23ef4f93ac09bc40b62d2291578a048d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20

Feedback is welcome Skysail Click on www. skysailtraining. co. uk Training for on line Colregs test and CEVNI test and to buy Weather, Colregs, VHF and more navigation skills charts Test Yourself - Online Exam RYA Day Skipper and Yachtmaster ICC / BSAC Seamanship Met - Weather Exam / Assessment Meteorology Weather at Sea Mouse click or Page Down to start 1 © 2009 SKYSAILTRAINING 9 th November 2009 © K M Bater 2010
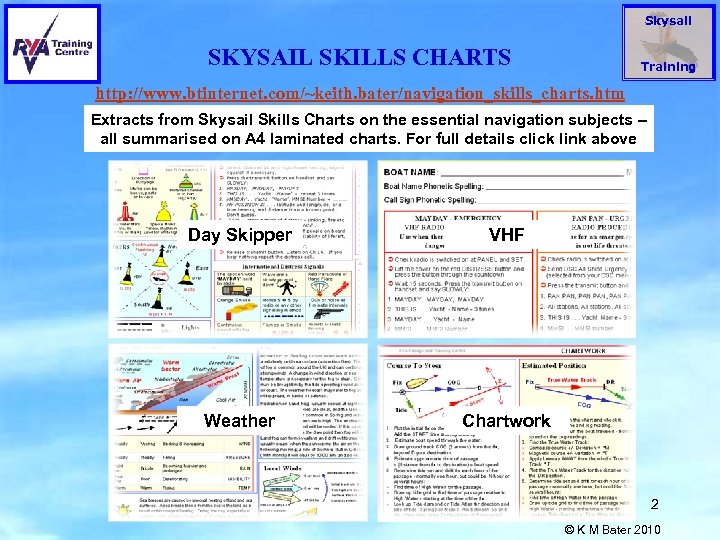
Skysail SKYSAIL SKILLS CHARTS Training http: //www. btinternet. com/~keith. bater/navigation_skills_charts. htm Extracts from Skysail Skills Charts on the essential navigation subjects – all summarised on A 4 laminated charts. For full details click link above Day Skipper VHF Weather Chartwork 2 © K M Bater 2010

Before the Meteorology tests Skysail Training • Here is the full weather presentation if you need it (2 MB): www. btinternet. com/~keith. bater/weather_for_course. pdf 3 © K M Bater 2010

Skysail Forecasts Training Where would you find weather forecasts? On land Ø Ø Ø Ø TV National radio Local radio Newspapers Teletext Web Barometer Mobile phone Day Skipper Weather At sea Ø Ø Ø Ø BBC radio Coastguard VHF Metfax to PC Navtex Barometer Observation Mobile phone 4 © K M Bater 2010

Skysail Forecasts Training What is the sequence of the Shipping Forecast? Gale warnings General Synopsis at time of issue Wind now - direction and force Wind later Sea state Weather - fair, rain, etc Visibility Day Skipper Weather 5 © K M Bater 2010

Skysail Shipping Forecast Terms Training What do the following mean? Imminent Soon Later Within 6 hours 6 to 12 hours After 12 hours Very poor < 1000 metres visibility < 2 Miles Poor of the time of issue of the forecast Moderate 2 - 5 Miles Wave height m Moderate 1. 25 – 2. 5 Good > 5 Miles Rough Fair No precipitation 2. 5 – 4. 0 Very rough 4. 0 – 6. 0 6 Day Skipper Weather © K M Bater 2010

Skysail Wave height Training What factors affect wave height? 1 Wind speed and duration 2 Tide speed and direction wind against tide gives higher waves 3 Depth of water 4 Fetch - the distance over which the wind blows 5 Swell - the wave pattern before the current weather Day Skipper Weather 7 © K M Bater 2010

Skysail Wind Training How do you define the following? Direction from which wind blows Cyclonic Rapid changes in wind direction (Possibly at the centre of a depression) Veering Changing direction clockwise Backing Changing direction anticlockwise Day Skipper Weather 8 © K M Bater 2010

