87cc0088f28fe82e3ab07ebf52689a1b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 58
 Federalism
Federalism
 Why Federalism • Issue: create a new central government that would be strong enough to meet nation’s need AND preserve the strength of existing States. • Few Framers favored strong central government based on British Model • Yet knew Articles proved too weak to deal with nation’s problems
Why Federalism • Issue: create a new central government that would be strong enough to meet nation’s need AND preserve the strength of existing States. • Few Framers favored strong central government based on British Model • Yet knew Articles proved too weak to deal with nation’s problems
 Why Federalism • Framers were dedicated to concept o limited government 1. Government power poses threat t individual liberty 2. Exercise of government power must be restrained 3. That to divide government power is to curb it and so prevent abuse
Why Federalism • Framers were dedicated to concept o limited government 1. Government power poses threat t individual liberty 2. Exercise of government power must be restrained 3. That to divide government power is to curb it and so prevent abuse
 Federalism • System of government with written constitution that divides the power between central/national and state o provinces government. • Division of power is in Constitution and spelled out in the Bill of Rights – 10 th Amendment “powers not delegated to the : U. S. by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it t the states is RESERVED to the States respectively, or to the people. ”
Federalism • System of government with written constitution that divides the power between central/national and state o provinces government. • Division of power is in Constitution and spelled out in the Bill of Rights – 10 th Amendment “powers not delegated to the : U. S. by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it t the states is RESERVED to the States respectively, or to the people. ”
 United States Constitution = • Supreme law of the land…. • US Constitution is over all levels of government. National Government is over the States. Some delegates feared the central government would National be too powerful. A Govt. federal govt. was created to allow states and local State Government govts to handle their own affairs. Powers of government are divided between a National, state and local governments. Powers of government are shared by all levels. Local Government Federal
United States Constitution = • Supreme law of the land…. • US Constitution is over all levels of government. National Government is over the States. Some delegates feared the central government would National be too powerful. A Govt. federal govt. was created to allow states and local State Government govts to handle their own affairs. Powers of government are divided between a National, state and local governments. Powers of government are shared by all levels. Local Government Federal
 United States Constitution = • Supreme law of the land…. • It is above all levels of government and no act, law or public policy can be in conflict with it. National Government is over the States. Supreme law
United States Constitution = • Supreme law of the land…. • It is above all levels of government and no act, law or public policy can be in conflict with it. National Government is over the States. Supreme law
 Division of Power
Division of Power
 Powers of the National Government • Exercises delegated powers granted by the Constitution 1. Expressed- spelled out, expressly in Constitution, “enumerated powers” • Article I, Sect. 8 collect money (taxes), coin money, regulate foreign and interstate commerce, raise armed forces, declare war, grant patents and copyrights.
Powers of the National Government • Exercises delegated powers granted by the Constitution 1. Expressed- spelled out, expressly in Constitution, “enumerated powers” • Article I, Sect. 8 collect money (taxes), coin money, regulate foreign and interstate commerce, raise armed forces, declare war, grant patents and copyrights.
