • Serfs worked on selfsufficient manors
Manoralism • Middle Ages in Europe • Serfs worked on selfsufficient manors
 Forms of Government • Autocracy: Single ruler with absolute power • Theocracy: Gov’t run by religious leaders/rules • Monarchy: King/Queens • Democracy: People vote for leaders • Totalitarian: one party/person controls every aspect of life (Communism, fascism) **Feudalism is also a form of government**
Forms of Government • Autocracy: Single ruler with absolute power • Theocracy: Gov’t run by religious leaders/rules • Monarchy: King/Queens • Democracy: People vote for leaders • Totalitarian: one party/person controls every aspect of life (Communism, fascism) **Feudalism is also a form of government**
 Hellenistic Age • Age of Alex the Great- he blended PIGE (Persian, Indian, Greek and Egyptian) cultures through his conquest. = cultural diffusion
Hellenistic Age • Age of Alex the Great- he blended PIGE (Persian, Indian, Greek and Egyptian) cultures through his conquest. = cultural diffusion
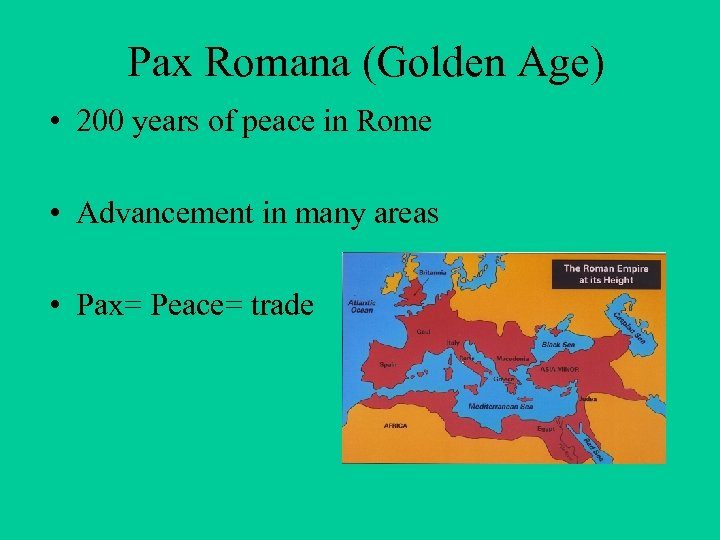 Pax Romana (Golden Age) • 200 years of peace in Rome • Advancement in many areas • Pax= Peace= trade
Pax Romana (Golden Age) • 200 years of peace in Rome • Advancement in many areas • Pax= Peace= trade
 Pax Mongolia • Peace in Asia created by Mongol Rule approx. 1280 -1350 • Prompted exchange of goods between East and West (China, Russia, Middle East) (C. D. )
Pax Mongolia • Peace in Asia created by Mongol Rule approx. 1280 -1350 • Prompted exchange of goods between East and West (China, Russia, Middle East) (C. D. )
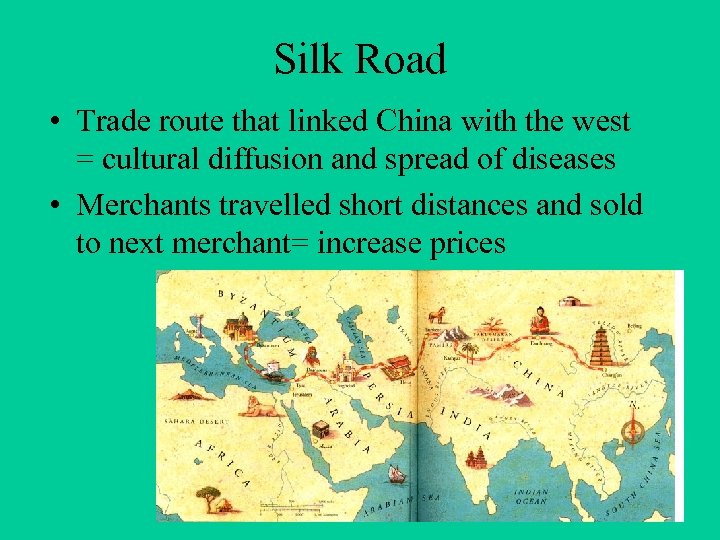 Silk Road • Trade route that linked China with the west = cultural diffusion and spread of diseases • Merchants travelled short distances and sold to next merchant= increase prices
Silk Road • Trade route that linked China with the west = cultural diffusion and spread of diseases • Merchants travelled short distances and sold to next merchant= increase prices
 Maurya and Gupta Dynasties • • Indian Empires- Hinduism and Islam Created Arabic numerals, decimals and Zero 200 Years reign Fell due to weak leadership and invasions
Maurya and Gupta Dynasties • • Indian Empires- Hinduism and Islam Created Arabic numerals, decimals and Zero 200 Years reign Fell due to weak leadership and invasions
 Golden Age of Islam • Many advancements by Muslim civilization – Art and architecture decorated cities – Recorded Qur’an – Developed algebra (solve for “x”) – Doctors had to pass exams after studying disease and medical books
Golden Age of Islam • Many advancements by Muslim civilization – Art and architecture decorated cities – Recorded Qur’an – Developed algebra (solve for “x”) – Doctors had to pass exams after studying disease and medical books
 Schism • A split within religion • Examples: -Protestant Reformation (95 theses) -Sunni and Shiite Islam (Iraq, Syria) -Eastern Orthodox (C. D. - Byzantine to Russia)
Schism • A split within religion • Examples: -Protestant Reformation (95 theses) -Sunni and Shiite Islam (Iraq, Syria) -Eastern Orthodox (C. D. - Byzantine to Russia)