Skysail Pressure / Wind / Waves Training What is likely if the pressure has changed by 6 millibars in the last 3 hours? A gale (whether the change is rising or falling) From these descriptions estimate what the Beaufort wind force is: a) Moderate waves, many white crests. Force 5 17 -21 knots b) Sea heaps up, spray, breaking waves, foam blows in streaks. Force 7 28 -33 knots Day Skipper Weather 9 © K M Bater 2010
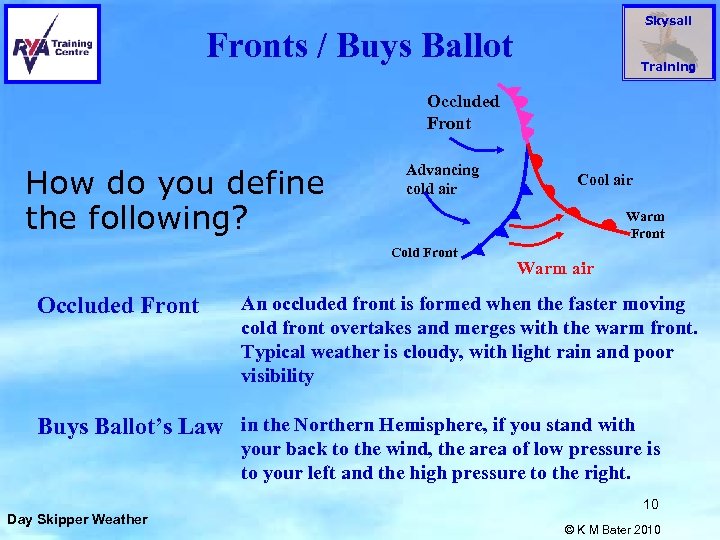
Skysail Fronts / Buys Ballot Training Occluded Front How do you define the following? Advancing cold air Warm Front Cold Front Occluded Front Cool air Warm air An occluded front is formed when the faster moving cold front overtakes and merges with the warm front. Typical weather is cloudy, with light rain and poor visibility Buys Ballot’s Law in the Northern Hemisphere, if you stand with your back to the wind, the area of low pressure is to your left and the high pressure to the right. Day Skipper Weather 10 © K M Bater 2010
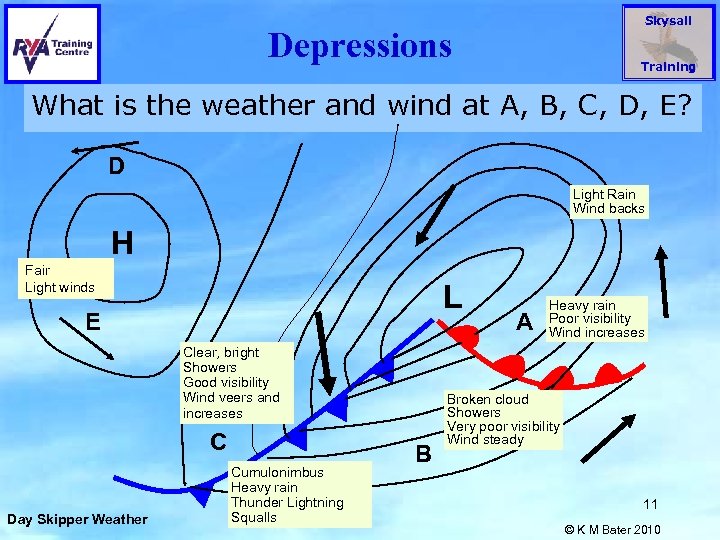
Skysail Depressions Training What is the weather and wind at A, B, C, D, E? D Light Rain Wind backs H Fair Light winds L E Clear, bright Showers Good visibility Wind veers and increases C Day Skipper Weather Cumulonimbus Heavy rain Thunder Lightning Squalls B A Heavy rain Poor visibility Wind increases Broken cloud Showers Very poor visibility Wind steady 11 © K M Bater 2010
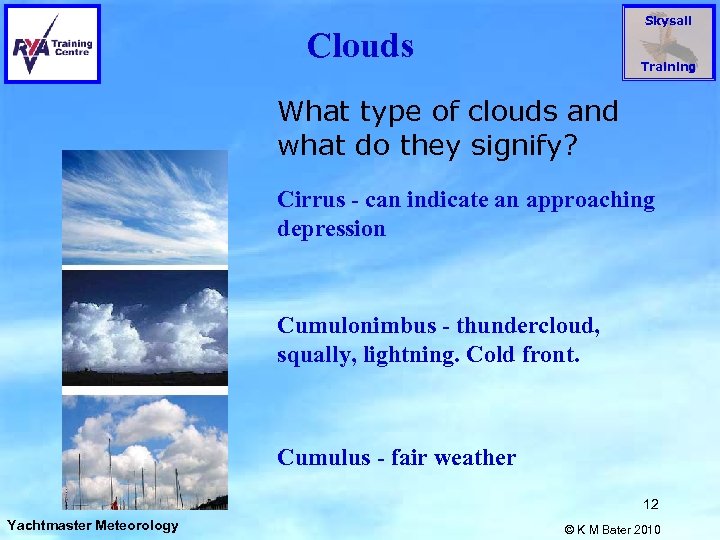
Skysail Clouds Training What type of clouds and what do they signify? Cirrus - can indicate an approaching depression Cumulonimbus - thundercloud, squally, lightning. Cold front. Cumulus - fair weather 12 Yachtmaster Meteorology © K M Bater 2010