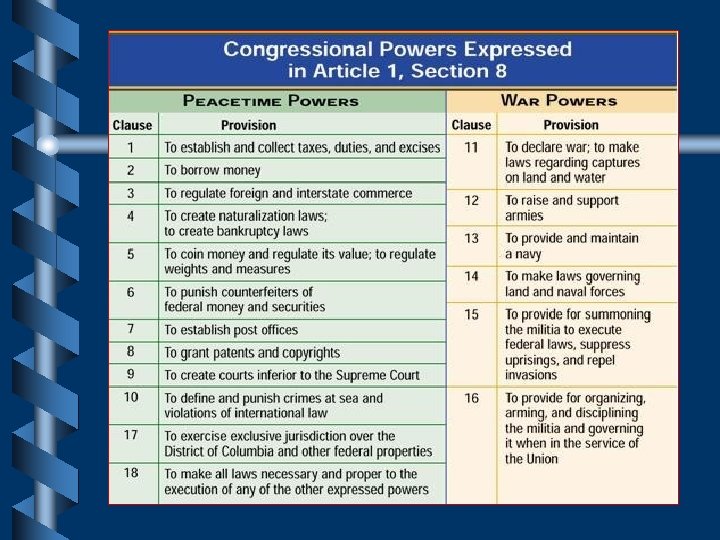
 Powers of the National Government 2. Implied Powers- not expressed but reasonably suggested • Article 1, Section 8, Clause 18 “necessary and proper clause” or elastic clause – Regulate labor/management relations, build hydroelectric dams, 42, 000 mile interstate highway system, prohibits racial discrimination discriminatio in restaurants, theater, hotels
Powers of the National Government 2. Implied Powers- not expressed but reasonably suggested • Article 1, Section 8, Clause 18 “necessary and proper clause” or elastic clause – Regulate labor/management relations, build hydroelectric dams, 42, 000 mile interstate highway system, prohibits racial discrimination discriminatio in restaurants, theater, hotels

 Powers of the National Government 3. Inherent Powers-belong to national government because it is a sovereign state – Regulate immigration, deport undocumented aliens, acquire territory, grant diplomatic recognition, protect against rebellion or attem to overthrow the government by force or violen – Inherent powers- not necessary to go to these lengths to find powers in the constitution. The powers exist because the U. S. exists
Powers of the National Government 3. Inherent Powers-belong to national government because it is a sovereign state – Regulate immigration, deport undocumented aliens, acquire territory, grant diplomatic recognition, protect against rebellion or attem to overthrow the government by force or violen – Inherent powers- not necessary to go to these lengths to find powers in the constitution. The powers exist because the U. S. exists


 Inherent Powers
Inherent Powers
 Powers Denied to the National Gov’t • Power to levy duties on exports • Override Bill of Rights – To prohibit freedom of religion, speech, press o assembly, illegal search and seizure, speedy tri and trial by jury • Create Public schools, enact uniform th marriage and divorce laws (14 amendment), set up local governments • Powers denied by federalism itself – Cannot tax states or local governments out of existance
Powers Denied to the National Gov’t • Power to levy duties on exports • Override Bill of Rights – To prohibit freedom of religion, speech, press o assembly, illegal search and seizure, speedy tri and trial by jury • Create Public schools, enact uniform th marriage and divorce laws (14 amendment), set up local governments • Powers denied by federalism itself – Cannot tax states or local governments out of existance
 The States • Reserved Powers those powers that the Constitution does not grant to National government BUT does not deny to the States – Forbid marriage under 18 without parental consent – Buy liquor under age of 21 st • ONLY Expressed power of States- 21 amendment – Permit or prohibit gambling – Licensed: doctors, lawyers, teachers