 Crusades 1000 s-1200 s • A series of religious wars attempting to obtain the holy land (Islam versus Catholicism) • Resulted in an increase of trade (C. D. ) and Feudal powers
Crusades 1000 s-1200 s • A series of religious wars attempting to obtain the holy land (Islam versus Catholicism) • Resulted in an increase of trade (C. D. ) and Feudal powers
 Belief Systems • Established, orderly ways to look at faith, life and death – Animism/ Shinto – Hinduism – Judaism – Christianity – Islam – Buddhism – Confucianism – Taoism
Belief Systems • Established, orderly ways to look at faith, life and death – Animism/ Shinto – Hinduism – Judaism – Christianity – Islam – Buddhism – Confucianism – Taoism
 STOP
STOP
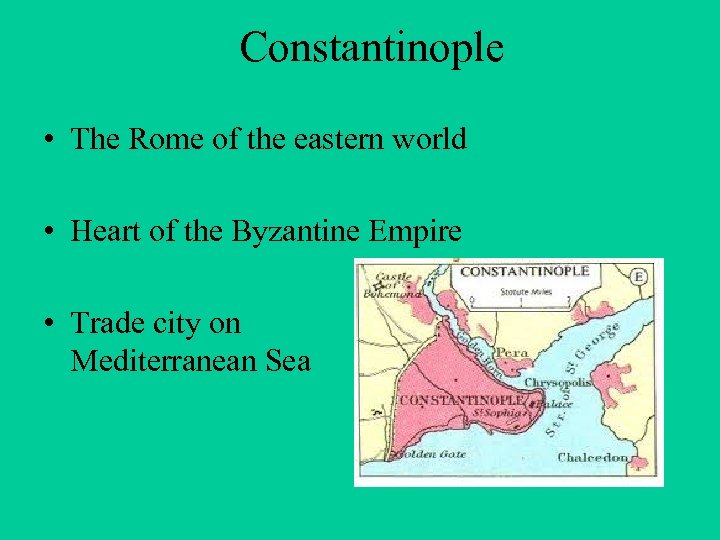 Constantinople • The Rome of the eastern world • Heart of the Byzantine Empire • Trade city on Mediterranean Sea
Constantinople • The Rome of the eastern world • Heart of the Byzantine Empire • Trade city on Mediterranean Sea
 Traditional Economy • Trade and bartering for goods • Distribution of goods based on customs, beliefs and habits *subsistence agriculture- growing just enough for your family*
Traditional Economy • Trade and bartering for goods • Distribution of goods based on customs, beliefs and habits *subsistence agriculture- growing just enough for your family*
 Protestant Reformation • A schism in the Catholic Church that created the Protestant religion. • Martin Luther 95 Theses • Catholic Church loses power
Protestant Reformation • A schism in the Catholic Church that created the Protestant religion. • Martin Luther 95 Theses • Catholic Church loses power
 95 Theses • List of grievances (complaints) written by Martin Luther against the sale of indulgences created the Protestant Reformation. • The Printing Press allowed copies of the 95 Theses to spread quickly
95 Theses • List of grievances (complaints) written by Martin Luther against the sale of indulgences created the Protestant Reformation. • The Printing Press allowed copies of the 95 Theses to spread quickly
 Age of Absolutism • Autocratic rules have complete authority, even in colonies- Divine Right – India- Akbar the Great – France- King Louis XIV (sun king) – Spain- Philip II – Russia- Ivan the Terrible AND Peter the Great (Westernized Russia)
Age of Absolutism • Autocratic rules have complete authority, even in colonies- Divine Right – India- Akbar the Great – France- King Louis XIV (sun king) – Spain- Philip II – Russia- Ivan the Terrible AND Peter the Great (Westernized Russia)
 Glorious Revolution • Non-violent overthrow of James II by William and Mary of Orange. • They signed the English Bill of Rights which further limited kings’ powers and created a limited monarchy.
Glorious Revolution • Non-violent overthrow of James II by William and Mary of Orange. • They signed the English Bill of Rights which further limited kings’ powers and created a limited monarchy.
 Magna Carta The English Bill of Rights • A charter signed by England’s King John in 1215 Placed limits on the King’s power • gave rights to the people and took power away from the monarchy 1689