Sea Breezes Skysail Training What is a sea breeze? What causes it? Sea breezes are caused by unequal heating of land sea surfaces. During the day, especially in summer, solar radiation heats the land surface to become warmer than the sea surface which stays cold all summer. The temperature difference rises to a maximum around mid afternoon. The warm air rises over the land cool air from the sea is drawn in, setting up an onshore wind. As the heating effect increases, the sea breeze strengthens, and may reach 15 knots (F 4). A land breeze develops at night as the land cools relative to the sea and an opposite but weaker circulation sets up. 13 Yachtmaster Meteorology © K M Bater 2010

Skysail Sea Fog 1. What causes sea fog? 2. In which season is it most frequent? 3. Will there be wind? 4. What Training It occurs when warm air flows over a cold sea surface (advection flow). Spring / early summer when the sea is still cold. Yes makes it clear? A change in wind direction or sea temperature 14 Yachtmaster Meteorology © K M Bater 2010

Skysail Land Fog 1. What causes land fog? 2. In which season is it most frequent? 3. Will there be wind? 4. What makes it clear? Yachtmaster Meteorology Training It occurs when land cools overnight by radiation of heat. The air cools and moisture condenses to form fog. Late Autumn / Winter when pressure is high and there is no cloud. No. Land fog can form in valleys and drift out to sea. The heat of the sun the following morning. 15 © K M Bater 2010
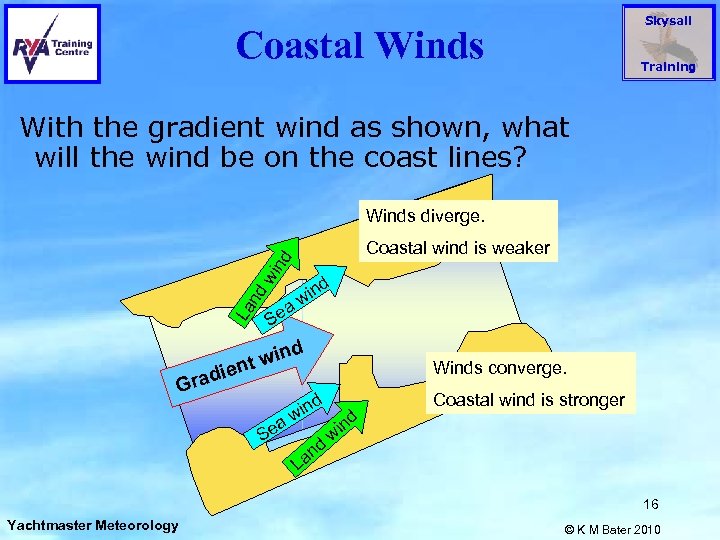
Skysail Coastal Winds Training With the gradient wind as shown, what will the wind be on the coast lines? Winds diverge. La n dw ind Coastal wind is weaker a Se ind w d win nt e radi G a Se ind w nd La Winds converge. d in w Coastal wind is stronger 16 Yachtmaster Meteorology © K M Bater 2010
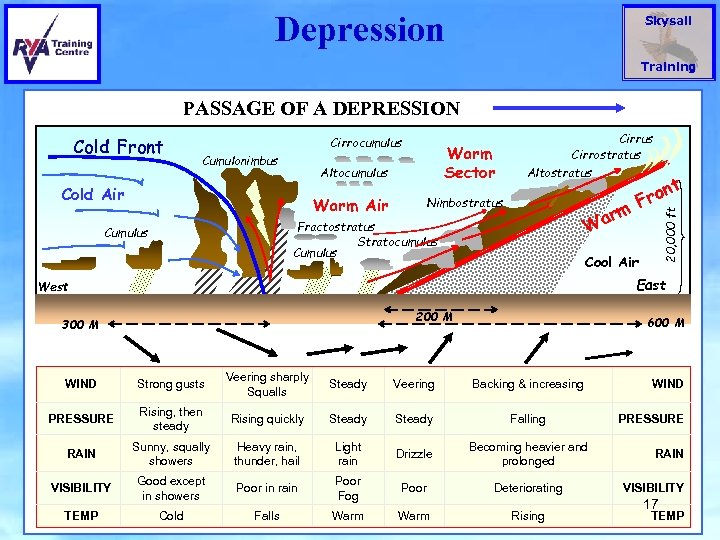
Depression Skysail Training PASSAGE OF A DEPRESSION Cirrocumulus Cumulonimbus Warm Sector Altocumulus Cold Air Warm Air Cirrus Cirrostratus Altostratus Nimbostratus arm W Fractostratus Stratocumulus Cumulus t n Fro 20, 000 ft Cold Front Cool Air East West 200 M 300 M 600 M WIND Strong gusts Veering sharply Squalls Steady Veering Backing & increasing PRESSURE Rising, then steady Rising quickly Steady Falling RAIN Sunny, squally showers Heavy rain, thunder, hail Light rain Drizzle Becoming heavier and prolonged VISIBILITY Good except in showers Poor in rain Poor Fog Poor Deteriorating TEMP Cold Falls Warm Rising WIND PRESSURE RAIN VISIBILITY 17 TEMP © K M Bater 2010