The States • Reserved Powers those powers that the Constitution does not grant to National government BUT does not deny to the States – Forbid marriage under 18 without parental consent – Buy liquor under age of 21 st • ONLY Expressed power of States- 21 amendment – Permit or prohibit gambling – Licensed: doctors, lawyers, teachers
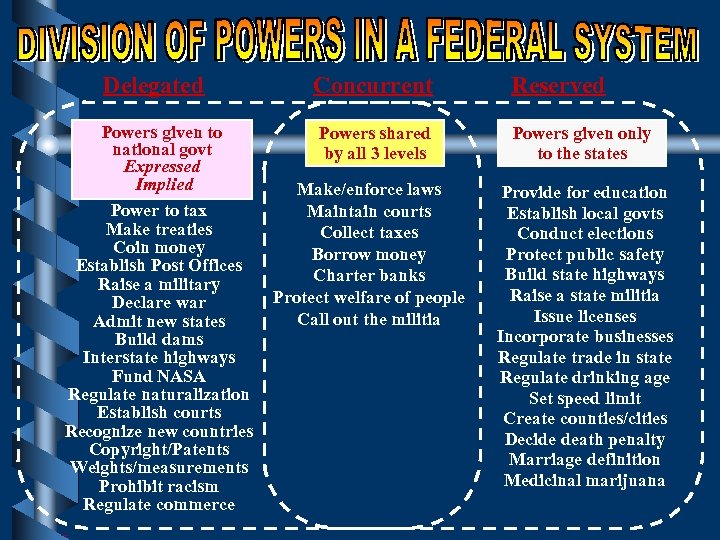 Delegated Concurrent Powers given to national govt Expressed Implied Power to tax Make treaties Coin money Establish Post Offices Raise a military Declare war Admit new states Build dams Interstate highways Fund NASA Regulate naturalization Establish courts Recognize new countries Copyright/Patents Weights/measurements Prohibit racism Regulate commerce Powers shared by all 3 levels Div of powers Make/enforce laws Maintain courts Collect taxes Borrow money Charter banks Protect welfare of people Call out the militia Reserved Powers given only to the states Provide for education Establish local govts Conduct elections Protect public safety Build state highways Raise a state militia Issue licenses Incorporate businesses Regulate trade in state Regulate drinking age Set speed limit Create counties/cities Decide death penalty Marriage definition Medicinal marijuana
Delegated Concurrent Powers given to national govt Expressed Implied Power to tax Make treaties Coin money Establish Post Offices Raise a military Declare war Admit new states Build dams Interstate highways Fund NASA Regulate naturalization Establish courts Recognize new countries Copyright/Patents Weights/measurements Prohibit racism Regulate commerce Powers shared by all 3 levels Div of powers Make/enforce laws Maintain courts Collect taxes Borrow money Charter banks Protect welfare of people Call out the militia Reserved Powers given only to the states Provide for education Establish local govts Conduct elections Protect public safety Build state highways Raise a state militia Issue licenses Incorporate businesses Regulate trade in state Regulate drinking age Set speed limit Create counties/cities Decide death penalty Marriage definition Medicinal marijuana


 Powers Denied to the States • Cannot enter into any treaty, alliance, or confederation • Print or coin money • Deprive any person life, liberty, o property without due process • Cannot tax any federal agencies o functions of National governmen (Mc. Culloch v. Maryland)
Powers Denied to the States • Cannot enter into any treaty, alliance, or confederation • Print or coin money • Deprive any person life, liberty, o property without due process • Cannot tax any federal agencies o functions of National governmen (Mc. Culloch v. Maryland)
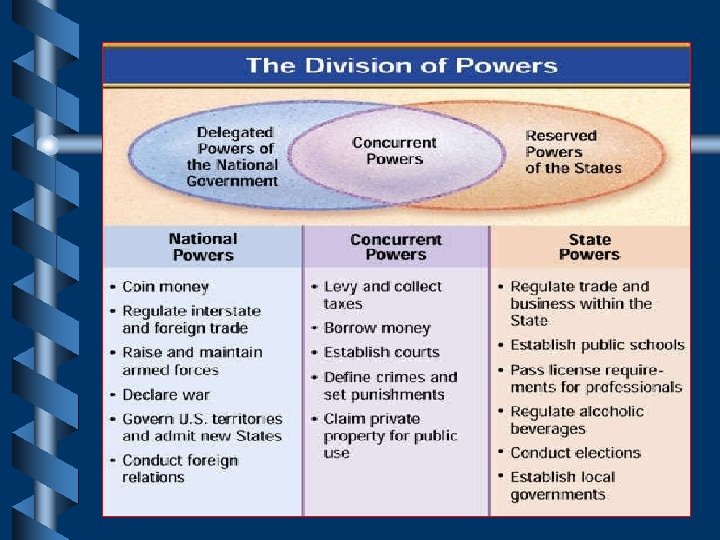
 State vs. Fed Govt. • Power can be: – Exclusive- only for Nat’l govt. • Regulate Interstate commerce and Foreign trade • Declare War – Concurrent- Shared powers that National and State government possess. • Levy taxes, establish courts,
