9e302752736c66adcc493bfa3339e558.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 113
 FDA Advisory Committee January 8, 2003 ™ KETEK (telithromycin) Aventis Pharmaceuticals Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-1
FDA Advisory Committee January 8, 2003 ™ KETEK (telithromycin) Aventis Pharmaceuticals Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-1
 Introduction Steve Caffe, MD Vice President, US Regulatory Affairs, Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-2
Introduction Steve Caffe, MD Vice President, US Regulatory Affairs, Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-2
 Telithromycin – Background • • Ketolide antibiotic Claimed indications: – community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) – acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis (AECB) – acute sinusitis (AS) • April 2001, Advisory Committee recommended additional data be gathered, including: – resistant S. pneumoniae – larger safety database Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-3
Telithromycin – Background • • Ketolide antibiotic Claimed indications: – community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) – acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis (AECB) – acute sinusitis (AS) • April 2001, Advisory Committee recommended additional data be gathered, including: – resistant S. pneumoniae – larger safety database Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-3
 Additional Safety and Efficacy Data • • June 2001, Approvable Letter for CAP, AECB, AS Clinical program designed in collaboration with the FDA, including: – PK studies in special populations – studies in CAP and AECB – large comparative study in a usual care setting (>24, 000 subjects) • Post-marketing data from 1. 5 million exposures (including Germany, France, Italy and Spain) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-4
Additional Safety and Efficacy Data • • June 2001, Approvable Letter for CAP, AECB, AS Clinical program designed in collaboration with the FDA, including: – PK studies in special populations – studies in CAP and AECB – large comparative study in a usual care setting (>24, 000 subjects) • Post-marketing data from 1. 5 million exposures (including Germany, France, Italy and Spain) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-4
 Telithromycin – Presentation Agenda Introduction Steve Caffe, MD Medical Need Paul Iannini, MD Microbiology Stephen Jenkins, Ph. D Clinical Efficacy Bruno Leroy, MD Human Pharmacology Vijay Bhargava, Ph. D Clinical Safety Paul Lagarenne, MD Conclusions Paul Iannini, MD Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-5
Telithromycin – Presentation Agenda Introduction Steve Caffe, MD Medical Need Paul Iannini, MD Microbiology Stephen Jenkins, Ph. D Clinical Efficacy Bruno Leroy, MD Human Pharmacology Vijay Bhargava, Ph. D Clinical Safety Paul Lagarenne, MD Conclusions Paul Iannini, MD Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-5
 Experts in Attendance (1) H. Bodenheimer, MD, Beth Israel Medical Center, New York, NY W. Craig, MD, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI J. Dohar, MD, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, Pittsburgh, PA D. Farrell, Ph. D, GR Micro Ltd, London, UK L. Fisher, Ph. D, University of Washington, Seattle, WA F. Fraunfelder, MD, Oregon Health Sciences University, Portland, OR G. Harding, MD, Aston University School of Medicine, Birmingham, UK P. Iannini, MD, Danbury Hospital, Danbury, CT S. Jenkins, Ph. D, Carolinas Medical Center, Charlotte, NC J. Jones, MD, The Degge Group Ltd, Arlington, VA Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-6
Experts in Attendance (1) H. Bodenheimer, MD, Beth Israel Medical Center, New York, NY W. Craig, MD, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI J. Dohar, MD, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, Pittsburgh, PA D. Farrell, Ph. D, GR Micro Ltd, London, UK L. Fisher, Ph. D, University of Washington, Seattle, WA F. Fraunfelder, MD, Oregon Health Sciences University, Portland, OR G. Harding, MD, Aston University School of Medicine, Birmingham, UK P. Iannini, MD, Danbury Hospital, Danbury, CT S. Jenkins, Ph. D, Carolinas Medical Center, Charlotte, NC J. Jones, MD, The Degge Group Ltd, Arlington, VA Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-6
 Experts in Attendance (2) J. Lewis, MD, Georgetown University Medical School, Georgetown, DC W. Maddrey, MD, Univ. of Texas Southwestern School of Medicine, Dallas, TX H. Paulus, MD, University of California at Los Angeles, CA C. Pratt, MD, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX E. Rubin, MD, Thomas Jefferson Univ. School of Medicine, Philadelphia, PA M. Sorrell, MD, University of Nebraska Medical School, Omaha, NE P. Watkins, MD, Univ. of North Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC G. Williams, MD, New York Medical College, Valhalla, NY Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-7
Experts in Attendance (2) J. Lewis, MD, Georgetown University Medical School, Georgetown, DC W. Maddrey, MD, Univ. of Texas Southwestern School of Medicine, Dallas, TX H. Paulus, MD, University of California at Los Angeles, CA C. Pratt, MD, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX E. Rubin, MD, Thomas Jefferson Univ. School of Medicine, Philadelphia, PA M. Sorrell, MD, University of Nebraska Medical School, Omaha, NE P. Watkins, MD, Univ. of North Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC G. Williams, MD, New York Medical College, Valhalla, NY Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-7
 Medical Need Paul Iannini, MD Danbury Hospital, Danbury, Connecticut Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-8
Medical Need Paul Iannini, MD Danbury Hospital, Danbury, Connecticut Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-8
 Medical Need for a New Anti-infective for Community-Acquired RTIs (1) • A clinician’s needs: – targeted spectrum that satisfies criteria for empiric therapy – high potency against S. pneumoniae – concentration-dependent, rapid killing – reduced impact on other bacterial flora – safe and well tolerated Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-9
Medical Need for a New Anti-infective for Community-Acquired RTIs (1) • A clinician’s needs: – targeted spectrum that satisfies criteria for empiric therapy – high potency against S. pneumoniae – concentration-dependent, rapid killing – reduced impact on other bacterial flora – safe and well tolerated Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-9
 Medical Need for a New Anti-infective for Community-Acquired RTIs (2) • CAP: S. pneumoniae infections, including bacteremia and L. pneumophila, which have the highest risk of mortality • AECB: patients with risk factors and documented obstruction • AS: avoid complications by choosing the right drug the first time • Once-daily dosage with short durations of therapy Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-10
Medical Need for a New Anti-infective for Community-Acquired RTIs (2) • CAP: S. pneumoniae infections, including bacteremia and L. pneumophila, which have the highest risk of mortality • AECB: patients with risk factors and documented obstruction • AS: avoid complications by choosing the right drug the first time • Once-daily dosage with short durations of therapy Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-10
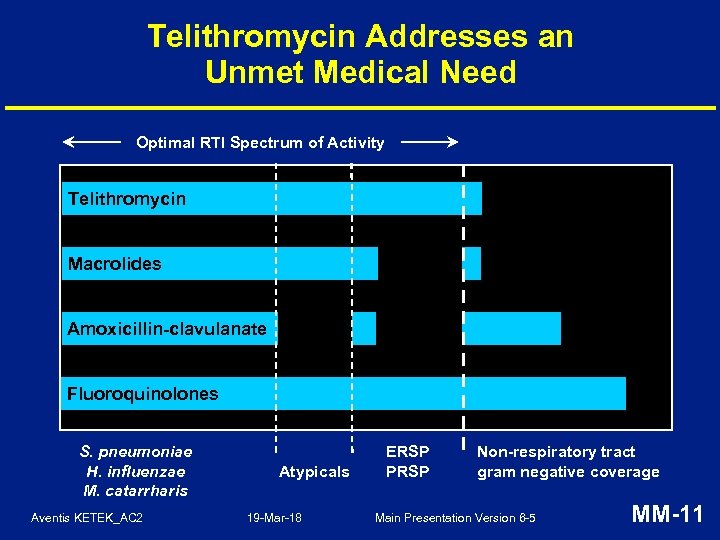 Telithromycin Addresses an Unmet Medical Need Optimal RTI Spectrum of Activity Telithromycin Macrolides Amoxicillin-clavulanate Fluoroquinolones S. pneumoniae H. influenzae M. catarrharis Aventis KETEK_AC 2 Atypicals 19 -Mar-18 ERSP PRSP Non-respiratory tract gram negative coverage Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-11
Telithromycin Addresses an Unmet Medical Need Optimal RTI Spectrum of Activity Telithromycin Macrolides Amoxicillin-clavulanate Fluoroquinolones S. pneumoniae H. influenzae M. catarrharis Aventis KETEK_AC 2 Atypicals 19 -Mar-18 ERSP PRSP Non-respiratory tract gram negative coverage Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-11
 S. pneumoniae Resistance in USA • Surveillance studies may overestimate resistance but trends are clear • Rates of resistance to macrolides range from 22 to 32% and for penicillin G from 18 to 24% a • Resistance to newer fluoroquinolones is low but increasing • • Multi-drug resistance rates (4 drugs) are ~10% a Useful life of older agents may be diminishing Source: CDC, 2000; PROTEKT Studies 2000 -2001; TRUST 2001 -2002 Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-12
S. pneumoniae Resistance in USA • Surveillance studies may overestimate resistance but trends are clear • Rates of resistance to macrolides range from 22 to 32% and for penicillin G from 18 to 24% a • Resistance to newer fluoroquinolones is low but increasing • • Multi-drug resistance rates (4 drugs) are ~10% a Useful life of older agents may be diminishing Source: CDC, 2000; PROTEKT Studies 2000 -2001; TRUST 2001 -2002 Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-12
 Implications of Increased Resistance • Available agents do not meet current clinical needs: – sub-optimal drug concentrations for current levels of resistance (MICs 8. 0 μg/m. L for amoxicillin, 16. 0 μg/m. L for macrolides, 4. 0 μg/m. L for fluoroquinolones) – clinical failures of commonly used agents are emerging Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-13
Implications of Increased Resistance • Available agents do not meet current clinical needs: – sub-optimal drug concentrations for current levels of resistance (MICs 8. 0 μg/m. L for amoxicillin, 16. 0 μg/m. L for macrolides, 4. 0 μg/m. L for fluoroquinolones) – clinical failures of commonly used agents are emerging Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-13
 Clinical Relevance of Resistance: A Debate • Increased mortality with S. pneumoniae with penicillin MICs 2. 0 or 4. 0 μg/m. L and a statistically significant increase in suppurative complications a • High likelihood of failure to prevent S. pneumoniae bacteremia with macrolide therapy for CAP caused by macrolide resistant strains b • Fluoroquinolone failures in subjects with S. pneumoniae initial or acquired resistance mutations during therapy c a b Metlay et al. CID 2000, Turret et al. CID; 1999, Fieken et al. Am J Pub Health. 2000. Lonks et al. CID 2002, Kelly et al. CID. 2000. c Davidson et al. NEJM. 2002, Urban et al. JID. 2001, Empy et al. Ann Pharmacotherapy. 2001. Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-14
Clinical Relevance of Resistance: A Debate • Increased mortality with S. pneumoniae with penicillin MICs 2. 0 or 4. 0 μg/m. L and a statistically significant increase in suppurative complications a • High likelihood of failure to prevent S. pneumoniae bacteremia with macrolide therapy for CAP caused by macrolide resistant strains b • Fluoroquinolone failures in subjects with S. pneumoniae initial or acquired resistance mutations during therapy c a b Metlay et al. CID 2000, Turret et al. CID; 1999, Fieken et al. Am J Pub Health. 2000. Lonks et al. CID 2002, Kelly et al. CID. 2000. c Davidson et al. NEJM. 2002, Urban et al. JID. 2001, Empy et al. Ann Pharmacotherapy. 2001. Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-14
 There is a Medical Need for a New Anti-infective in Community-Acquired RTIs • Optimal therapy for community-acquired RTIs requires antibiotics with a targeted spectrum that includes common and atypical pathogens • Increased bacterial resistance to current antibiotics commonly used in therapy of RTIs may shorten useful life Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-15
There is a Medical Need for a New Anti-infective in Community-Acquired RTIs • Optimal therapy for community-acquired RTIs requires antibiotics with a targeted spectrum that includes common and atypical pathogens • Increased bacterial resistance to current antibiotics commonly used in therapy of RTIs may shorten useful life Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-15
 Microbiology Stephen Jenkins, Ph. D Carolinas Medical Center Charlotte, North Carolina Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-16
