8c3d734567a42755571011068dd8eb6f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 Feline Hepatic Lipidosis
Feline Hepatic Lipidosis
 Overview The most common form of liver disease in cat. l Almost all cases are associated with OBESITY l Primary HL and 2 ndary HL 1) Primary - Etiology is undetermined but associated with a period of anorexia * about 50% of cases 2) 2 ndary – underlying dz ; DM, IBD, pancreatitis, cholangiohepatitis, gastric FB, FLUTD, cancer… l
Overview The most common form of liver disease in cat. l Almost all cases are associated with OBESITY l Primary HL and 2 ndary HL 1) Primary - Etiology is undetermined but associated with a period of anorexia * about 50% of cases 2) 2 ndary – underlying dz ; DM, IBD, pancreatitis, cholangiohepatitis, gastric FB, FLUTD, cancer… l
 Signalment - obese, middle-aged(4 -15), house cat l - recent history of stress or starvation * duration of anorexia : median 2 -3 wks l - domestic shorthair cats l - female>male l
Signalment - obese, middle-aged(4 -15), house cat l - recent history of stress or starvation * duration of anorexia : median 2 -3 wks l - domestic shorthair cats l - female>male l
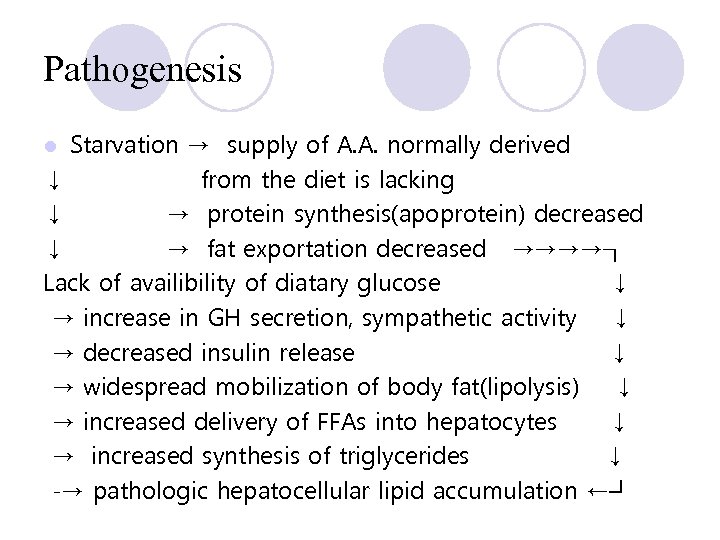 Pathogenesis Starvation → supply of A. A. normally derived ↓ from the diet is lacking ↓ → protein synthesis(apoprotein) decreased ↓ → fat exportation decreased →→→→┒ Lack of availibility of diatary glucose ↓ → increase in GH secretion, sympathetic activity ↓ → decreased insulin release ↓ → widespread mobilization of body fat(lipolysis) ↓ → increased delivery of FFAs into hepatocytes ↓ → increased synthesis of triglycerides ↓ -→ pathologic hepatocellular lipid accumulation ←┛ l