Magna Carta The English Bill of Rights • A charter signed by England’s King John in 1215 Placed limits on the King’s power • gave rights to the people and took power away from the monarchy 1689
 Scientific Revolution • 1500’s and 1600’s new way of thinking that challenged traditional ideas of the Catholic Church. • Based on Reason and Inquiry
Scientific Revolution • 1500’s and 1600’s new way of thinking that challenged traditional ideas of the Catholic Church. • Based on Reason and Inquiry
 Renaissance • Time period when people began to question the Church, a time of Rebirth of science, arts and literature (start in Italy) • Focus on secular (worldly/ non-religious) • Humanism= emphasis on the individual
Renaissance • Time period when people began to question the Church, a time of Rebirth of science, arts and literature (start in Italy) • Focus on secular (worldly/ non-religious) • Humanism= emphasis on the individual
 Enlightenment • People started to question the relationship between themselves and their government. • Period in the 1700 s in which people rejected traditional ideas and supported a human reason.
Enlightenment • People started to question the relationship between themselves and their government. • Period in the 1700 s in which people rejected traditional ideas and supported a human reason.
 Social Contract • There is a unwritten contract between Gov’t and the people. • If the gov’t isn't taking care of people’s needs they can get rid of it
Social Contract • There is a unwritten contract between Gov’t and the people. • If the gov’t isn't taking care of people’s needs they can get rid of it
 Geography Terms • Savannah or Steppe: Grassy plain • Peninsula: land surrounded by water on 3 sides • Archipelago: chain of islands • Climate: weather patterns over time (tropical, dry) • Region: areas of land with unifying features (Mideast-political, rainforests)
Geography Terms • Savannah or Steppe: Grassy plain • Peninsula: land surrounded by water on 3 sides • Archipelago: chain of islands • Climate: weather patterns over time (tropical, dry) • Region: areas of land with unifying features (Mideast-political, rainforests)
 Socialism • Economic system where all goods are shared so everyone’s needs are met • Common ownership
Socialism • Economic system where all goods are shared so everyone’s needs are met • Common ownership
 Capitalism • Economic system based on trade and capital, money is used for investment. • Free Market • Supply and Demand
Capitalism • Economic system based on trade and capital, money is used for investment. • Free Market • Supply and Demand
 Laissez Faire • Government should keep hands off economic concerns • Supply and Demand should regulate the economy • Root of Capitalism Money and debt video ^
Laissez Faire • Government should keep hands off economic concerns • Supply and Demand should regulate the economy • Root of Capitalism Money and debt video ^
 STOP
STOP
 Age of Exploration • European demand for goods led to exploration to find shorter, safer and cheaper trade routes.