State vs. Fed Govt. • Power can be: – Exclusive- only for Nat’l govt. • Regulate Interstate commerce and Foreign trade • Declare War – Concurrent- Shared powers that National and State government possess. • Levy taxes, establish courts,
 The Supreme Law of the Land • Framers expected conflict between National and State government • Article VI, Sect. 2 Constitution nation’s supreme law of the land – “The Constitution and laws of the Unite States…shall be the supreme Law of the Land. ” – Supremacy Clause- “linchpin of the Constitution” as it joins the federa gov’t into single unit
The Supreme Law of the Land • Framers expected conflict between National and State government • Article VI, Sect. 2 Constitution nation’s supreme law of the land – “The Constitution and laws of the Unite States…shall be the supreme Law of the Land. ” – Supremacy Clause- “linchpin of the Constitution” as it joins the federa gov’t into single unit

 Theory of Nullification
Theory of Nullification
 Virginia Kentucky Resolutions
Virginia Kentucky Resolutions
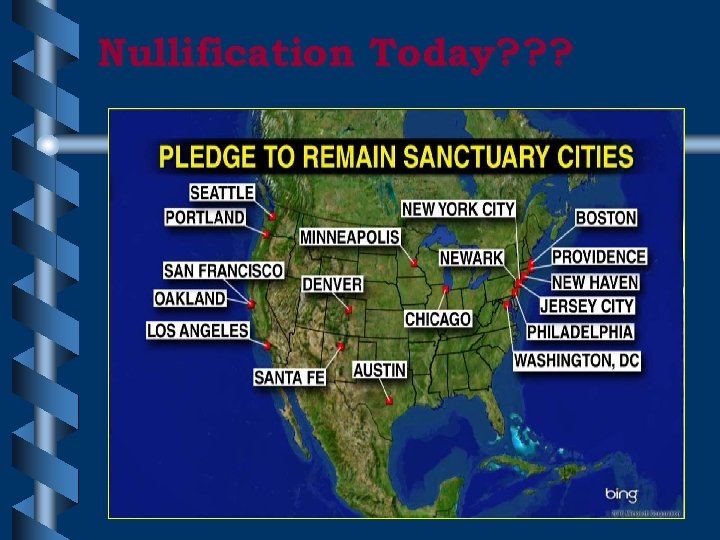 Nullification Today? ? ?
Nullification Today? ? ?
 The Nation’s Obligations to the States • Ensure each State has a republican govt. or representative gov’t – Article IV, Section 4 – Luther v. Borden, 1849 • Protect States against foreign invasion & domestic violence
The Nation’s Obligations to the States • Ensure each State has a republican govt. or representative gov’t – Article IV, Section 4 – Luther v. Borden, 1849 • Protect States against foreign invasion & domestic violence
 Constitution Requires National Govt. to • Provide assistance if State needs help with internal disorder • Respect territorial integrity of State – It can’t create new State without permission of original State – Article V A state cannot be deprived representation in the Senate without its own consent
Constitution Requires National Govt. to • Provide assistance if State needs help with internal disorder • Respect territorial integrity of State – It can’t create new State without permission of original State – Article V A state cannot be deprived representation in the Senate without its own consent
 Admitting New States • Only Congress has the power to admit new States to the Union – Congress has admitted 37 states – Vermont, Kentucky, Tennessee, Maine, and W. Virginia created by existing states – Texas was independent Republic – California admitted after ceded by Mexico – Other 30 only after longer period of time
Admitting New States • Only Congress has the power to admit new States to the Union – Congress has admitted 37 states – Vermont, Kentucky, Tennessee, Maine, and W. Virginia created by existing states – Texas was independent Republic – California admitted after ceded by Mexico – Other 30 only after longer period of time
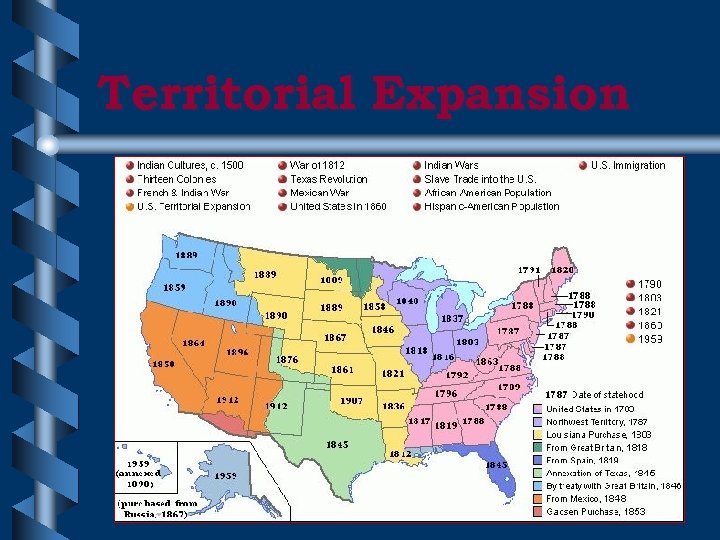 Territorial Expansion
Territorial Expansion