Pathogenesis Starvation → supply of A. A. normally derived ↓ from the diet is lacking ↓ → protein synthesis(apoprotein) decreased ↓ → fat exportation decreased →→→→┒ Lack of availibility of diatary glucose ↓ → increase in GH secretion, sympathetic activity ↓ → decreased insulin release ↓ → widespread mobilization of body fat(lipolysis) ↓ → increased delivery of FFAs into hepatocytes ↓ → increased synthesis of triglycerides ↓ -→ pathologic hepatocellular lipid accumulation ←┛ l
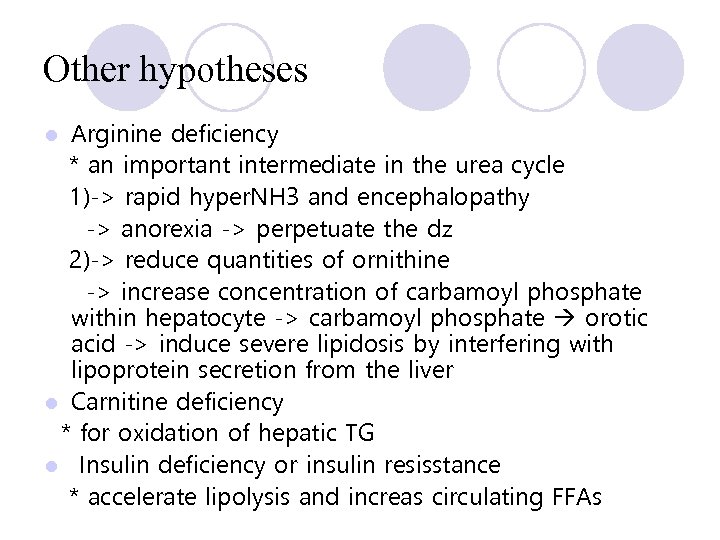 Other hypotheses Arginine deficiency * an important intermediate in the urea cycle 1)-> rapid hyper. NH 3 and encephalopathy -> anorexia -> perpetuate the dz 2)-> reduce quantities of ornithine -> increase concentration of carbamoyl phosphate within hepatocyte -> carbamoyl phosphate orotic acid -> induce severe lipidosis by interfering with lipoprotein secretion from the liver l Carnitine deficiency * for oxidation of hepatic TG l Insulin deficiency or insulin resisstance * accelerate lipolysis and increas circulating FFAs l
Other hypotheses Arginine deficiency * an important intermediate in the urea cycle 1)-> rapid hyper. NH 3 and encephalopathy -> anorexia -> perpetuate the dz 2)-> reduce quantities of ornithine -> increase concentration of carbamoyl phosphate within hepatocyte -> carbamoyl phosphate orotic acid -> induce severe lipidosis by interfering with lipoprotein secretion from the liver l Carnitine deficiency * for oxidation of hepatic TG l Insulin deficiency or insulin resisstance * accelerate lipolysis and increas circulating FFAs l