Age of Exploration • European demand for goods led to exploration to find shorter, safer and cheaper trade routes.
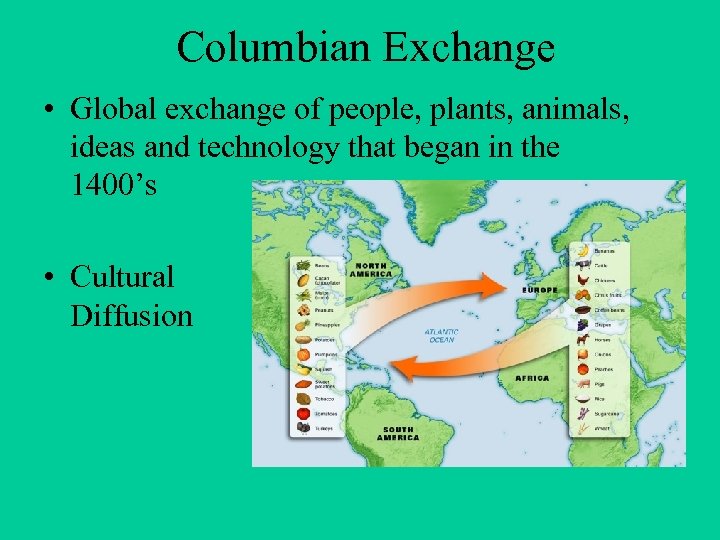 Columbian Exchange • Global exchange of people, plants, animals, ideas and technology that began in the 1400’s • Cultural Diffusion
Columbian Exchange • Global exchange of people, plants, animals, ideas and technology that began in the 1400’s • Cultural Diffusion
 Middle Passage • The voyage from Africa to the Americas (slave trade)
Middle Passage • The voyage from Africa to the Americas (slave trade)
 Encomienda • Racial class structure that made American natives slaves
Encomienda • Racial class structure that made American natives slaves
 Mercantilism • Economic policy; export more than import • Raw materials sold cheaply to mother nation; expensive manufactured goods sold to colonies
Mercantilism • Economic policy; export more than import • Raw materials sold cheaply to mother nation; expensive manufactured goods sold to colonies
 Law Codes Napoleonic Code. Equality after French Rev Justinian’s Code. Byzantine law code Laws of the Roman Twelve Tables. Basis of today's legal system Hammurabi's Code. Eye for an eye
Law Codes Napoleonic Code. Equality after French Rev Justinian’s Code. Byzantine law code Laws of the Roman Twelve Tables. Basis of today's legal system Hammurabi's Code. Eye for an eye
 Imperialism • When a stronger nation takes over a weaker nation’s social, economic and political life • Justified by Social Darwinism • Established colonies
Imperialism • When a stronger nation takes over a weaker nation’s social, economic and political life • Justified by Social Darwinism • Established colonies
 Nationalism • A feeling of pride for one’s nation or group • Has led to conflict ex: WWI (MAIN) Decolonization
Nationalism • A feeling of pride for one’s nation or group • Has led to conflict ex: WWI (MAIN) Decolonization
 Congress of Vienna • Led by Metternich after Napoleon's defeat • Conservative: returned monarchs to power • Re-drew the map of Europe to balance power • Surrounded France with strong countries • Created a lasting peace until WWI
Congress of Vienna • Led by Metternich after Napoleon's defeat • Conservative: returned monarchs to power • Re-drew the map of Europe to balance power • Surrounded France with strong countries • Created a lasting peace until WWI
 Coup d’etat • A quick and sudden overthrow of a government Examples: -Iranian Revolution (Ayatollah Khomeini) -Cuban Revolution (Castro) -Egyptian Revolution (Mubarak)
Coup d’etat • A quick and sudden overthrow of a government Examples: -Iranian Revolution (Ayatollah Khomeini) -Cuban Revolution (Castro) -Egyptian Revolution (Mubarak)
 Pan-Slavism Pan-Arabism Pan-Africanism • Nationalist movement to unite all similar people in each respective group.
