1566dcde4d15de2568914c4930c98184.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 FERRELL | HIRT | FERRELL 3 e Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
FERRELL | HIRT | FERRELL 3 e Mc. Graw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2013 by The Mc. Graw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 PART 1 • CHAPTER 1 The Dynamics of Business and Economics • CHAPTER 2 Business Ethics and Social Responsibility • CHAPTER 3 Business in a Borderless World 2 -2
PART 1 • CHAPTER 1 The Dynamics of Business and Economics • CHAPTER 2 Business Ethics and Social Responsibility • CHAPTER 3 Business in a Borderless World 2 -2
 BUSINESS ETHICS An identifiable problem, situation, or opportunity that requires a person to choose from among several actions that may be evaluated as right or wrong, ethical or unethical 2 -3
BUSINESS ETHICS An identifiable problem, situation, or opportunity that requires a person to choose from among several actions that may be evaluated as right or wrong, ethical or unethical 2 -3
 ETHICAL DECISIONS IN ORGANIZATIONS Most unethical activities are supported by a culture encouraging employees to bend the rules v Countrywide Financial § ‘Liar loans’ § Culture that encouraged cutting corners in order to make profits v American International Group § Manipulation of accounting § Overstatement of earnings– forced to restate earnings $3. 9 billion lower 2 -4
ETHICAL DECISIONS IN ORGANIZATIONS Most unethical activities are supported by a culture encouraging employees to bend the rules v Countrywide Financial § ‘Liar loans’ § Culture that encouraged cutting corners in order to make profits v American International Group § Manipulation of accounting § Overstatement of earnings– forced to restate earnings $3. 9 billion lower 2 -4
 SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY Business’s obligation is to maximize its positive impact and minimize its negative impact on society § § § Known for high-end luxury shoes and accessories Launched a lower-cost brand Ferragamo WORLD Aimed at socially conscious consumers Eco-friendly materials Proceeds go to help the Acumen Fund, which provides funding for businesses in East Africa, India and Pakistan 2 -5
SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY Business’s obligation is to maximize its positive impact and minimize its negative impact on society § § § Known for high-end luxury shoes and accessories Launched a lower-cost brand Ferragamo WORLD Aimed at socially conscious consumers Eco-friendly materials Proceeds go to help the Acumen Fund, which provides funding for businesses in East Africa, India and Pakistan 2 -5
 A TIMELINE OF ETHICAL AND SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY CONCERNS 2 -6
A TIMELINE OF ETHICAL AND SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY CONCERNS 2 -6
 LAWS AND REGULATIONS § Laws and regulations encourage businesses to conform to society’s basic standards, values, and attitudes. § Sarbanes-Oxley Act, 2002 § Troubled Assets Relief Program 2 -7
LAWS AND REGULATIONS § Laws and regulations encourage businesses to conform to society’s basic standards, values, and attitudes. § Sarbanes-Oxley Act, 2002 § Troubled Assets Relief Program 2 -7
 THE ROLE OF ETHICS IN BUSINESS Growing concerns about legal and ethical issues in business § Antitrust violations § Accounting fraud § Cybercrimes § Unfair competitive practices § Tax fraud 2 -8
THE ROLE OF ETHICS IN BUSINESS Growing concerns about legal and ethical issues in business § Antitrust violations § Accounting fraud § Cybercrimes § Unfair competitive practices § Tax fraud 2 -8
 ETHICAL ISSUES An identifiable problem, situation, or opportunity that requires a person to choose from among several actions that may be evaluated as right or wrong, ethical or unethical 2 -9