Microbiology Stephen Jenkins, Ph. D Carolinas Medical Center Charlotte, North Carolina Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-16
 Overview of the Microbiology Features of Telithromycin • • • First ketolide antibiotic derived from macrolides • Especially active against S. pneumoniae, including macrolide-, penicillin-, and/or multiple antibiotic-resistant strains Novel dual binding mechanism Focused spectrum of activity against all common outpatient RTI pathogens (minimal impact on usual bacterial host flora) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-17
Overview of the Microbiology Features of Telithromycin • • • First ketolide antibiotic derived from macrolides • Especially active against S. pneumoniae, including macrolide-, penicillin-, and/or multiple antibiotic-resistant strains Novel dual binding mechanism Focused spectrum of activity against all common outpatient RTI pathogens (minimal impact on usual bacterial host flora) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-17
 Telithromycin Mechanism of Action (1) • Prevents bacterial protein synthesis by: – binding to two specific sites on the bacterial ribosome – interfering with elongation of nascent polypeptide chains • • Interacts strongly with both domain V and, unlike available macrolides, domain II of the 23 S r. RNA Result: Activity against most macrolide-resistant strains of S. pneumoniae (MIC 99 = 1 µg/m. L) a a Source: PROTEKT Studies (data on file) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-18
Telithromycin Mechanism of Action (1) • Prevents bacterial protein synthesis by: – binding to two specific sites on the bacterial ribosome – interfering with elongation of nascent polypeptide chains • • Interacts strongly with both domain V and, unlike available macrolides, domain II of the 23 S r. RNA Result: Activity against most macrolide-resistant strains of S. pneumoniae (MIC 99 = 1 µg/m. L) a a Source: PROTEKT Studies (data on file) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-18
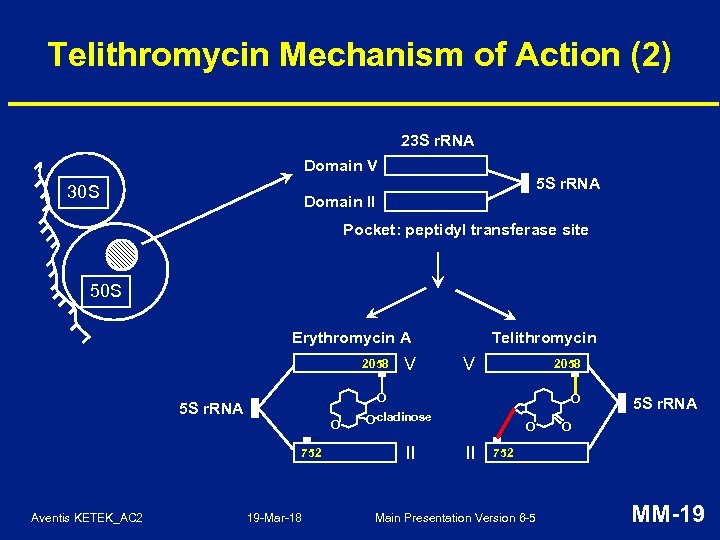 Telithromycin Mechanism of Action (2) 23 S r. RNA Domain V 5 S r. RNA 30 S Domain II Pocket: peptidyl transferase site 50 S Erythromycin A 2058 V 2058 O 5 S r. RNA O 752 Aventis KETEK_AC 2 V Telithromycin 19 -Mar-18 O -cladinose O II 5 S r. RNA O 752 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-19
Telithromycin Mechanism of Action (2) 23 S r. RNA Domain V 5 S r. RNA 30 S Domain II Pocket: peptidyl transferase site 50 S Erythromycin A 2058 V 2058 O 5 S r. RNA O 752 Aventis KETEK_AC 2 V Telithromycin 19 -Mar-18 O -cladinose O II 5 S r. RNA O 752 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-19
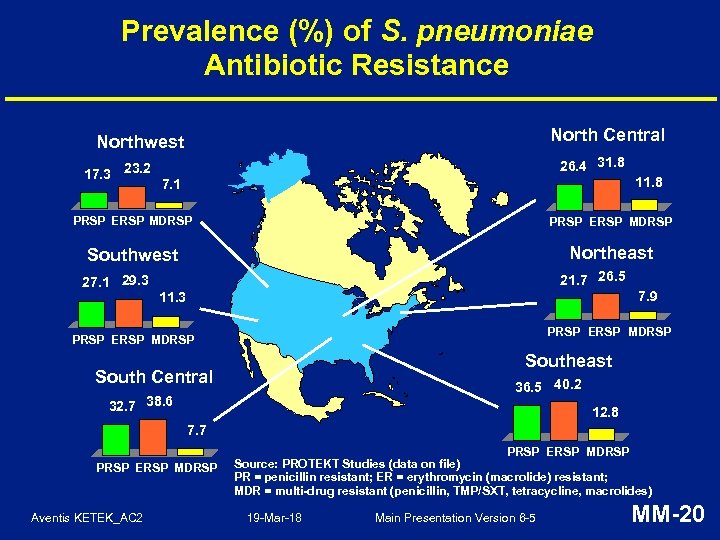 Prevalence (%) of S. pneumoniae Antibiotic Resistance North Central Northwest 17. 3 23. 2 26. 4 31. 8 11. 8 7. 1 PRSP ERSP MDRSP Southwest Northeast 27. 1 29. 3 21. 7 26. 5 7. 9 11. 3 PRSP ERSP MDRSP Southeast South Central 36. 5 40. 2 32. 7 38. 6 12. 8 7. 7 PRSP ERSP MDRSP Aventis KETEK_AC 2 PRSP ERSP MDRSP Source: PROTEKT Studies (data on file) PR = penicillin resistant; ER = erythromycin (macrolide) resistant; MDR = multi-drug resistant (penicillin, TMP/SXT, tetracycline, macrolides) 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-20
Prevalence (%) of S. pneumoniae Antibiotic Resistance North Central Northwest 17. 3 23. 2 26. 4 31. 8 11. 8 7. 1 PRSP ERSP MDRSP Southwest Northeast 27. 1 29. 3 21. 7 26. 5 7. 9 11. 3 PRSP ERSP MDRSP Southeast South Central 36. 5 40. 2 32. 7 38. 6 12. 8 7. 7 PRSP ERSP MDRSP Aventis KETEK_AC 2 PRSP ERSP MDRSP Source: PROTEKT Studies (data on file) PR = penicillin resistant; ER = erythromycin (macrolide) resistant; MDR = multi-drug resistant (penicillin, TMP/SXT, tetracycline, macrolides) 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-20
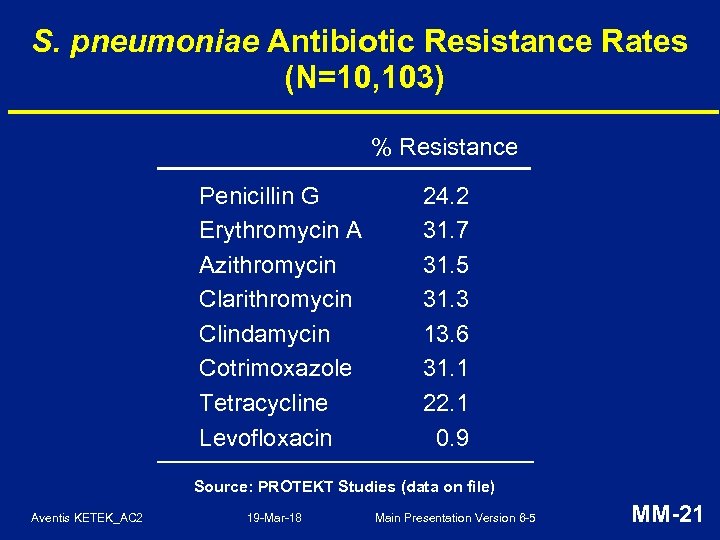 S. pneumoniae Antibiotic Resistance Rates (N=10, 103) % Resistance Penicillin G Erythromycin A Azithromycin Clarithromycin Clindamycin Cotrimoxazole Tetracycline Levofloxacin 24. 2 31. 7 31. 5 31. 3 13. 6 31. 1 22. 1 0. 9 Source: PROTEKT Studies (data on file) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-21
S. pneumoniae Antibiotic Resistance Rates (N=10, 103) % Resistance Penicillin G Erythromycin A Azithromycin Clarithromycin Clindamycin Cotrimoxazole Tetracycline Levofloxacin 24. 2 31. 7 31. 5 31. 3 13. 6 31. 1 22. 1 0. 9 Source: PROTEKT Studies (data on file) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-21
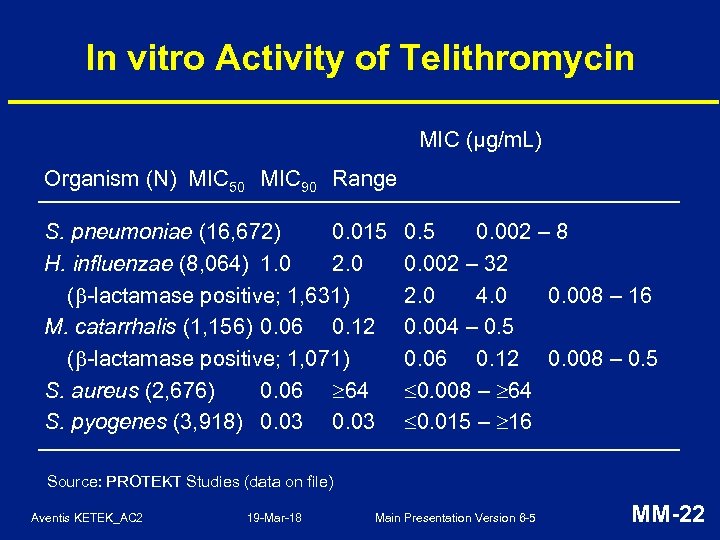 In vitro Activity of Telithromycin MIC (µg/m. L) Organism (N) MIC 50 MIC 90 Range S. pneumoniae (16, 672) 0. 015 H. influenzae (8, 064) 1. 0 2. 0 ( -lactamase positive; 1, 631) M. catarrhalis (1, 156) 0. 06 0. 12 ( -lactamase positive; 1, 071) S. aureus (2, 676) 0. 06 64 S. pyogenes (3, 918) 0. 03 0. 5 0. 002 – 8 0. 002 – 32 2. 0 4. 0 0. 008 – 16 0. 004 – 0. 5 0. 06 0. 12 0. 008 – 0. 5 0. 008 – 64 0. 015 – 16 Source: PROTEKT Studies (data on file) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-22
In vitro Activity of Telithromycin MIC (µg/m. L) Organism (N) MIC 50 MIC 90 Range S. pneumoniae (16, 672) 0. 015 H. influenzae (8, 064) 1. 0 2. 0 ( -lactamase positive; 1, 631) M. catarrhalis (1, 156) 0. 06 0. 12 ( -lactamase positive; 1, 071) S. aureus (2, 676) 0. 06 64 S. pyogenes (3, 918) 0. 03 0. 5 0. 002 – 8 0. 002 – 32 2. 0 4. 0 0. 008 – 16 0. 004 – 0. 5 0. 06 0. 12 0. 008 – 0. 5 0. 008 – 64 0. 015 – 16 Source: PROTEKT Studies (data on file) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-22
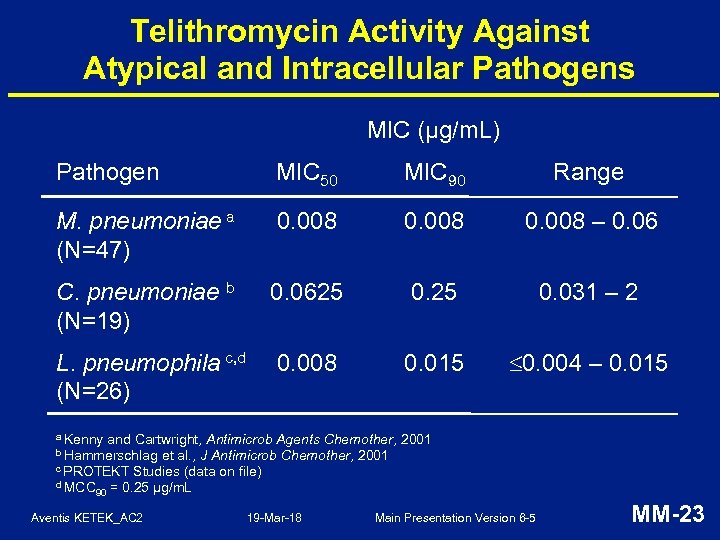 Telithromycin Activity Against Atypical and Intracellular Pathogens MIC (µg/m. L) Pathogen MIC 50 MIC 90 Range M. pneumoniae a (N=47) 0. 008 – 0. 06 C. pneumoniae b (N=19) 0. 0625 0. 031 – 2 L. pneumophila c, d (N=26) 0. 008 0. 015 0. 004 – 0. 015 a Kenny and Cartwright, Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 2001 et al. , J Antimicrob Chemother, 2001 c PROTEKT Studies (data on file) d MCC 90 = 0. 25 μg/m. L b Hammerschlag Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-23
Telithromycin Activity Against Atypical and Intracellular Pathogens MIC (µg/m. L) Pathogen MIC 50 MIC 90 Range M. pneumoniae a (N=47) 0. 008 – 0. 06 C. pneumoniae b (N=19) 0. 0625 0. 031 – 2 L. pneumophila c, d (N=26) 0. 008 0. 015 0. 004 – 0. 015 a Kenny and Cartwright, Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 2001 et al. , J Antimicrob Chemother, 2001 c PROTEKT Studies (data on file) d MCC 90 = 0. 25 μg/m. L b Hammerschlag Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-23
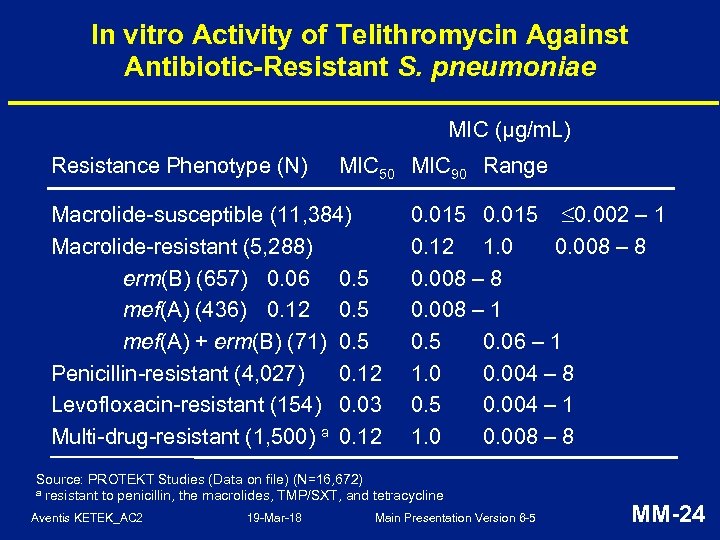 In vitro Activity of Telithromycin Against Antibiotic-Resistant S. pneumoniae MIC (µg/m. L) Resistance Phenotype (N) MIC 50 MIC 90 Range Macrolide-susceptible (11, 384) Macrolide-resistant (5, 288) erm(B) (657) 0. 06 0. 5 mef(A) (436) 0. 12 0. 5 mef(A) + erm(B) (71) 0. 5 Penicillin-resistant (4, 027) 0. 12 Levofloxacin-resistant (154) 0. 03 Multi-drug-resistant (1, 500) a 0. 12 0. 015 0. 002 – 1 0. 12 1. 0 0. 008 – 8 0. 008 – 1 0. 5 0. 06 – 1 1. 0 0. 004 – 8 0. 5 0. 004 – 1 1. 0 0. 008 – 8 Source: PROTEKT Studies (Data on file) (N=16, 672) a resistant to penicillin, the macrolides, TMP/SXT, and tetracycline Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-24
In vitro Activity of Telithromycin Against Antibiotic-Resistant S. pneumoniae MIC (µg/m. L) Resistance Phenotype (N) MIC 50 MIC 90 Range Macrolide-susceptible (11, 384) Macrolide-resistant (5, 288) erm(B) (657) 0. 06 0. 5 mef(A) (436) 0. 12 0. 5 mef(A) + erm(B) (71) 0. 5 Penicillin-resistant (4, 027) 0. 12 Levofloxacin-resistant (154) 0. 03 Multi-drug-resistant (1, 500) a 0. 12 0. 015 0. 002 – 1 0. 12 1. 0 0. 008 – 8 0. 008 – 1 0. 5 0. 06 – 1 1. 0 0. 004 – 8 0. 5 0. 004 – 1 1. 0 0. 008 – 8 Source: PROTEKT Studies (Data on file) (N=16, 672) a resistant to penicillin, the macrolides, TMP/SXT, and tetracycline Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-24
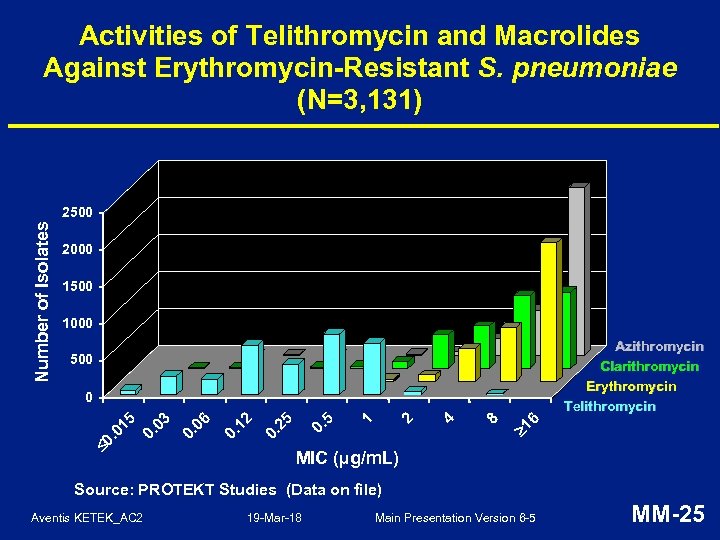 Activities of Telithromycin and Macrolides Against Erythromycin-Resistant S. pneumoniae (N=3, 131) Number of Isolates 2500 2000 1500 1000 Azithromycin Clarithromycin Erythromycin Telithromycin 500 6 1 8 4 2 1 0. 5 25 0. 12 0. 06 0. 03 0. 0 . 0 15 0 MIC (µg/m. L) Source: PROTEKT Studies (Data on file) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-25
Activities of Telithromycin and Macrolides Against Erythromycin-Resistant S. pneumoniae (N=3, 131) Number of Isolates 2500 2000 1500 1000 Azithromycin Clarithromycin Erythromycin Telithromycin 500 6 1 8 4 2 1 0. 5 25 0. 12 0. 06 0. 03 0. 0 . 0 15 0 MIC (µg/m. L) Source: PROTEKT Studies (Data on file) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-25
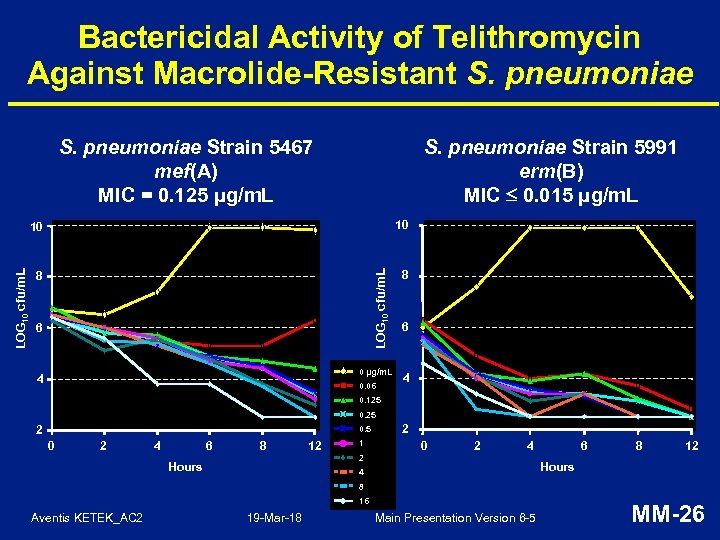 Bactericidal Activity of Telithromycin Against Macrolide-Resistant S. pneumoniae Strain 5467 mef(A) MIC = 0. 125 μg/m. L S. pneumoniae Strain 5991 erm(B) MIC 0. 015 μg/m. L 10 8 8 LOG 10 cfu/m. L 10 6 0 µg/m. L 4 0. 06 6 4 0. 125 0. 25 2 0. 5 0 2 4 6 8 12 1 2 0 2 4 2 Hours 6 8 12 Hours 4 8 16 Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-26
Bactericidal Activity of Telithromycin Against Macrolide-Resistant S. pneumoniae Strain 5467 mef(A) MIC = 0. 125 μg/m. L S. pneumoniae Strain 5991 erm(B) MIC 0. 015 μg/m. L 10 8 8 LOG 10 cfu/m. L 10 6 0 µg/m. L 4 0. 06 6 4 0. 125 0. 25 2 0. 5 0 2 4 6 8 12 1 2 0 2 4 2 Hours 6 8 12 Hours 4 8 16 Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-26
 Decreased Propensity of Telithromycin to Induce or Select for Antibiotic Resistance • In vitro: – telithromycin does not induce MLSB resistance – in serial passage experiments, telithromycin less efficient in selecting resistant mutants of S. pneumoniae than azithromycin, clarithromycin, erythromycin, roxithromycin, or clindamycin • In vivo: – in a clinical trial, telithromycin was shown to be less likely to select populations of mutants resistant to itself among the usual oropharyngeal viridans group streptococci than clarithromycin Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-27
Decreased Propensity of Telithromycin to Induce or Select for Antibiotic Resistance • In vitro: – telithromycin does not induce MLSB resistance – in serial passage experiments, telithromycin less efficient in selecting resistant mutants of S. pneumoniae than azithromycin, clarithromycin, erythromycin, roxithromycin, or clindamycin • In vivo: – in a clinical trial, telithromycin was shown to be less likely to select populations of mutants resistant to itself among the usual oropharyngeal viridans group streptococci than clarithromycin Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-27
 Summary of Microbiology Features of Telithromycin • • • First ketolide antibiotic • • Low propensity to select antibiotic-resistant mutants Unlike macrolides: dual, strong binding mechanism Focused spectrum of activity against usual typical and atypical/intracellular RTI pathogens with minimal impact on GI or oropharyngeal flora Especially active against S. pneumoniae, including macrolide-, penicillin-, and/or multiple antibioticresistant strains Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-28
Summary of Microbiology Features of Telithromycin • • • First ketolide antibiotic • • Low propensity to select antibiotic-resistant mutants Unlike macrolides: dual, strong binding mechanism Focused spectrum of activity against usual typical and atypical/intracellular RTI pathogens with minimal impact on GI or oropharyngeal flora Especially active against S. pneumoniae, including macrolide-, penicillin-, and/or multiple antibioticresistant strains Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-28
 Clinical Efficacy Bruno Leroy, MD Senior Director, Clinical Development Anti-infectives, Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-29
Clinical Efficacy Bruno Leroy, MD Senior Director, Clinical Development Anti-infectives, Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-29