Pan-Slavism Pan-Arabism Pan-Africanism • Nationalist movement to unite all similar people in each respective group.
 Treaty of Kanagawa • The treaty that forced Japan to open its ports to trade ending isolation (Meiji Restoration) • Commodore Perry and his battleships “politely asked” Japan to trade
Treaty of Kanagawa • The treaty that forced Japan to open its ports to trade ending isolation (Meiji Restoration) • Commodore Perry and his battleships “politely asked” Japan to trade
 Meiji Restoration • Time when Japan Westernized • Modernized- led to imperialism • Ended isolation
Meiji Restoration • Time when Japan Westernized • Modernized- led to imperialism • Ended isolation
 Opium War • The British forced Indians to grow Opium, then sold it to China • China fought to have opium shipments stopped • Ended by Treaty of Nanjing
Opium War • The British forced Indians to grow Opium, then sold it to China • China fought to have opium shipments stopped • Ended by Treaty of Nanjing
 Forms of Imperial Control • Sphere of Influence: claim exclusive trading rights • Colony: expensive to run- control all aspects of life • Protectorate: minimal influence- control local leaders
Forms of Imperial Control • Sphere of Influence: claim exclusive trading rights • Colony: expensive to run- control all aspects of life • Protectorate: minimal influence- control local leaders
 Treaty of Nanjing • The treaty that Britain forced China to sign after the Opium War • Hong Kong taken as a 200 Year lease • Opened China to Foreigners
Treaty of Nanjing • The treaty that Britain forced China to sign after the Opium War • Hong Kong taken as a 200 Year lease • Opened China to Foreigners
 Boer War • South African War over gold and diamonds • British vs. Dutch “Boers” • Britain won and created the racial segregation policy known as apartheid.
Boer War • South African War over gold and diamonds • British vs. Dutch “Boers” • Britain won and created the racial segregation policy known as apartheid.
 Total War • The complete and total involvement of a nation in a war effort. • Civilians at home and soldiers on battlefield all contribute • WWI & WWII
Total War • The complete and total involvement of a nation in a war effort. • Civilians at home and soldiers on battlefield all contribute • WWI & WWII
 Propaganda • The spreading of an idea to promote a cause
Propaganda • The spreading of an idea to promote a cause
 Russian (Bolshevik) Revolution • 1917 - food shortages and WWI deaths pushed Russians to revolt • Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (exit WWI) • Lenin turned Russia into a communist state USSR • Land, Bread, Peace
Russian (Bolshevik) Revolution • 1917 - food shortages and WWI deaths pushed Russians to revolt • Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (exit WWI) • Lenin turned Russia into a communist state USSR • Land, Bread, Peace
 5 Year Plan • Stalin’s plans to improve the USSR’s economy and increase food production. • Only area of success was in building heavy industry. • Farming collectives
5 Year Plan • Stalin’s plans to improve the USSR’s economy and increase food production. • Only area of success was in building heavy industry. • Farming collectives
 World War I “The Great War” Causes: M- Militarism A-alliances I-imperialism N-nationalism (Balkan Powder Keg) Spark- assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand
World War I “The Great War” Causes: M- Militarism A-alliances I-imperialism N-nationalism (Balkan Powder Keg) Spark- assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand
 Treaty of Versailles • The peace treaty signed after WWI • Placed blame on Germany- reparations, blame and lost land • Established new countries • Wilson’s 14 points largely ignored