ETHICAL ISSUES An identifiable problem, situation, or opportunity that requires a person to choose from among several actions that may be evaluated as right or wrong, ethical or unethical 2 -9
 ETHICAL ISSUES § Involve all organizational activities • For profit businesses • Non-profits • Government • Schools and universities § Learning to recognize and resolve ethical issues are important in maintaining an ethical business climate 2 -10
ETHICAL ISSUES § Involve all organizational activities • For profit businesses • Non-profits • Government • Schools and universities § Learning to recognize and resolve ethical issues are important in maintaining an ethical business climate 2 -10
 ETHICAL CONDUCT HELPS TO: § Build Trust § Promote confidence § Validate relationships 2 -11
ETHICAL CONDUCT HELPS TO: § Build Trust § Promote confidence § Validate relationships 2 -11
 HOW TO JUDGE THE ETHICS OF A SITUATION § Examine the situation from your stakeholders’ position, including customers and competitors § People often need years of experience to accurately recognize and react to ethical situations § Ethical situations vary by culture 2 -12
HOW TO JUDGE THE ETHICS OF A SITUATION § Examine the situation from your stakeholders’ position, including customers and competitors § People often need years of experience to accurately recognize and react to ethical situations § Ethical situations vary by culture 2 -12
 HIGHLY ETHICAL COMPANIES ARE GENERALLY MORE PROFITABLE! § Recognized as highly ethical § Awarded ‘Corporation of the Year’ by Michigan Minority Business Development Council § Perfect score three years in a row in a Competitive Enterprise Institute ranking § History of environmental advocacy and stakeholder awareness 2 -13
HIGHLY ETHICAL COMPANIES ARE GENERALLY MORE PROFITABLE! § Recognized as highly ethical § Awarded ‘Corporation of the Year’ by Michigan Minority Business Development Council § Perfect score three years in a row in a Competitive Enterprise Institute ranking § History of environmental advocacy and stakeholder awareness 2 -13
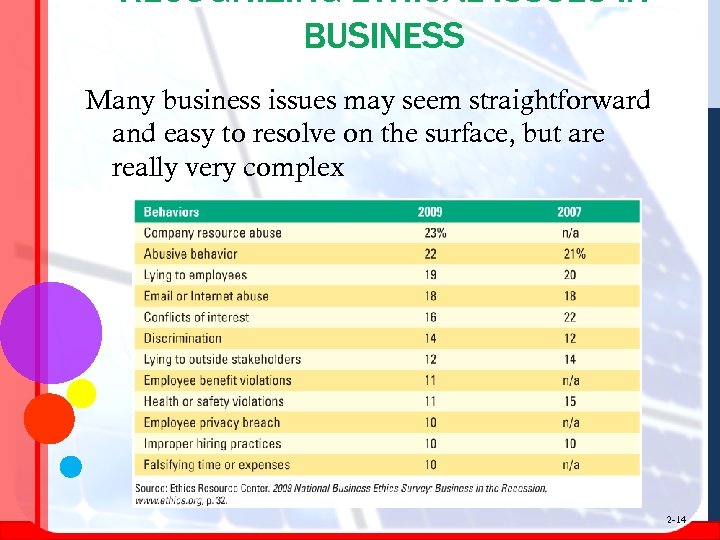 RECOGNIZING ETHICAL ISSUES IN BUSINESS Many business issues may seem straightforward and easy to resolve on the surface, but are really very complex 2 -14
RECOGNIZING ETHICAL ISSUES IN BUSINESS Many business issues may seem straightforward and easy to resolve on the surface, but are really very complex 2 -14
 BUSINESS § § § Misuse of company resources Abusive & intimidating behavior Conflict of interest Fairness & honesty Communications Business relationships 2 -15
BUSINESS § § § Misuse of company resources Abusive & intimidating behavior Conflict of interest Fairness & honesty Communications Business relationships 2 -15
 SOURCES OF UNETHICAL BEHAVIOR Misuse of Company Resources § The most commonly observed misconduct üTime theft üUse of personal email and social networking sites at work is a growing problem üStealing office supplies üUnauthorized use of equipment and software 2 -16
SOURCES OF UNETHICAL BEHAVIOR Misuse of Company Resources § The most commonly observed misconduct üTime theft üUse of personal email and social networking sites at work is a growing problem üStealing office supplies üUnauthorized use of equipment and software 2 -16
 SOURCES OF UNETHICAL BEHAVIOR Abusive and Intimidating Behavior / Bullying 2 -17
SOURCES OF UNETHICAL BEHAVIOR Abusive and Intimidating Behavior / Bullying 2 -17
 BEHAVIOR IN ORGANIZATIONS Conflict of interest § Advance personal interest over others’ interests § Benefit self at the expense of the company Bribes represent a conflict of interest because they benefit an individual at the expense of an organization or society 2 -18