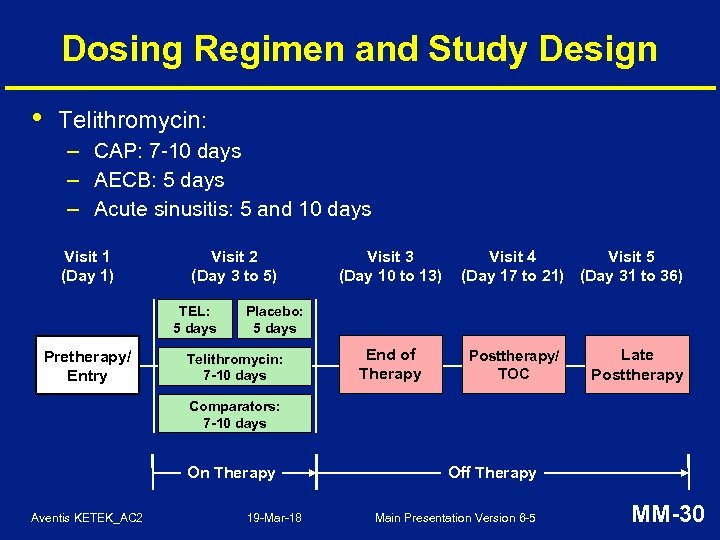 Dosing Regimen and Study Design • Telithromycin: – CAP: 7 -10 days – AECB: 5 days – Acute sinusitis: 5 and 10 days Visit 1 (Day 1) Visit 2 (Day 3 to 5) TEL: 5 days Pretherapy/ Entry Visit 3 (Day 10 to 13) Visit 4 Visit 5 (Day 17 to 21) (Day 31 to 36) Placebo: 5 days Telithromycin: 7 -10 days End of Therapy Posttherapy/ TOC Late Posttherapy Comparators: 7 -10 days On Therapy Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Off Therapy Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-30
Dosing Regimen and Study Design • Telithromycin: – CAP: 7 -10 days – AECB: 5 days – Acute sinusitis: 5 and 10 days Visit 1 (Day 1) Visit 2 (Day 3 to 5) TEL: 5 days Pretherapy/ Entry Visit 3 (Day 10 to 13) Visit 4 Visit 5 (Day 17 to 21) (Day 31 to 36) Placebo: 5 days Telithromycin: 7 -10 days End of Therapy Posttherapy/ TOC Late Posttherapy Comparators: 7 -10 days On Therapy Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Off Therapy Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-30
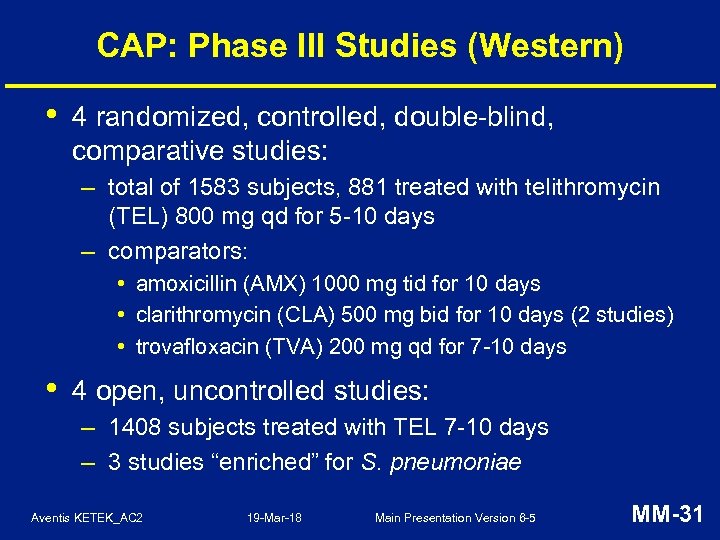 CAP: Phase III Studies (Western) • 4 randomized, controlled, double-blind, comparative studies: – total of 1583 subjects, 881 treated with telithromycin (TEL) 800 mg qd for 5 -10 days – comparators: • amoxicillin (AMX) 1000 mg tid for 10 days • clarithromycin (CLA) 500 mg bid for 10 days (2 studies) • trovafloxacin (TVA) 200 mg qd for 7 -10 days • 4 open, uncontrolled studies: – 1408 subjects treated with TEL 7 -10 days – 3 studies “enriched” for S. pneumoniae Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-31
CAP: Phase III Studies (Western) • 4 randomized, controlled, double-blind, comparative studies: – total of 1583 subjects, 881 treated with telithromycin (TEL) 800 mg qd for 5 -10 days – comparators: • amoxicillin (AMX) 1000 mg tid for 10 days • clarithromycin (CLA) 500 mg bid for 10 days (2 studies) • trovafloxacin (TVA) 200 mg qd for 7 -10 days • 4 open, uncontrolled studies: – 1408 subjects treated with TEL 7 -10 days – 3 studies “enriched” for S. pneumoniae Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-31
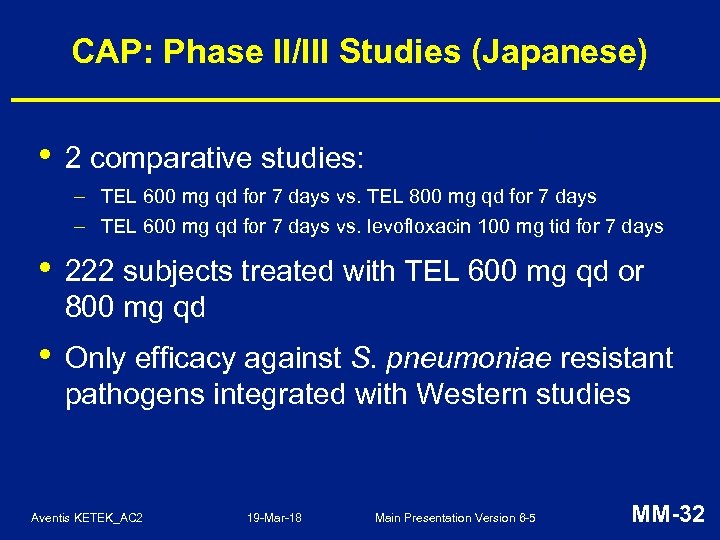 CAP: Phase II/III Studies (Japanese) • 2 comparative studies: – TEL 600 mg qd for 7 days vs. TEL 800 mg qd for 7 days – TEL 600 mg qd for 7 days vs. levofloxacin 100 mg tid for 7 days • 222 subjects treated with TEL 600 mg qd or 800 mg qd • Only efficacy against S. pneumoniae resistant pathogens integrated with Western studies Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-32
CAP: Phase II/III Studies (Japanese) • 2 comparative studies: – TEL 600 mg qd for 7 days vs. TEL 800 mg qd for 7 days – TEL 600 mg qd for 7 days vs. levofloxacin 100 mg tid for 7 days • 222 subjects treated with TEL 600 mg qd or 800 mg qd • Only efficacy against S. pneumoniae resistant pathogens integrated with Western studies Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-32
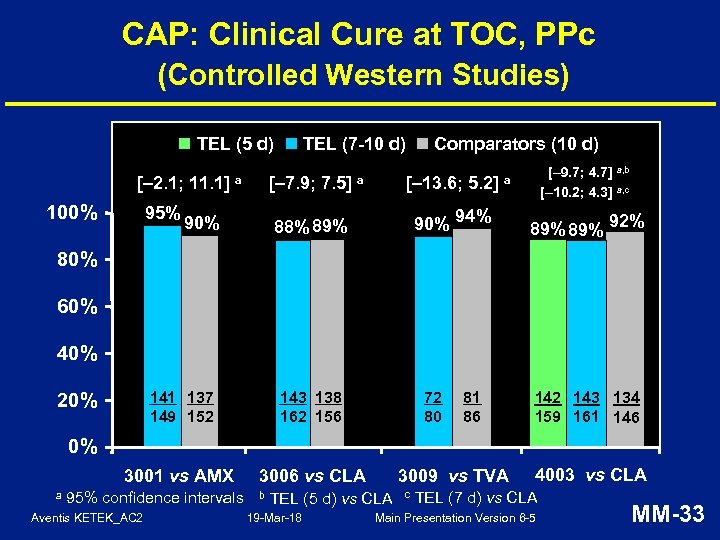 CAP: Clinical Cure at TOC, PPc (Controlled Western Studies) TEL (7 -10 d) TEL (5 d) [– 2. 1; 11. 1] 100% 95% [– 7. 9; 7. 5] a 90% Comparators (10 d) [– 13. 6; 5. 2] a 90% 94% 88% 89% [– 9. 7; 4. 7] a, b [– 10. 2; 4. 3] a, c a 89% 92% 80% 60% 40% 141 137 149 152 143 138 162 156 3001 vs AMX 3006 vs CLA 20% 72 80 81 86 142 143 134 159 161 146 0% a 95% confidence intervals Aventis KETEK_AC 2 b 3009 vs TVA TEL (5 d) vs CLA 19 -Mar-18 c 4003 vs CLA TEL (7 d) vs CLA Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-33
CAP: Clinical Cure at TOC, PPc (Controlled Western Studies) TEL (7 -10 d) TEL (5 d) [– 2. 1; 11. 1] 100% 95% [– 7. 9; 7. 5] a 90% Comparators (10 d) [– 13. 6; 5. 2] a 90% 94% 88% 89% [– 9. 7; 4. 7] a, b [– 10. 2; 4. 3] a, c a 89% 92% 80% 60% 40% 141 137 149 152 143 138 162 156 3001 vs AMX 3006 vs CLA 20% 72 80 81 86 142 143 134 159 161 146 0% a 95% confidence intervals Aventis KETEK_AC 2 b 3009 vs TVA TEL (5 d) vs CLA 19 -Mar-18 c 4003 vs CLA TEL (7 d) vs CLA Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-33
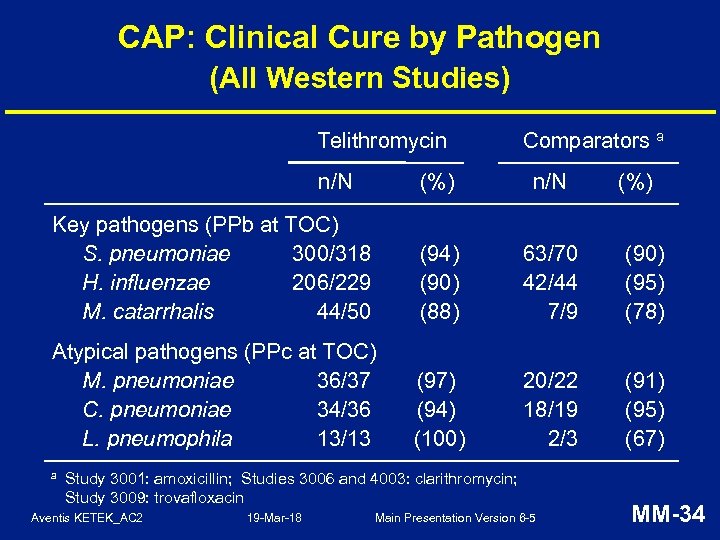 CAP: Clinical Cure by Pathogen (All Western Studies) Telithromycin n/N Comparators a (%) n/N Key pathogens (PPb at TOC) S. pneumoniae 300/318 H. influenzae 206/229 M. catarrhalis 44/50 (94) (90) (88) 63/70 42/44 7/9 (90) (95) (78) Atypical pathogens (PPc at TOC) M. pneumoniae 36/37 C. pneumoniae 34/36 L. pneumophila 13/13 (97) (94) (100) 20/22 18/19 2/3 (91) (95) (67) a Study 3001: amoxicillin; Studies 3006 and 4003: clarithromycin; Study 3009: trovafloxacin Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 (%) MM-34
CAP: Clinical Cure by Pathogen (All Western Studies) Telithromycin n/N Comparators a (%) n/N Key pathogens (PPb at TOC) S. pneumoniae 300/318 H. influenzae 206/229 M. catarrhalis 44/50 (94) (90) (88) 63/70 42/44 7/9 (90) (95) (78) Atypical pathogens (PPc at TOC) M. pneumoniae 36/37 C. pneumoniae 34/36 L. pneumophila 13/13 (97) (94) (100) 20/22 18/19 2/3 (91) (95) (67) a Study 3001: amoxicillin; Studies 3006 and 4003: clarithromycin; Study 3009: trovafloxacin Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 (%) MM-34
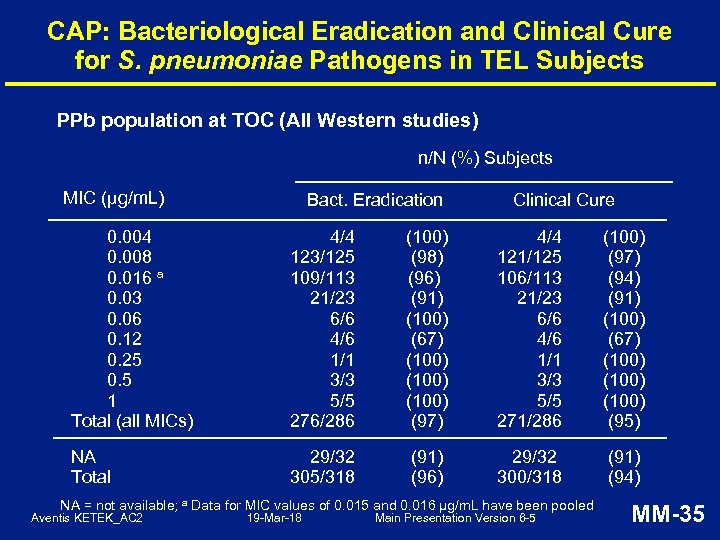 CAP: Bacteriological Eradication and Clinical Cure for S. pneumoniae Pathogens in TEL Subjects PPb population at TOC (All Western studies) n/N (%) Subjects MIC (μg/m. L) Bact. Eradication Clinical Cure 0. 004 0. 008 0. 016 a 0. 03 0. 06 0. 12 0. 25 0. 5 1 Total (all MICs) 4/4 123/125 109/113 21/23 6/6 4/6 1/1 3/3 5/5 276/286 (100) (98) (96) (91) (100) (67) (100) (97) 4/4 121/125 106/113 21/23 6/6 4/6 1/1 3/3 5/5 271/286 (100) (97) (94) (91) (100) (67) (100) (95) NA Total 29/32 305/318 (91) (96) 29/32 300/318 (91) (94) NA = not available; a Data for MIC values of 0. 015 and 0. 016 µg/m. L have been pooled Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-35
CAP: Bacteriological Eradication and Clinical Cure for S. pneumoniae Pathogens in TEL Subjects PPb population at TOC (All Western studies) n/N (%) Subjects MIC (μg/m. L) Bact. Eradication Clinical Cure 0. 004 0. 008 0. 016 a 0. 03 0. 06 0. 12 0. 25 0. 5 1 Total (all MICs) 4/4 123/125 109/113 21/23 6/6 4/6 1/1 3/3 5/5 276/286 (100) (98) (96) (91) (100) (67) (100) (97) 4/4 121/125 106/113 21/23 6/6 4/6 1/1 3/3 5/5 271/286 (100) (97) (94) (91) (100) (67) (100) (95) NA Total 29/32 305/318 (91) (96) 29/32 300/318 (91) (94) NA = not available; a Data for MIC values of 0. 015 and 0. 016 µg/m. L have been pooled Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-35
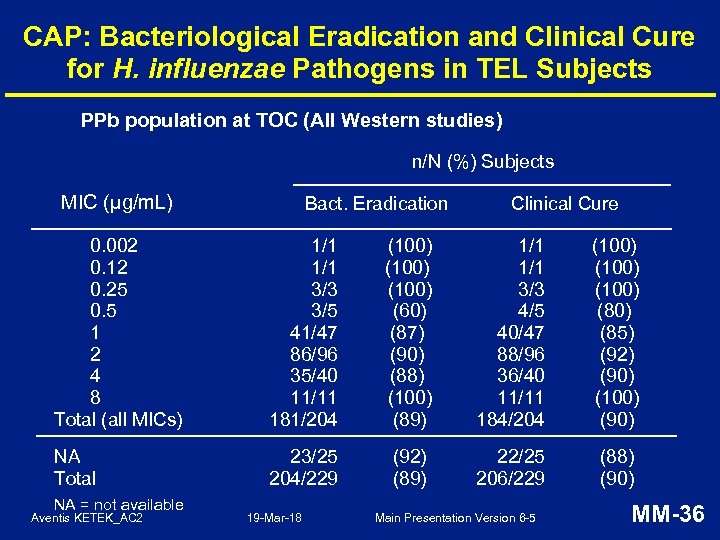 CAP: Bacteriological Eradication and Clinical Cure for H. influenzae Pathogens in TEL Subjects PPb population at TOC (All Western studies) n/N (%) Subjects MIC (μg/m. L) Bact. Eradication Clinical Cure 0. 002 0. 12 0. 25 0. 5 1 2 4 8 Total (all MICs) 1/1 3/3 3/5 41/47 86/96 35/40 11/11 181/204 (100) (60) (87) (90) (88) (100) (89) 1/1 3/3 4/5 40/47 88/96 36/40 11/11 184/204 (100) (85) (92) (90) (100) (90) NA Total 23/25 204/229 (92) (89) 22/25 206/229 (88) (90) NA = not available Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-36
CAP: Bacteriological Eradication and Clinical Cure for H. influenzae Pathogens in TEL Subjects PPb population at TOC (All Western studies) n/N (%) Subjects MIC (μg/m. L) Bact. Eradication Clinical Cure 0. 002 0. 12 0. 25 0. 5 1 2 4 8 Total (all MICs) 1/1 3/3 3/5 41/47 86/96 35/40 11/11 181/204 (100) (60) (87) (90) (88) (100) (89) 1/1 3/3 4/5 40/47 88/96 36/40 11/11 184/204 (100) (85) (92) (90) (100) (90) NA Total 23/25 204/229 (92) (89) 22/25 206/229 (88) (90) NA = not available Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-36
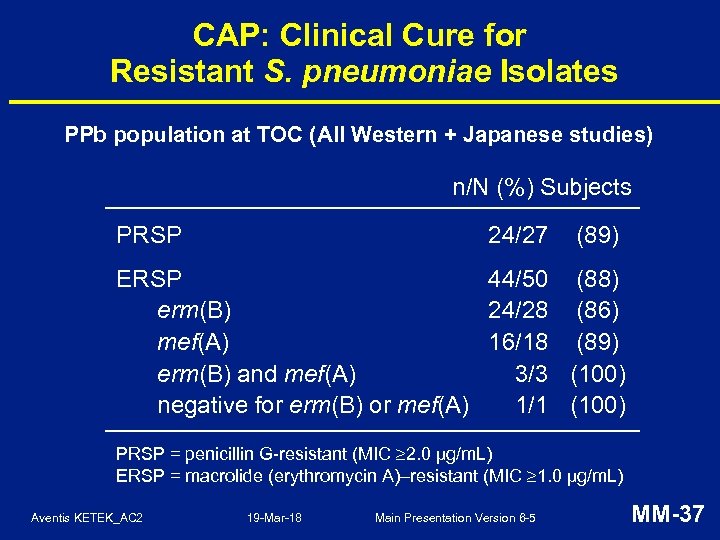 CAP: Clinical Cure for Resistant S. pneumoniae Isolates PPb population at TOC (All Western + Japanese studies) n/N (%) Subjects PRSP 24/27 (89) ERSP 44/50 (88) erm(B) 24/28 (86) mef(A) 16/18 (89) erm(B) and mef(A) 3/3 (100) negative for erm(B) or mef(A) 1/1 (100) PRSP = penicillin G-resistant (MIC 2. 0 µg/m. L) ERSP = macrolide (erythromycin A)–resistant (MIC 1. 0 µg/m. L) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-37
CAP: Clinical Cure for Resistant S. pneumoniae Isolates PPb population at TOC (All Western + Japanese studies) n/N (%) Subjects PRSP 24/27 (89) ERSP 44/50 (88) erm(B) 24/28 (86) mef(A) 16/18 (89) erm(B) and mef(A) 3/3 (100) negative for erm(B) or mef(A) 1/1 (100) PRSP = penicillin G-resistant (MIC 2. 0 µg/m. L) ERSP = macrolide (erythromycin A)–resistant (MIC 1. 0 µg/m. L) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-37
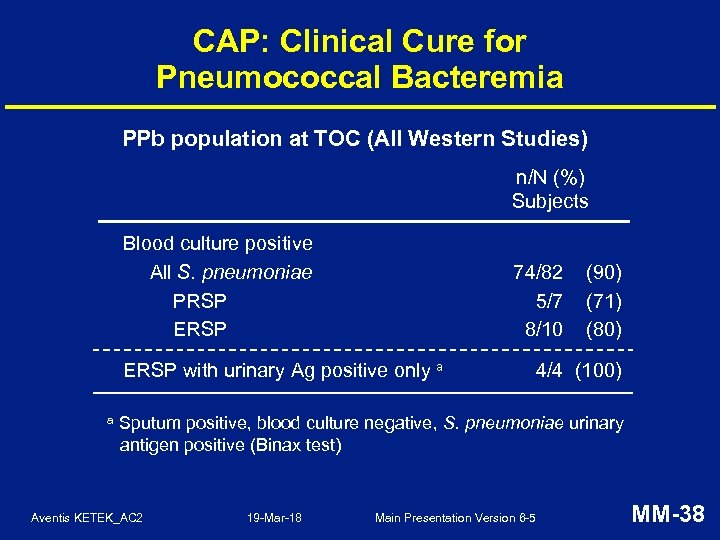 CAP: Clinical Cure for Pneumococcal Bacteremia PPb population at TOC (All Western Studies) n/N (%) Subjects Blood culture positive All S. pneumoniae PRSP ERSP 74/82 5/7 8/10 ERSP with urinary Ag positive only a a (90) (71) (80) 4/4 (100) Sputum positive, blood culture negative, S. pneumoniae urinary antigen positive (Binax test) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-38
CAP: Clinical Cure for Pneumococcal Bacteremia PPb population at TOC (All Western Studies) n/N (%) Subjects Blood culture positive All S. pneumoniae PRSP ERSP 74/82 5/7 8/10 ERSP with urinary Ag positive only a a (90) (71) (80) 4/4 (100) Sputum positive, blood culture negative, S. pneumoniae urinary antigen positive (Binax test) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-38
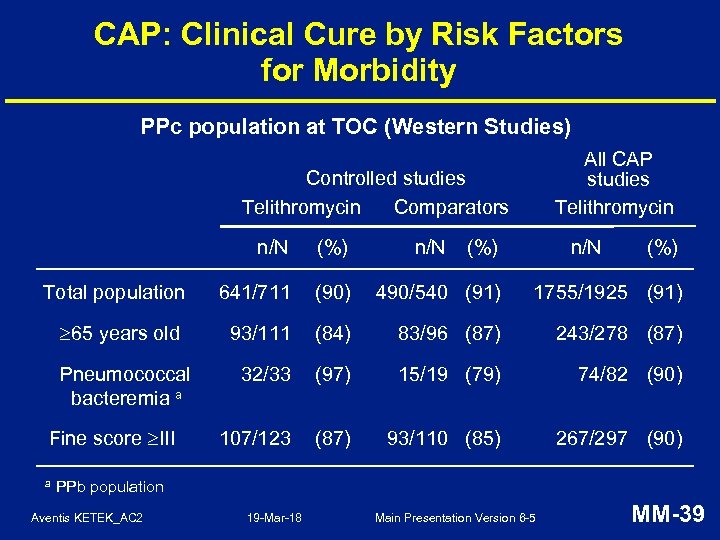 CAP: Clinical Cure by Risk Factors for Morbidity PPc population at TOC (Western Studies) All CAP studies Telithromycin Controlled studies Telithromycin Comparators n/N (%) Total population 641/711 (90) 490/540 (91) 1755/1925 (91) 65 years old 93/111 (84) 83/96 (87) 243/278 (87) Pneumococcal bacteremia a 32/33 (97) 15/19 (79) 74/82 (90) 107/123 (87) 93/110 (85) 267/297 (90) Fine score III a n/N (%) PPb population Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-39
CAP: Clinical Cure by Risk Factors for Morbidity PPc population at TOC (Western Studies) All CAP studies Telithromycin Controlled studies Telithromycin Comparators n/N (%) Total population 641/711 (90) 490/540 (91) 1755/1925 (91) 65 years old 93/111 (84) 83/96 (87) 243/278 (87) Pneumococcal bacteremia a 32/33 (97) 15/19 (79) 74/82 (90) 107/123 (87) 93/110 (85) 267/297 (90) Fine score III a n/N (%) PPb population Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-39
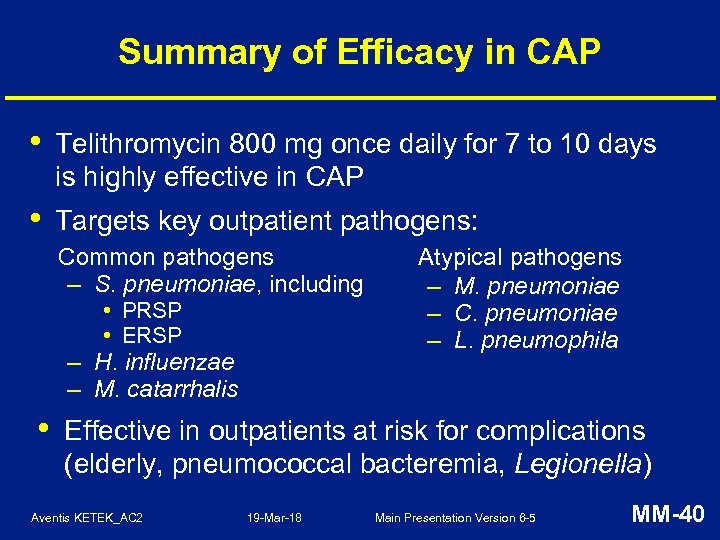 Summary of Efficacy in CAP • Telithromycin 800 mg once daily for 7 to 10 days is highly effective in CAP • Targets key outpatient pathogens: Common pathogens – S. pneumoniae, including • PRSP • ERSP – H. influenzae – M. catarrhalis • Atypical pathogens – M. pneumoniae – C. pneumoniae – L. pneumophila Effective in outpatients at risk for complications (elderly, pneumococcal bacteremia, Legionella) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-40
Summary of Efficacy in CAP • Telithromycin 800 mg once daily for 7 to 10 days is highly effective in CAP • Targets key outpatient pathogens: Common pathogens – S. pneumoniae, including • PRSP • ERSP – H. influenzae – M. catarrhalis • Atypical pathogens – M. pneumoniae – C. pneumoniae – L. pneumophila Effective in outpatients at risk for complications (elderly, pneumococcal bacteremia, Legionella) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-40
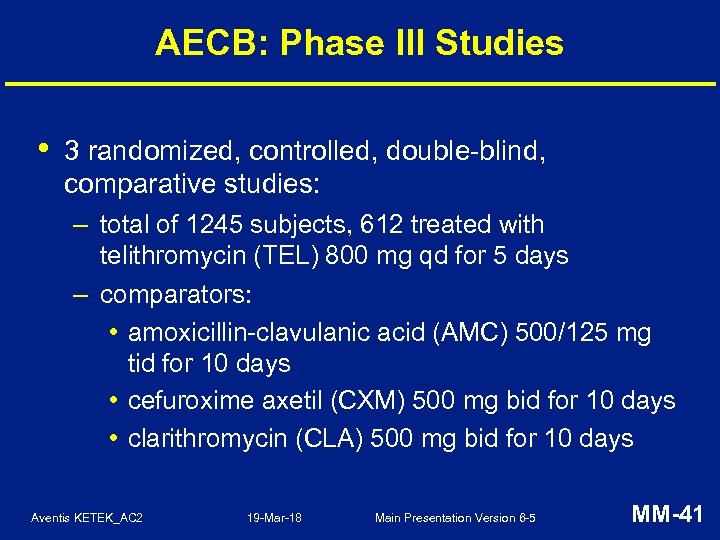 AECB: Phase III Studies • 3 randomized, controlled, double-blind, comparative studies: – total of 1245 subjects, 612 treated with telithromycin (TEL) 800 mg qd for 5 days – comparators: • amoxicillin-clavulanic acid (AMC) 500/125 mg tid for 10 days • cefuroxime axetil (CXM) 500 mg bid for 10 days • clarithromycin (CLA) 500 mg bid for 10 days Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-41
AECB: Phase III Studies • 3 randomized, controlled, double-blind, comparative studies: – total of 1245 subjects, 612 treated with telithromycin (TEL) 800 mg qd for 5 days – comparators: • amoxicillin-clavulanic acid (AMC) 500/125 mg tid for 10 days • cefuroxime axetil (CXM) 500 mg bid for 10 days • clarithromycin (CLA) 500 mg bid for 10 days Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-41
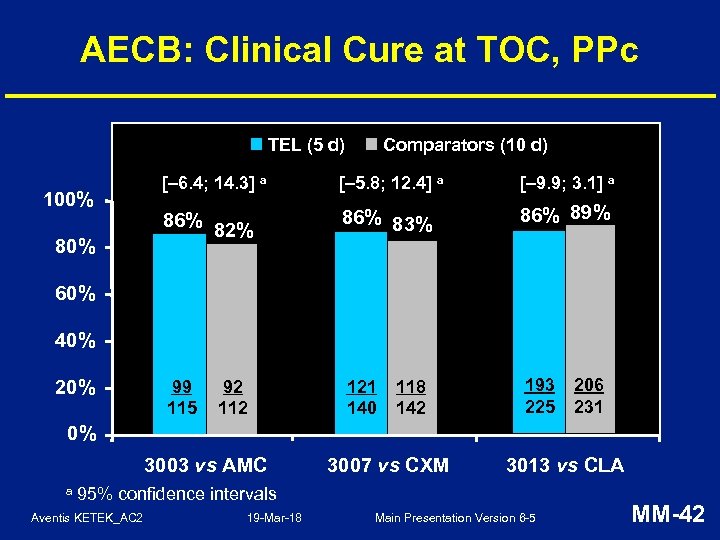 AECB: Clinical Cure at TOC, PPc TEL (5 d) 100% 80% Comparators (10 d) [– 6. 4; 14. 3] a [– 5. 8; 12. 4] a [– 9. 9; 3. 1] a 86% 82% 86% 83% 86% 89% 99 115 121 140 193 225 60% 40% 20% 92 118 142 206 231 0% 3003 vs AMC a 3007 vs CXM 3013 vs CLA 95% confidence intervals Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-42
