91144a2b086fbed0cfe3388ce2c3db98.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Female Reproductive System HS-101
Female Reproductive System HS-101
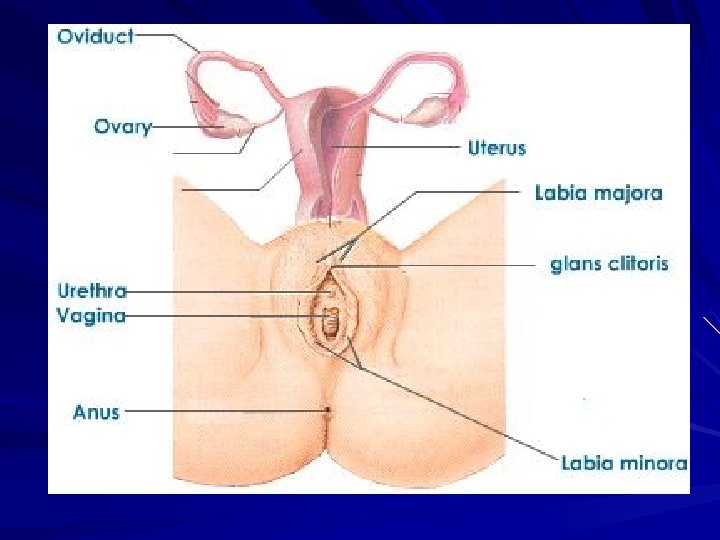
 External Organs The Vulva consists of: – Mons Pubis – Labia Majora – Labia Minora – Clitoris – Vaginal opening
External Organs The Vulva consists of: – Mons Pubis – Labia Majora – Labia Minora – Clitoris – Vaginal opening
 External Organs Mons Pubis – Rounded fatty pad of tissue – Front of the body; directly on top of pubic bone – Pubic hair begins to grow during puberty
External Organs Mons Pubis – Rounded fatty pad of tissue – Front of the body; directly on top of pubic bone – Pubic hair begins to grow during puberty
 External Organs Labia Majora – Heavy outer fold of tissue surrounding the vaginal opening; also covered in pubic hair – Serve as first line of protection against germs – Richly supplied with nerve endings & blood vessels to aid in sexual arousal
External Organs Labia Majora – Heavy outer fold of tissue surrounding the vaginal opening; also covered in pubic hair – Serve as first line of protection against germs – Richly supplied with nerve endings & blood vessels to aid in sexual arousal
 External Organs Labia Minora – Inner folds between the labia majora that extend forward to cover clitoris – Vary in size and color – Contain sweat and oil glands – Richly supplied with nerve endings and blood vessels
External Organs Labia Minora – Inner folds between the labia majora that extend forward to cover clitoris – Vary in size and color – Contain sweat and oil glands – Richly supplied with nerve endings and blood vessels
 External Organs Clitoris – Small knob of tissue that projects between the labia minora – Labia Minora form a hood over it – Full of blood vessels and nerve ending for sexual arousal – Enlarges during sexual arousal – No reproductive function
External Organs Clitoris – Small knob of tissue that projects between the labia minora – Labia Minora form a hood over it – Full of blood vessels and nerve ending for sexual arousal – Enlarges during sexual arousal – No reproductive function