Treaty of Versailles • The peace treaty signed after WWI • Placed blame on Germany- reparations, blame and lost land • Established new countries • Wilson’s 14 points largely ignored
 League of Nations • A peace keeping organization formed after WWI • Too weak to enforce ban on war • United States did not join
League of Nations • A peace keeping organization formed after WWI • Too weak to enforce ban on war • United States did not join
 STOP
STOP
 Zionism • Desire to create a Jewish state in Palestine • Led to the Balfour Declaration after WWI • 1948 Israel is created
Zionism • Desire to create a Jewish state in Palestine • Led to the Balfour Declaration after WWI • 1948 Israel is created
 Mandate • Territory being controlled by a foreign power • Typically gifted to the “winners” of a war
Mandate • Territory being controlled by a foreign power • Typically gifted to the “winners” of a war
 Fascism • An authoritarian government that is not communist. • Mussolini, Hitler, Franco
Fascism • An authoritarian government that is not communist. • Mussolini, Hitler, Franco
 Appeasement • Giving in to one’s demands to avoid a conflict • Example: Hitler and the Sudetenland (Munich Pact)
Appeasement • Giving in to one’s demands to avoid a conflict • Example: Hitler and the Sudetenland (Munich Pact)
 United Nations • A peace organization formed after WWII • Much stronger than League of Nations post WWI
United Nations • A peace organization formed after WWII • Much stronger than League of Nations post WWI
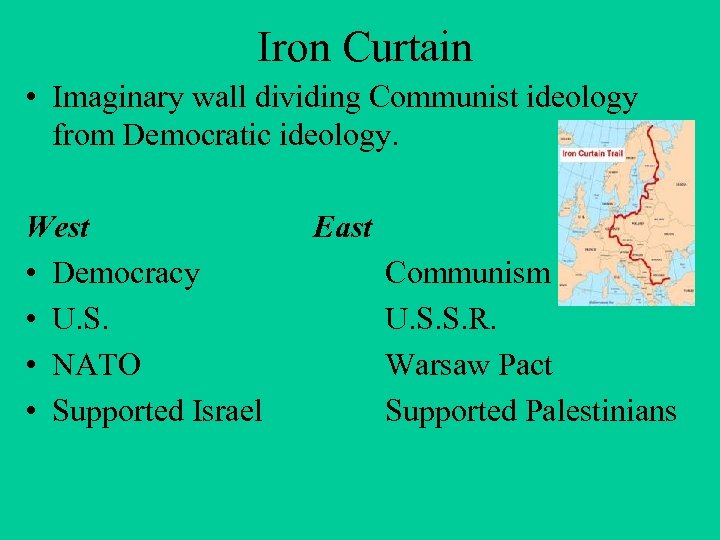 Iron Curtain • Imaginary wall dividing Communist ideology from Democratic ideology. West • Democracy • U. S. • NATO • Supported Israel East Communism U. S. S. R. Warsaw Pact Supported Palestinians
Iron Curtain • Imaginary wall dividing Communist ideology from Democratic ideology. West • Democracy • U. S. • NATO • Supported Israel East Communism U. S. S. R. Warsaw Pact Supported Palestinians
 Cold War • A state of tension between the Superpowers (U. S. and U. S. S. R. ) • Fear of spread of communism and nuclear weapons • Events: Cuban Missile Crisis, Vietnam War, Korean War, Afghanistan aid
Cold War • A state of tension between the Superpowers (U. S. and U. S. S. R. ) • Fear of spread of communism and nuclear weapons • Events: Cuban Missile Crisis, Vietnam War, Korean War, Afghanistan aid
 Containment • Stop the Spread of Communism beyond the Iron Curtain • Used money to avoid communist takeovers (make communism less appealing)
Containment • Stop the Spread of Communism beyond the Iron Curtain • Used money to avoid communist takeovers (make communism less appealing)
 Marshall Plan • Give aid to foreign nations to avoid communism’s spread • Communism looks less appealing if you have food, shelter and work
Marshall Plan • Give aid to foreign nations to avoid communism’s spread • Communism looks less appealing if you have food, shelter and work
 Truman Doctrine • An economic and military program to promote democracy established by President Truman
Truman Doctrine • An economic and military program to promote democracy established by President Truman
 Détente • A state of relaxed tensions between the US and the USSR (end of Cold War)
Détente • A state of relaxed tensions between the US and the USSR (end of Cold War)
 Perestroika Glasnost Gorbachev’s reforms to prevents the collapse of the Soviet Economy A policy of openness under Gorbachev in USSR • Both failed and the USSR collapsed • Replaced with Russian Republic
Perestroika Glasnost Gorbachev’s reforms to prevents the collapse of the Soviet Economy A policy of openness under Gorbachev in USSR • Both failed and the USSR collapsed • Replaced with Russian Republic
 OPEC • Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries • Regulates oil prices and production • Oil Embargo of 1970 s affected world