AECB: Clinical Cure at TOC, PPc TEL (5 d) 100% 80% Comparators (10 d) [– 6. 4; 14. 3] a [– 5. 8; 12. 4] a [– 9. 9; 3. 1] a 86% 82% 86% 83% 86% 89% 99 115 121 140 193 225 60% 40% 20% 92 118 142 206 231 0% 3003 vs AMC a 3007 vs CXM 3013 vs CLA 95% confidence intervals Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-42
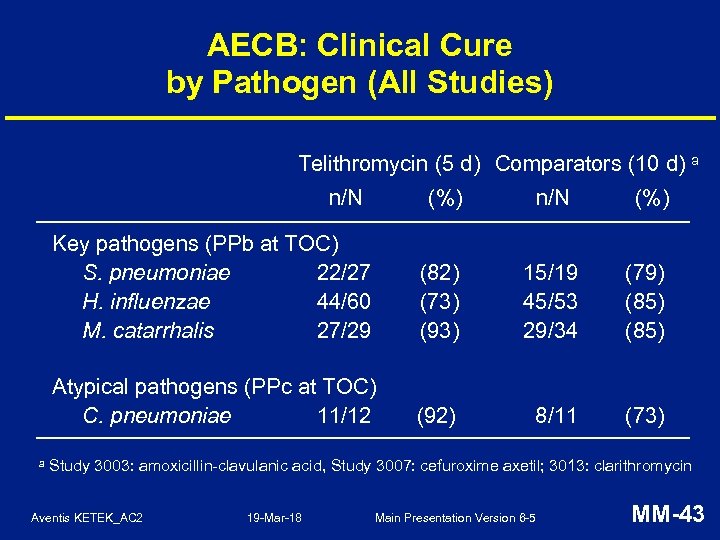 AECB: Clinical Cure by Pathogen (All Studies) Telithromycin (5 d) Comparators (10 d) a n/N Key pathogens (PPb at TOC) S. pneumoniae 22/27 H. influenzae 44/60 M. catarrhalis 27/29 (82) (73) (93) 15/19 45/53 29/34 (79) (85) Atypical pathogens (PPc at TOC) C. pneumoniae 11/12 a (%) (92) 8/11 (73) Study 3003: amoxicillin-clavulanic acid, Study 3007: cefuroxime axetil; 3013: clarithromycin Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-43
AECB: Clinical Cure by Pathogen (All Studies) Telithromycin (5 d) Comparators (10 d) a n/N Key pathogens (PPb at TOC) S. pneumoniae 22/27 H. influenzae 44/60 M. catarrhalis 27/29 (82) (73) (93) 15/19 45/53 29/34 (79) (85) Atypical pathogens (PPc at TOC) C. pneumoniae 11/12 a (%) (92) 8/11 (73) Study 3003: amoxicillin-clavulanic acid, Study 3007: cefuroxime axetil; 3013: clarithromycin Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-43
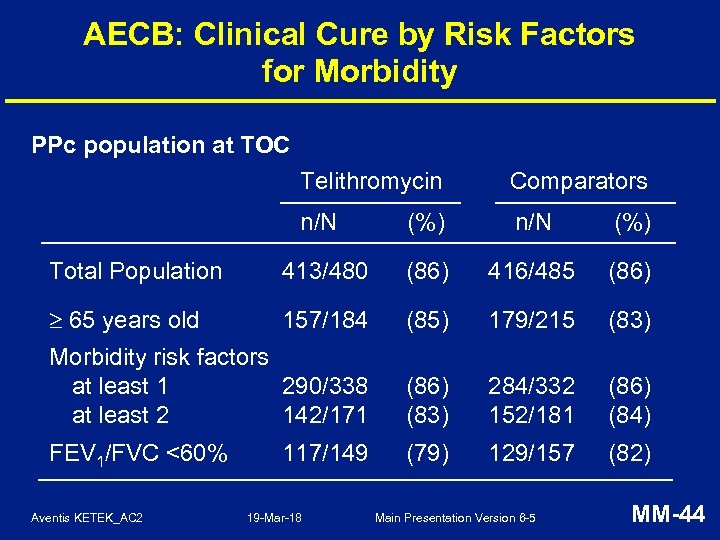 AECB: Clinical Cure by Risk Factors for Morbidity PPc population at TOC Telithromycin Comparators n/N (%) Total Population 413/480 (86) 416/485 (86) 65 years old 157/184 (85) 179/215 (83) Morbidity risk factors at least 1 290/338 at least 2 142/171 (86) (83) 284/332 152/181 (86) (84) FEV 1/FVC <60% (79) 129/157 (82) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 117/149 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-44
AECB: Clinical Cure by Risk Factors for Morbidity PPc population at TOC Telithromycin Comparators n/N (%) Total Population 413/480 (86) 416/485 (86) 65 years old 157/184 (85) 179/215 (83) Morbidity risk factors at least 1 290/338 at least 2 142/171 (86) (83) 284/332 152/181 (86) (84) FEV 1/FVC <60% (79) 129/157 (82) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 117/149 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-44
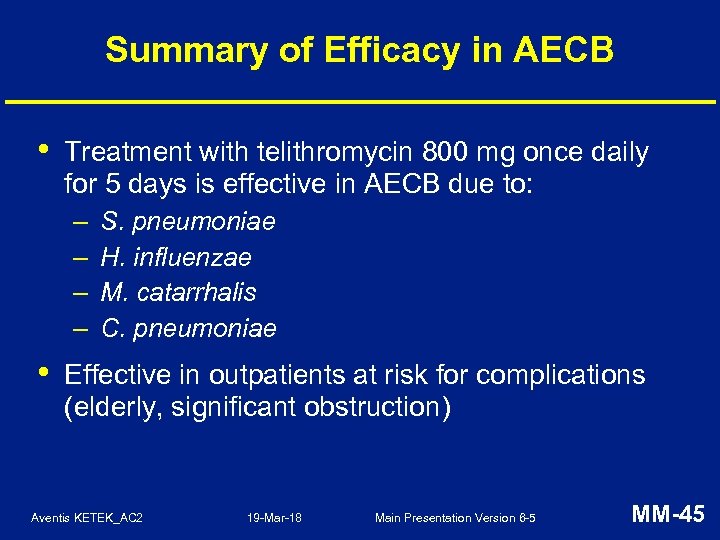 Summary of Efficacy in AECB • Treatment with telithromycin 800 mg once daily for 5 days is effective in AECB due to: – – • S. pneumoniae H. influenzae M. catarrhalis C. pneumoniae Effective in outpatients at risk for complications (elderly, significant obstruction) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-45
Summary of Efficacy in AECB • Treatment with telithromycin 800 mg once daily for 5 days is effective in AECB due to: – – • S. pneumoniae H. influenzae M. catarrhalis C. pneumoniae Effective in outpatients at risk for complications (elderly, significant obstruction) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-45
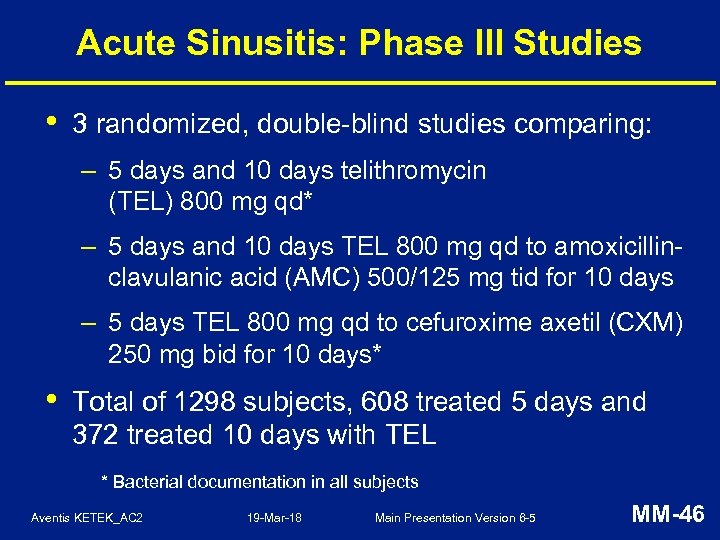 Acute Sinusitis: Phase III Studies • 3 randomized, double-blind studies comparing: – 5 days and 10 days telithromycin (TEL) 800 mg qd* – 5 days and 10 days TEL 800 mg qd to amoxicillinclavulanic acid (AMC) 500/125 mg tid for 10 days – 5 days TEL 800 mg qd to cefuroxime axetil (CXM) 250 mg bid for 10 days* • Total of 1298 subjects, 608 treated 5 days and 372 treated 10 days with TEL * Bacterial documentation in all subjects Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-46
Acute Sinusitis: Phase III Studies • 3 randomized, double-blind studies comparing: – 5 days and 10 days telithromycin (TEL) 800 mg qd* – 5 days and 10 days TEL 800 mg qd to amoxicillinclavulanic acid (AMC) 500/125 mg tid for 10 days – 5 days TEL 800 mg qd to cefuroxime axetil (CXM) 250 mg bid for 10 days* • Total of 1298 subjects, 608 treated 5 days and 372 treated 10 days with TEL * Bacterial documentation in all subjects Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-46
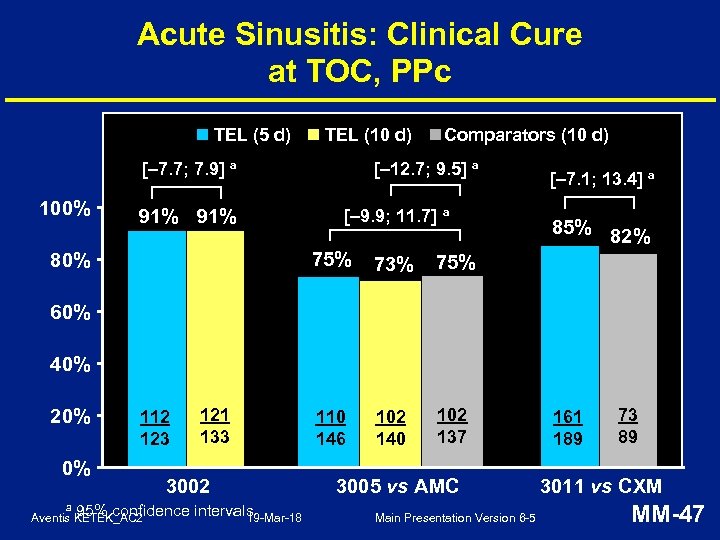 Acute Sinusitis: Clinical Cure at TOC, PPc TEL (5 d) TEL (10 d) [– 7. 7; 7. 9] a 100% 91% Comparators (10 d) [– 12. 7; 9. 5] a [– 9. 9; 11. 7] a 75% 80% 73% 102 140 102 137 85% 82% 75% 110 146 [– 7. 1; 13. 4] a 60% 40% 20% 112 123 0% a 121 133 3002 95% confidence intervals 19 -Mar-18 Aventis KETEK_AC 2 3005 vs AMC Main Presentation Version 6 -5 161 189 73 89 3011 vs CXM MM-47
Acute Sinusitis: Clinical Cure at TOC, PPc TEL (5 d) TEL (10 d) [– 7. 7; 7. 9] a 100% 91% Comparators (10 d) [– 12. 7; 9. 5] a [– 9. 9; 11. 7] a 75% 80% 73% 102 140 102 137 85% 82% 75% 110 146 [– 7. 1; 13. 4] a 60% 40% 20% 112 123 0% a 121 133 3002 95% confidence intervals 19 -Mar-18 Aventis KETEK_AC 2 3005 vs AMC Main Presentation Version 6 -5 161 189 73 89 3011 vs CXM MM-47
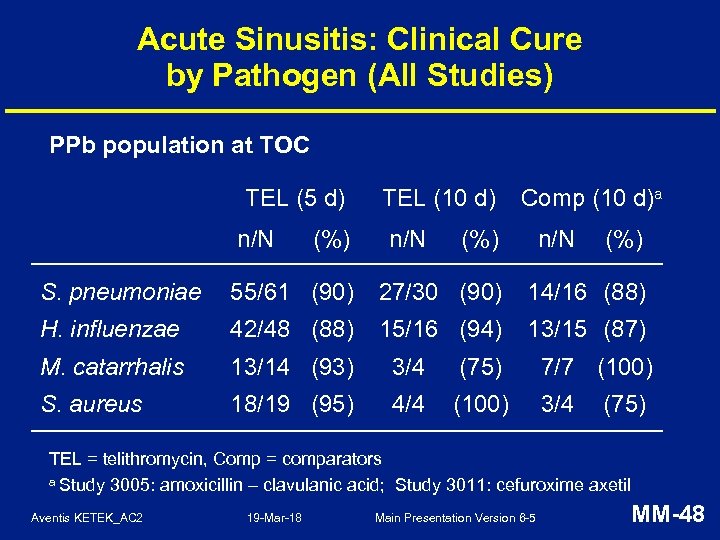 Acute Sinusitis: Clinical Cure by Pathogen (All Studies) PPb population at TOC TEL (5 d) n/N (%) TEL (10 d) n/N Comp (10 d)a (%) n/N (%) S. pneumoniae 55/61 (90) 27/30 (90) 14/16 (88) H. influenzae 42/48 (88) 15/16 (94) 13/15 (87) M. catarrhalis 13/14 (93) 3/4 (75) 7/7 (100) S. aureus 18/19 (95) 4/4 (100) 3/4 (75) TEL = telithromycin, Comp = comparators a Study 3005: amoxicillin – clavulanic acid; Study 3011: cefuroxime axetil Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-48
Acute Sinusitis: Clinical Cure by Pathogen (All Studies) PPb population at TOC TEL (5 d) n/N (%) TEL (10 d) n/N Comp (10 d)a (%) n/N (%) S. pneumoniae 55/61 (90) 27/30 (90) 14/16 (88) H. influenzae 42/48 (88) 15/16 (94) 13/15 (87) M. catarrhalis 13/14 (93) 3/4 (75) 7/7 (100) S. aureus 18/19 (95) 4/4 (100) 3/4 (75) TEL = telithromycin, Comp = comparators a Study 3005: amoxicillin – clavulanic acid; Study 3011: cefuroxime axetil Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-48
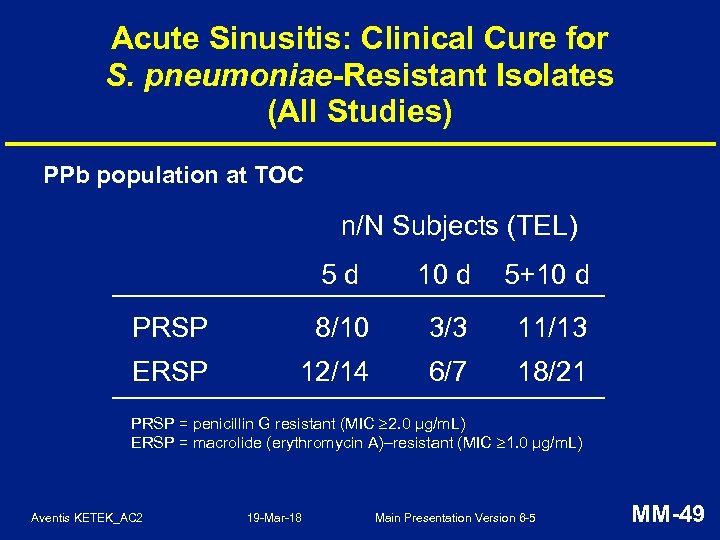 Acute Sinusitis: Clinical Cure for S. pneumoniae-Resistant Isolates (All Studies) PPb population at TOC n/N Subjects (TEL) 5 d 10 d 5+10 d PRSP 8/10 3/3 11/13 ERSP 12/14 6/7 18/21 PRSP = penicillin G resistant (MIC 2. 0 µg/m. L) ERSP = macrolide (erythromycin A)–resistant (MIC 1. 0 µg/m. L) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-49
Acute Sinusitis: Clinical Cure for S. pneumoniae-Resistant Isolates (All Studies) PPb population at TOC n/N Subjects (TEL) 5 d 10 d 5+10 d PRSP 8/10 3/3 11/13 ERSP 12/14 6/7 18/21 PRSP = penicillin G resistant (MIC 2. 0 µg/m. L) ERSP = macrolide (erythromycin A)–resistant (MIC 1. 0 µg/m. L) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-49
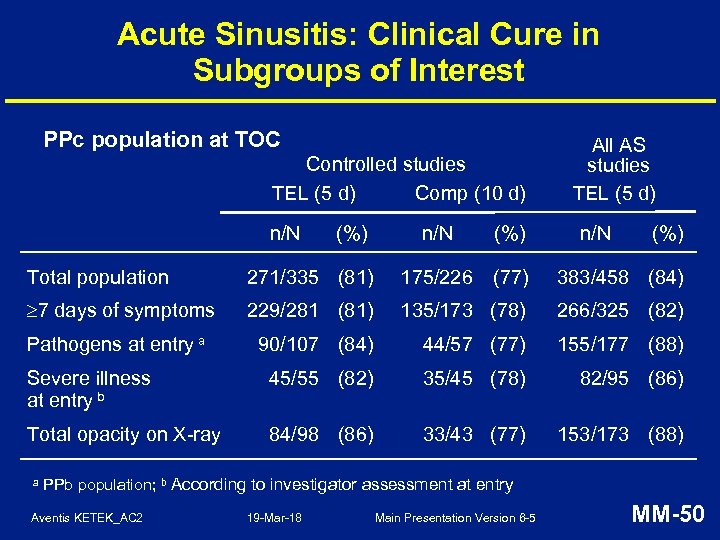 Acute Sinusitis: Clinical Cure in Subgroups of Interest PPc population at TOC Controlled studies TEL (5 d) Comp (10 d) n/N (%) All AS studies TEL (5 d) n/N (%) Total population 271/335 (81) 175/226 (77) 383/458 (84) 7 days of symptoms 229/281 (81) 135/173 (78) 266/325 (82) Pathogens at entry a 90/107 (84) 44/57 (77) 155/177 (88) Severe illness at entry b 45/55 (82) 35/45 (78) 82/95 (86) Total opacity on X-ray 84/98 (86) 33/43 (77) 153/173 (88) a PPb population; b According to investigator assessment at entry Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-50
Acute Sinusitis: Clinical Cure in Subgroups of Interest PPc population at TOC Controlled studies TEL (5 d) Comp (10 d) n/N (%) All AS studies TEL (5 d) n/N (%) Total population 271/335 (81) 175/226 (77) 383/458 (84) 7 days of symptoms 229/281 (81) 135/173 (78) 266/325 (82) Pathogens at entry a 90/107 (84) 44/57 (77) 155/177 (88) Severe illness at entry b 45/55 (82) 35/45 (78) 82/95 (86) Total opacity on X-ray 84/98 (86) 33/43 (77) 153/173 (88) a PPb population; b According to investigator assessment at entry Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-50
 Summary of Efficacy in Acute Sinusitis • Telithromycin 800 mg once daily for 5 days equivalent to 10 days of treatment with amoxicillin-clavulanic acid or cefuroxime axetil • 5 -day treatment effective against: – S. pneumoniae, including • PRSP • ERSP – H. influenzae – M. catarrhalis – S. aureus Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-51
Summary of Efficacy in Acute Sinusitis • Telithromycin 800 mg once daily for 5 days equivalent to 10 days of treatment with amoxicillin-clavulanic acid or cefuroxime axetil • 5 -day treatment effective against: – S. pneumoniae, including • PRSP • ERSP – H. influenzae – M. catarrhalis – S. aureus Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-51
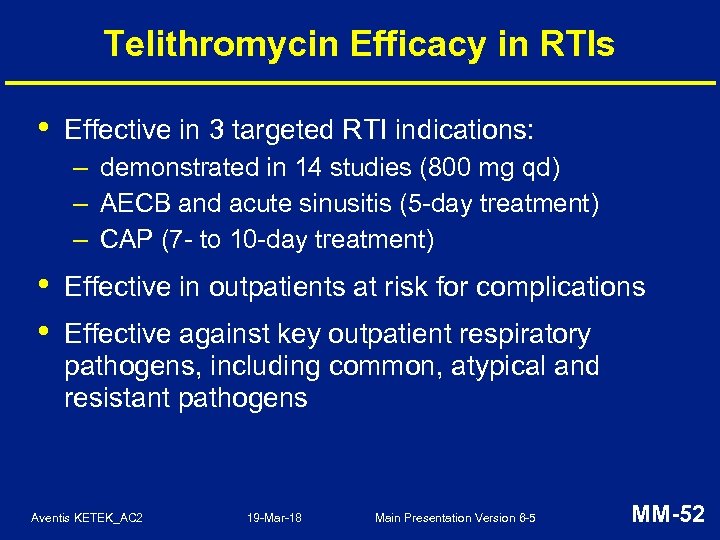 Telithromycin Efficacy in RTIs • Effective in 3 targeted RTI indications: – demonstrated in 14 studies (800 mg qd) – AECB and acute sinusitis (5 -day treatment) – CAP (7 - to 10 -day treatment) • • Effective in outpatients at risk for complications Effective against key outpatient respiratory pathogens, including common, atypical and resistant pathogens Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-52
Telithromycin Efficacy in RTIs • Effective in 3 targeted RTI indications: – demonstrated in 14 studies (800 mg qd) – AECB and acute sinusitis (5 -day treatment) – CAP (7 - to 10 -day treatment) • • Effective in outpatients at risk for complications Effective against key outpatient respiratory pathogens, including common, atypical and resistant pathogens Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-52
 Human Pharmacology Vijay Bhargava, Ph. D Senior Director, Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics, Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-53
Human Pharmacology Vijay Bhargava, Ph. D Senior Director, Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics, Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-53
 Human Pharmacology Program • Telithromycin has been extensively studied: – plasma and tissue pharmacokinetics – effect of impairment of elimination pathways on exposure of telithromycin – effect of telithromycin on exposure of other drugs (CYP 3 A 4 substrates) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-54
Human Pharmacology Program • Telithromycin has been extensively studied: – plasma and tissue pharmacokinetics – effect of impairment of elimination pathways on exposure of telithromycin – effect of telithromycin on exposure of other drugs (CYP 3 A 4 substrates) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-54
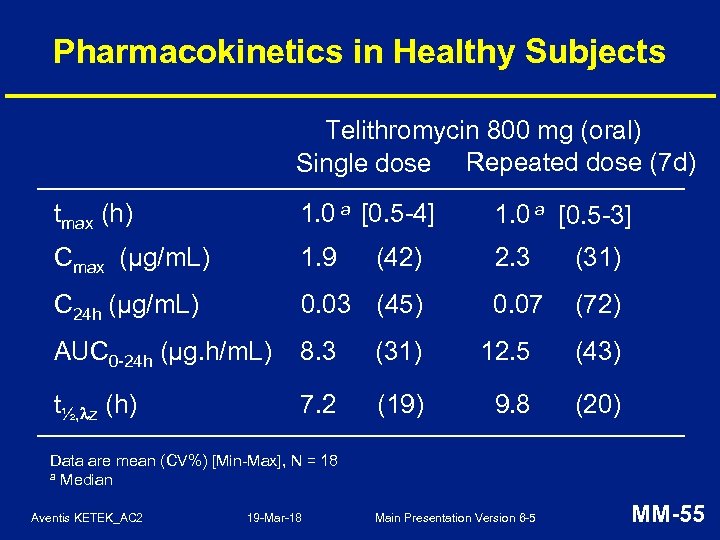 Pharmacokinetics in Healthy Subjects Telithromycin 800 mg (oral) Single dose Repeated dose (7 d) tmax (h) 1. 0 a [0. 5 -4] 1. 0 a [0. 5 -3] Cmax (µg/m. L) 1. 9 2. 3 (31) C 24 h (µg/m. L) 0. 03 (45) 0. 07 (72) AUC 0 -24 h (µg. h/m. L) 8. 3 (31) 12. 5 (43) t½, z (h) 7. 2 (19) 9. 8 (20) (42) Data are mean (CV%) [Min-Max], N = 18 a Median Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-55
Pharmacokinetics in Healthy Subjects Telithromycin 800 mg (oral) Single dose Repeated dose (7 d) tmax (h) 1. 0 a [0. 5 -4] 1. 0 a [0. 5 -3] Cmax (µg/m. L) 1. 9 2. 3 (31) C 24 h (µg/m. L) 0. 03 (45) 0. 07 (72) AUC 0 -24 h (µg. h/m. L) 8. 3 (31) 12. 5 (43) t½, z (h) 7. 2 (19) 9. 8 (20) (42) Data are mean (CV%) [Min-Max], N = 18 a Median Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-55
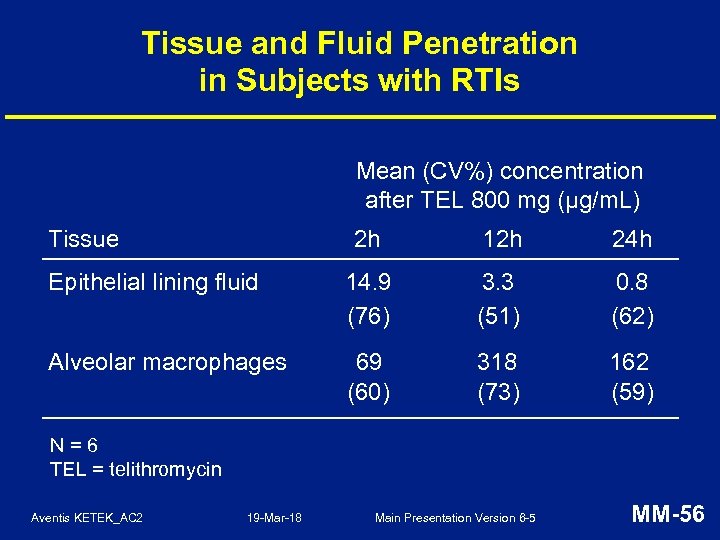 Tissue and Fluid Penetration in Subjects with RTIs Mean (CV%) concentration after TEL 800 mg (µg/m. L) Tissue 2 h 12 h 24 h Epithelial lining fluid 14. 9 (76) 3. 3 (51) 0. 8 (62) Alveolar macrophages 69 (60) 318 (73) 162 (59) N=6 TEL = telithromycin Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-56
Tissue and Fluid Penetration in Subjects with RTIs Mean (CV%) concentration after TEL 800 mg (µg/m. L) Tissue 2 h 12 h 24 h Epithelial lining fluid 14. 9 (76) 3. 3 (51) 0. 8 (62) Alveolar macrophages 69 (60) 318 (73) 162 (59) N=6 TEL = telithromycin Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-56
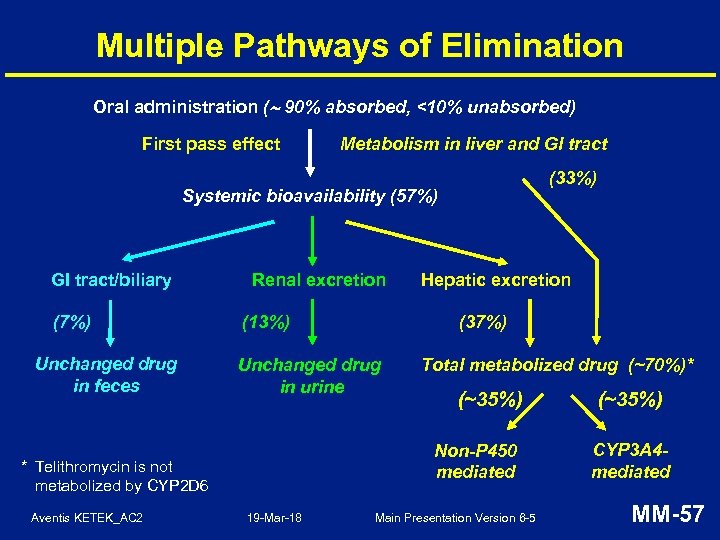 Multiple Pathways of Elimination Oral administration ( 90% absorbed, <10% unabsorbed) First pass effect Metabolism in liver and GI tract (33%) Systemic bioavailability (57%) GI tract/biliary (7%) Unchanged drug in feces Renal excretion (37%) (13%) Unchanged drug in urine Total metabolized drug (~70%)* (~35%) Non-P 450 mediated * Telithromycin is not metabolized by CYP 2 D 6 Aventis KETEK_AC 2 Hepatic excretion 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 (~35%) CYP 3 A 4 mediated MM-57