 External Organs Vaginal Opening – Visible when labia are parted – Hymen - thin membrane that stretches across opening about an inch up inside; has an opening to allow for menstrual flow – This is where the babies head crowns during the 2 nd stage of childbirth
External Organs Vaginal Opening – Visible when labia are parted – Hymen - thin membrane that stretches across opening about an inch up inside; has an opening to allow for menstrual flow – This is where the babies head crowns during the 2 nd stage of childbirth
 External Organs Breasts – Organs consisting of fatty tissue and mammary glands – After childbirth, the mammary glands produce milk for breastfeeding
External Organs Breasts – Organs consisting of fatty tissue and mammary glands – After childbirth, the mammary glands produce milk for breastfeeding
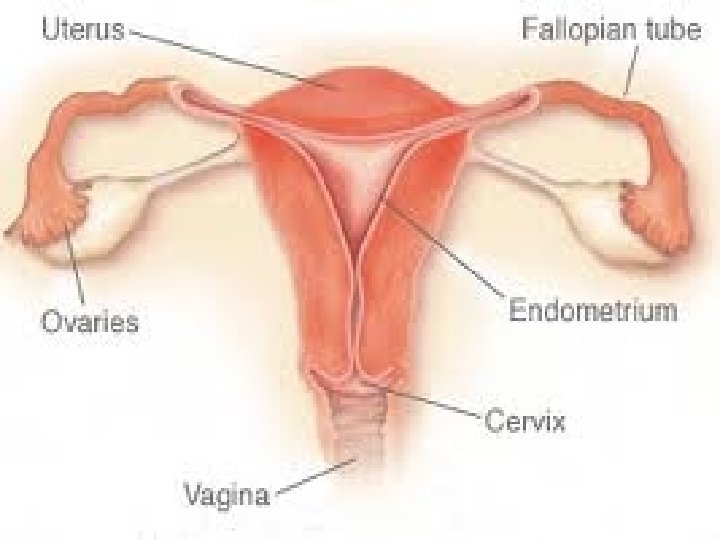
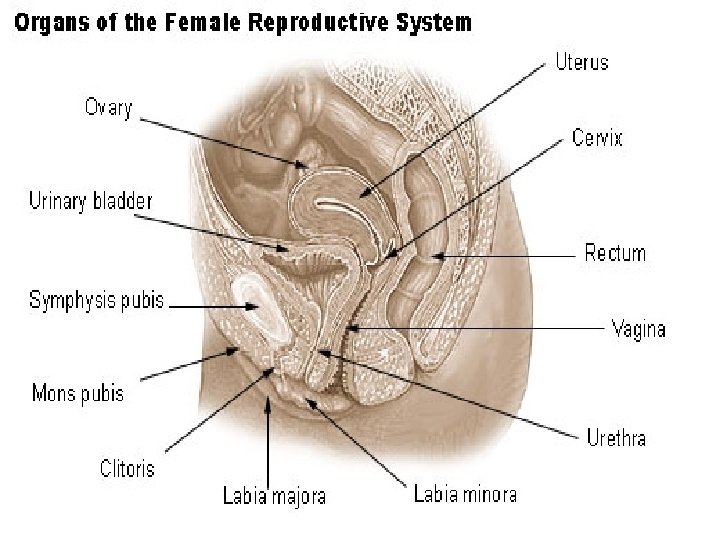
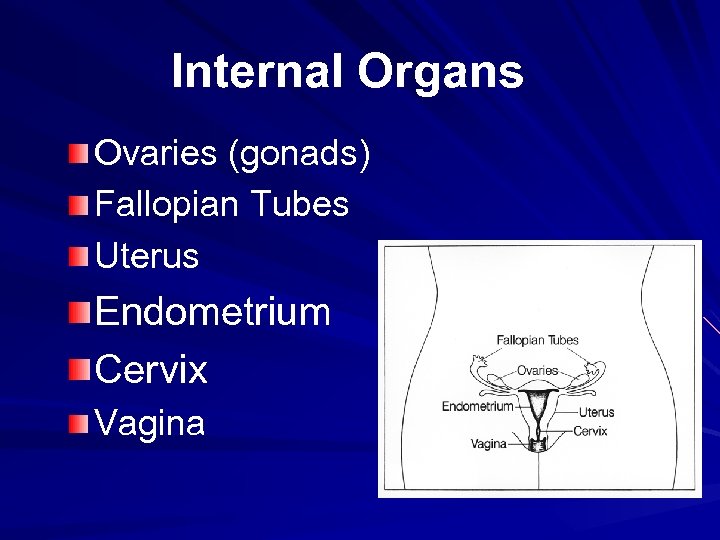 Internal Organs Ovaries (gonads) Fallopian Tubes Uterus Endometrium Cervix Vagina
Internal Organs Ovaries (gonads) Fallopian Tubes Uterus Endometrium Cervix Vagina
 Ovaries Gonads - female sex glands that produce hormones Produce estrogen & progesterone Two of them; one on either side of uterus House and release ova, or egg cells
Ovaries Gonads - female sex glands that produce hormones Produce estrogen & progesterone Two of them; one on either side of uterus House and release ova, or egg cells
 Female Hormones Estrogen – female hormone that produces female secondary sex characteristics and affects the menstrual cycle Progesterone – hormone that initiates the thickening of the uterine lining to receive the ovum
Female Hormones Estrogen – female hormone that produces female secondary sex characteristics and affects the menstrual cycle Progesterone – hormone that initiates the thickening of the uterine lining to receive the ovum
 Preparing for Ovulation Each month the uterus prepares for possible pregnancy by producing menses Menses – building up of blood and other tissue on uterine wall. If fertilized, the ovum moves to the uterus and attaches to this lining. If not fertilized, it dies and passes into the uterus, and menstruation will occur.