 Admission Procedure • The Area first asks Congress for admission • Enabling Act-Directing the people of the territory to frame a proposed Stat Constitution • Constitution voted on & submitted to Congress • Act of Admission Congress by • President signs act
Admission Procedure • The Area first asks Congress for admission • Enabling Act-Directing the people of the territory to frame a proposed Stat Constitution • Constitution voted on & submitted to Congress • Act of Admission Congress by • President signs act
 Hawaii and Alaska in 1959
Hawaii and Alaska in 1959
 Cooperative Federalism • The National Government provides financial assistance to States – Grants-in-Aid – Federal Grants – Block Grants – Revenue Sharing – Categorical Grants
Cooperative Federalism • The National Government provides financial assistance to States – Grants-in-Aid – Federal Grants – Block Grants – Revenue Sharing – Categorical Grants
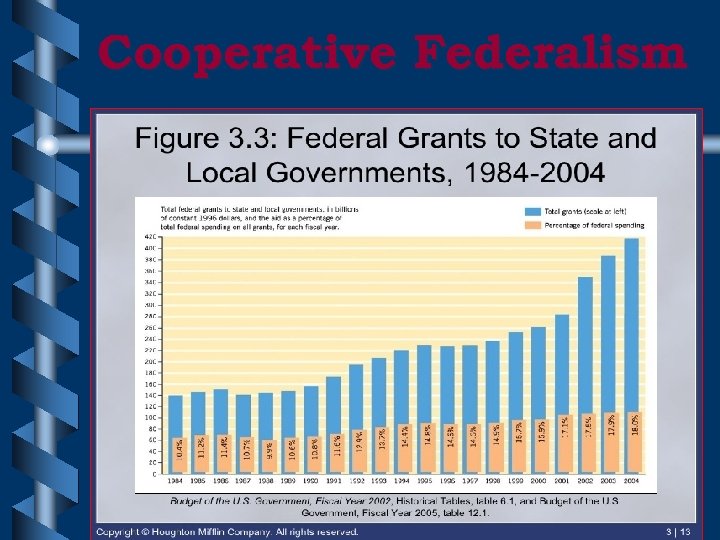 Cooperative Federalism
Cooperative Federalism
 Grants-in-Aid • Grant of federal money to States – Many of these governments are strapped for funds for everyday functions – Land for public schools, colleges, roads and canals, flood control work, militias – New Deal in 1930 s (Great Depression) • More than 500 in operation today – Educ. , Mass transit, highways, health care, onthe-job training – $275 billion or 25% of State an local spending
Grants-in-Aid • Grant of federal money to States – Many of these governments are strapped for funds for everyday functions – Land for public schools, colleges, roads and canals, flood control work, militias – New Deal in 1930 s (Great Depression) • More than 500 in operation today – Educ. , Mass transit, highways, health care, onthe-job training – $275 billion or 25% of State an local spending
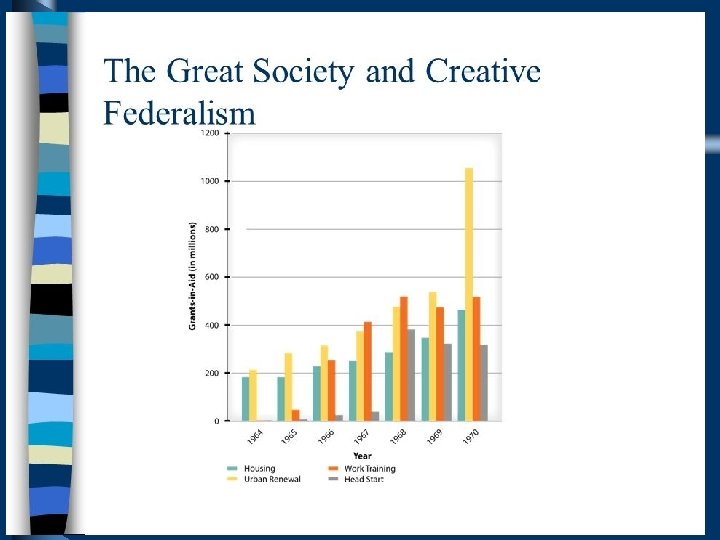
 Revenue Sharing • Federal monetary aid 1972 -1987 • Congress gave an annual share of federal revenue to States and Local governments • Virtually no strings attached to mone • Popular and strongly supported but opposed by Reagan Admin. – Feel victim to deficient ridden National Gov’t
Revenue Sharing • Federal monetary aid 1972 -1987 • Congress gave an annual share of federal revenue to States and Local governments • Virtually no strings attached to mone • Popular and strongly supported but opposed by Reagan Admin. – Feel victim to deficient ridden National Gov’t

 Categorical Grants • Most common • Specified purpose • Strings: – Use for specified purposes – States make contribution – Agency to manage grant – Obey Federal guidelines
Categorical Grants • Most common • Specified purpose • Strings: – Use for specified purposes – States make contribution – Agency to manage grant – Obey Federal guidelines
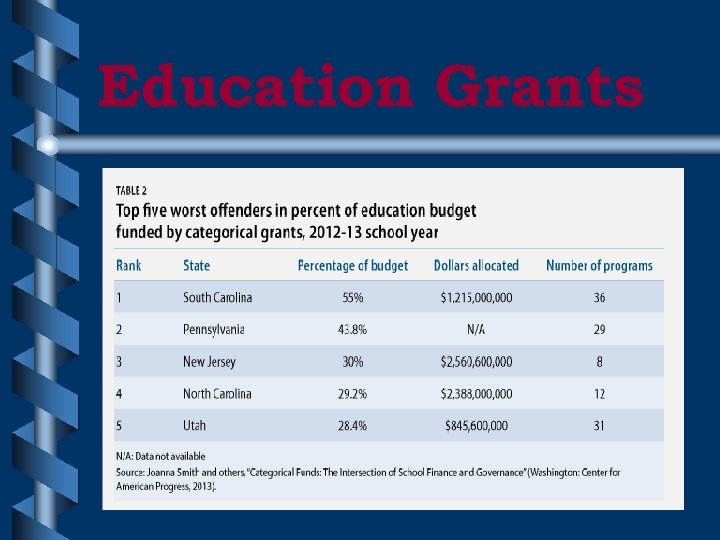 Education Grants
Education Grants
 Block Grants • More broad purposes – Health care, social services, and an welfare • Fewer strings- States have greater freedom in spending