Multiple Pathways of Elimination Oral administration ( 90% absorbed, <10% unabsorbed) First pass effect Metabolism in liver and GI tract (33%) Systemic bioavailability (57%) GI tract/biliary (7%) Unchanged drug in feces Renal excretion (37%) (13%) Unchanged drug in urine Total metabolized drug (~70%)* (~35%) Non-P 450 mediated * Telithromycin is not metabolized by CYP 2 D 6 Aventis KETEK_AC 2 Hepatic excretion 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 (~35%) CYP 3 A 4 mediated MM-57
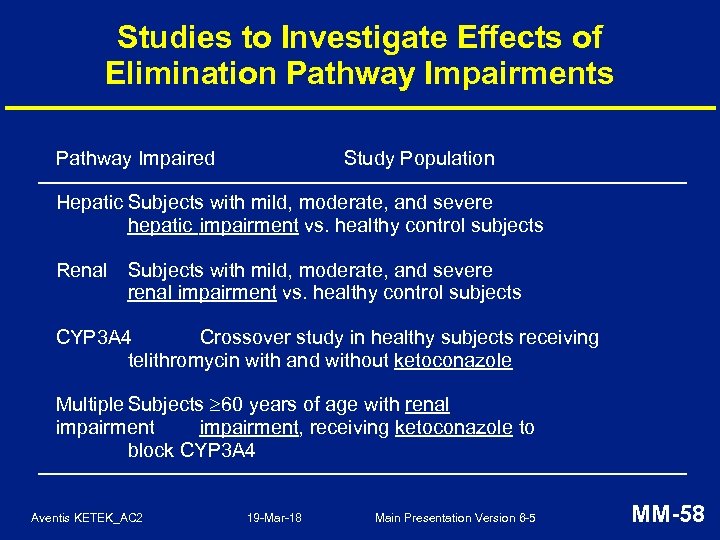 Studies to Investigate Effects of Elimination Pathway Impairments Pathway Impaired Study Population Hepatic Subjects with mild, moderate, and severe hepatic impairment vs. healthy control subjects Renal Subjects with mild, moderate, and severe renal impairment vs. healthy control subjects CYP 3 A 4 Crossover study in healthy subjects receiving telithromycin with and without ketoconazole Multiple Subjects 60 years of age with renal impairment, receiving ketoconazole to block CYP 3 A 4 Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-58
Studies to Investigate Effects of Elimination Pathway Impairments Pathway Impaired Study Population Hepatic Subjects with mild, moderate, and severe hepatic impairment vs. healthy control subjects Renal Subjects with mild, moderate, and severe renal impairment vs. healthy control subjects CYP 3 A 4 Crossover study in healthy subjects receiving telithromycin with and without ketoconazole Multiple Subjects 60 years of age with renal impairment, receiving ketoconazole to block CYP 3 A 4 Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-58
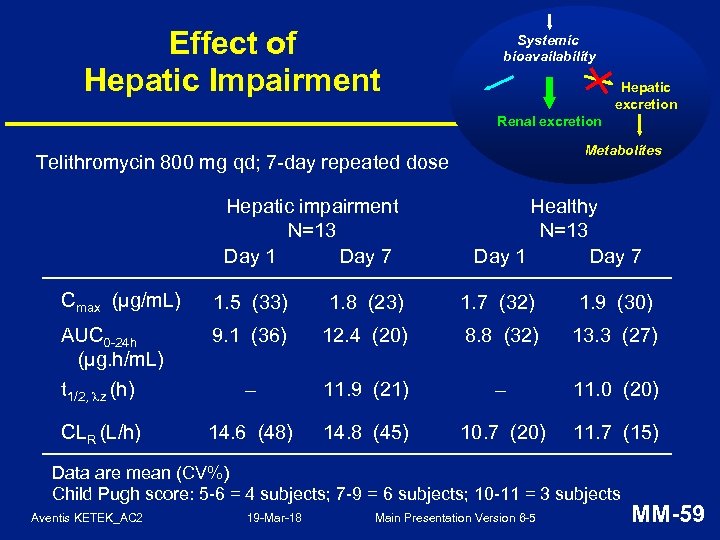 Effect of Hepatic Impairment Systemic bioavailability Hepatic excretion Renal excretion Metabolites Telithromycin 800 mg qd; 7 -day repeated dose Hepatic impairment N=13 Day 1 Day 7 Healthy N=13 Day 1 Day 7 Cmax (µg/m. L) 1. 5 (33) 1. 8 (23) 1. 7 (32) 1. 9 (30) AUC 0 -24 h (µg. h/m. L) t 1/2, z (h) 9. 1 (36) 12. 4 (20) 8. 8 (32) 13. 3 (27) – 11. 9 (21) – 11. 0 (20) CLR (L/h) 14. 6 (48) 14. 8 (45) 10. 7 (20) 11. 7 (15) Data are mean (CV%) Child Pugh score: 5 -6 = 4 subjects; 7 -9 = 6 subjects; 10 -11 = 3 subjects Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-59
Effect of Hepatic Impairment Systemic bioavailability Hepatic excretion Renal excretion Metabolites Telithromycin 800 mg qd; 7 -day repeated dose Hepatic impairment N=13 Day 1 Day 7 Healthy N=13 Day 1 Day 7 Cmax (µg/m. L) 1. 5 (33) 1. 8 (23) 1. 7 (32) 1. 9 (30) AUC 0 -24 h (µg. h/m. L) t 1/2, z (h) 9. 1 (36) 12. 4 (20) 8. 8 (32) 13. 3 (27) – 11. 9 (21) – 11. 0 (20) CLR (L/h) 14. 6 (48) 14. 8 (45) 10. 7 (20) 11. 7 (15) Data are mean (CV%) Child Pugh score: 5 -6 = 4 subjects; 7 -9 = 6 subjects; 10 -11 = 3 subjects Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-59
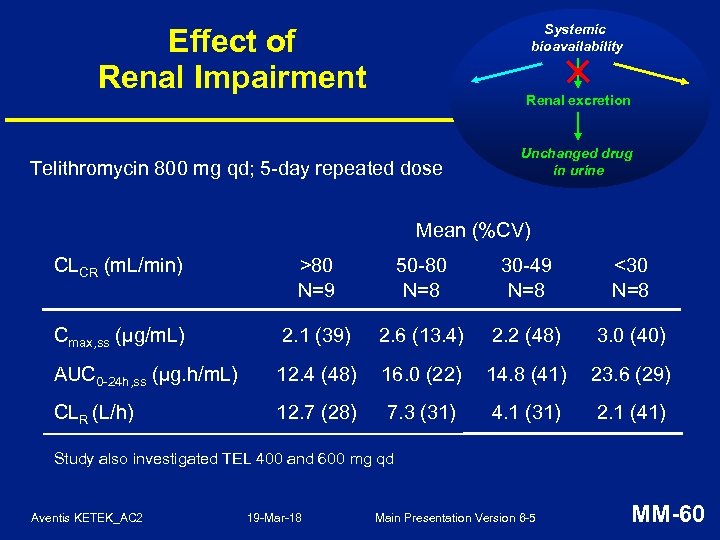 Systemic bioavailability Effect of Renal Impairment Renal excretion Telithromycin 800 mg qd; 5 -day repeated dose Unchanged drug in urine Mean (%CV) CLCR (m. L/min) >80 N=9 50 -80 N=8 30 -49 N=8 <30 N=8 Cmax, ss (µg/m. L) 2. 1 (39) 2. 6 (13. 4) 2. 2 (48) 3. 0 (40) AUC 0 -24 h, ss (µg. h/m. L) 12. 4 (48) 16. 0 (22) 14. 8 (41) 23. 6 (29) CLR (L/h) 12. 7 (28) 7. 3 (31) 4. 1 (31) 2. 1 (41) Study also investigated TEL 400 and 600 mg qd Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-60
Systemic bioavailability Effect of Renal Impairment Renal excretion Telithromycin 800 mg qd; 5 -day repeated dose Unchanged drug in urine Mean (%CV) CLCR (m. L/min) >80 N=9 50 -80 N=8 30 -49 N=8 <30 N=8 Cmax, ss (µg/m. L) 2. 1 (39) 2. 6 (13. 4) 2. 2 (48) 3. 0 (40) AUC 0 -24 h, ss (µg. h/m. L) 12. 4 (48) 16. 0 (22) 14. 8 (41) 23. 6 (29) CLR (L/h) 12. 7 (28) 7. 3 (31) 4. 1 (31) 2. 1 (41) Study also investigated TEL 400 and 600 mg qd Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-60
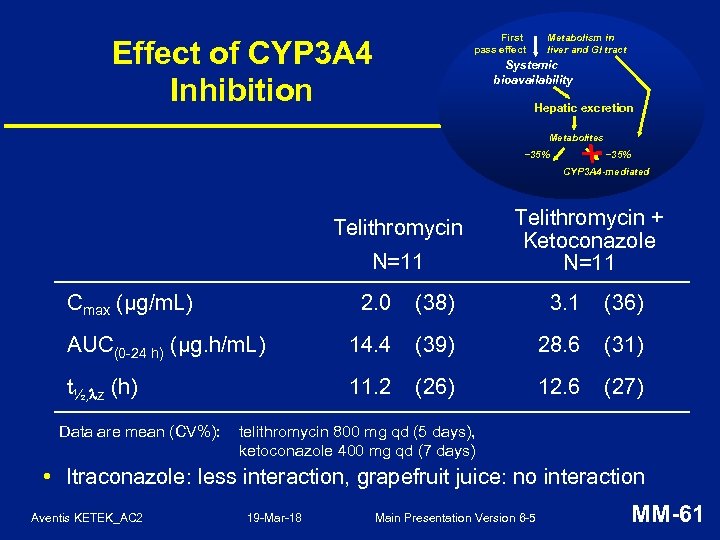 First pass effect Effect of CYP 3 A 4 Inhibition Metabolism in liver and GI tract Systemic bioavailability Hepatic excretion Metabolites ~35% CYP 3 A 4 -mediated Telithromycin N=11 Cmax (µg/m. L) Telithromycin + Ketoconazole N=11 2. 0 (38) 3. 1 (36) AUC(0 -24 h) (µg. h/m. L) 14. 4 (39) 28. 6 (31) t½, z (h) 11. 2 (26) 12. 6 (27) Data are mean (CV%): telithromycin 800 mg qd (5 days), ketoconazole 400 mg qd (7 days) • Itraconazole: less interaction, grapefruit juice: no interaction Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-61
First pass effect Effect of CYP 3 A 4 Inhibition Metabolism in liver and GI tract Systemic bioavailability Hepatic excretion Metabolites ~35% CYP 3 A 4 -mediated Telithromycin N=11 Cmax (µg/m. L) Telithromycin + Ketoconazole N=11 2. 0 (38) 3. 1 (36) AUC(0 -24 h) (µg. h/m. L) 14. 4 (39) 28. 6 (31) t½, z (h) 11. 2 (26) 12. 6 (27) Data are mean (CV%): telithromycin 800 mg qd (5 days), ketoconazole 400 mg qd (7 days) • Itraconazole: less interaction, grapefruit juice: no interaction Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-61
 Effect of Multiple Impairments (Renal + Ketoconazole) First pass effect Metabolism in liver and GI tract Systemic bioavailability Hepatic excretion Renal excretion Unchanged drug in urine Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 ~35% non-CYP 3 A 4 mediated metabolites Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-62
Effect of Multiple Impairments (Renal + Ketoconazole) First pass effect Metabolism in liver and GI tract Systemic bioavailability Hepatic excretion Renal excretion Unchanged drug in urine Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 ~35% non-CYP 3 A 4 mediated metabolites Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-62
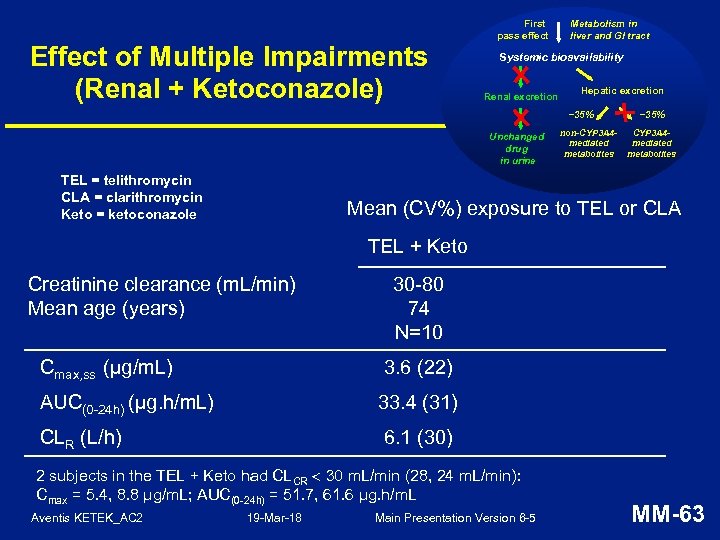 Effect of Multiple Impairments (Renal + Ketoconazole) First pass effect Metabolism in liver and GI tract Systemic bioavailability Renal excretion Hepatic excretion ~35% Unchanged drug in urine TEL = telithromycin CLA = clarithromycin Keto = ketoconazole non-CYP 3 A 4 mediated metabolites ~35% CYP 3 A 4 mediated metabolites Mean (CV%) exposure to TEL or CLA TEL + Keto Creatinine clearance (m. L/min) Mean age (years) 30 -80 74 N=10 Cmax, ss (µg/m. L) 3. 6 (22) AUC(0 -24 h) (µg. h/m. L) 33. 4 (31) CLR (L/h) 6. 1 (30) 2 subjects in the TEL + Keto had CLCR 30 m. L/min (28, 24 m. L/min): Cmax = 5. 4, 8. 8 μg/m. L; AUC(0 -24 h) = 51. 7, 61. 6 μg. h/m. L Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-63
Effect of Multiple Impairments (Renal + Ketoconazole) First pass effect Metabolism in liver and GI tract Systemic bioavailability Renal excretion Hepatic excretion ~35% Unchanged drug in urine TEL = telithromycin CLA = clarithromycin Keto = ketoconazole non-CYP 3 A 4 mediated metabolites ~35% CYP 3 A 4 mediated metabolites Mean (CV%) exposure to TEL or CLA TEL + Keto Creatinine clearance (m. L/min) Mean age (years) 30 -80 74 N=10 Cmax, ss (µg/m. L) 3. 6 (22) AUC(0 -24 h) (µg. h/m. L) 33. 4 (31) CLR (L/h) 6. 1 (30) 2 subjects in the TEL + Keto had CLCR 30 m. L/min (28, 24 m. L/min): Cmax = 5. 4, 8. 8 μg/m. L; AUC(0 -24 h) = 51. 7, 61. 6 μg. h/m. L Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-63
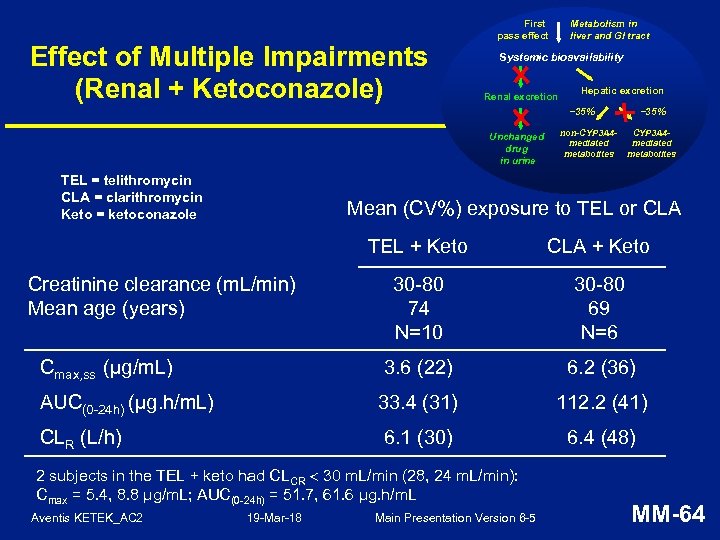 Effect of Multiple Impairments (Renal + Ketoconazole) First pass effect Metabolism in liver and GI tract Systemic bioavailability Renal excretion Hepatic excretion ~35% Unchanged drug in urine TEL = telithromycin CLA = clarithromycin Keto = ketoconazole non-CYP 3 A 4 mediated metabolites ~35% CYP 3 A 4 mediated metabolites Mean (CV%) exposure to TEL or CLA TEL + Keto CLA + Keto 30 -80 74 N=10 30 -80 69 N=6 Cmax, ss (µg/m. L) 3. 6 (22) 6. 2 (36) AUC(0 -24 h) (µg. h/m. L) 33. 4 (31) 112. 2 (41) CLR (L/h) 6. 1 (30) 6. 4 (48) Creatinine clearance (m. L/min) Mean age (years) 2 subjects in the TEL + keto had CLCR 30 m. L/min (28, 24 m. L/min): Cmax = 5. 4, 8. 8 μg/m. L; AUC(0 -24 h) = 51. 7, 61. 6 μg. h/m. L Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-64
Effect of Multiple Impairments (Renal + Ketoconazole) First pass effect Metabolism in liver and GI tract Systemic bioavailability Renal excretion Hepatic excretion ~35% Unchanged drug in urine TEL = telithromycin CLA = clarithromycin Keto = ketoconazole non-CYP 3 A 4 mediated metabolites ~35% CYP 3 A 4 mediated metabolites Mean (CV%) exposure to TEL or CLA TEL + Keto CLA + Keto 30 -80 74 N=10 30 -80 69 N=6 Cmax, ss (µg/m. L) 3. 6 (22) 6. 2 (36) AUC(0 -24 h) (µg. h/m. L) 33. 4 (31) 112. 2 (41) CLR (L/h) 6. 1 (30) 6. 4 (48) Creatinine clearance (m. L/min) Mean age (years) 2 subjects in the TEL + keto had CLCR 30 m. L/min (28, 24 m. L/min): Cmax = 5. 4, 8. 8 μg/m. L; AUC(0 -24 h) = 51. 7, 61. 6 μg. h/m. L Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-64
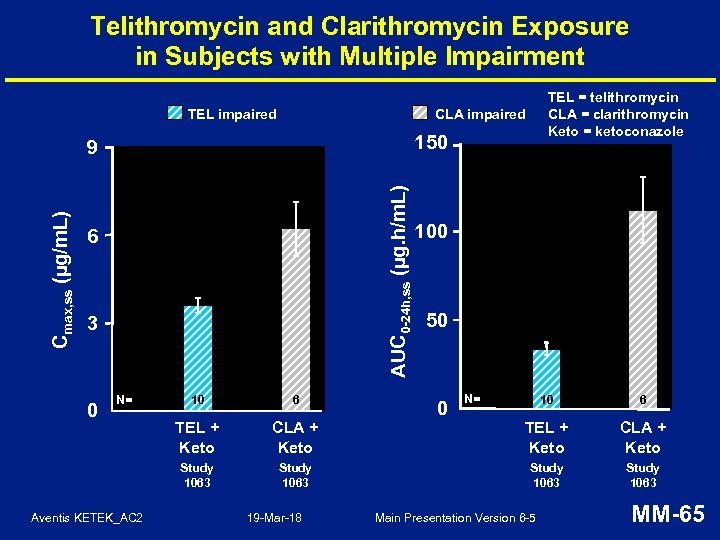 Telithromycin and Clarithromycin Exposure in Subjects with Multiple Impairment TEL impaired CLA impaired 150 AUC 0 -24 h, ss (µg. h/m. L) Cmax, ss (µg/m. L) 9 6 3 N= Aventis KETEK_AC 2 10 6 TEL + Keto Study 1063 0 TEL = telithromycin CLA = clarithromycin Keto = ketoconazole 100 50 N= 10 6 CLA + Keto TEL + Keto CLA + Keto Study 1063 19 -Mar-18 0 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-65
Telithromycin and Clarithromycin Exposure in Subjects with Multiple Impairment TEL impaired CLA impaired 150 AUC 0 -24 h, ss (µg. h/m. L) Cmax, ss (µg/m. L) 9 6 3 N= Aventis KETEK_AC 2 10 6 TEL + Keto Study 1063 0 TEL = telithromycin CLA = clarithromycin Keto = ketoconazole 100 50 N= 10 6 CLA + Keto TEL + Keto CLA + Keto Study 1063 19 -Mar-18 0 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-65
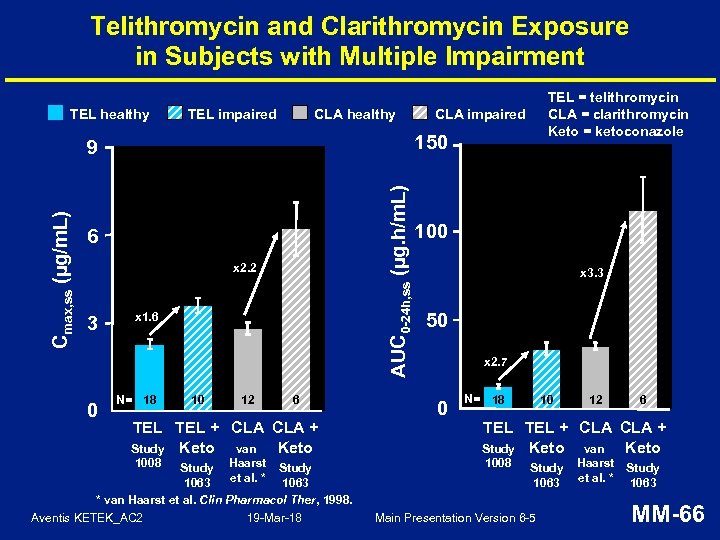 Telithromycin and Clarithromycin Exposure in Subjects with Multiple Impairment TEL healthy TEL impaired CLA healthy AUC 0 -24 h, ss (µg. h/m. L) Cmax, ss (µg/m. L) 6 x 2. 2 0 CLA impaired 150 9 3 TEL = telithromycin CLA = clarithromycin Keto = ketoconazole x 1. 6 N= 18 10 12 6 100 x 3. 3 50 x 2. 7 0 N= 18 10 12 6 TEL TEL + CLA CLA + Keto Study Keto van 1008 Study Haarst Study et al. * 1063 * van Haarst et al. Clin Pharmacol Ther, 1998. Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Study 1063 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 Haarst Study et al. * 1063 MM-66
Telithromycin and Clarithromycin Exposure in Subjects with Multiple Impairment TEL healthy TEL impaired CLA healthy AUC 0 -24 h, ss (µg. h/m. L) Cmax, ss (µg/m. L) 6 x 2. 2 0 CLA impaired 150 9 3 TEL = telithromycin CLA = clarithromycin Keto = ketoconazole x 1. 6 N= 18 10 12 6 100 x 3. 3 50 x 2. 7 0 N= 18 10 12 6 TEL TEL + CLA CLA + Keto Study Keto van 1008 Study Haarst Study et al. * 1063 * van Haarst et al. Clin Pharmacol Ther, 1998. Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Study 1063 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 Haarst Study et al. * 1063 MM-66
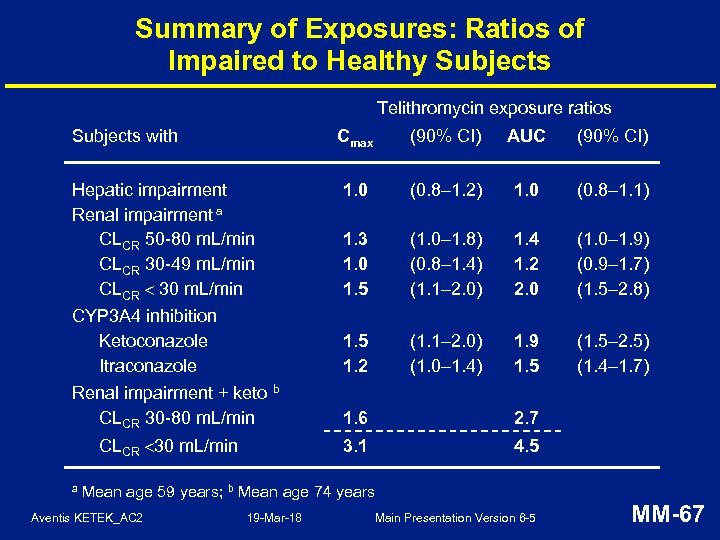 Summary of Exposures: Ratios of Impaired to Healthy Subjects Telithromycin exposure ratios Subjects with Cmax Hepatic impairment Renal impairment a CLCR 50 -80 m. L/min CLCR 30 -49 m. L/min CLCR 30 m. L/min CYP 3 A 4 inhibition Ketoconazole Itraconazole Renal impairment + keto b CLCR 30 -80 m. L/min AUC (90% CI) 1. 0 (0. 8– 1. 2) 1. 0 (0. 8– 1. 1) 1. 3 1. 0 1. 5 (1. 0– 1. 8) (0. 8– 1. 4) (1. 1– 2. 0) 1. 4 1. 2 2. 0 (1. 0– 1. 9) (0. 9– 1. 7) (1. 5– 2. 8) 1. 5 1. 2 (1. 1– 2. 0) (1. 0– 1. 4) 1. 9 1. 5 (1. 5– 2. 5) (1. 4– 1. 7) 1. 6 2. 7 3. 1 CLCR 30 m. L/min a (90% CI) 4. 5 Mean age 59 years; b Mean age 74 years Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-67
Summary of Exposures: Ratios of Impaired to Healthy Subjects Telithromycin exposure ratios Subjects with Cmax Hepatic impairment Renal impairment a CLCR 50 -80 m. L/min CLCR 30 -49 m. L/min CLCR 30 m. L/min CYP 3 A 4 inhibition Ketoconazole Itraconazole Renal impairment + keto b CLCR 30 -80 m. L/min AUC (90% CI) 1. 0 (0. 8– 1. 2) 1. 0 (0. 8– 1. 1) 1. 3 1. 0 1. 5 (1. 0– 1. 8) (0. 8– 1. 4) (1. 1– 2. 0) 1. 4 1. 2 2. 0 (1. 0– 1. 9) (0. 9– 1. 7) (1. 5– 2. 8) 1. 5 1. 2 (1. 1– 2. 0) (1. 0– 1. 4) 1. 9 1. 5 (1. 5– 2. 5) (1. 4– 1. 7) 1. 6 2. 7 3. 1 CLCR 30 m. L/min a (90% CI) 4. 5 Mean age 59 years; b Mean age 74 years Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-67