Preparing for Ovulation Each month the uterus prepares for possible pregnancy by producing menses Menses – building up of blood and other tissue on uterine wall. If fertilized, the ovum moves to the uterus and attaches to this lining. If not fertilized, it dies and passes into the uterus, and menstruation will occur.
 Ova (Eggs) At birth, a female has 200, 000 to 300, 000 immature ova in her ovaries During puberty the ova begins to mature Once a month, ovulation occurs. This is the release of an egg from the ovary into the fallopian tubes.
Ova (Eggs) At birth, a female has 200, 000 to 300, 000 immature ova in her ovaries During puberty the ova begins to mature Once a month, ovulation occurs. This is the release of an egg from the ovary into the fallopian tubes.
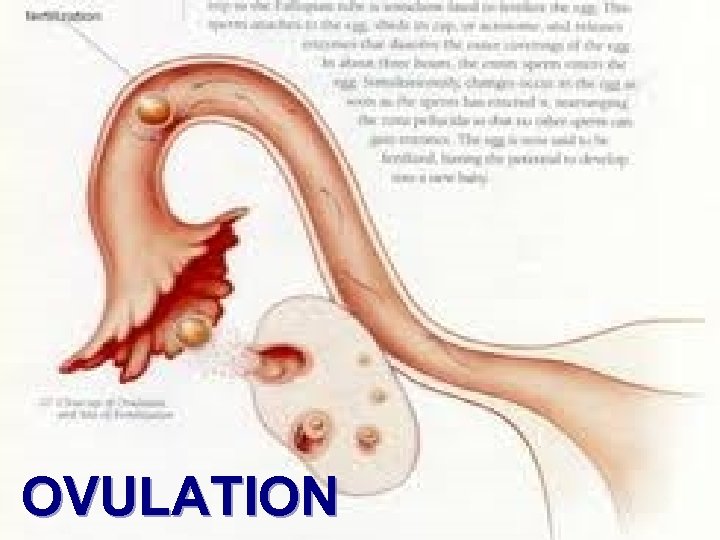 OVULATION
OVULATION
 Fallopian Tubes Narrow tubes that extend from the ovaries to the uterus on each side Lined with cilia to transport ova Site for fertilization of the egg
Fallopian Tubes Narrow tubes that extend from the ovaries to the uterus on each side Lined with cilia to transport ova Site for fertilization of the egg
 Uterus Strong, elastic muscle the size of a fist Holds & nourishes a developing fetus Contracts during childbirth to help delivery
Uterus Strong, elastic muscle the size of a fist Holds & nourishes a developing fetus Contracts during childbirth to help delivery
 Uterus Endometrium (inner lining) – Builds up with blood tissue to prepare to receive a fertilized ovum – Has many glands and blood vessels – Sheds buildup each month as menstral flow
Uterus Endometrium (inner lining) – Builds up with blood tissue to prepare to receive a fertilized ovum – Has many glands and blood vessels – Sheds buildup each month as menstral flow
 Uterus Cervix – Lowest part of the uterus – During Pregnancy Narrows to keep the growing embryo inside the womb during pregnancy Creates mucus plug that seals uterus off – When not pregnant, glands continuously secret dead cells and mucus – Pap Smear – scraping the wall of the cervix
Uterus Cervix – Lowest part of the uterus – During Pregnancy Narrows to keep the growing embryo inside the womb during pregnancy Creates mucus plug that seals uterus off – When not pregnant, glands continuously secret dead cells and mucus – Pap Smear – scraping the wall of the cervix
 Vagina Elastic, tube-like passageway about 4 -5 inches long from cervix to opening Stretches to allow for birth and sexual intercourse Moist and acidic environment that constantly sheds dead cell helps prevents infection from outside pathogens
Vagina Elastic, tube-like passageway about 4 -5 inches long from cervix to opening Stretches to allow for birth and sexual intercourse Moist and acidic environment that constantly sheds dead cell helps prevents infection from outside pathogens
 Concerns Dysmenorrhea – painful contractions during menstruation, pressure in pelvic region, bloating, headaches, backaches and nausea PMS (Premenstrual Syndrome)symptoms include: weight gain, cramps, bloating, swollen breasts, mood swings, cravings, nervous tension, anxiety, irritability, depression, and fatigue
Concerns Dysmenorrhea – painful contractions during menstruation, pressure in pelvic region, bloating, headaches, backaches and nausea PMS (Premenstrual Syndrome)symptoms include: weight gain, cramps, bloating, swollen breasts, mood swings, cravings, nervous tension, anxiety, irritability, depression, and fatigue
 Concerns Toxic Shock Syndrome – women become seriously ill during their menstrual cycle while using tampons and not changing them frequently enough. Sterility- can be caused by blocking of both tubes, no ovulation, or endometriosis.
