9a880bee9d627b8c5fb39e30ff5cabd9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14

FEBRUARY 22, 2014 Goal: Evaluate colonial reactions to British actions in Pre-Revolutionary America. QOD: The colonists and British were not getting along up to this point and immediately following the French and Indian war? Predict why? Agenda: PPT with notes

FINISH LAST OF MOHICANS (ABOUT 10 MIN. )

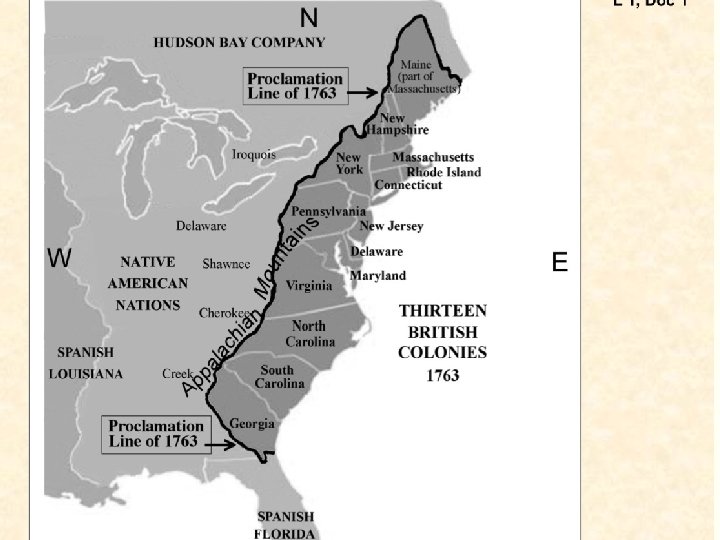
Proclamation of 1763 • The end of the French and Indian War in 1763 was a cause for great celebration in the colonies, for it removed several barriers and opened up a host of new opportunities for the colonists. • The French had effectively hemmed in the British settlers and had, from the perspective of the settlers, played the "Indians" against them. • The first thing on the minds of colonists was the great western frontier that had opened to them when the French ceded that contested territory to the British. • The royal proclamation of 1763 did much to dampen that celebration. The proclamation, closed off the frontier to colonial expansion. Colonists could not cross the Appalachians • The King and his council presented the proclamation as a measure to calm the fears of the Indians, who felt that the colonists would drive them from their lands as they expanded westward. • Colonists ignored the proclamation and moved west anyway

Stamp Act of 1765 • First serious attempt to govern the colonies • Placed a tax on all paper products • Colonial Reaction: – Rumblings begin, raises tension – Claimed taxes were unfair because colonists had no reps in Parliament

Creation of the Sons of Liberty (their battle cry: Taxation without representation!) Group committed to rights of the colonists Get the Stamp Act Repealed but England then issues the Declaratory Act- all laws in the colonies will be made by England since they are her possession Famous People in the Sons of Liberty: John Adams, Samuel Adams, Patrick Henry (Give me liberty or give me death) Paul Revere (the British are coming!!) Passive and Aggressive Acts: Hung a tax collector from a tree, tarred and feathered tax collectors, burned down tax collectors houses, dressed up as Indians and threw tea overboard, used propaganda in newspaper to incite the colonists!! Scene from John Adams: https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=h. FWZ 925 z. K 0 A


Townshend Acts of 1767 • Taxed – Glass, paint, oil, lead, paper, and tea • Purpose: – to raise money for the administrative costs of the colonies • Colonial Reactions– Colonists claimed they had no obligation to pay taxes imposed by a lawmaking body in which they had no representation – Crowds mobbed British officials and forced them to hide out on a ship which led to British occupation of Boston – Women began to boycott goods • British merchants stepped in and fought for the colonies

John Hancock • • • The Liberty Affair arose following the Townshend Acts. In 1768 the new Customs Officers at Boston seized a sloop called the Liberty, owned by John Hancock, that was carrying a cargo of Madeira wine. The Liberty was seized because John Hancock had not paid the taxes on the wine. The customs officers seized the sloop and towed her under the guns of a warship which was in Boston harbor. The people of Boston could not recapture the Liberty but they managed to seize the warship They Bostonians carried the boat to the Common, and had a famous bonfire. John Hancock who was a wealthy patriot was charged with smuggling, but was acquitted. John Hancock was a wealthy patriot and in 1765 John Hancock and Samuel Adams had founded the Sons of Liberty. John Hancock was to serve as president of Congress and was the first to sign the Declaration of Independence. • British will send troops into Boston

Boston Massacre • March 5, 1770 • Colonists throw “snowballs” at soldiers. They retaliate by opening fire and killing 5 • The first real casualty of the American Revolution was Crispus Attucks, an African American who organized the “attack” on the British soldiers. • https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=Yc. Do. N -KEi. KQ •

Boston Massacre Continued • Paul Revere propaganda? • John Adams was the lawyer for the British even though we know him as one of America’s great patriots. Why?

Tea Act of 1773 • Designed to help the failing East India company by giving them a monopoly on tea sales in America • Lowered imported cost of tea from Britain • Raise taxes on all other tea (monopoly) Forced colonists to buy tea from the East India Company • Colonial Reactions– Viewed it as a way to undercut American merchants – Tea ships turned away from ports in Philadelphia and NY, tea left to rot on docks in NC – Boston Tea Party http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=32 e. KEg 65 p. Q s (4: 41)

Intolerable Acts of 1774 • British answer to the Boston Tea Party • Set of 5 Acts designed to subjugate Massachusetts and recoup lost funds from the destruction of shipments. – Closed Boston ports – No self government in Mass. – Quartering Act: House all British soldiers – All royal courts (could not get a jury of their peers) – No town meetings

Colonists Reaction • Begin preparation for a revolution! Americans unite to support Boston. • Start stockpiling weapons • Cache in Concord Mass. • British march to destroy weapons • Skirmishes along the way • Paul Revere http: //www. bing. com/videos/search? q=ride+of+paul+revere&&view=detail&mid=E 47 E 85 A 6228 CF 0307865 E 47 E 85 A 6228 CF 0307865&rvsmid=27036 E 524693 F 5 A 2 A 972&FORM=VDFSRV&fsscr=0 • Sybil Ludington (http: //www. cc. com/video-clips/04 l 4 i 7/drunk-historysybil-ludington-s-midnight-ride • First shots fired in Lexington Mass to start the Revolution!
9a880bee9d627b8c5fb39e30ff5cabd9.ppt