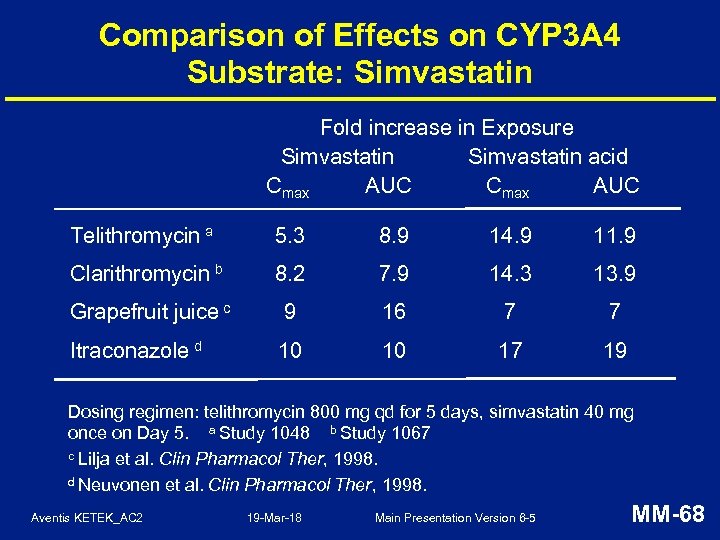 Comparison of Effects on CYP 3 A 4 Substrate: Simvastatin Fold increase in Exposure Simvastatin acid Cmax AUC Telithromycin a 5. 3 8. 9 14. 9 11. 9 Clarithromycin b 8. 2 7. 9 14. 3 13. 9 Grapefruit juice c 9 16 7 7 Itraconazole d 10 10 17 19 Dosing regimen: telithromycin 800 mg qd for 5 days, simvastatin 40 mg once on Day 5. a Study 1048 b Study 1067 c Lilja et al. Clin Pharmacol Ther, 1998. d Neuvonen et al. Clin Pharmacol Ther, 1998. Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-68
Comparison of Effects on CYP 3 A 4 Substrate: Simvastatin Fold increase in Exposure Simvastatin acid Cmax AUC Telithromycin a 5. 3 8. 9 14. 9 11. 9 Clarithromycin b 8. 2 7. 9 14. 3 13. 9 Grapefruit juice c 9 16 7 7 Itraconazole d 10 10 17 19 Dosing regimen: telithromycin 800 mg qd for 5 days, simvastatin 40 mg once on Day 5. a Study 1048 b Study 1067 c Lilja et al. Clin Pharmacol Ther, 1998. d Neuvonen et al. Clin Pharmacol Ther, 1998. Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-68
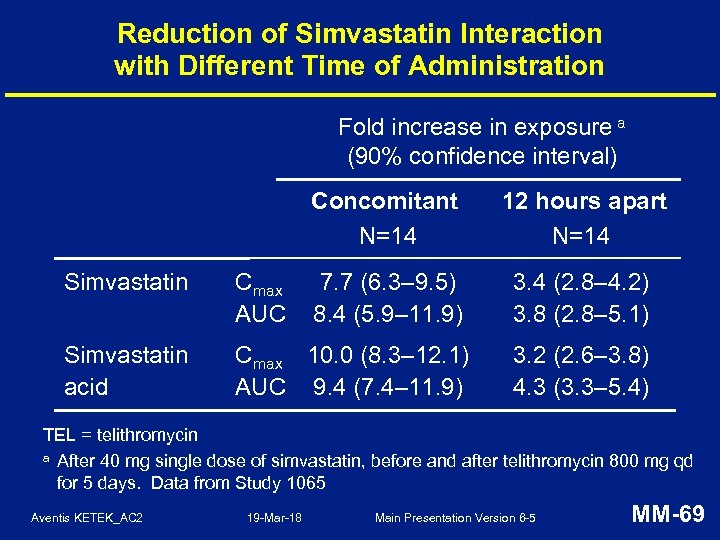 Reduction of Simvastatin Interaction with Different Time of Administration Fold increase in exposure a (90% confidence interval) Concomitant N=14 12 hours apart N=14 Simvastatin Cmax AUC 7. 7 (6. 3– 9. 5) 8. 4 (5. 9– 11. 9) 3. 4 (2. 8– 4. 2) 3. 8 (2. 8– 5. 1) Simvastatin acid Cmax 10. 0 (8. 3– 12. 1) AUC 9. 4 (7. 4– 11. 9) 3. 2 (2. 6– 3. 8) 4. 3 (3. 3– 5. 4) TEL = telithromycin a After 40 mg single dose of simvastatin, before and after telithromycin 800 mg qd for 5 days. Data from Study 1065 Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-69
Reduction of Simvastatin Interaction with Different Time of Administration Fold increase in exposure a (90% confidence interval) Concomitant N=14 12 hours apart N=14 Simvastatin Cmax AUC 7. 7 (6. 3– 9. 5) 8. 4 (5. 9– 11. 9) 3. 4 (2. 8– 4. 2) 3. 8 (2. 8– 5. 1) Simvastatin acid Cmax 10. 0 (8. 3– 12. 1) AUC 9. 4 (7. 4– 11. 9) 3. 2 (2. 6– 3. 8) 4. 3 (3. 3– 5. 4) TEL = telithromycin a After 40 mg single dose of simvastatin, before and after telithromycin 800 mg qd for 5 days. Data from Study 1065 Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-69
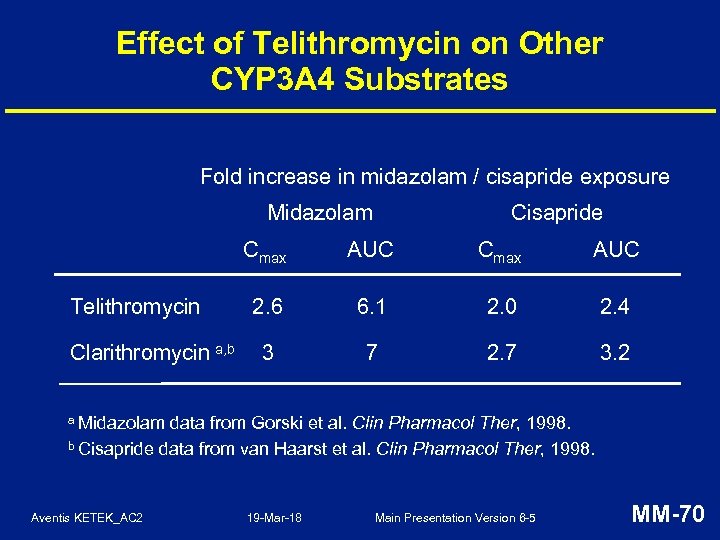 Effect of Telithromycin on Other CYP 3 A 4 Substrates Fold increase in midazolam / cisapride exposure Midazolam Cisapride Cmax Telithromycin Clarithromycin a, b AUC Cmax AUC 2. 6 6. 1 2. 0 2. 4 3 7 2. 7 3. 2 a Midazolam data from Gorski et al. Clin Pharmacol Ther, 1998. b Cisapride data from van Haarst et al. Clin Pharmacol Ther, 1998. Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-70
Effect of Telithromycin on Other CYP 3 A 4 Substrates Fold increase in midazolam / cisapride exposure Midazolam Cisapride Cmax Telithromycin Clarithromycin a, b AUC Cmax AUC 2. 6 6. 1 2. 0 2. 4 3 7 2. 7 3. 2 a Midazolam data from Gorski et al. Clin Pharmacol Ther, 1998. b Cisapride data from van Haarst et al. Clin Pharmacol Ther, 1998. Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-70
 Summary of Telithromycin Human Pharmacology • Pharmacokinetics reproducible and predictable under various conditions • Targeted plasma and respiratory tissue concentrations rapidly achieved • Multiple elimination pathways limit the potential for increased exposure in special populations • Similar CYP 3 A 4 inhibition to clarithromycin, but telithromycin is dosed once daily and for shorter treatment duration in RTIs Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-71
Summary of Telithromycin Human Pharmacology • Pharmacokinetics reproducible and predictable under various conditions • Targeted plasma and respiratory tissue concentrations rapidly achieved • Multiple elimination pathways limit the potential for increased exposure in special populations • Similar CYP 3 A 4 inhibition to clarithromycin, but telithromycin is dosed once daily and for shorter treatment duration in RTIs Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-71
 Clinical Safety Paul Lagarenne, MD VP, Clinical Safety Analysis, Aventis Global Pharmacovigilance Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-72
Clinical Safety Paul Lagarenne, MD VP, Clinical Safety Analysis, Aventis Global Pharmacovigilance Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-72
 Clinical Safety of Telithromycin • Phase III studies: – 4, 472 telithromycin subjects, including 2, 702 in controlled studies • Large comparative study in usual care setting (Study 3014): – 12, 159 telithromycin subjects • Post-marketing experience: – 1. 5 million exposures as of December 1 st, 2002* * based upon Aventis internal sales data to retail and outpatient pharmacies Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-73
Clinical Safety of Telithromycin • Phase III studies: – 4, 472 telithromycin subjects, including 2, 702 in controlled studies • Large comparative study in usual care setting (Study 3014): – 12, 159 telithromycin subjects • Post-marketing experience: – 1. 5 million exposures as of December 1 st, 2002* * based upon Aventis internal sales data to retail and outpatient pharmacies Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-73
 Phase III Clinical Studies Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-74
Phase III Clinical Studies Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-74
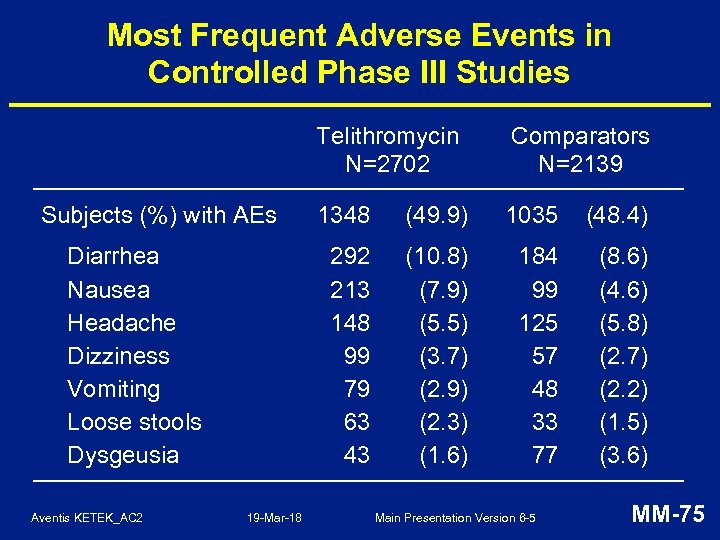 Most Frequent Adverse Events in Controlled Phase III Studies Telithromycin N=2702 Diarrhea Nausea Headache Dizziness Vomiting Loose stools Dysgeusia Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 1348 (49. 9) 1035 (48. 4) 292 213 148 99 79 63 43 Subjects (%) with AEs Comparators N=2139 (10. 8) (7. 9) (5. 5) (3. 7) (2. 9) (2. 3) (1. 6) 184 99 125 57 48 33 77 (8. 6) (4. 6) (5. 8) (2. 7) (2. 2) (1. 5) (3. 6) Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-75
Most Frequent Adverse Events in Controlled Phase III Studies Telithromycin N=2702 Diarrhea Nausea Headache Dizziness Vomiting Loose stools Dysgeusia Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 1348 (49. 9) 1035 (48. 4) 292 213 148 99 79 63 43 Subjects (%) with AEs Comparators N=2139 (10. 8) (7. 9) (5. 5) (3. 7) (2. 9) (2. 3) (1. 6) 184 99 125 57 48 33 77 (8. 6) (4. 6) (5. 8) (2. 7) (2. 2) (1. 5) (3. 6) Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-75
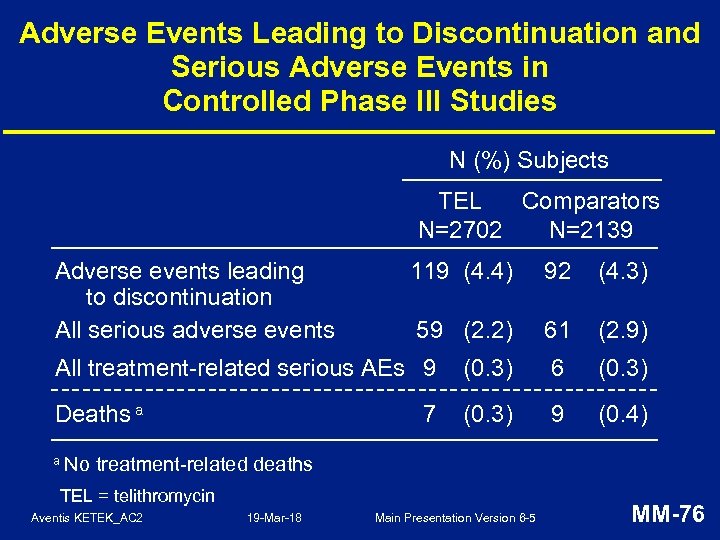 Adverse Events Leading to Discontinuation and Serious Adverse Events in Controlled Phase III Studies N (%) Subjects TEL Comparators N=2702 N=2139 Adverse events leading to discontinuation All serious adverse events 119 (4. 4) 92 (4. 3) 59 (2. 2) 61 (2. 9) All treatment-related serious AEs 9 (0. 3) 6 (0. 3) Deaths a (0. 3) 9 (0. 4) a No 7 treatment-related deaths TEL = telithromycin Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-76
Adverse Events Leading to Discontinuation and Serious Adverse Events in Controlled Phase III Studies N (%) Subjects TEL Comparators N=2702 N=2139 Adverse events leading to discontinuation All serious adverse events 119 (4. 4) 92 (4. 3) 59 (2. 2) 61 (2. 9) All treatment-related serious AEs 9 (0. 3) 6 (0. 3) Deaths a (0. 3) 9 (0. 4) a No 7 treatment-related deaths TEL = telithromycin Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-76
 Blurred Vision with Telithromycin in Controlled Phase III Studies • • • Uncommon event: 0. 6% subjects Generally mild Limited duration and fully reversible No sequelae No serious reports Single subject required discontinuation of drug Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-77
Blurred Vision with Telithromycin in Controlled Phase III Studies • • • Uncommon event: 0. 6% subjects Generally mild Limited duration and fully reversible No sequelae No serious reports Single subject required discontinuation of drug Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-77
 Investigation of Visual Effects • Two Phase I studies with high doses (2400 mg): – mostly described as a delay in focusing from near to far vision – onset within a few hours (median: 3 h) – rapid recovery within 2 to 3 h – no decreases in visual acuity – severe etiologies ruled out (e. g. , angle-closure glaucoma or retinopathy) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-78
Investigation of Visual Effects • Two Phase I studies with high doses (2400 mg): – mostly described as a delay in focusing from near to far vision – onset within a few hours (median: 3 h) – rapid recovery within 2 to 3 h – no decreases in visual acuity – severe etiologies ruled out (e. g. , angle-closure glaucoma or retinopathy) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-78
 ECG Analysis in Phase III Studies • ECGs performed at pretherapy and on-therapy (Day 3 -5) in 12 Phase III studies (N = 2411 subjects) • Minimal change in mean QTc* interval of approximately 1. 5 ms • No difference in QTc outliers vs. comparators * Bazett correction formula Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-79
ECG Analysis in Phase III Studies • ECGs performed at pretherapy and on-therapy (Day 3 -5) in 12 Phase III studies (N = 2411 subjects) • Minimal change in mean QTc* interval of approximately 1. 5 ms • No difference in QTc outliers vs. comparators * Bazett correction formula Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-79
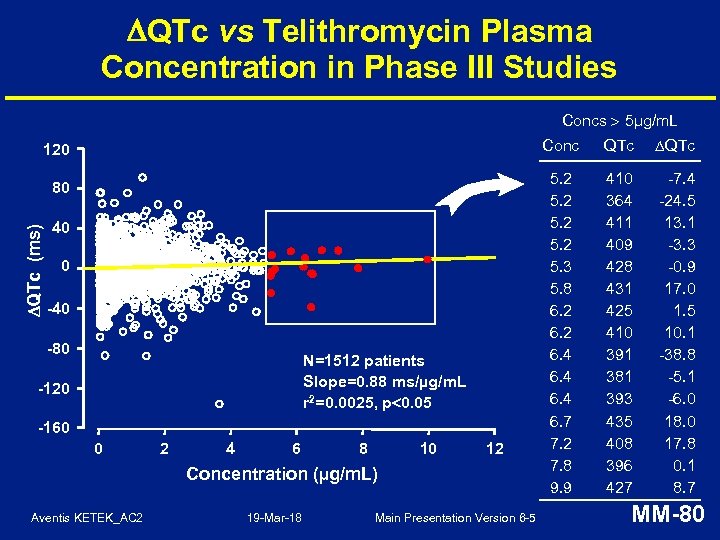 QTc vs Telithromycin Plasma Concentration in Phase III Studies Concs 5µg/m. L Conc 120 QTc (ms) 80 40 0 -40 -80 N=1512 patients Slope=0. 88 ms/µg/m. L r 2=0. 0025, p 0. 05 -120 -160 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 Concentration (µg/m. L) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 QTc 5. 2 5. 3 5. 8 6. 2 6. 4 6. 7 7. 2 7. 8 9. 9 410 364 411 409 428 431 425 410 391 381 393 435 408 396 427 -7. 4 -24. 5 13. 1 -3. 3 -0. 9 17. 0 1. 5 10. 1 -38. 8 -5. 1 -6. 0 18. 0 17. 8 0. 1 8. 7 MM-80
QTc vs Telithromycin Plasma Concentration in Phase III Studies Concs 5µg/m. L Conc 120 QTc (ms) 80 40 0 -40 -80 N=1512 patients Slope=0. 88 ms/µg/m. L r 2=0. 0025, p 0. 05 -120 -160 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 Concentration (µg/m. L) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 QTc 5. 2 5. 3 5. 8 6. 2 6. 4 6. 7 7. 2 7. 8 9. 9 410 364 411 409 428 431 425 410 391 381 393 435 408 396 427 -7. 4 -24. 5 13. 1 -3. 3 -0. 9 17. 0 1. 5 10. 1 -38. 8 -5. 1 -6. 0 18. 0 17. 8 0. 1 8. 7 MM-80
 Hepatic Events in Controlled Phase III Studies • • • ALT >3 x ULN in 1. 6% TEL and 1. 7% comparator subjects Hepatic adverse events in 3. 4% TEL and 3. 2% comparator subjects Single subject with clinical hepatitis: – first episode: • pre-existing ALT elevation and eosinophilia • liver biopsy: scattered lesions, predominant macrophages, background eosinophils – second episode: • 9 months later without re-exposure to telithromycin • second biopsy: autoimmune hepatitis and early cirrhosis – no recurrence since November 1998 Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-81
Hepatic Events in Controlled Phase III Studies • • • ALT >3 x ULN in 1. 6% TEL and 1. 7% comparator subjects Hepatic adverse events in 3. 4% TEL and 3. 2% comparator subjects Single subject with clinical hepatitis: – first episode: • pre-existing ALT elevation and eosinophilia • liver biopsy: scattered lesions, predominant macrophages, background eosinophils – second episode: • 9 months later without re-exposure to telithromycin • second biopsy: autoimmune hepatitis and early cirrhosis – no recurrence since November 1998 Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-81
 Large Comparative Study in Usual Care Setting (Study 3014) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-82
Large Comparative Study in Usual Care Setting (Study 3014) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-82
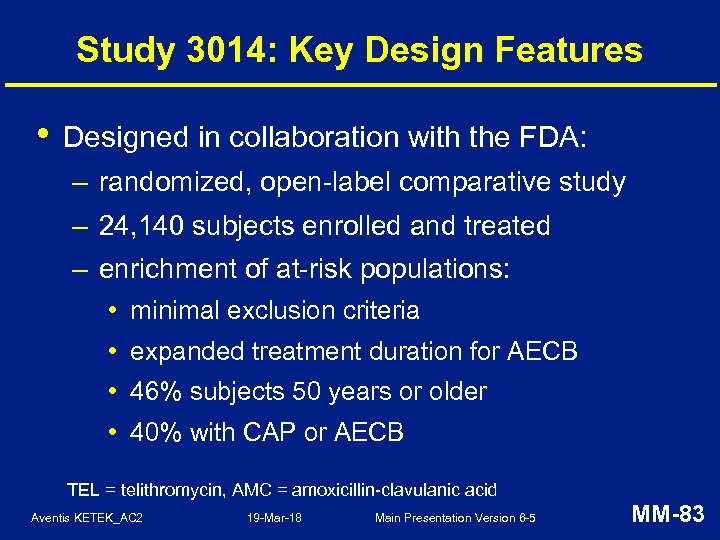 Study 3014: Key Design Features • Designed in collaboration with the FDA: – randomized, open-label comparative study – 24, 140 subjects enrolled and treated – enrichment of at-risk populations: • minimal exclusion criteria • expanded treatment duration for AECB • 46% subjects 50 years or older • 40% with CAP or AECB TEL = telithromycin, AMC = amoxicillin-clavulanic acid Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-83
Study 3014: Key Design Features • Designed in collaboration with the FDA: – randomized, open-label comparative study – 24, 140 subjects enrolled and treated – enrichment of at-risk populations: • minimal exclusion criteria • expanded treatment duration for AECB • 46% subjects 50 years or older • 40% with CAP or AECB TEL = telithromycin, AMC = amoxicillin-clavulanic acid Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-83