Concerns Toxic Shock Syndrome – women become seriously ill during their menstrual cycle while using tampons and not changing them frequently enough. Sterility- can be caused by blocking of both tubes, no ovulation, or endometriosis.
 Concerns Vaginitis- very common, will affect most females during their lives. There are 3 most common: – Yeast infections (Candidiasis) – Nonspecific Vaginitis – Trichomonas's & STI’s At least 15 percent of women in the U. S. are infertile due to tubal damage caused by pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), the result of an untreated STD.
Concerns Vaginitis- very common, will affect most females during their lives. There are 3 most common: – Yeast infections (Candidiasis) – Nonspecific Vaginitis – Trichomonas's & STI’s At least 15 percent of women in the U. S. are infertile due to tubal damage caused by pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), the result of an untreated STD.
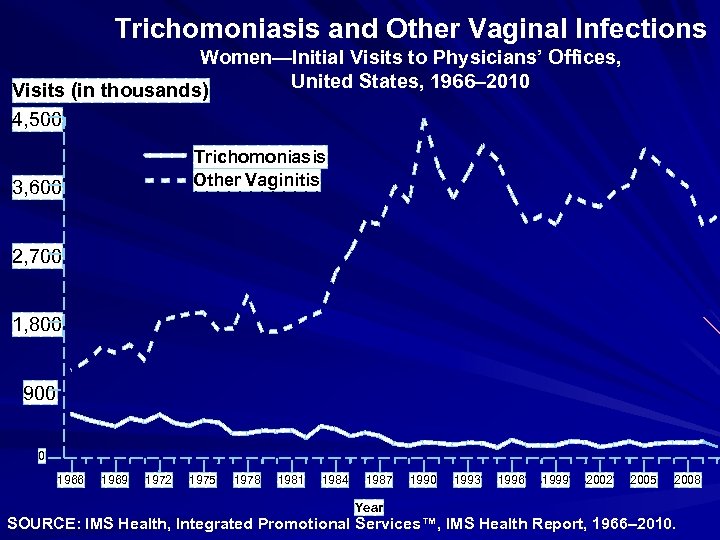 Trichomoniasis and Other Vaginal Infections Women—Initial Visits to Physicians’ Offices, United States, 1966– 2010 Visits (in thousands) 4, 500 Trichomoniasis Other Vaginitis 3, 600 2, 700 1, 800 900 0 1966 1969 1972 1975 1978 1981 1984 1987 Year 1990 1993 1996 1999 2002 2005 2008 SOURCE: IMS Health, Integrated Promotional Services™, IMS Health Report, 1966– 2010.
Trichomoniasis and Other Vaginal Infections Women—Initial Visits to Physicians’ Offices, United States, 1966– 2010 Visits (in thousands) 4, 500 Trichomoniasis Other Vaginitis 3, 600 2, 700 1, 800 900 0 1966 1969 1972 1975 1978 1981 1984 1987 Year 1990 1993 1996 1999 2002 2005 2008 SOURCE: IMS Health, Integrated Promotional Services™, IMS Health Report, 1966– 2010.
 Breast Cancer Malignant tumors grow in breast tissue Second leading cause of death in women after lung cancer No one know what causes it Can be treatable and curable Symptoms include: – Change in appearance – Lumps or swelling in breast or underarm Video for girls
Breast Cancer Malignant tumors grow in breast tissue Second leading cause of death in women after lung cancer No one know what causes it Can be treatable and curable Symptoms include: – Change in appearance – Lumps or swelling in breast or underarm Video for girls