OPEC • Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries • Regulates oil prices and production • Oil Embargo of 1970 s affected world
 Long March • When Mao and the communists fled to northern China avoiding the Guomindang (nationalists) led by Chaing Kai Shek. • Mao recruited supporters to the communist movement along the way (peasants)
Long March • When Mao and the communists fled to northern China avoiding the Guomindang (nationalists) led by Chaing Kai Shek. • Mao recruited supporters to the communist movement along the way (peasants)
 Great Leap Forward • Mao’s plan for China (like Stalin’s 5 year plans) • Attempted to create self sufficiency by using farming collectives • Failed= starvation/ famine
Great Leap Forward • Mao’s plan for China (like Stalin’s 5 year plans) • Attempted to create self sufficiency by using farming collectives • Failed= starvation/ famine
 Cultural Revolution • Mao’s program to eliminate any opposition to his plans. • Forced people to live “Mao’s Way” • Red Guard- Corrupted Youths monitored people for signs of anti-communism
Cultural Revolution • Mao’s program to eliminate any opposition to his plans. • Forced people to live “Mao’s Way” • Red Guard- Corrupted Youths monitored people for signs of anti-communism
 Tiananmen Square 1989 • A Pro-Democracy protest where students gathered to demand freedom in the government. • The Gov’t sent in tanks to disperse the crowd • Chinese gov’t still totalitarian
Tiananmen Square 1989 • A Pro-Democracy protest where students gathered to demand freedom in the government. • The Gov’t sent in tanks to disperse the crowd • Chinese gov’t still totalitarian
 PLO • Palestinian Liberation Organization • Yassir Arafat original leader • Goal is the destruction of Israel
PLO • Palestinian Liberation Organization • Yassir Arafat original leader • Goal is the destruction of Israel
 Islamic Fundamentalism • Belief Islam is corrupted by outside ways- need to return to the basics of Islam • Uses Sharia law (traditional Islamic Law)
Islamic Fundamentalism • Belief Islam is corrupted by outside ways- need to return to the basics of Islam • Uses Sharia law (traditional Islamic Law)
 Ethnic Cleansing • The deliberate and intentional attempt to get rid of a race or ethnic group • Genocide • Bosnia, Chechnya, Serbia
Ethnic Cleansing • The deliberate and intentional attempt to get rid of a race or ethnic group • Genocide • Bosnia, Chechnya, Serbia
 NAFTA • North American Free Trade Agreement • Increases trade between North American nations (Canada, U. S. and Mexico) • Reduces Tariffs along borders to promote trade
NAFTA • North American Free Trade Agreement • Increases trade between North American nations (Canada, U. S. and Mexico) • Reduces Tariffs along borders to promote trade
 Pre Post Before After Pre- World War I Europe • A term used to describe conditions in Europe prior to World War I Post-Colonialism • A term used to describe conditions in nations that were once colonies
Pre Post Before After Pre- World War I Europe • A term used to describe conditions in Europe prior to World War I Post-Colonialism • A term used to describe conditions in nations that were once colonies
 Trade Deficit • When a nation imports more than it exports • Buys more than it sells
Trade Deficit • When a nation imports more than it exports • Buys more than it sells
 IMF • International Monetary Fund • Loans money to countries for development
IMF • International Monetary Fund • Loans money to countries for development
 IRA • Irish Republican Army • Fighting for Irish Independence from Britain
IRA • Irish Republican Army • Fighting for Irish Independence from Britain
 Human Rights Declaration • A document meant to protect basic rights for all • Created by the United Nations after the Holocaust (post WWII).