 Study 3014: Collection of Safety Data • • Designed to capture adverse events of special interest (AESIs) Office visits at pretherapy (Day 1) and post-therapy (Day 17 -22) • Follow-up contact at late post-therapy (Day 30 -35) • Hepatic laboratory testing at pretherapy and post-therapy • Investigators reviewed all AEs, with particular focus on AESIs Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-84
Study 3014: Collection of Safety Data • • Designed to capture adverse events of special interest (AESIs) Office visits at pretherapy (Day 1) and post-therapy (Day 17 -22) • Follow-up contact at late post-therapy (Day 30 -35) • Hepatic laboratory testing at pretherapy and post-therapy • Investigators reviewed all AEs, with particular focus on AESIs Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-84
 Study 3014: AESI Criteria Hepatic: Hepatitis, jaundice, any worsening of a pre-existing hepatic condition, alanine aminotransferase (ALT) values 3 x ULN Cardiac: Torsades de pointes, ventricular arrhythmias, syncope, cardiac arrest, or unwitnessed or unexplained death Visual: Blurred vision Vasculitic: Purpura or other signs of vasculitis • Broadly defined to capture all potential endpoint cases Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-85
Study 3014: AESI Criteria Hepatic: Hepatitis, jaundice, any worsening of a pre-existing hepatic condition, alanine aminotransferase (ALT) values 3 x ULN Cardiac: Torsades de pointes, ventricular arrhythmias, syncope, cardiac arrest, or unwitnessed or unexplained death Visual: Blurred vision Vasculitic: Purpura or other signs of vasculitis • Broadly defined to capture all potential endpoint cases Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-85
 Study 3014: Investigation of AESIs • All AEs and lab values reviewed to ensure complete collection of AESIs • • AESIs investigated using standardized questionnaires ALT 3 x ULN investigated using standardized lab kits: – bilirubin, ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, CBC with differential, prothrombin time, viral hepatitis serologies • • AESIs followed up to clinical resolution All AESIs reviewed by independent, blinded clinical events committees (CECs) and adjudicated to identify safety endpoints Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-86
Study 3014: Investigation of AESIs • All AEs and lab values reviewed to ensure complete collection of AESIs • • AESIs investigated using standardized questionnaires ALT 3 x ULN investigated using standardized lab kits: – bilirubin, ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, CBC with differential, prothrombin time, viral hepatitis serologies • • AESIs followed up to clinical resolution All AESIs reviewed by independent, blinded clinical events committees (CECs) and adjudicated to identify safety endpoints Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-86
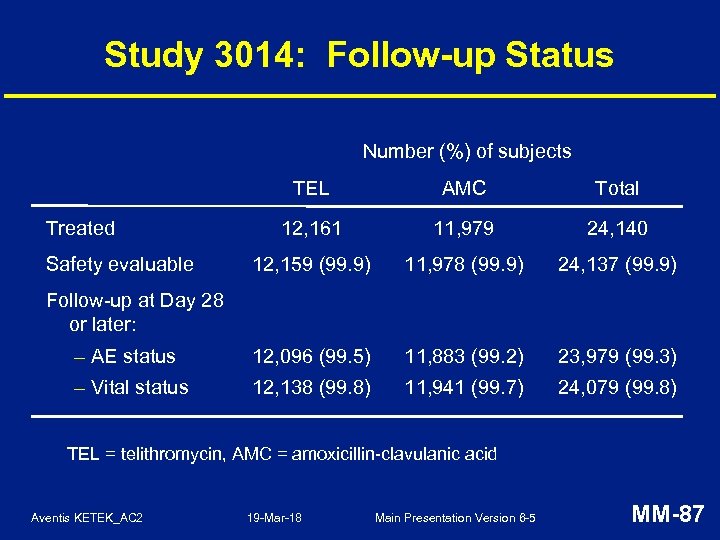 Study 3014: Follow-up Status Number (%) of subjects TEL AMC Total 12, 161 11, 979 24, 140 12, 159 (99. 9) 11, 978 (99. 9) 24, 137 (99. 9) – AE status 12, 096 (99. 5) 11, 883 (99. 2) 23, 979 (99. 3) – Vital status 12, 138 (99. 8) 11, 941 (99. 7) 24, 079 (99. 8) Treated Safety evaluable Follow-up at Day 28 or later: TEL = telithromycin, AMC = amoxicillin-clavulanic acid Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-87
Study 3014: Follow-up Status Number (%) of subjects TEL AMC Total 12, 161 11, 979 24, 140 12, 159 (99. 9) 11, 978 (99. 9) 24, 137 (99. 9) – AE status 12, 096 (99. 5) 11, 883 (99. 2) 23, 979 (99. 3) – Vital status 12, 138 (99. 8) 11, 941 (99. 7) 24, 079 (99. 8) Treated Safety evaluable Follow-up at Day 28 or later: TEL = telithromycin, AMC = amoxicillin-clavulanic acid Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-87
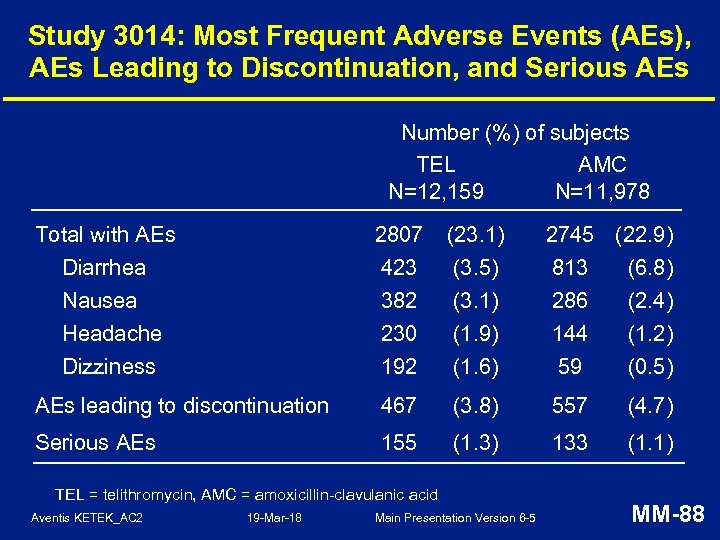 Study 3014: Most Frequent Adverse Events (AEs), AEs Leading to Discontinuation, and Serious AEs Number (%) of subjects TEL AMC N=12, 159 N=11, 978 Total with AEs Diarrhea Nausea Headache 2807 423 382 230 (23. 1) (3. 5) (3. 1) (1. 9) Dizziness 192 (1. 6) 59 (0. 5) AEs leading to discontinuation 467 (3. 8) 557 (4. 7) Serious AEs 155 (1. 3) 133 (1. 1) TEL = telithromycin, AMC = amoxicillin-clavulanic acid Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 2745 (22. 9) 813 (6. 8) 286 (2. 4) 144 (1. 2) MM-88
Study 3014: Most Frequent Adverse Events (AEs), AEs Leading to Discontinuation, and Serious AEs Number (%) of subjects TEL AMC N=12, 159 N=11, 978 Total with AEs Diarrhea Nausea Headache 2807 423 382 230 (23. 1) (3. 5) (3. 1) (1. 9) Dizziness 192 (1. 6) 59 (0. 5) AEs leading to discontinuation 467 (3. 8) 557 (4. 7) Serious AEs 155 (1. 3) 133 (1. 1) TEL = telithromycin, AMC = amoxicillin-clavulanic acid Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 2745 (22. 9) 813 (6. 8) 286 (2. 4) 144 (1. 2) MM-88
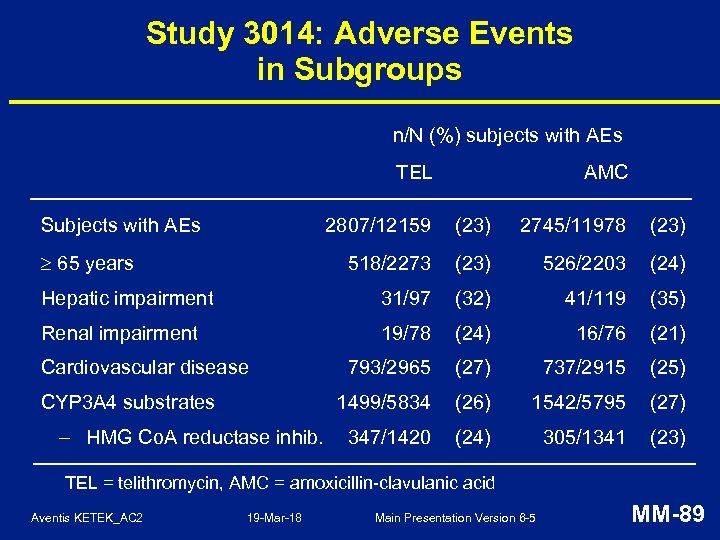 Study 3014: Adverse Events in Subgroups n/N (%) subjects with AEs TEL Subjects with AEs AMC 2807/12159 (23) 2745/11978 (23) 518/2273 (23) 526/2203 (24) Hepatic impairment 31/97 (32) 41/119 (35) Renal impairment 19/78 (24) 16/76 (21) 793/2965 (27) 737/2915 (25) 1499/5834 (26) 1542/5795 (27) 347/1420 (24) 305/1341 (23) 65 years Cardiovascular disease CYP 3 A 4 substrates – HMG Co. A reductase inhib. TEL = telithromycin, AMC = amoxicillin-clavulanic acid Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-89
Study 3014: Adverse Events in Subgroups n/N (%) subjects with AEs TEL Subjects with AEs AMC 2807/12159 (23) 2745/11978 (23) 518/2273 (23) 526/2203 (24) Hepatic impairment 31/97 (32) 41/119 (35) Renal impairment 19/78 (24) 16/76 (21) 793/2965 (27) 737/2915 (25) 1499/5834 (26) 1542/5795 (27) 347/1420 (24) 305/1341 (23) 65 years Cardiovascular disease CYP 3 A 4 substrates – HMG Co. A reductase inhib. TEL = telithromycin, AMC = amoxicillin-clavulanic acid Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-89
 Study 3014: Hepatic AESIs • Uncommon and balanced: – TEL: 111 (0. 9%), AMC: 98 (0. 8%) • All AESIs followed up to clinical and/or lab resolution – except 1 AMC subject • No chronic or immune-mediated hepatic injury • No drug-related severe hepatotoxicity (hepatic failure, liver transplant, death) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-90
Study 3014: Hepatic AESIs • Uncommon and balanced: – TEL: 111 (0. 9%), AMC: 98 (0. 8%) • All AESIs followed up to clinical and/or lab resolution – except 1 AMC subject • No chronic or immune-mediated hepatic injury • No drug-related severe hepatotoxicity (hepatic failure, liver transplant, death) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-90
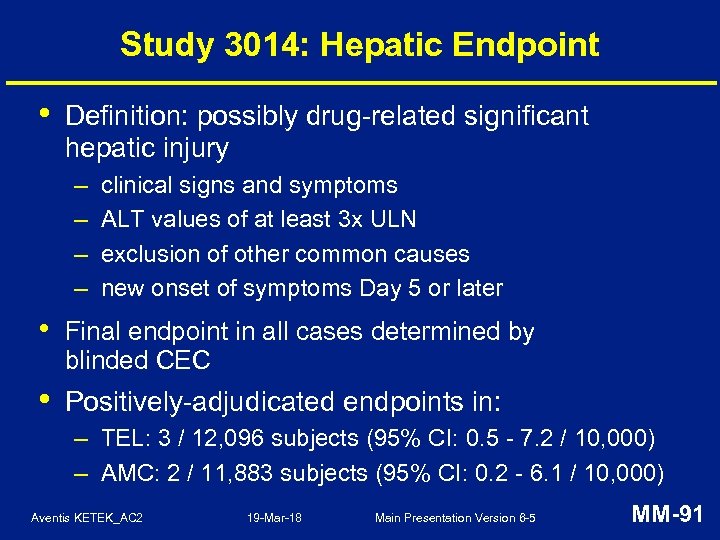 Study 3014: Hepatic Endpoint • Definition: possibly drug-related significant hepatic injury – – clinical signs and symptoms ALT values of at least 3 x ULN exclusion of other common causes new onset of symptoms Day 5 or later • Final endpoint in all cases determined by blinded CEC • Positively-adjudicated endpoints in: – TEL: 3 / 12, 096 subjects (95% CI: 0. 5 - 7. 2 / 10, 000) – AMC: 2 / 11, 883 subjects (95% CI: 0. 2 - 6. 1 / 10, 000) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-91
Study 3014: Hepatic Endpoint • Definition: possibly drug-related significant hepatic injury – – clinical signs and symptoms ALT values of at least 3 x ULN exclusion of other common causes new onset of symptoms Day 5 or later • Final endpoint in all cases determined by blinded CEC • Positively-adjudicated endpoints in: – TEL: 3 / 12, 096 subjects (95% CI: 0. 5 - 7. 2 / 10, 000) – AMC: 2 / 11, 883 subjects (95% CI: 0. 2 - 6. 1 / 10, 000) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-91
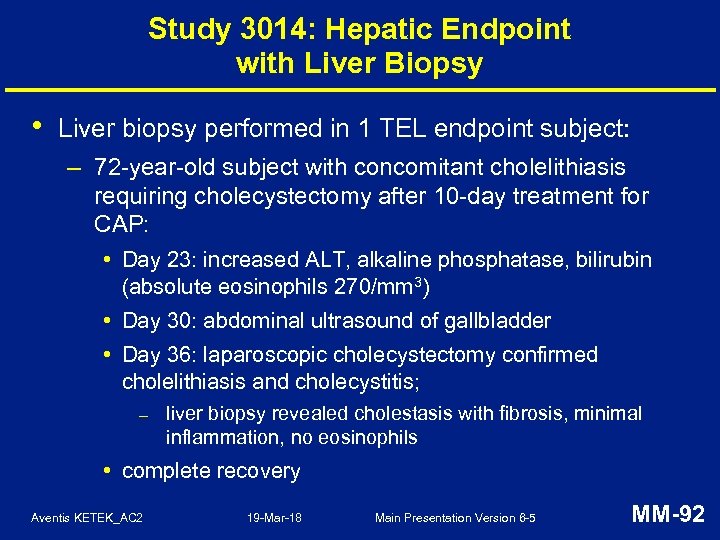 Study 3014: Hepatic Endpoint with Liver Biopsy • Liver biopsy performed in 1 TEL endpoint subject: – 72 -year-old subject with concomitant cholelithiasis requiring cholecystectomy after 10 -day treatment for CAP: • Day 23: increased ALT, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin (absolute eosinophils 270/mm 3) • Day 30: abdominal ultrasound of gallbladder • Day 36: laparoscopic cholecystectomy confirmed cholelithiasis and cholecystitis; – liver biopsy revealed cholestasis with fibrosis, minimal inflammation, no eosinophils • complete recovery Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-92
Study 3014: Hepatic Endpoint with Liver Biopsy • Liver biopsy performed in 1 TEL endpoint subject: – 72 -year-old subject with concomitant cholelithiasis requiring cholecystectomy after 10 -day treatment for CAP: • Day 23: increased ALT, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin (absolute eosinophils 270/mm 3) • Day 30: abdominal ultrasound of gallbladder • Day 36: laparoscopic cholecystectomy confirmed cholelithiasis and cholecystitis; – liver biopsy revealed cholestasis with fibrosis, minimal inflammation, no eosinophils • complete recovery Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-92
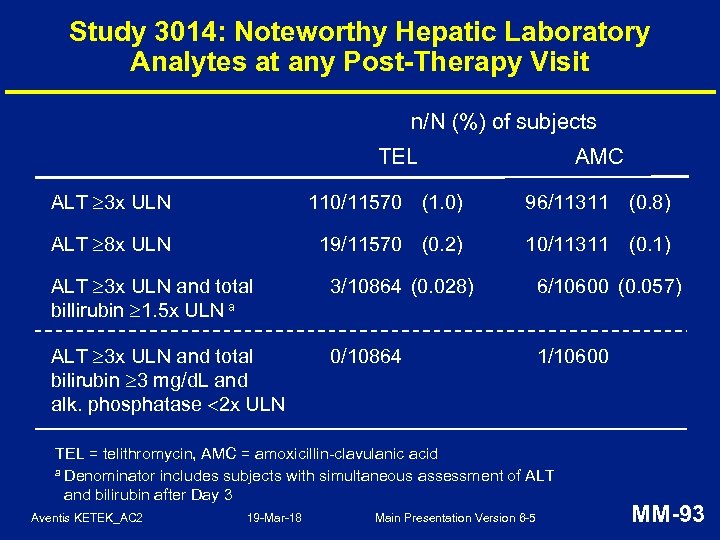 Study 3014: Noteworthy Hepatic Laboratory Analytes at any Post-Therapy Visit n/N (%) of subjects TEL AMC ALT 3 x ULN 110/11570 (1. 0) 96/11311 (0. 8) ALT 8 x ULN 19/11570 (0. 2) 10/11311 (0. 1) ALT 3 x ULN and total billirubin 1. 5 x ULN a 3/10864 (0. 028) 6/10600 (0. 057) ALT 3 x ULN and total bilirubin 3 mg/d. L and alk. phosphatase 2 x ULN 0/10864 1/10600 TEL = telithromycin, AMC = amoxicillin-clavulanic acid a Denominator includes subjects with simultaneous assessment of ALT and bilirubin after Day 3 Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-93
Study 3014: Noteworthy Hepatic Laboratory Analytes at any Post-Therapy Visit n/N (%) of subjects TEL AMC ALT 3 x ULN 110/11570 (1. 0) 96/11311 (0. 8) ALT 8 x ULN 19/11570 (0. 2) 10/11311 (0. 1) ALT 3 x ULN and total billirubin 1. 5 x ULN a 3/10864 (0. 028) 6/10600 (0. 057) ALT 3 x ULN and total bilirubin 3 mg/d. L and alk. phosphatase 2 x ULN 0/10864 1/10600 TEL = telithromycin, AMC = amoxicillin-clavulanic acid a Denominator includes subjects with simultaneous assessment of ALT and bilirubin after Day 3 Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-93
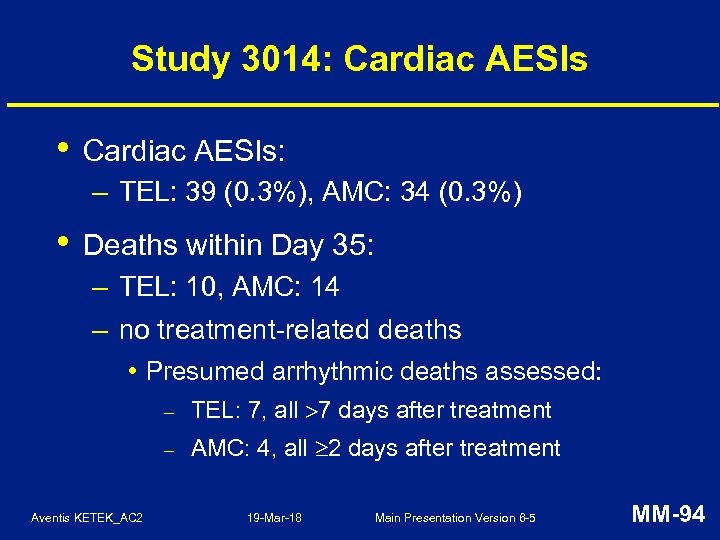 Study 3014: Cardiac AESIs • Cardiac AESIs: – TEL: 39 (0. 3%), AMC: 34 (0. 3%) • Deaths within Day 35: – TEL: 10, AMC: 14 – no treatment-related deaths • Presumed arrhythmic deaths assessed: – – Aventis KETEK_AC 2 TEL: 7, all 7 days after treatment AMC: 4, all 2 days after treatment 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-94
Study 3014: Cardiac AESIs • Cardiac AESIs: – TEL: 39 (0. 3%), AMC: 34 (0. 3%) • Deaths within Day 35: – TEL: 10, AMC: 14 – no treatment-related deaths • Presumed arrhythmic deaths assessed: – – Aventis KETEK_AC 2 TEL: 7, all 7 days after treatment AMC: 4, all 2 days after treatment 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-94
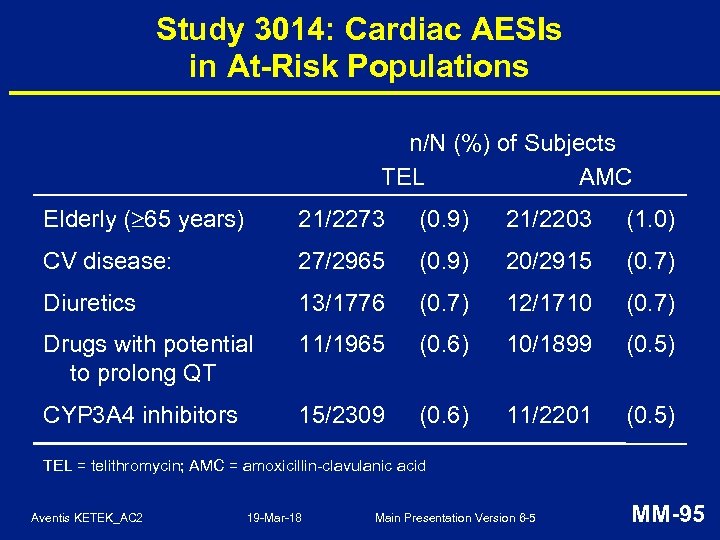 Study 3014: Cardiac AESIs in At-Risk Populations n/N (%) of Subjects TEL AMC Elderly ( 65 years) 21/2273 (0. 9) 21/2203 (1. 0) CV disease: 27/2965 (0. 9) 20/2915 (0. 7) Diuretics 13/1776 (0. 7) 12/1710 (0. 7) Drugs with potential to prolong QT 11/1965 (0. 6) 10/1899 (0. 5) CYP 3 A 4 inhibitors 15/2309 (0. 6) 11/2201 (0. 5) TEL = telithromycin; AMC = amoxicillin-clavulanic acid Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-95
Study 3014: Cardiac AESIs in At-Risk Populations n/N (%) of Subjects TEL AMC Elderly ( 65 years) 21/2273 (0. 9) 21/2203 (1. 0) CV disease: 27/2965 (0. 9) 20/2915 (0. 7) Diuretics 13/1776 (0. 7) 12/1710 (0. 7) Drugs with potential to prolong QT 11/1965 (0. 6) 10/1899 (0. 5) CYP 3 A 4 inhibitors 15/2309 (0. 6) 11/2201 (0. 5) TEL = telithromycin; AMC = amoxicillin-clavulanic acid Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-95
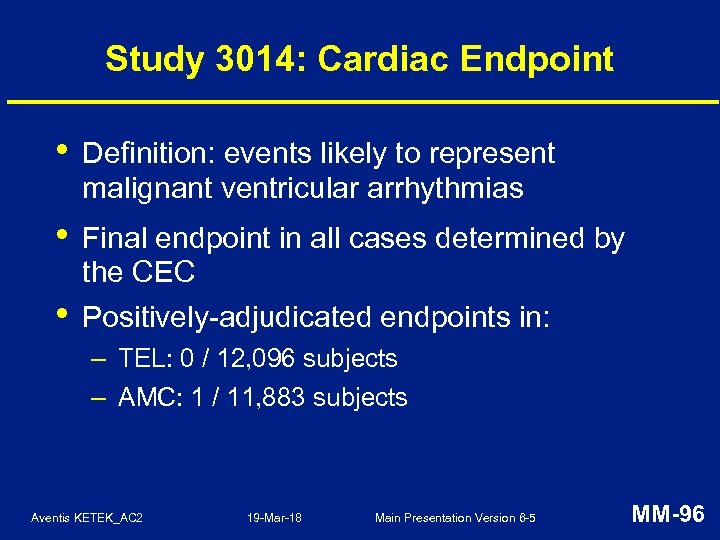 Study 3014: Cardiac Endpoint • Definition: events likely to represent malignant ventricular arrhythmias • Final endpoint in all cases determined by the CEC • Positively-adjudicated endpoints in: – TEL: 0 / 12, 096 subjects – AMC: 1 / 11, 883 subjects Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-96