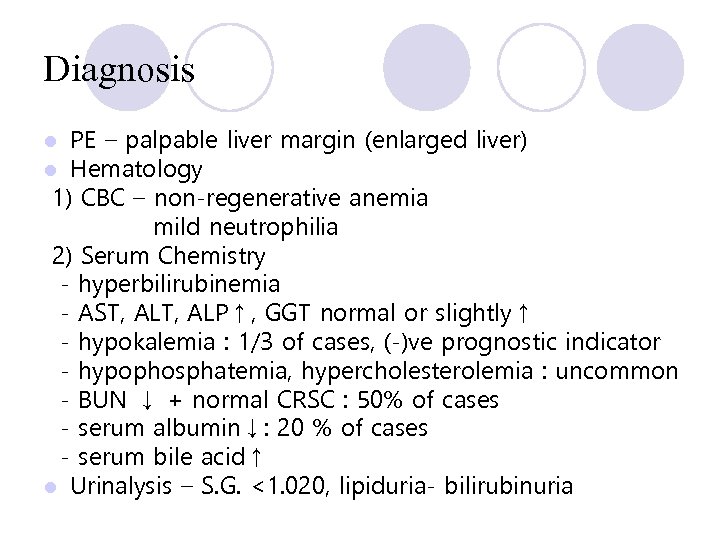 Diagnosis PE – palpable liver margin (enlarged liver) Hematology 1) CBC – non-regenerative anemia mild neutrophilia 2) Serum Chemistry - hyperbilirubinemia - AST, ALP↑, GGT normal or slightly↑ - hypokalemia : 1/3 of cases, (-)ve prognostic indicator - hypophosphatemia, hypercholesterolemia : uncommon - BUN ↓ + normal CRSC : 50% of cases - serum albumin↓: 20 % of cases - serum bile acid↑ l Urinalysis – S. G. <1. 020, lipiduria- bilirubinuria l l
Diagnosis PE – palpable liver margin (enlarged liver) Hematology 1) CBC – non-regenerative anemia mild neutrophilia 2) Serum Chemistry - hyperbilirubinemia - AST, ALP↑, GGT normal or slightly↑ - hypokalemia : 1/3 of cases, (-)ve prognostic indicator - hypophosphatemia, hypercholesterolemia : uncommon - BUN ↓ + normal CRSC : 50% of cases - serum albumin↓: 20 % of cases - serum bile acid↑ l Urinalysis – S. G. <1. 020, lipiduria- bilirubinuria l l
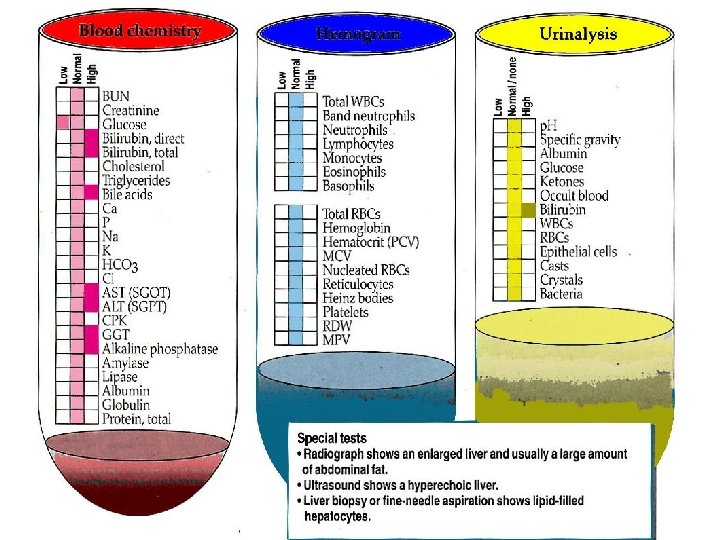
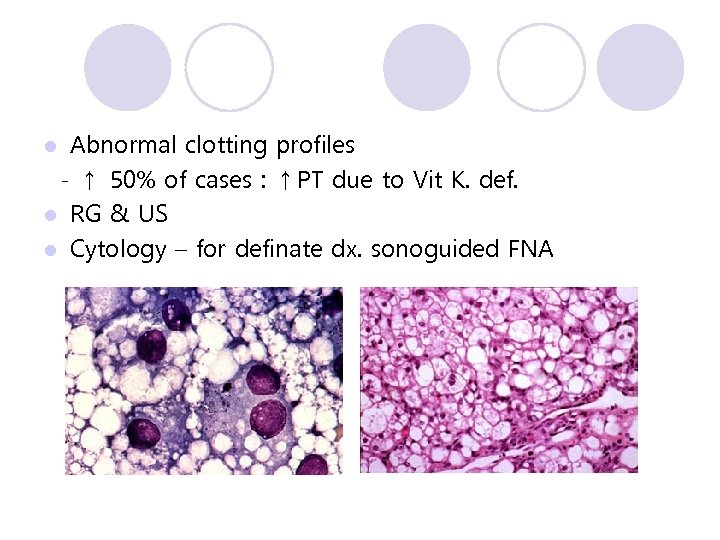 Abnormal clotting profiles - ↑ 50% of cases : ↑PT due to Vit K. def. l RG & US l Cytology – for definate dx. sonoguided FNA l
Abnormal clotting profiles - ↑ 50% of cases : ↑PT due to Vit K. def. l RG & US l Cytology – for definate dx. sonoguided FNA l
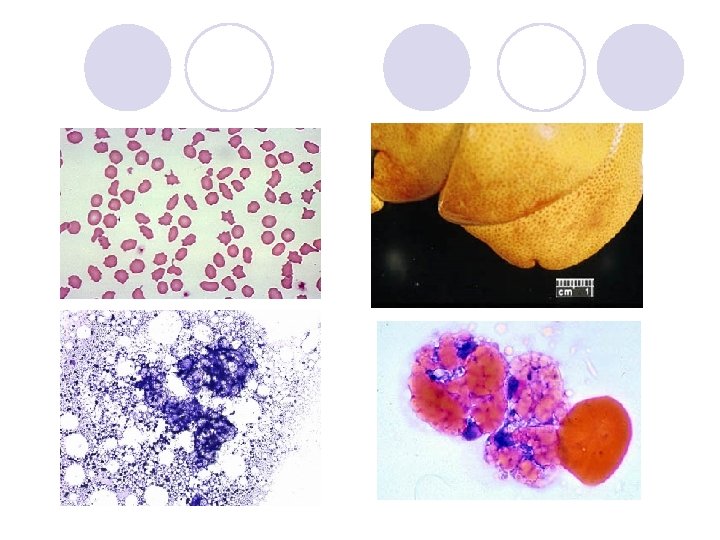
 biopsy When to persue a Liver biopsy? - feeding attempts fail, bilirubin does not decline, clinical illness persists at a several lv after 7 -10 days of critical supportive care l >80% of hepatocyte -> vacuolated l Not necessary for dx but ddx with cholangiohepatitis/cholangitis l l 상태 안정화 전에 실시하면 sudden death 가능.