Block Grants • More broad purposes – Health care, social services, and an welfare • Fewer strings- States have greater freedom in spending



 Project Grants • Applied for and given to state localities, private agencies – Dept. of Health and Human Service – Research on cancer, diabetes, neurological disease, job training and employment programs
Project Grants • Applied for and given to state localities, private agencies – Dept. of Health and Human Service – Research on cancer, diabetes, neurological disease, job training and employment programs
 Assistance • States provide service to National Govt. : – Administering/paying for national elections – Assisting in federal law enforcement efforts (FBI) – Naturalization process
Assistance • States provide service to National Govt. : – Administering/paying for national elections – Assisting in federal law enforcement efforts (FBI) – Naturalization process
 Interstate Relations • State cannot : – enter into treaties, alliances & confederations • States can : – form interstate compacts between themselves & with foreign states • New York and New Jersey form Port Authority (1921)
Interstate Relations • State cannot : – enter into treaties, alliances & confederations • States can : – form interstate compacts between themselves & with foreign states • New York and New Jersey form Port Authority (1921)
 Interstate Relations • Constitution requires each State to respect the validity o – laws, official records, & court actions of other States in civil matters – Full Faith & Credit Clause – 2 exceptions (criminal matters, not all divorces)
Interstate Relations • Constitution requires each State to respect the validity o – laws, official records, & court actions of other States in civil matters – Full Faith & Credit Clause – 2 exceptions (criminal matters, not all divorces)

 Interstate Relations • Extradition Each State must return fugitives to justice from State from which they fled – Sometimes contested by governors • Kentucky v. Dennison 1861 - word , “shall” had to read as “may”
Interstate Relations • Extradition Each State must return fugitives to justice from State from which they fled – Sometimes contested by governors • Kentucky v. Dennison 1861 - word , “shall” had to read as “may”

 Interstate Relations • Privileges & Immunities – No State can draw unreasonable distinctions between residents – Each state must recognize the righ of any American to travel in or become resident of that State – Allow to use courts, make contract buy, own rent or sell property, marry within its borders
Interstate Relations • Privileges & Immunities – No State can draw unreasonable distinctions between residents – Each state must recognize the righ of any American to travel in or become resident of that State – Allow to use courts, make contract buy, own rent or sell property, marry within its borders