Human Rights Declaration • A document meant to protect basic rights for all • Created by the United Nations after the Holocaust (post WWII).
 STOP
STOP
 Urbanization • The movement of people from the country to the city • Industrial Revolution
Urbanization • The movement of people from the country to the city • Industrial Revolution
 Green Revolution • Using technology and science to produce more food (India) • Seeds were chemically altered to be more resistant to disease and produce more
Green Revolution • Using technology and science to produce more food (India) • Seeds were chemically altered to be more resistant to disease and produce more
 Deforestation/ Desertification • The destruction of the forest (Amazon) • The changing of farm land to desert (Africa)
Deforestation/ Desertification • The destruction of the forest (Amazon) • The changing of farm land to desert (Africa)
 Dissident • Some one or a group that speaks out against their government. • Example: Egyptian Revolution Cyber dissidents ; Ai Wei
Dissident • Some one or a group that speaks out against their government. • Example: Egyptian Revolution Cyber dissidents ; Ai Wei
 Autonomy • Desire by a peoples to have their own country. • Self rule
Autonomy • Desire by a peoples to have their own country. • Self rule
 Arab Spring • Revolutionary movement in Middle East of get rid of their dictator leaders • Fueled by social media • Tunisia, Egypt, Libya, Syria
Arab Spring • Revolutionary movement in Middle East of get rid of their dictator leaders • Fueled by social media • Tunisia, Egypt, Libya, Syria
 Animism • Belief that spirits live in the natural world • Similar to Shintoism and Taoism
Animism • Belief that spirits live in the natural world • Similar to Shintoism and Taoism
 Hinduism • • • Religion India Polytheistic Reincarnation Karma Dharma Caste system (social structure) Moksha Upanishads, Gita, Vedas
Hinduism • • • Religion India Polytheistic Reincarnation Karma Dharma Caste system (social structure) Moksha Upanishads, Gita, Vedas
 Buddhism • • • Religion No gods Reincarnation Karma Dharma No caste system 4 Noble Truths and 8 Fold Path Nirvana 3 Baskets of Wisdom
Buddhism • • • Religion No gods Reincarnation Karma Dharma No caste system 4 Noble Truths and 8 Fold Path Nirvana 3 Baskets of Wisdom
 Islam • • Religion Allah Muhammad 622 AD 5 Pillars (Hajj, Ramadan) mosque Quran (Koran)
Islam • • Religion Allah Muhammad 622 AD 5 Pillars (Hajj, Ramadan) mosque Quran (Koran)
 Taoism and Shintoism Means “The Way” • Balance and harmony • NATURE Japan
Taoism and Shintoism Means “The Way” • Balance and harmony • NATURE Japan
 Confucianism • • • Philosophy China 5 Relationships (set examples and follow them) Filial Piety Order, structure The Analects (sacred book)
Confucianism • • • Philosophy China 5 Relationships (set examples and follow them) Filial Piety Order, structure The Analects (sacred book)
 Christianity • • 10 Commandments Jesus Church Bible
Christianity • • 10 Commandments Jesus Church Bible
 Polytheism • Belief in more than one god
Polytheism • Belief in more than one god
 Monotheism Belief in only one God Christianity, Islam and Judaism
Monotheism Belief in only one God Christianity, Islam and Judaism
 Diaspora Mass dispersal by force Jewish Diaspora out of their Holy Land
Diaspora Mass dispersal by force Jewish Diaspora out of their Holy Land