BEHAVIOR IN ORGANIZATIONS Conflict of interest § Advance personal interest over others’ interests § Benefit self at the expense of the company Bribes represent a conflict of interest because they benefit an individual at the expense of an organization or society 2 -18
 CORRUPTION PERCEPTIONS INDEX Least Corrupt Countries… 1. New Zealand 12. Hong King/Luxembourg (tied) 2. Denmark 14. Australia 3. Singapore/ Sweden (tied) 16. Germany/ Ireland (tied) 5. Switzerland 17. Japan/ United Kingdom 6. Finland/Netherlands (tied) 19. United States 8. Australia/Canada/Iceland (3 way tie) 20. Barbados 11. Norway Source: “Corruption Perceptions Index 2009, ” Transparency International, http: //www. transparency. org/policy_research/ surveys_indices/cpi/2009/cpi_2009_table (accessed January 22, 2010). 2 -19
CORRUPTION PERCEPTIONS INDEX Least Corrupt Countries… 1. New Zealand 12. Hong King/Luxembourg (tied) 2. Denmark 14. Australia 3. Singapore/ Sweden (tied) 16. Germany/ Ireland (tied) 5. Switzerland 17. Japan/ United Kingdom 6. Finland/Netherlands (tied) 19. United States 8. Australia/Canada/Iceland (3 way tie) 20. Barbados 11. Norway Source: “Corruption Perceptions Index 2009, ” Transparency International, http: //www. transparency. org/policy_research/ surveys_indices/cpi/2009/cpi_2009_table (accessed January 22, 2010). 2 -19
 FAIRNESS & HONESTY Are at the heart of business ethics § How employees use resources § No deceit, coercion, or misrepresentations § Fair competition § Disclosure of potential harm caused by products 2 -20
FAIRNESS & HONESTY Are at the heart of business ethics § How employees use resources § No deceit, coercion, or misrepresentations § Fair competition § Disclosure of potential harm caused by products 2 -20
 ETHICAL CONCERNS IN COMMUNICATIONS § False/misleading advertising § Deceptive personal selling tactics § Truthfulness in product safety and quality § Unsubstantiated claims § Product labeling 2 -21
ETHICAL CONCERNS IN COMMUNICATIONS § False/misleading advertising § Deceptive personal selling tactics § Truthfulness in product safety and quality § Unsubstantiated claims § Product labeling 2 -21
 ETHICAL CONCERNS IN BUSINESS RELATIONSHIPS Relationships with customers, suppliers and co-workers § Ethical behavior within a business is important üKeeping company secrets üMeeting obligations and responsibilities üAvoiding undue pressure § Managers’ responsibility to create ethical work environment and provide a positive example 2 -22
ETHICAL CONCERNS IN BUSINESS RELATIONSHIPS Relationships with customers, suppliers and co-workers § Ethical behavior within a business is important üKeeping company secrets üMeeting obligations and responsibilities üAvoiding undue pressure § Managers’ responsibility to create ethical work environment and provide a positive example 2 -22
 PLAGIARISM § The act of taking someone else’s work and presenting it as your own without mentioning the source ØA major problem in schools and business § Students copying others’ work § A manager taking credit for a subordinate’s work § Employees copying reports and passing the work off as their own 2 -23
PLAGIARISM § The act of taking someone else’s work and presenting it as your own without mentioning the source ØA major problem in schools and business § Students copying others’ work § A manager taking credit for a subordinate’s work § Employees copying reports and passing the work off as their own 2 -23
 DETERMINING WHETHER AN ACTION IS ETHICAL Open discussion of ethical issues does not eliminate ethical problems; it does promote trust and learning in an organization 2 -24
DETERMINING WHETHER AN ACTION IS ETHICAL Open discussion of ethical issues does not eliminate ethical problems; it does promote trust and learning in an organization 2 -24