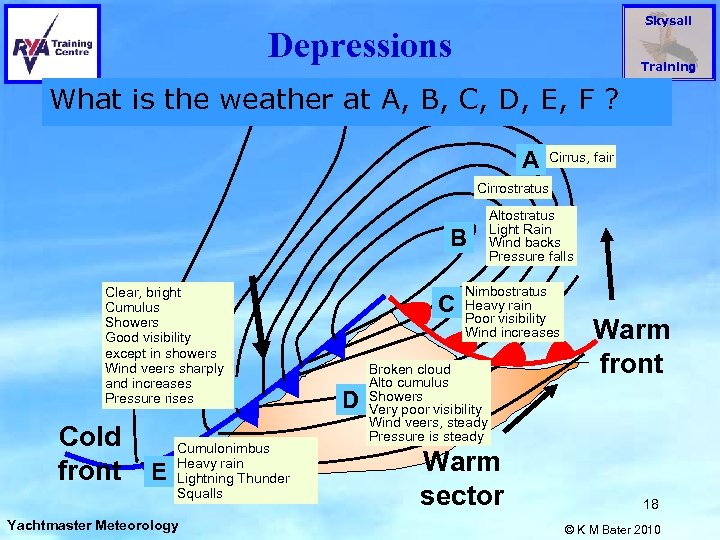
Skysail Depressions Training What is the weather at A, B, C, D, E, F ? A Cirrus, fair Cirrostratus B Clear, bright Cumulus Showers Good visibility except in showers Wind veers sharply and increases Pressure rises F Cold front E Cumulonimbus Heavy rain Lightning Thunder Squalls Yachtmaster Meteorology C D Altostratus Light Rain Wind backs Pressure falls Nimbostratus Heavy rain Poor visibility Wind increases Broken cloud Alto cumulus Showers Very poor visibility Wind veers, steady Pressure is steady Warm sector Warm front 18 © K M Bater 2010
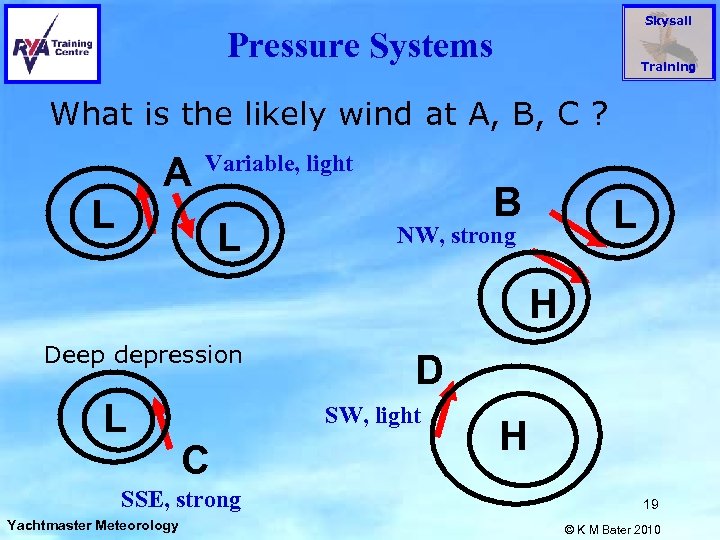
Skysail Pressure Systems Training What is the likely wind at A, B, C ? A L Variable, light L B L NW, strong H Deep depression L SW, light C SSE, strong Yachtmaster Meteorology D H 19 © K M Bater 2010
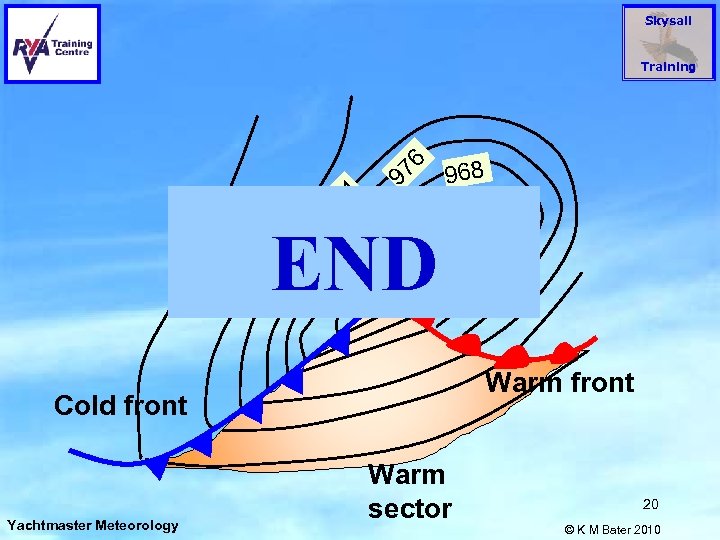
Skysail 968 98 END 992 100 0 4 97 6 Training Warm front Cold front Yachtmaster Meteorology 60 9 Warm sector 20 © K M Bater 2010
23ef4f93ac09bc40b62d2291578a048d.ppt