Study 3014: Cardiac Endpoint • Definition: events likely to represent malignant ventricular arrhythmias • Final endpoint in all cases determined by the CEC • Positively-adjudicated endpoints in: – TEL: 0 / 12, 096 subjects – AMC: 1 / 11, 883 subjects Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-96
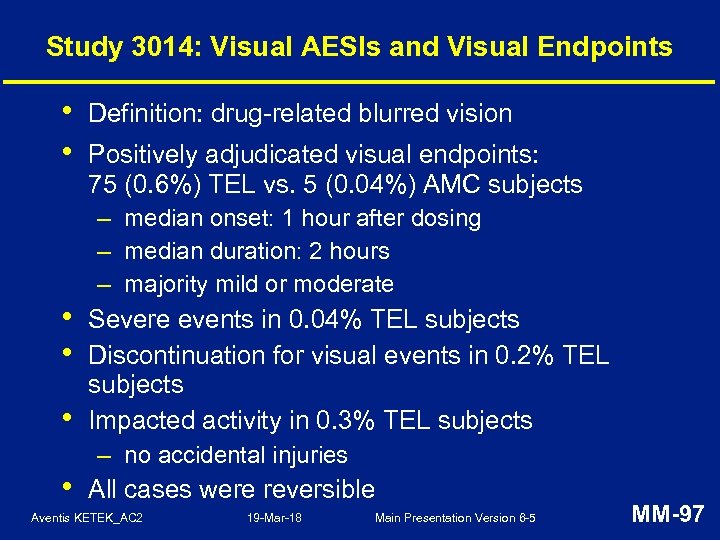 Study 3014: Visual AESIs and Visual Endpoints • • • Definition: drug-related blurred vision Positively adjudicated visual endpoints: 75 (0. 6%) TEL vs. 5 (0. 04%) AMC subjects – median onset: 1 hour after dosing – median duration: 2 hours – majority mild or moderate Severe events in 0. 04% TEL subjects Discontinuation for visual events in 0. 2% TEL subjects Impacted activity in 0. 3% TEL subjects – no accidental injuries All cases were reversible Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-97
Study 3014: Visual AESIs and Visual Endpoints • • • Definition: drug-related blurred vision Positively adjudicated visual endpoints: 75 (0. 6%) TEL vs. 5 (0. 04%) AMC subjects – median onset: 1 hour after dosing – median duration: 2 hours – majority mild or moderate Severe events in 0. 04% TEL subjects Discontinuation for visual events in 0. 2% TEL subjects Impacted activity in 0. 3% TEL subjects – no accidental injuries All cases were reversible Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-97
 Post-marketing Experience Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-98
Post-marketing Experience Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-98
 Post-Marketing Experience • 1. 5 million post-marketing exposures to TEL since first marketed in Europe in October 2001: – includes Germany, France, Belgium, Italy, Spain, Brazil, Mexico • ~1 million exposures in Germany and France • • 10% of prescriptions are re-exposure Intensive follow-up of all adverse events: – use of standard questionnaires as guidance for AESI follow-up • No new or unexpected safety signals identified Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-99
Post-Marketing Experience • 1. 5 million post-marketing exposures to TEL since first marketed in Europe in October 2001: – includes Germany, France, Belgium, Italy, Spain, Brazil, Mexico • ~1 million exposures in Germany and France • • 10% of prescriptions are re-exposure Intensive follow-up of all adverse events: – use of standard questionnaires as guidance for AESI follow-up • No new or unexpected safety signals identified Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-99
 Visual Findings in Post-Marketing Experience • Visual events generally similar to clinical trial experience: – most common events: blurred vision, abnormal accommodation, visual abnormality – 78% reported in patients 50 years of age – generally of limited duration, with full recovery noted – no sequelae identified – no reports of accidental injuries Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-100
Visual Findings in Post-Marketing Experience • Visual events generally similar to clinical trial experience: – most common events: blurred vision, abnormal accommodation, visual abnormality – 78% reported in patients 50 years of age – generally of limited duration, with full recovery noted – no sequelae identified – no reports of accidental injuries Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-100
 Cardiac Findings in Post-Marketing Experience • No increased risk for ventricular arrhythmic events: – no reports of sudden, unexplained death – no confirmed torsades de pointes in 1. 5 million exposures: • 2 questionable reports: 1) terminal VF in CAD patient; no QT prolongation or torsades de pointes on ECG, as confirmed by expert review 2) no identifiable patient, no event confirmed; no record of admission or treatment for torsades de pointes or other ventricular arrhythmia Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-101
Cardiac Findings in Post-Marketing Experience • No increased risk for ventricular arrhythmic events: – no reports of sudden, unexplained death – no confirmed torsades de pointes in 1. 5 million exposures: • 2 questionable reports: 1) terminal VF in CAD patient; no QT prolongation or torsades de pointes on ECG, as confirmed by expert review 2) no identifiable patient, no event confirmed; no record of admission or treatment for torsades de pointes or other ventricular arrhythmia Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-101
 Hepatic Findings in Post-Marketing Experience (1) • Hepatic events were uncommon (64 events in 28 patients) • No patients with hepatocellular jaundice: – 4 patients with cholestatic jaundice: • one with acute mononucleosis • all recovered • No chronic or immune-mediated hepatic injury Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-102
Hepatic Findings in Post-Marketing Experience (1) • Hepatic events were uncommon (64 events in 28 patients) • No patients with hepatocellular jaundice: – 4 patients with cholestatic jaundice: • one with acute mononucleosis • all recovered • No chronic or immune-mediated hepatic injury Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-102
 Hepatic Findings in Post-Marketing Experience (2) • No reports of drug-related severe hepatotoxicity (hepatic failure, liver transplant, death) • Fatal acute hepatitis A (Ig. M) with hepatic failure in an elderly man – case also confounded by: • high-dose ( 4 g daily) acetaminophen use for 4 -5 days prior to event • pre-existing underlying hard nodular liver • concurrent acute Q fever • Overall experience comparable to marketed antibiotics Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-103
Hepatic Findings in Post-Marketing Experience (2) • No reports of drug-related severe hepatotoxicity (hepatic failure, liver transplant, death) • Fatal acute hepatitis A (Ig. M) with hepatic failure in an elderly man – case also confounded by: • high-dose ( 4 g daily) acetaminophen use for 4 -5 days prior to event • pre-existing underlying hard nodular liver • concurrent acute Q fever • Overall experience comparable to marketed antibiotics Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-103
 Safety Summary (1) • Extensive experience: – 16, 000 subjects in clinical studies and 1. 5 million post-marketing exposures • Overall safety profile similar to marketed antibiotics: – gastrointestinal events most common – low discontinuation rate Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-104
Safety Summary (1) • Extensive experience: – 16, 000 subjects in clinical studies and 1. 5 million post-marketing exposures • Overall safety profile similar to marketed antibiotics: – gastrointestinal events most common – low discontinuation rate Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-104
 Safety Summary (2) • Uncommon visual events: – generally mild and limited duration – mechanism consistent with delay in focusing – severe etiologies excluded – no permanent sequelae – no accidental injuries Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-105
Safety Summary (2) • Uncommon visual events: – generally mild and limited duration – mechanism consistent with delay in focusing – severe etiologies excluded – no permanent sequelae – no accidental injuries Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-105
 Safety Summary (3) • Extensive cardiac evaluation, with no confirmed cardiac safety signal: – no increase in cardiac events or deaths in Phase III studies or Study 3014 – no increase in ventricular arrhythmic events in post-marketing surveillance: • no torsades de pointes Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-106
Safety Summary (3) • Extensive cardiac evaluation, with no confirmed cardiac safety signal: – no increase in cardiac events or deaths in Phase III studies or Study 3014 – no increase in ventricular arrhythmic events in post-marketing surveillance: • no torsades de pointes Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-106
 Safety Summary (4) • Extensive hepatic evaluation, with no confirmed hepatic safety signal: – no difference in clinical hepatic events – no hepatocellular jaundice – no chronic or immune-mediated hepatic injury – no drug-related severe hepatotoxicity (hepatic failure, liver transplant, death) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-107
Safety Summary (4) • Extensive hepatic evaluation, with no confirmed hepatic safety signal: – no difference in clinical hepatic events – no hepatocellular jaundice – no chronic or immune-mediated hepatic injury – no drug-related severe hepatotoxicity (hepatic failure, liver transplant, death) Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-107
 Summary and Conclusions Paul Iannini, MD Danbury Hospital, Danbury, Connecticut Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-108
Summary and Conclusions Paul Iannini, MD Danbury Hospital, Danbury, Connecticut Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-108
 There is a Medical Need for a New Anti-infective in Community-Acquired RTIs • Optimal therapy for community-acquired RTIs requires antibiotics with a targeted spectrum that includes common and atypical pathogens • Increased bacterial resistance to current antibiotics commonly used in therapy of RTIs may shorten useful life Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-109
There is a Medical Need for a New Anti-infective in Community-Acquired RTIs • Optimal therapy for community-acquired RTIs requires antibiotics with a targeted spectrum that includes common and atypical pathogens • Increased bacterial resistance to current antibiotics commonly used in therapy of RTIs may shorten useful life Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-109
 Limitations of Current Therapy in Community-Acquired RTIs • β-lactams: – atypicals – penicillin-resistant S. pneumoniae – β-lactamase positive H. influenzae • Macrolides: – macrolide-resistant S. pneumoniae • Fluoroquinolones: – not targeted to RTI pathogens Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-110
Limitations of Current Therapy in Community-Acquired RTIs • β-lactams: – atypicals – penicillin-resistant S. pneumoniae – β-lactamase positive H. influenzae • Macrolides: – macrolide-resistant S. pneumoniae • Fluoroquinolones: – not targeted to RTI pathogens Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-110
 Efficacy of Telithromycin • • Highly effective in CAP, AECB, and AS Key added benefits: – novel mechanism of action – concentration-dependent, rapid killing – targeted RTI spectrum – active against emerging resistant strains of S. pneumoniae – short treatment duration Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-111
Efficacy of Telithromycin • • Highly effective in CAP, AECB, and AS Key added benefits: – novel mechanism of action – concentration-dependent, rapid killing – targeted RTI spectrum – active against emerging resistant strains of S. pneumoniae – short treatment duration Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-111
 Safety of Telithromycin • Extensive exposure ( 1. 5 million subjects) • Safety comparable to widely prescribed antibiotics: – most common side effects were gastrointestinal – uncommon, mild, reversible visual events – no increased cardiac risk – no difference in clinical hepatic events – limited drug-drug interactions Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-112
Safety of Telithromycin • Extensive exposure ( 1. 5 million subjects) • Safety comparable to widely prescribed antibiotics: – most common side effects were gastrointestinal – uncommon, mild, reversible visual events – no increased cardiac risk – no difference in clinical hepatic events – limited drug-drug interactions Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-112
 Telithromycin • Fulfills a medical need • Brings additional benefits • Safety profile comparable to marketed antibiotics • Valuable option for the treatment of CAP, AECB, and AS in outpatients Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-113
Telithromycin • Fulfills a medical need • Brings additional benefits • Safety profile comparable to marketed antibiotics • Valuable option for the treatment of CAP, AECB, and AS in outpatients Aventis KETEK_AC 2 19 -Mar-18 Main Presentation Version 6 -5 MM-113