 PERSONAL ETHICS Is honesty important to students? § In a survey of 25, 000 high school students: ü 62% cheated on exams at least once ü 35% copied documents from the Internet ü 27% shoplifted ü 23% cheated to win at sports (Source: “The Biennial Report Card: The Ethics of American Youth, ” Josephson Institute of Ethics, www. josephsoninstitute. org/survey 2004) 2 -25
PERSONAL ETHICS Is honesty important to students? § In a survey of 25, 000 high school students: ü 62% cheated on exams at least once ü 35% copied documents from the Internet ü 27% shoplifted ü 23% cheated to win at sports (Source: “The Biennial Report Card: The Ethics of American Youth, ” Josephson Institute of Ethics, www. josephsoninstitute. org/survey 2004) 2 -25
 Ethical Decisions in an Organization are Influenced by Three Key Factors 2 -26
Ethical Decisions in an Organization are Influenced by Three Key Factors 2 -26
 CODE OF ETHICS Formalized rules and standards that describe what a company expects of its employees 2 -27
CODE OF ETHICS Formalized rules and standards that describe what a company expects of its employees 2 -27
 WHISTLEBLOWING Occurs when an employee exposes an employer’s wrongdoing to outsiders § Many companies have internal reporting mechanisms in place • Avoid legal action • Negative publicity § Whistleblowers often treated negatively and have a difficult time finding other work 2 -28
WHISTLEBLOWING Occurs when an employee exposes an employer’s wrongdoing to outsiders § Many companies have internal reporting mechanisms in place • Avoid legal action • Negative publicity § Whistleblowers often treated negatively and have a difficult time finding other work 2 -28
 FOUR DIMENSIONS TO SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY 1. Economic 2. Legal 3. Ethical 4. Voluntary 2 -29
FOUR DIMENSIONS TO SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY 1. Economic 2. Legal 3. Ethical 4. Voluntary 2 -29
 THE PYRAMID OF SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY 2 -30
THE PYRAMID OF SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY 2 -30
 CORPORATE CITIZENSHIP The extent to which businesses meet the legal, ethical, economic, and voluntary responsibilities placed on them by their stakeholders 2 -31
CORPORATE CITIZENSHIP The extent to which businesses meet the legal, ethical, economic, and voluntary responsibilities placed on them by their stakeholders 2 -31
 BEST CORPORATE CITIZENS 1. Bristol Myers-Squibb 2. General Mills, Inc. 3. IBM Corp. 4. Merck & Co. , Inc. 5. HP Co, LP 6. Cisco Systems, Inc. 7. Mattel, Inc. 8. Abbott Laboratories 9. Kimberly-Clark Corp. 10. Entergy Corp. 11. Exxon. Mobil Corp. 12. Wisconsin Energy Corp. 13. Intel Corp. 14. Proctor & Gamble Co. 15. Hess Corp. 16. Xerox Corp. 17. 3 M Co. 18. Avon Products, Inc. 19. Baxter International Inc. 20. Monsanto Co. 2 -32
BEST CORPORATE CITIZENS 1. Bristol Myers-Squibb 2. General Mills, Inc. 3. IBM Corp. 4. Merck & Co. , Inc. 5. HP Co, LP 6. Cisco Systems, Inc. 7. Mattel, Inc. 8. Abbott Laboratories 9. Kimberly-Clark Corp. 10. Entergy Corp. 11. Exxon. Mobil Corp. 12. Wisconsin Energy Corp. 13. Intel Corp. 14. Proctor & Gamble Co. 15. Hess Corp. 16. Xerox Corp. 17. 3 M Co. 18. Avon Products, Inc. 19. Baxter International Inc. 20. Monsanto Co. 2 -32
 FORMAL ETHICS AND COMPLIANCE PROGRAMS Arguments for and against these programs 2 -33
FORMAL ETHICS AND COMPLIANCE PROGRAMS Arguments for and against these programs 2 -33
 STAKEHOLDER RELATIONSHIPS: SHAREHOLDERS § § Primarily concerned with profit or ROI Financial community at large Proper accounting procedures Protecting owner’s rights and investments 2 -34
STAKEHOLDER RELATIONSHIPS: SHAREHOLDERS § § Primarily concerned with profit or ROI Financial community at large Proper accounting procedures Protecting owner’s rights and investments 2 -34
 STAKEHOLDER RELATIONSHIPS: SHAREHOLDERS § Provide a safe workplace § Adequate compensation § Listen to grievances § Fair treatment 2 -35