biopsy When to persue a Liver biopsy? - feeding attempts fail, bilirubin does not decline, clinical illness persists at a several lv after 7 -10 days of critical supportive care l >80% of hepatocyte -> vacuolated l Not necessary for dx but ddx with cholangiohepatitis/cholangitis l l 상태 안정화 전에 실시하면 sudden death 가능.
 Procedure for liver biopsy 1. position the cat ventral recumbency 2. 25 G needle, 1/5 inch long, with a 3 cc syringe. 3. mild sedation using ketamine(2 mg/kg, IV) 4. between 8 -9 or 9 -10 intercostal space at the costochondral junction and take sample 5. make smear and stained with DQ, examined under 100 x & 1000 x l
Procedure for liver biopsy 1. position the cat ventral recumbency 2. 25 G needle, 1/5 inch long, with a 3 cc syringe. 3. mild sedation using ketamine(2 mg/kg, IV) 4. between 8 -9 or 9 -10 intercostal space at the costochondral junction and take sample 5. make smear and stained with DQ, examined under 100 x & 1000 x l
 Treatment cornerstone of tx. -> reverse the process of fat accumulation in the liver. supply full caloric requirement l caution - forced feeding 하지 않는편이 좋다 1. full caloric need 충족시키기 어려움 2. 먹는것 자체에 거부반응을 일으킬 수 있음 l
Treatment cornerstone of tx. -> reverse the process of fat accumulation in the liver. supply full caloric requirement l caution - forced feeding 하지 않는편이 좋다 1. full caloric need 충족시키기 어려움 2. 먹는것 자체에 거부반응을 일으킬 수 있음 l
 Treatment – fluid & treatments Fluid tx - avoid lactate containing and dextrose supplemented fluids l Potassium supplementation 1. KCl – do not exceed 0. 5 m. Eq/kg/hr 2. K Phosphate - initial 0. 01 -0. 03 mmol/kg/hr & monitor every 3 -6 hr - discontinue when serum phosphate>2 mg/dl l Vit K 1 – 0. 5 -1. 5 mg/kg at 12 hr intervals perenterally *NOT PO and IV, 2 -3 doses only l Vit E – 10 IU/Kg PO per day l
Treatment – fluid & treatments Fluid tx - avoid lactate containing and dextrose supplemented fluids l Potassium supplementation 1. KCl – do not exceed 0. 5 m. Eq/kg/hr 2. K Phosphate - initial 0. 01 -0. 03 mmol/kg/hr & monitor every 3 -6 hr - discontinue when serum phosphate>2 mg/dl l Vit K 1 – 0. 5 -1. 5 mg/kg at 12 hr intervals perenterally *NOT PO and IV, 2 -3 doses only l Vit E – 10 IU/Kg PO per day l
 Water soluble vitamines – 1 -2 ml B soluble vit. Per liter l Thiamine(Vit B 1) – 100 mg PO, use B soluble vit *NOT SQ or IM l L carnitine - 250 mg PO l GSH donors l N-acetylcysteine l S-adenosylmethionine l Amoxicillin 10 mg/kg/SC/bid or Enrofloxacin 2 mg/kg/Sc or PO/bid l
Water soluble vitamines – 1 -2 ml B soluble vit. Per liter l Thiamine(Vit B 1) – 100 mg PO, use B soluble vit *NOT SQ or IM l L carnitine - 250 mg PO l GSH donors l N-acetylcysteine l S-adenosylmethionine l Amoxicillin 10 mg/kg/SC/bid or Enrofloxacin 2 mg/kg/Sc or PO/bid l
 Treatment – nutritional support l - l 1. 2. 3. - Initial feeding oral feeding/nasogastric tube -> E-tube do not place until eletrolytes, Vit K suppl. Hydration have been established : 48 -72 hr If persistent vomiting Check electrolytes : hypokalemia, hypophosphatemia Feeding tube problems : contrast RG, US Antiemetics metoclopramide 0. 01 -0. 02 mg/kg/hr-24 hrs or 0. 2 -0. 4 mg/kg SQ 20 min, before meal ondansetron 0. 1 -1. 0 mg/kg q 12 -24 hr/PO famotidine 0. 1 mg/kg/bid/IV
Treatment – nutritional support l - l 1. 2. 3. - Initial feeding oral feeding/nasogastric tube -> E-tube do not place until eletrolytes, Vit K suppl. Hydration have been established : 48 -72 hr If persistent vomiting Check electrolytes : hypokalemia, hypophosphatemia Feeding tube problems : contrast RG, US Antiemetics metoclopramide 0. 01 -0. 02 mg/kg/hr-24 hrs or 0. 2 -0. 4 mg/kg SQ 20 min, before meal ondansetron 0. 1 -1. 0 mg/kg q 12 -24 hr/PO famotidine 0. 1 mg/kg/bid/IV
 Tube feeding - 1 -3개월간의 tube feeding 필요 -> 장기간 control이 가능한 esophagear or gastric tube 장착 * nasogastric tube 장착시 후각세포 damage - tube 장착 후 2 -8주내에 점진적으로 간수치 정상화 - 완전히 회복되기 전에는 oral feeding 하지 않는다. - 퇴원 후에는 14일마다 내원하여 tube 장착 상태 체크 l
Tube feeding - 1 -3개월간의 tube feeding 필요 -> 장기간 control이 가능한 esophagear or gastric tube 장착 * nasogastric tube 장착시 후각세포 damage - tube 장착 후 2 -8주내에 점진적으로 간수치 정상화 - 완전히 회복되기 전에는 oral feeding 하지 않는다. - 퇴원 후에는 14일마다 내원하여 tube 장착 상태 체크 l
 Diet to food : 일반 시판되는 cat food - DO NOT restrict protein unless HE signs develops - blend specific suppelments -> KCL, Vit B complex, Choline, Tauine, L-carnitine. . l How much to feed - 60 -90 kcal/kg/day - Start with a liquid diet : initially 5 ml at 2 hr intervals 2 -3 times increasing 2 -4 days * AVOID relience on appetite modifiers! l
Diet to food : 일반 시판되는 cat food - DO NOT restrict protein unless HE signs develops - blend specific suppelments -> KCL, Vit B complex, Choline, Tauine, L-carnitine. . l How much to feed - 60 -90 kcal/kg/day - Start with a liquid diet : initially 5 ml at 2 hr intervals 2 -3 times increasing 2 -4 days * AVOID relience on appetite modifiers! l
 Prognosis 일반적으로 10일 이내에 total bilirubin concentration이 50% 이상 떨어지고 다른 혈액검사 수치가 정상적으로 떨어지는 경우 예후 양호 l 입원기간은 대개 7일에서 21일 l 입원후 96시간 이상 생존시 85% 이상 회복 l
Prognosis 일반적으로 10일 이내에 total bilirubin concentration이 50% 이상 떨어지고 다른 혈액검사 수치가 정상적으로 떨어지는 경우 예후 양호 l 입원기간은 대개 7일에서 21일 l 입원후 96시간 이상 생존시 85% 이상 회복 l