STAKEHOLDER RELATIONSHIPS: SHAREHOLDERS § Provide a safe workplace § Adequate compensation § Listen to grievances § Fair treatment 2 -35
 STAKEHOLDER RELATIONSHIPS: CONSUMERS Consumerism § Activities that independent individuals, groups and organizations undertake to protect their rights as consumers Ø Critical issue is business’s responsibility to customers to provide satisfying, safe products and to protect their rights as consumers. 2 -36
STAKEHOLDER RELATIONSHIPS: CONSUMERS Consumerism § Activities that independent individuals, groups and organizations undertake to protect their rights as consumers Ø Critical issue is business’s responsibility to customers to provide satisfying, safe products and to protect their rights as consumers. 2 -36
 KENNEDY’S CONSUMER BILL OF RIGHTS § The right to safety § The right to be informed § The right to choose § The right to be heard 2 -37
KENNEDY’S CONSUMER BILL OF RIGHTS § The right to safety § The right to be informed § The right to choose § The right to be heard 2 -37
 STAKEHOLDER RELATIONSHIPS: THE ENVIRONMENT & SUSTAINABILITY ISSUES Sustainability means conducting activities with the long-term well-being of the natural environment in mind. § Involves interaction between üNature üIndividuals üOrganizations üBusiness strategies 2 -38
STAKEHOLDER RELATIONSHIPS: THE ENVIRONMENT & SUSTAINABILITY ISSUES Sustainability means conducting activities with the long-term well-being of the natural environment in mind. § Involves interaction between üNature üIndividuals üOrganizations üBusiness strategies 2 -38
 STAKEHOLDER RELATIONSHIPS: THE ENVIRONMENT & SUSTAINABILITY ISSUES § Pollution • Land • Water • Air § Waste disposal § Future of energy • Alternative energy 2 -39
STAKEHOLDER RELATIONSHIPS: THE ENVIRONMENT & SUSTAINABILITY ISSUES § Pollution • Land • Water • Air § Waste disposal § Future of energy • Alternative energy 2 -39
 RESPONSE TO ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES § § Many companies have a President of Environmental Affairs Position Most Fortune 500 companies have in place: üWritten environmental policy üRecycling programs üWaste-reduction initiatives § § Environmental consciousness can save money through reducing waste Greenwashing, or creating a positive association with environmental issues for an unsuitable product, service or practice • Is a growing problem 2 -40
RESPONSE TO ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES § § Many companies have a President of Environmental Affairs Position Most Fortune 500 companies have in place: üWritten environmental policy üRecycling programs üWaste-reduction initiatives § § Environmental consciousness can save money through reducing waste Greenwashing, or creating a positive association with environmental issues for an unsuitable product, service or practice • Is a growing problem 2 -40
 STAKEHOLDER RELATIONSHIPS: THE COMMUNITY General community and global welfare § The Avon Foundation Ø Breast Cancer Awareness Crusade § Target’s Take Charge of Education program Ø 1% of Target Red Card purchases donated to educational causes Hardcore unemployed • National Alliance of Business funds training to help • hard-core unemployed to find work and gain selfsufficiency Enhanced self-esteem; help people become productive members of society 2 -41
STAKEHOLDER RELATIONSHIPS: THE COMMUNITY General community and global welfare § The Avon Foundation Ø Breast Cancer Awareness Crusade § Target’s Take Charge of Education program Ø 1% of Target Red Card purchases donated to educational causes Hardcore unemployed • National Alliance of Business funds training to help • hard-core unemployed to find work and gain selfsufficiency Enhanced self-esteem; help people become productive members of society 2 -41


